一 time与datetime模块
在Python中,通常有这几种方式来表示时间:
- 时间戳(timestamp):通常来说,时间戳表示的是从1970年1月1日00:00:00开始按秒计算的偏移量。我们运行“type(time.time())”,返回的是float类型。
- 格式化的时间字符串(Format String)
- 结构化的时间(struct_time):struct_time元组共有9个元素共九个元素:(年,月,日,时,分,秒,一年中第几周,一年中第几天,夏令时)
1 import time 2 #--------------------------我们先以当前时间为准,让大家快速认识三种形式的时间 3 print(time.time()) # 时间戳:1487130156.419527 4 print(time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %X")) #格式化的时间字符串:‘2017-02-15 11:40:53‘ 5 6 print(time.localtime()) #本地时区的struct_time time.struct_time(tm_year=2018, tm_mon=1, tm_mday=10, tm_hour=16, tm_min=56, tm_sec=26, tm_wday=2, tm_yday=10, tm_isdst=0)
print(time.localtime().tm_mday) #把日取出来
7 print(time.gmtime()) #UTC时区的struct_time time.struct_time(tm_year=2018, tm_mon=1, tm_mday=10, tm_hour=8, tm_min=58, tm_sec=36, tm_wday=2, tm_yday=10, tm_isdst=0)

%a 星期几的简写 %A 星期几的全称 %b 月分的简写 %B 月份的全称 %c 标准的日期的时间串 %C 年份的后两位数字 %d 十进制表示的每月的第几天 %D 月/天/年 %e 在两字符域中,十进制表示的每月的第几天 %F 年-月-日 %g 年份的后两位数字,使用基于周的年 %G 年分,使用基于周的年 %h 简写的月份名 %H 24小时制的小时 %I 12小时制的小时 %j 十进制表示的每年的第几天 %m 十进制表示的月份 %M 十时制表示的分钟数 %n 新行符 %p 本地的AM或PM的等价显示 %r 12小时的时间 %R 显示小时和分钟:hh:mm %S 十进制的秒数 %t 水平制表符 %T 显示时分秒:hh:mm:ss %u 每周的第几天,星期一为第一天 (值从0到6,星期一为0) %U 第年的第几周,把星期日做为第一天(值从0到53) %V 每年的第几周,使用基于周的年 %w 十进制表示的星期几(值从0到6,星期天为0) %W 每年的第几周,把星期一做为第一天(值从0到53) %x 标准的日期串 %X 标准的时间串 %y 不带世纪的十进制年份(值从0到99) %Y 带世纪部分的十制年份 %z,%Z 时区名称,如果不能得到时区名称则返回空字符。 %% 百分号
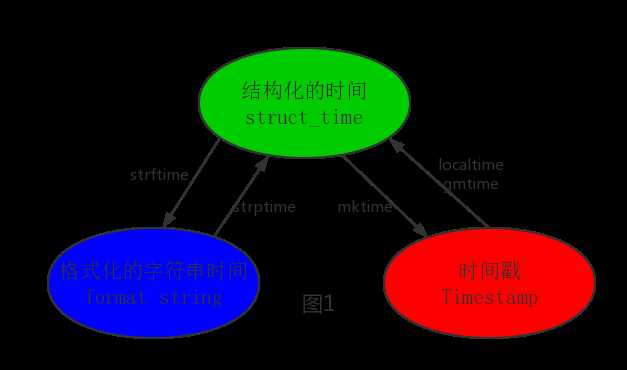
1 #--------------------------按图1转换时间 2 # localtime([secs]) 3 # 将一个时间戳转换为当前时区的struct_time。secs参数未提供,则以当前时间为准。 4 time.localtime() 5 time.localtime(1473525444.037215) 6 7 # gmtime([secs]) 和localtime()方法类似,gmtime()方法是将一个时间戳转换为UTC时区(0时区)的struct_time。 8 9 # mktime(t) : 将一个struct_time转化为时间戳。 10 print(time.mktime(time.localtime()))#1473525749.0 11 12 13 # strftime(format[, t]) : 把一个代表时间的元组或者struct_time(如由time.localtime()和 14 # time.gmtime()返回)转化为格式化的时间字符串。如果t未指定,将传入time.localtime()。如果元组中任何一个 15 # 元素越界,ValueError的错误将会被抛出。 16 print(time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %X", time.localtime()))#2016-09-11 00:49:56 17 18 # time.strptime(string[, format]) 19 # 把一个格式化时间字符串转化为struct_time。实际上它和strftime()是逆操作。 20 print(time.strptime(‘2011-05-05 16:37:06‘, ‘%Y-%m-%d %X‘)) 21 #time.struct_time(tm_year=2011, tm_mon=5, tm_mday=5, tm_hour=16, tm_min=37, tm_sec=6, 22 # tm_wday=3, tm_yday=125, tm_isdst=-1) 23 #在这个函数中,format默认为:"%a %b %d %H:%M:%S %Y"。
