Client
Thrift客户端有两种:同步客户端和异步客户端。
同步客户端
同步客户端比较简单,以RPC-Thrift(一)中的的例子为基础进行研究源码,先看一下类图。
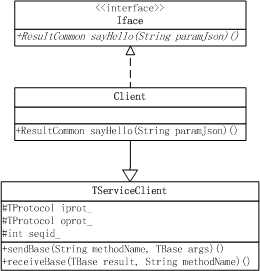
TServiceClient:用于以同步方式与TService进行通信;
Iface接口和Client类都是通过Thrift文件自动生成的代码。
TServiceClient
TServiceClient定义了基础的向Server发送请求和从Server接收响应的方法。
public abstract class TServiceClient { public TServiceClient(TProtocol prot) { this(prot, prot); } public TServiceClient(TProtocol iprot, TProtocol oprot) { iprot_ = iprot; oprot_ = oprot; } protected TProtocol iprot_;//输入TProtocol protected TProtocol oprot_;//输出TProtocol protected int seqid_;//序列号 public TProtocol getInputProtocol() { return this.iprot_; } public TProtocol getOutputProtocol() { return this.oprot_; } //向Server发送请求 protected void sendBase(String methodName, TBase args) throws TException { //写消息头,seqid_只是简单的++,非线程安全,接收响应时要进行seqid_的校验 oprot_.writeMessageBegin(new TMessage(methodName, TMessageType.CALL, ++seqid_)); args.write(oprot_);//写参数 oprot_.writeMessageEnd(); oprot_.getTransport().flush();//发送 } //从Server接收响应 protected void receiveBase(TBase result, String methodName) throws TException { TMessage msg = iprot_.readMessageBegin();//读消息头,若没有数据一直等待,详见TTransport的实现 if (msg.type == TMessageType.EXCEPTION) { //异常消息通过TApplicationException读取 TApplicationException x = TApplicationException.read(iprot_); iprot_.readMessageEnd(); throw x; } if (msg.seqid != seqid_) { //序列号不一致报异常 throw new TApplicationException(TApplicationException.BAD_SEQUENCE_ID, methodName + " failed: out of sequence response"); } result.read(iprot_);//读数据,由其result子类实现 iprot_.readMessageEnd(); } }
Iface
public interface Iface { //thrift中定义的方法 public ResultCommon sayHello(String paramJson) throws org.apache.thrift.TException; }
Client
public static class Client extends org.apache.thrift.TServiceClient implements Iface { //Client工厂类 public static class Factory implements org.apache.thrift.TServiceClientFactory<Client> { public Factory() {} public Client getClient(org.apache.thrift.protocol.TProtocol prot) { return new Client(prot); } public Client getClient(org.apache.thrift.protocol.TProtocol iprot, org.apache.thrift.protocol.TProtocol oprot) { return new Client(iprot, oprot); } } public Client(org.apache.thrift.protocol.TProtocol prot) { super(prot, prot); } public Client(org.apache.thrift.protocol.TProtocol iprot, org.apache.thrift.protocol.TProtocol oprot) { super(iprot, oprot); } //sayHello方法调用入口 public ResultCommon sayHello(String paramJson) throws org.apache.thrift.TException { send_sayHello(paramJson);//发送请求 return recv_sayHello();//接收响应 } //发送请求 public void send_sayHello(String paramJson) throws org.apache.thrift.TException { sayHello_args args = new sayHello_args();//组装参数 args.setParamJson(paramJson); sendBase("sayHello", args);//调用父类的sendBase方法发送请求 } //接收响应 public ResultCommon recv_sayHello() throws org.apache.thrift.TException { sayHello_result result = new sayHello_result(); receiveBase(result, "sayHello");//调用父类的receiveBase方法发送请求 if (result.isSetSuccess()) { return result.success; } throw new org.apache.thrift.TApplicationException(org.apache.thrift.TApplicationException.MISSING_RESULT, "sayHello failed: unknown result"); } }