了解:
其中计算机认识的时间只能是‘时间戳‘格式,而程序员可处理的或者说人类能看懂的时间有: ‘格式化的时间字符串‘,‘结构化的时间‘ ,于是有了下图的转换关系
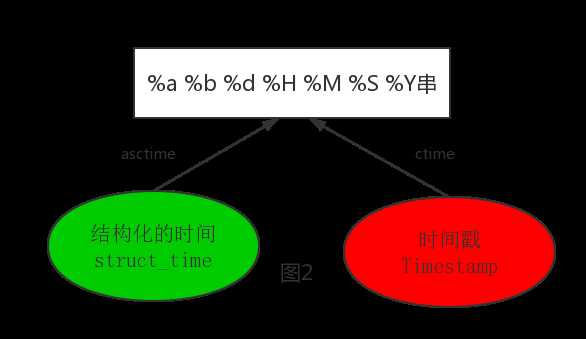
1 #--------------------------按图2转换时间 2 # asctime([t]) : 把一个表示时间的元组或者struct_time表示为这种形式:‘Sun Jun 20 23:21:05 1993‘。 3 # 如果没有参数,将会将time.localtime()作为参数传入。 4 print(time.asctime())#Sun Sep 11 00:43:43 2016 5 6 # ctime([secs]) : 把一个时间戳(按秒计算的浮点数)转化为time.asctime()的形式。如果参数未给或者为 7 # None的时候,将会默认time.time()为参数。它的作用相当于time.asctime(time.localtime(secs))。 8 print(time.ctime()) # Sun Sep 11 00:46:38 2016 9 print(time.ctime(time.time())) # Sun Sep 11 00:46:38 2016 复制代码 1 #--------------------------其他用法 2 # sleep(secs) 3 # 线程推迟指定的时间运行,单位为秒。 复制代码 #时间加减 import datetime # print(datetime.datetime.now()) #返回 2016-08-19 12:47:03.941925 #print(datetime.date.fromtimestamp(time.time()) ) # 时间戳直接转成日期格式 2016-08-19 # print(datetime.datetime.now() ) # print(datetime.datetime.now() + datetime.timedelta(3)) #当前时间+3天 # print(datetime.datetime.now() + datetime.timedelta(-3)) #当前时间-3天 # print(datetime.datetime.now() + datetime.timedelta(hours=3)) #当前时间+3小时 # print(datetime.datetime.now() + datetime.timedelta(minutes=30)) #当前时间+30分 # # c_time = datetime.datetime.now() # print(c_time.replace(minute=3,hour=2)) #时间替换
二 logging模块
一、日志级别
CRITICAL = 50 #FATAL = CRITICAL ERROR = 40 WARNING = 30 #WARN = WARNING INFO = 20 DEBUG = 10 NOTSET = 0 #不设置
二 默认级别为warning,默认打印到终端
import logging logging.debug(‘调试debug‘) logging.info(‘消息info‘) logging.warning(‘警告warn‘) logging.error(‘错误error‘) logging.critical(‘严重critical‘) ‘‘‘ WARNING:root:警告warn ERROR:root:错误error CRITICAL:root:严重critical ‘‘‘
三 为logging模块指定全局配置,针对所有logger有效,控制打印到文件中

可在logging.basicConfig()函数中通过具体参数来更改logging模块默认行为,可用参数有 filename:用指定的文件名创建FiledHandler(后边会具体讲解handler的概念),这样日志会被存储在指定的文件中。 filemode:文件打开方式,在指定了filename时使用这个参数,默认值为“a”还可指定为“w”。 format:指定handler使用的日志显示格式。 datefmt:指定日期时间格式。 level:设置rootlogger(后边会讲解具体概念)的日志级别 stream:用指定的stream创建StreamHandler。可以指定输出到sys.stderr,sys.stdout或者文件,默认为sys.stderr。若同时列出了filename和stream两个参数,则stream参数会被忽略。 #格式 %(name)s:Logger的名字,并非用户名,详细查看 %(levelno)s:数字形式的日志级别 %(levelname)s:文本形式的日志级别 %(pathname)s:调用日志输出函数的模块的完整路径名,可能没有 %(filename)s:调用日志输出函数的模块的文件名 %(module)s:调用日志输出函数的模块名 %(funcName)s:调用日志输出函数的函数名 %(lineno)d:调用日志输出函数的语句所在的代码行 %(created)f:当前时间,用UNIX标准的表示时间的浮 点数表示 %(relativeCreated)d:输出日志信息时的,自Logger创建以 来的毫秒数 %(asctime)s:字符串形式的当前时间。默认格式是 “2003-07-08 16:49:45,896”。逗号后面的是毫秒 %(thread)d:线程ID。可能没有 %(threadName)s:线程名。可能没有 %(process)d:进程ID。可能没有 %(message)s:用户输出的消息

可在logging.basicConfig()函数中通过具体参数来更改logging模块默认行为,可用参数有 filename:用指定的文件名创建FiledHandler(后边会具体讲解handler的概念),这样日志会被存储在指定的文件中。 filemode:文件打开方式,在指定了filename时使用这个参数,默认值为“a”还可指定为“w”。 format:指定handler使用的日志显示格式。 datefmt:指定日期时间格式。 level:设置rootlogger(后边会讲解具体概念)的日志级别 stream:用指定的stream创建StreamHandler。可以指定输出到sys.stderr,sys.stdout或者文件,默认为sys.stderr。若同时列出了filename和stream两个参数,则stream参数会被忽略。 #格式 %(name)s:Logger的名字,并非用户名,详细查看 %(levelno)s:数字形式的日志级别 %(levelname)s:文本形式的日志级别 %(pathname)s:调用日志输出函数的模块的完整路径名,可能没有 %(filename)s:调用日志输出函数的模块的文件名 %(module)s:调用日志输出函数的模块名 %(funcName)s:调用日志输出函数的函数名 %(lineno)d:调用日志输出函数的语句所在的代码行 %(created)f:当前时间,用UNIX标准的表示时间的浮 点数表示 %(relativeCreated)d:输出日志信息时的,自Logger创建以 来的毫秒数 %(asctime)s:字符串形式的当前时间。默认格式是 “2003-07-08 16:49:45,896”。逗号后面的是毫秒 %(thread)d:线程ID。可能没有 %(threadName)s:线程名。可能没有 %(process)d:进程ID。可能没有 %(message)s:用户输出的消息
四 logging模块的Formatter,Handler,Logger,Filter对象
原理图:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1skWyTT7
#logger:产生日志的对象 #Filter:过滤日志的对象 #Handler:接收日志然后控制打印到不同的地方,FileHandler用来打印到文件中,StreamHandler用来打印到终端 #Formatter对象:可以定制不同的日志格式对象,然后绑定给不同的Handler对象使用,以此来控制不同的Handler的日志格式

十三 re模块 一:什么是正则? 正则就是用一些具有特殊含义的符号组合到一起(称为正则表达式)来描述字符或者字符串的方法。或者说:正则就是用来描述一类事物的规则。(在Python中)它内嵌在Python中,并通过 re 模块实现。正则表达式模式被编译成一系列的字节码,然后由用 C 编写的匹配引擎执行。 生活中处处都是正则: 比如我们描述:4条腿 你可能会想到的是四条腿的动物或者桌子,椅子等 继续描述:4条腿,活的 就只剩下四条腿的动物这一类了 二:常用匹配模式(元字符) http://blog.csdn.net/yufenghyc/article/details/51078107 复制代码 # =================================匹配模式================================= #一对一的匹配 # ‘hello‘.replace(old,new) # ‘hello‘.find(‘pattern‘) #正则匹配 import re #\w与\W print(re.findall(‘\w‘,‘hello egon 123‘)) #[‘h‘, ‘e‘, ‘l‘, ‘l‘, ‘o‘, ‘e‘, ‘g‘, ‘o‘, ‘n‘, ‘1‘, ‘2‘, ‘3‘] print(re.findall(‘\W‘,‘hello egon 123‘)) #[‘ ‘, ‘ ‘] #\s与\S print(re.findall(‘\s‘,‘hello egon 123‘)) #[‘ ‘, ‘ ‘, ‘ ‘, ‘ ‘] print(re.findall(‘\S‘,‘hello egon 123‘)) #[‘h‘, ‘e‘, ‘l‘, ‘l‘, ‘o‘, ‘e‘, ‘g‘, ‘o‘, ‘n‘, ‘1‘, ‘2‘, ‘3‘] #\n \t都是空,都可以被\s匹配 print(re.findall(‘\s‘,‘hello \n egon \t 123‘)) #[‘ ‘, ‘\n‘, ‘ ‘, ‘ ‘, ‘\t‘, ‘ ‘] #\n与\t print(re.findall(r‘\n‘,‘hello egon \n123‘)) #[‘\n‘] print(re.findall(r‘\t‘,‘hello egon\t123‘)) #[‘\n‘] #\d与\D print(re.findall(‘\d‘,‘hello egon 123‘)) #[‘1‘, ‘2‘, ‘3‘] print(re.findall(‘\D‘,‘hello egon 123‘)) #[‘h‘, ‘e‘, ‘l‘, ‘l‘, ‘o‘, ‘ ‘, ‘e‘, ‘g‘, ‘o‘, ‘n‘, ‘ ‘] #\A与\Z print(re.findall(‘\Ahe‘,‘hello egon 123‘)) #[‘he‘],\A==>^ print(re.findall(‘123\Z‘,‘hello egon 123‘)) #[‘he‘],\Z==>$ #^与$ print(re.findall(‘^h‘,‘hello egon 123‘)) #[‘h‘] print(re.findall(‘3$‘,‘hello egon 123‘)) #[‘3‘] # 重复匹配:| . | * | ? | .* | .*? | + | {n,m} | #. print(re.findall(‘a.b‘,‘a1b‘)) #[‘a1b‘] print(re.findall(‘a.b‘,‘a1b a*b a b aaab‘)) #[‘a1b‘, ‘a*b‘, ‘a b‘, ‘aab‘] print(re.findall(‘a.b‘,‘a\nb‘)) #[] print(re.findall(‘a.b‘,‘a\nb‘,re.S)) #[‘a\nb‘] print(re.findall(‘a.b‘,‘a\nb‘,re.DOTALL)) #[‘a\nb‘]同上一条意思一样 #* print(re.findall(‘ab*‘,‘bbbbbbb‘)) #[] print(re.findall(‘ab*‘,‘a‘)) #[‘a‘] print(re.findall(‘ab*‘,‘abbbb‘)) #[‘abbbb‘] #? print(re.findall(‘ab?‘,‘a‘)) #[‘a‘] print(re.findall(‘ab?‘,‘abbb‘)) #[‘ab‘] #匹配所有包含小数在内的数字 print(re.findall(‘\d+\.?\d*‘,"asdfasdf123as1.13dfa12adsf1asdf3")) #[‘123‘, ‘1.13‘, ‘12‘, ‘1‘, ‘3‘] #.*默认为贪婪匹配 print(re.findall(‘a.*b‘,‘a1b22222222b‘)) #[‘a1b22222222b‘] #.*?为非贪婪匹配:推荐使用 print(re.findall(‘a.*?b‘,‘a1b22222222b‘)) #[‘a1b‘] #+ print(re.findall(‘ab+‘,‘a‘)) #[] print(re.findall(‘ab+‘,‘abbb‘)) #[‘abbb‘] #{n,m} print(re.findall(‘ab{2}‘,‘abbb‘)) #[‘abb‘] print(re.findall(‘ab{2,4}‘,‘abbb‘)) #[‘abb‘] print(re.findall(‘ab{1,}‘,‘abbb‘)) #‘ab{1,}‘ ===> ‘ab+‘ print(re.findall(‘ab{0,}‘,‘abbb‘)) #‘ab{0,}‘ ===> ‘ab*‘ #[] print(re.findall(‘a[1*-]b‘,‘a1b a*b a-b‘)) #[]内的都为普通字符了,且如果-没有被转意的话,应该放到[]的开头或结尾 print(re.findall(‘a[^1*-]b‘,‘a1b a*b a-b a=b‘)) #[]内的^代表的意思是取反,所以结果为[‘a=b‘] print(re.findall(‘a[0-9]b‘,‘a1b a*b a-b a=b‘)) #[]内的^代表的意思是取反,所以结果为[‘a=b‘] print(re.findall(‘a[a-z]b‘,‘a1b a*b a-b a=b aeb‘)) #[]内的^代表的意思是取反,所以结果为[‘a=b‘] print(re.findall(‘a[a-zA-Z]b‘,‘a1b a*b a-b a=b aeb aEb‘)) #[]内的^代表的意思是取反,所以结果为[‘a=b‘] #\# print(re.findall(‘a\\c‘,‘a\c‘)) #对于正则来说a\\c确实可以匹配到a\c,但是在python解释器读取a\\c时,会发生转义,然后交给re去执行,所以抛出异常 print(re.findall(r‘a\\c‘,‘a\c‘)) #r代表告诉解释器使用rawstring,即原生字符串,把我们正则内的所有符号都当普通字符处理,不要转义 