异步客户端
异步客户端实现比较复杂,通过回调实现,先看一个异步客户端的例子。异步客户端需要使用TNonblockingSocket,通过AsyncMethodCallback接收服务端的回调。
1 String paramJson = "{\"wewe\":\"111\"}"; 2 TNonblockingSocket tNonblockingSocket = new TNonblockingSocket("127.0.0.1", 8090);//使用非阻塞TNonblockingSocket 3 TAsyncClientManager tAsyncClientManager = new TAsyncClientManager(); 4 HelloService.AsyncClient asyncClient = new HelloService.AsyncClient.Factory(tAsyncClientManager, new TBinaryProtocol.Factory()).getAsyncClient(tNonblockingSocket); 5 asyncClient.sayHello(paramJson, new AsyncMethodCallback<HelloService.AsyncClient.sayHello_call>() { 6 @Override 7 public void onError(Exception exception) { 8 //... 9 } 10 @Override 11 public void onComplete(sayHello_call response) { 12 ResultCommon resultCommon = response.getResult(); 13 System.out.println(resultCommon.getDesc()); 14 } 15 });
涉及到的类结构图如下:
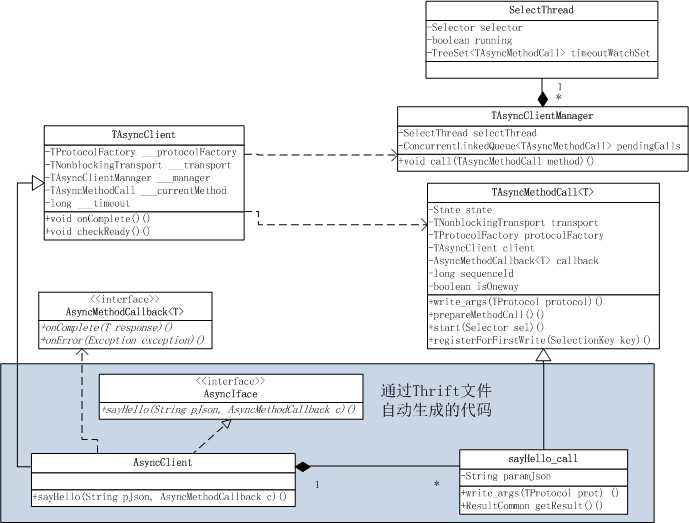
TAsyncClient:异步客户端抽象类,通过Thrift文件生成的AsyncClient需继承该类;
TAsyncClientManager:异步客户端管理类,包含一个selector线程,用于转换方法调用对象;
TAsyncMethodCall:封装了异步方法调用,Thrift文件定义的所有方法都会在AsyncClient中生成对应的继承于TAsyncMethodCall的内部类(如sayHello_call);
AsyncMethodCallback:接收服务端回调的接口,用户需要定义实现该接口的类。
TAsyncClient
TAsyncClient为异步客户端提供了公共的属性和方法。
public abstract class TAsyncClient { protected final TProtocolFactory ___protocolFactory; protected final TNonblockingTransport ___transport; protected final TAsyncClientManager ___manager;//异步客户端管理类 protected TAsyncMethodCall ___currentMethod;//异步方法调用 private Exception ___error; private long ___timeout; public TAsyncClient(TProtocolFactory protocolFactory, TAsyncClientManager manager, TNonblockingTransport transport) { this(protocolFactory, manager, transport, 0); } public TAsyncClient(TProtocolFactory protocolFactory, TAsyncClientManager manager, TNonblockingTransport transport, long timeout) { this.___protocolFactory = protocolFactory; this.___manager = manager; this.___transport = transport; this.___timeout = timeout; } public TProtocolFactory getProtocolFactory() { return ___protocolFactory; } public long getTimeout() { return ___timeout; } public boolean hasTimeout() { return ___timeout > 0; } public void setTimeout(long timeout) { this.___timeout = timeout; } //客户端是否处于异常状态 public boolean hasError() { return ___error != null; } public Exception getError() { return ___error; } //检查是否准备就绪,如果当前Cilent正在执行一个方法或处于error状态则报异常 protected void checkReady() { if (___currentMethod != null) { throw new IllegalStateException("Client is currently executing another method: " + ___currentMethod.getClass().getName()); } if (___error != null) { throw new IllegalStateException("Client has an error!", ___error); } } //执行完成时delegate方法会调用该方法,将___currentMethod置为null protected void onComplete() { ___currentMethod = null; } //执行出现异常时delegate方法会调用该方法, protected void onError(Exception exception) { ___transport.close();//关闭连接 ___currentMethod = null;//将___currentMethod置为null ___error = exception;//异常信息 } }