print(re.findall(‘a\\\\c‘,‘a\c‘)) #同上面的意思一样,和上面的结果一样都是[‘a\\c‘] #():分组 print(re.findall(‘ab+‘,‘ababab123‘)) #[‘ab‘, ‘ab‘, ‘ab‘] print(re.findall(‘(ab)+123‘,‘ababab123‘)) #[‘ab‘],匹配到末尾的ab123中的ab print(re.findall(‘(?:ab)+123‘,‘ababab123‘)) #findall的结果不是匹配的全部内容,而是组内的内容,?:可以让结果为匹配的全部内容 print(re.findall(‘href="(.*?)"‘,‘<a href="http://www.baidu.com">点击</a>‘))#[‘http://www.baidu.com‘] print(re.findall(‘href="(?:.*?)"‘,‘<a href="http://www.baidu.com">点击</a>‘))#[‘href="http://www.baidu.com"‘] #| print(re.findall(‘compan(?:y|ies)‘,‘Too many companies have gone bankrupt, and the next one is my company‘)) 复制代码 复制代码 # ===========================re模块提供的方法介绍=========================== import re #1 print(re.findall(‘e‘,‘alex make love‘) ) #[‘e‘, ‘e‘, ‘e‘],返回所有满足匹配条件的结果,放在列表里 #2 print(re.search(‘e‘,‘alex make love‘).group()) #e,只到找到第一个匹配然后返回一个包含匹配信息的对象,该对象可以通过调用group()方法得到匹配的字符串,如果字符串没有匹配,则返回None。 #3 print(re.match(‘e‘,‘alex make love‘)) #None,同search,不过在字符串开始处进行匹配,完全可以用search+^代替match #4 print(re.split(‘[ab]‘,‘abcd‘)) #[‘‘, ‘‘, ‘cd‘],先按‘a‘分割得到‘‘和‘bcd‘,再对‘‘和‘bcd‘分别按‘b‘分割 #5 print(‘===>‘,re.sub(‘a‘,‘A‘,‘alex make love‘)) #===> Alex mAke love,不指定n,默认替换所有 print(‘===>‘,re.sub(‘a‘,‘A‘,‘alex make love‘,1)) #===> Alex make love print(‘===>‘,re.sub(‘a‘,‘A‘,‘alex make love‘,2)) #===> Alex mAke love print(‘===>‘,re.sub(‘^(\w+)(.*?\s)(\w+)(.*?\s)(\w+)(.*?)$‘,r‘\5\2\3\4\1‘,‘alex make love‘)) #===> love make alex print(‘===>‘,re.subn(‘a‘,‘A‘,‘alex make love‘)) #===> (‘Alex mAke love‘, 2),结果带有总共替换的个数 #6 obj=re.compile(‘\d{2}‘) print(obj.search(‘abc123eeee‘).group()) #12 print(obj.findall(‘abc123eeee‘)) #[‘12‘],重用了obj 复制代码 补充一 补充二 #计算器作业参考:http://www.cnblogs.com/wupeiqi/articles/4949995.html expression=‘1-2*((60+2*(-3-40.0/5)*(9-2*5/3+7/3*99/4*2998+10*568/14))-(-4*3)/(16-3*2))‘ content=re.search(‘\(([\-\+\*\/]*\d+\.?\d*)+\)‘,expression).group() #(-3-40.0/5) search与findall View Code
五 Logger与Handler的级别
logger是第一级过滤,然后才能到handler,我们可以给logger和handler同时设置level,但是需要注意的是

Logger is also the first to filter the message based on a level — if you set the logger to INFO, and all handlers to DEBUG, you still won‘t receive DEBUG messages on handlers — they‘ll be rejected by the logger itself. If you set logger to DEBUG, but all handlers to INFO, you won‘t receive any DEBUG messages either — because while the logger says "ok, process this", the handlers reject it (DEBUG < INFO). #验证 import logging form=logging.Formatter(‘%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s -%(module)s: %(message)s‘, datefmt=‘%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S %p‘,) ch=logging.StreamHandler() ch.setFormatter(form) # ch.setLevel(10) ch.setLevel(20) l1=logging.getLogger(‘root‘) # l1.setLevel(20) l1.setLevel(10) l1.addHandler(ch) l1.debug(‘l1 debug‘) 重要,重要,重要!!!
六 Logger的继承(了解)

import logging formatter=logging.Formatter(‘%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s -%(module)s: %(message)s‘, datefmt=‘%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S %p‘,) ch=logging.StreamHandler() ch.setFormatter(formatter) logger1=logging.getLogger(‘root‘) logger2=logging.getLogger(‘root.child1‘) logger3=logging.getLogger(‘root.child1.child2‘) logger1.addHandler(ch) logger2.addHandler(ch) logger3.addHandler(ch) logger1.setLevel(10) logger2.setLevel(10) logger3.setLevel(10) logger1.debug(‘log1 debug‘) logger2.debug(‘log2 debug‘) logger3.debug(‘log3 debug‘) ‘‘‘ 2017-07-28 22:22:05 PM - root - DEBUG -test: log1 debug 2017-07-28 22:22:05 PM - root.child1 - DEBUG -test: log2 debug 2017-07-28 22:22:05 PM - root.child1 - DEBUG -test: log2 debug 2017-07-28 22:22:05 PM - root.child1.child2 - DEBUG -test: log3 debug 2017-07-28 22:22:05 PM - root.child1.child2 - DEBUG -test: log3 debug 2017-07-28 22:22:05 PM - root.child1.child2 - DEBUG -test: log3 debug ‘‘‘
七 应用

""" logging配置 """ import os import logging.config # 定义三种日志输出格式 开始 standard_format = ‘[%(asctime)s][%(threadName)s:%(thread)d][task_id:%(name)s][%(filename)s:%(lineno)d]‘ ‘[%(levelname)s][%(message)s]‘ #其中name为getlogger指定的名字 simple_format = ‘[%(levelname)s][%(asctime)s][%(filename)s:%(lineno)d]%(message)s‘ id_simple_format = ‘[%(levelname)s][%(asctime)s] %(message)s‘ # 定义日志输出格式 结束 logfile_dir = os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__)) # log文件的目录 logfile_name = ‘all2.log‘ # log文件名 # 如果不存在定义的日志目录就创建一个 if not os.path.isdir(logfile_dir): os.mkdir(logfile_dir) # log文件的全路径 logfile_path = os.path.join(logfile_dir, logfile_name) # log配置字典 