AsyncClient
AsyncClient类是通过Thrift文件自动生成的,在该类中含有每个方法的调用入口,并且为每个方法生成了一个方法调用类方法名_call,如sayHello_call。sayHello_call实现了父类TAsyncMethodCall的连个抽象方法:write_args和getResult,因为每个方法的参数和返回值不同,所以这两个方法需要具体子类实现。
public static class AsyncClient extends org.apache.thrift.async.TAsyncClient implements AsyncIface { //AsyncClient工厂类 public static class Factory implements org.apache.thrift.async.TAsyncClientFactory<AsyncClient> { private org.apache.thrift.async.TAsyncClientManager clientManager; private org.apache.thrift.protocol.TProtocolFactory protocolFactory; public Factory(org.apache.thrift.async.TAsyncClientManager clientManager, org.apache.thrift.protocol.TProtocolFactory protocolFactory) { this.clientManager = clientManager; this.protocolFactory = protocolFactory; } public AsyncClient getAsyncClient(org.apache.thrift.transport.TNonblockingTransport transport) { return new AsyncClient(protocolFactory, clientManager, transport); } } public AsyncClient(org.apache.thrift.protocol.TProtocolFactory protocolFactory, org.apache.thrift.async.TAsyncClientManager clientManager, org.apache.thrift.transport.TNonblockingTransport transport) { super(protocolFactory, clientManager, transport); } //sayHello方法调用入口 public void sayHello(String paramJson, org.apache.thrift.async.AsyncMethodCallback<sayHello_call> resultHandler) throws org.apache.thrift.TException { checkReady();//检查当前Client是否可用 //创建方法调用实例 sayHello_call method_call = new sayHello_call(paramJson, resultHandler, this, ___protocolFactory, ___transport); this.___currentMethod = method_call; //调用TAsyncClientManager的call方法 ___manager.call(method_call); } public static class sayHello_call extends org.apache.thrift.async.TAsyncMethodCall { private String paramJson; public sayHello_call(String paramJson, org.apache.thrift.async.AsyncMethodCallback<sayHello_call> resultHandler, org.apache.thrift.async.TAsyncClient client, org.apache.thrift.protocol.TProtocolFactory protocolFactory, org.apache.thrift.transport.TNonblockingTransport transport) throws org.apache.thrift.TException { super(client, protocolFactory, transport, resultHandler, false); this.paramJson = paramJson; } //发送请求 public void write_args(org.apache.thrift.protocol.TProtocol prot) throws org.apache.thrift.TException { prot.writeMessageBegin(new org.apache.thrift.protocol.TMessage("sayHello", org.apache.thrift.protocol.TMessageType.CALL, 0)); sayHello_args args = new sayHello_args(); args.setParamJson(paramJson); args.write(prot); prot.writeMessageEnd(); } //获取返回结果 public ResultCommon getResult() throws org.apache.thrift.TException { if (getState() != org.apache.thrift.async.TAsyncMethodCall.State.RESPONSE_READ) { throw new IllegalStateException("Method call not finished!"); } org.apache.thrift.transport.TMemoryInputTransport memoryTransport = new org.apache.thrift.transport.TMemoryInputTransport(getFrameBuffer().array()); org.apache.thrift.protocol.TProtocol prot = client.getProtocolFactory().getProtocol(memoryTransport); return (new Client(prot)).recv_sayHello(); } } }
TAsyncClientManager
TAsyncClientManager是异步客户端管理类,它为维护了一个待处理的方法调用队列pendingCalls,并通过SelectThread线程监听selector事件,当有就绪事件时进行方法调用的处理。
public class TAsyncClientManager { private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(TAsyncClientManager.class.getName()); private final SelectThread selectThread; //TAsyncMethodCall待处理队列 private final ConcurrentLinkedQueue<TAsyncMethodCall> pendingCalls = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue<TAsyncMethodCall>(); //初始化TAsyncClientManager,新建selectThread线程并启动 public TAsyncClientManager() throws IOException { this.selectThread = new SelectThread(); selectThread.start(); } //方法调用 public void call(TAsyncMethodCall method) throws TException { if (!isRunning()) { throw new TException("SelectThread is not running"); } method.prepareMethodCall();//做方法调用前的准备 pendingCalls.add(method);//加入待处理队列 selectThread.getSelector().wakeup();//唤醒selector,很重要,因为首次执行方法调用时select Thread还阻塞在selector.select()上 } public void stop() { selectThread.finish(); } public boolean isRunning() { return selectThread.isAlive(); } //SelectThread线程类,处理方法调用的核心 private class SelectThread extends Thread { private final Selector selector; private volatile boolean running; private final TreeSet<TAsyncMethodCall> timeoutWatchSet = new TreeSet<TAsyncMethodCall>(new TAsyncMethodCallTimeoutComparator()); public SelectThread() throws IOException { this.selector = SelectorProvider.provider().openSelector(); this.running = true; this.setName("TAsyncClientManager#SelectorThread " + this.getId()); setDaemon(true);//非守护线程 } public Selector getSelector() { return selector; } public void finish() { running = false; selector.wakeup(); } public void run() { while (running) { try { try { if (timeoutWatchSet.size() == 0) { //如果超时TAsyncMethodCall监控集合为空,直接无限期阻塞监听select()事件。TAsyncClientManager刚初始化时是空的 selector.select(); } else { //如果超时TAsyncMethodCall监控集合不为空,则计算Set中第一个元素的超时时间戳是否到期 long nextTimeout = timeoutWatchSet.first().getTimeoutTimestamp(); long selectTime = nextTimeout - System.currentTimeMillis(); if (selectTime > 0) { //还没有到期,超时监听select()事件,超过selectTime自动唤醒selector selector.select(selectTime); } else { //已经到期,立刻监听select()事件,不会阻塞selector selector.selectNow(); } } } catch (IOException e) { LOGGER.error("Caught IOException in TAsyncClientManager!", e); } //监听到就绪事件或者selector被唤醒会执行到此处 transitionMethods();//处理就绪keys timeoutMethods();//超时方法调用处理 startPendingMethods();//处理pending的方法调用 } catch (Exception exception) { LOGGER.error("Ignoring uncaught exception in SelectThread", exception); } } } //监听到就绪事件或者selector被唤醒,如果有就绪的SelectionKey就调用methodCall.transition(key); private void transitionMethods() { try { Iterator<SelectionKey> keys = selector.selectedKeys().iterator(); while (keys.hasNext()) { SelectionKey key = keys.next(); keys.remove(); if (!key.isValid()) { //跳过无效key,方法调用出现异常或key被取消等会导致无效key continue; } TAsyncMethodCall methodCall = (TAsyncMethodCall)key.attachment(); //调用methodCall的transition方法,执行相关的动作并将methodCall的状态转换为下一个状态 methodCall.transition(key); //如果完成或发生错误,从timeoutWatchSet删除该methodCall if (methodCall.isFinished() || methodCall.getClient().hasError()) { timeoutWatchSet.remove(methodCall); } } } catch (ClosedSelectorException e) { LOGGER.error("Caught ClosedSelectorException in TAsyncClientManager!", e); } } //超时方法调用处理 private void timeoutMethods() { Iterator<TAsyncMethodCall> iterator = timeoutWatchSet.iterator(); long currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); while (iterator.hasNext()) { TAsyncMethodCall methodCall = iterator.next(); if (currentTime >= methodCall.getTimeoutTimestamp()) { //如果超时,从timeoutWatchSet中删除并调用onError()方法 iterator.remove(); methodCall.onError(new TimeoutException("Operation " + methodCall.getClass() + " timed out after " + (currentTime - methodCall.getStartTime()) + " ms.")); } else { //如果没有超时,说明之后的TAsyncMethodCall也不会超时,跳出循环,因为越早进入timeoutWatchSet的TAsyncMethodCall越先超时。 break; } } } //开始等待的方法调用,循环处理pendingCalls中的methodCall private void startPendingMethods() { TAsyncMethodCall methodCall; while ((methodCall = pendingCalls.poll()) != null) { // Catch registration errors. method will catch transition errors and cleanup. try { //向selector注册并设置初次状态 methodCall.start(selector); //如果客户端指定了超时时间且transition成功,将methodCall加入到timeoutWatchSet TAsyncClient client = methodCall.getClient(); if (client.hasTimeout() && !client.hasError()) { timeoutWatchSet.add(methodCall); } } catch (Exception exception) { //异常处理 LOGGER.warn("Caught exception in TAsyncClientManager!", exception); methodCall.onError(exception); } } } } //TreeSet用的比较器,判断是否是同一个TAsyncMethodCall实例 private static class TAsyncMethodCallTimeoutComparator implements Comparator<TAsyncMethodCall> { public int compare(TAsyncMethodCall left, TAsyncMethodCall right) { if (left.getTimeoutTimestamp() == right.getTimeoutTimestamp()) { return (int)(left.getSequenceId() - right.getSequenceId()); } else { return (int)(left.getTimeoutTimestamp() - right.getTimeoutTimestamp()); } } } }
TAsyncMethodCall
TAsyncMethodCall实现了对方法调用的封装。一次方法调用过程就是一个TAsyncMethodCall实例的生命周期。TAsyncMethodCall实例在整个生命周期内有以下状态,正常情况下的状态状态过程为:CONNECTING -> WRITING_REQUEST_SIZE -> WRITING_REQUEST_BODY -> READING_RESPONSE_SIZE -> READING_RESPONSE_BODY -> RESPONSE_READ,如果任何一个过程中发生了异常则直接转换为ERROR状态。
public static enum State { CONNECTING,//连接状态 WRITING_REQUEST_SIZE,//写请求size WRITING_REQUEST_BODY,//写请求体 READING_RESPONSE_SIZE,//读响应size READING_RESPONSE_BODY,//读响应体 RESPONSE_READ,//读响应完成 ERROR;//异常状态 }
TAsyncMethodCall的源码分析如下:
public abstract class TAsyncMethodCall<T> { private static final int INITIAL_MEMORY_BUFFER_SIZE = 128; private static AtomicLong sequenceIdCounter = new AtomicLong(0);//序列号计数器private State state = null;//状态在start()方法中初始化 protected final TNonblockingTransport transport; private final TProtocolFactory protocolFactory; protected final TAsyncClient client; private final AsyncMethodCallback<T> callback;//回调实例 private final boolean isOneway; private long sequenceId;//序列号 private ByteBuffer sizeBuffer;//Java NIO概念,frameSize buffer private final byte[] sizeBufferArray = new byte[4];//4字节的消息Size字节数组 private ByteBuffer frameBuffer;//Java NIO概念,frame buffer private long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); protected TAsyncMethodCall(TAsyncClient client, TProtocolFactory protocolFactory, TNonblockingTransport transport, AsyncMethodCallback<T> callback, boolean isOneway) { this.transport = transport; this.callback = callback; this.protocolFactory = protocolFactory; this.client = client; this.isOneway = isOneway; this.sequenceId = TAsyncMethodCall.sequenceIdCounter.getAndIncrement(); } protected State getState() { return state; } protected boolean isFinished() { return state == State.RESPONSE_READ; } protected long getStartTime() { return startTime; } protected long getSequenceId() { return sequenceId; } public TAsyncClient getClient() { return client; } public boolean hasTimeout() { return client.hasTimeout(); } public long getTimeoutTimestamp() { return client.getTimeout() + startTime; } //将请求写入protocol,由子类实现 protected abstract void write_args(TProtocol protocol) throws TException; //方法调用前的准备处理,初始化frameBuffer和sizeBuffer protected void prepareMethodCall() throws TException { //TMemoryBuffer内存缓存传输类,继承了TTransport TMemoryBuffer memoryBuffer = new TMemoryBuffer(INITIAL_MEMORY_BUFFER_SIZE); TProtocol protocol = protocolFactory.getProtocol(memoryBuffer); write_args(protocol);//将请求写入protocol int length = memoryBuffer.length(); frameBuffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(memoryBuffer.getArray(), 0, length); TFramedTransport.encodeFrameSize(length, sizeBufferArray); sizeBuffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(sizeBufferArray); } //向selector注册并设置开始状态,可能是连接状态或写状态 void start(Selector sel) throws IOException { SelectionKey key; if (transport.isOpen()) { state = State.WRITING_REQUEST_SIZE; key = transport.registerSelector(sel, SelectionKey.OP_WRITE); } else { state = State.CONNECTING; key = transport.registerSelector(sel, SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT); //如果是非阻塞连接初始化会立即成功,转换为写状态并修改感兴趣事件 if (transport.startConnect()) { registerForFirstWrite(key); } } key.attach(this);//将本methodCall附加在key上 } void registerForFirstWrite(SelectionKey key) throws IOException { state = State.WRITING_REQUEST_SIZE; key.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_WRITE); } protected ByteBuffer getFrameBuffer() { return frameBuffer; } //转换为下一个状态,根据不同的状态做不同的处理。该方法只会在selector thread中被调用,不用担心并发 protected void transition(SelectionKey key) { // 确保key是有效的 if (!key.isValid()) { key.cancel(); Exception e = new TTransportException("Selection key not valid!"); onError(e); return; } try { switch (state) { case CONNECTING: doConnecting(key);//建连接 break; case WRITING_REQUEST_SIZE: doWritingRequestSize();//写请求size break; case WRITING_REQUEST_BODY: doWritingRequestBody(key);//写请求体 break; case READING_RESPONSE_SIZE: doReadingResponseSize();//读响应size break; case READING_RESPONSE_BODY: doReadingResponseBody(key);//读响应体 break; default: // RESPONSE_READ, ERROR, or bug throw new IllegalStateException("Method call in state " + state + " but selector called transition method. Seems like a bug..."); } } catch (Exception e) { key.cancel(); key.attach(null); onError(e); } } //出现异常时的处理 protected void onError(Exception e) { client.onError(e);//置Client异常信息 callback.onError(e);//回调异常方法 state = State.ERROR;//置当前对象为ERROR状态 } //读响应消息体 private void doReadingResponseBody(SelectionKey key) throws IOException { if (transport.read(frameBuffer) < 0) { throw new IOException("Read call frame failed"); } if (frameBuffer.remaining() == 0) { cleanUpAndFireCallback(key); } } //方法调用完成的处理 private void cleanUpAndFireCallback(SelectionKey key) { state = State.RESPONSE_READ;//状态转换为读取response完成 key.interestOps(0);//清空感兴趣事件 key.attach(null);//清理key的附加信息 client.onComplete();//将client的___currentMethod置为null callback.onComplete((T)this);//回调onComplete方法 } //读响应size,同样可能需要多多次直到把sizeBuffer读满 private void doReadingResponseSize() throws IOException { if (transport.read(sizeBuffer) < 0) { throw new IOException("Read call frame size failed"); } if (sizeBuffer.remaining() == 0) { state = State.READING_RESPONSE_BODY; //读取FrameSize完成,为frameBuffer分配FrameSize大小的空间用于读取响应体 frameBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(TFramedTransport.decodeFrameSize(sizeBufferArray)); } } //写请求体 private void doWritingRequestBody(SelectionKey key) throws IOException { if (transport.write(frameBuffer) < 0) { throw new IOException("Write call frame failed"); } if (frameBuffer.remaining() == 0) { if (isOneway) { //如果是单向RPC,此时方法调用已经结束,清理key并进行回调 cleanUpAndFireCallback(key); } else { //非单向RPC,状态转换为READING_RESPONSE_SIZE state = State.READING_RESPONSE_SIZE; //重置sizeBuffer,准备读取frame size sizeBuffer.rewind(); key.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_READ);//修改感兴趣事件 } } } //写请求size到transport,可能会写多次直到sizeBuffer.remaining() == 0才转换状态 private void doWritingRequestSize() throws IOException { if (transport.write(sizeBuffer) < 0) { throw new IOException("Write call frame size failed"); } if (sizeBuffer.remaining() == 0) { state = State.WRITING_REQUEST_BODY; } } //建立连接 private void doConnecting(SelectionKey key) throws IOException { if (!key.isConnectable() || !transport.finishConnect()) { throw new IOException("not connectable or finishConnect returned false after we got an OP_CONNECT"); } registerForFirstWrite(key); } }
总结
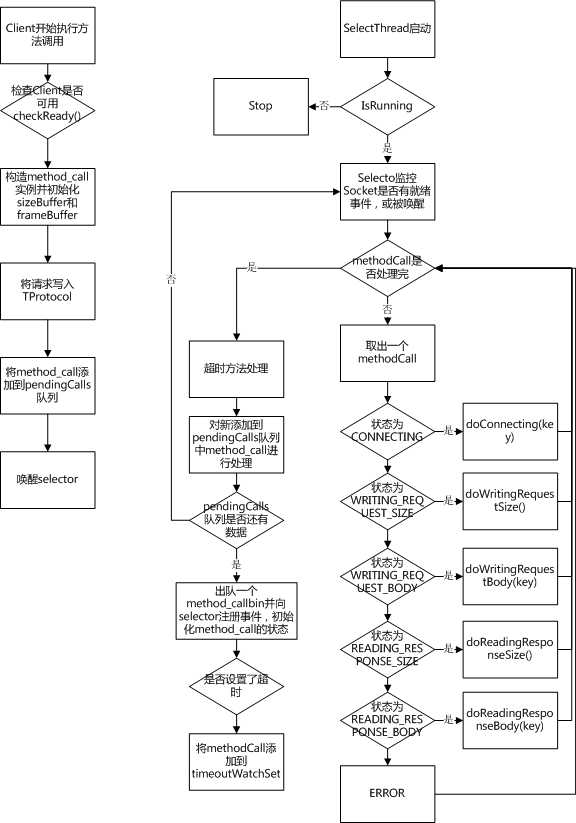
最后总结一下异步客户端的处理流程,如下图所示。
需要注意的是,一个AsyncClient实例只能同时处理一个方法调用,必须等待前一个方法调用完成后才能使用该AsyncClient实例调用其他方法,疑问:和同步客户端相比有什么优势?不用等返回结果,可以干其他的活?又能干什么活呢?如果客户端使用了连接池(也是AsyncClient实例池,一个AsyncClient实例对应一个连接),该线程不用等待前一个连接进行方法调用的返回结果,就可以去线程池获取一个可用的连接,使用新的连接进行方法调用,而原来的连接在收到返回结果后,状态变为可用,返回给连接池。这样相对于同步客户端单个线程串行发送请求的情况,异步客户端单个线程进行发送请求的效率会大大提高,需要的线程数变小,但是可能需要的连接数会增大,单个请求的响应时间会变长。在线程数是性能瓶颈,或对请求的响应时间要求不高的情况下,使用异步客户端比较合适。