LOGGING_DIC = { ‘version‘: 1, ‘disable_existing_loggers‘: False, ‘formatters‘: { ‘standard‘: { ‘format‘: standard_format }, ‘simple‘: { ‘format‘: simple_format }, }, ‘filters‘: {}, ‘handlers‘: { #打印到终端的日志 ‘console‘: { ‘level‘: ‘DEBUG‘, ‘class‘: ‘logging.StreamHandler‘, # 打印到屏幕 ‘formatter‘: ‘simple‘ }, #打印到文件的日志,收集info及以上的日志 ‘default‘: { ‘level‘: ‘DEBUG‘, ‘class‘: ‘logging.handlers.RotatingFileHandler‘, # 保存到文件 ‘formatter‘: ‘standard‘, ‘filename‘: logfile_path, # 日志文件 ‘maxBytes‘: 1024*1024*5, # 日志大小 5M ‘backupCount‘: 5, ‘encoding‘: ‘utf-8‘, # 日志文件的编码,再也不用担心中文log乱码了 }, }, ‘loggers‘: { #logging.getLogger(__name__)拿到的logger配置 ‘‘: { ‘handlers‘: [‘default‘, ‘console‘], # 这里把上面定义的两个handler都加上,即log数据既写入文件又打印到屏幕 ‘level‘: ‘DEBUG‘, ‘propagate‘: True, # 向上(更高level的logger)传递 }, }, } def load_my_logging_cfg(): logging.config.dictConfig(LOGGING_DIC) # 导入上面定义的logging配置 logger = logging.getLogger(__name__) # 生成一个log实例 logger.info(‘It works!‘) # 记录该文件的运行状态 if __name__ == ‘__main__‘: load_my_logging_cfg() logging配置文件

""" MyLogging Test """ import time import logging import my_logging # 导入自定义的logging配置 logger = logging.getLogger(__name__) # 生成logger实例 def demo(): logger.debug("start range... time:{}".format(time.time())) logger.info("中文测试开始。。。") for i in range(10): logger.debug("i:{}".format(i)) time.sleep(0.2) else: logger.debug("over range... time:{}".format(time.time())) logger.info("中文测试结束。。。") if __name__ == "__main__": my_logging.load_my_logging_cfg() # 在你程序文件的入口加载自定义logging配置 demo() 使用

注意注意注意: #1、有了上述方式我们的好处是:所有与logging模块有关的配置都写到字典中就可以了,更加清晰,方便管理 #2、我们需要解决的问题是: 1、从字典加载配置:logging.config.dictConfig(settings.LOGGING_DIC) 2、拿到logger对象来产生日志 logger对象都是配置到字典的loggers 键对应的子字典中的 按照我们对logging模块的理解,要想获取某个东西都是通过名字,也就是key来获取的 于是我们要获取不同的logger对象就是 logger=logging.getLogger(‘loggers子字典的key名‘) 但问题是:如果我们想要不同logger名的logger对象都共用一段配置,那么肯定不能在loggers子字典中定义n个key ‘loggers‘: { ‘l1‘: { ‘handlers‘: [‘default‘, ‘console‘], # ‘level‘: ‘DEBUG‘, ‘propagate‘: True, # 向上(更高level的logger)传递 }, ‘l2: { ‘handlers‘: [‘default‘, ‘console‘ ], ‘level‘: ‘DEBUG‘, ‘propagate‘: False, # 向上(更高level的logger)传递 }, ‘l3‘: { ‘handlers‘: [‘default‘, ‘console‘], # ‘level‘: ‘DEBUG‘, ‘propagate‘: True, # 向上(更高level的logger)传递 }, } #我们的解决方式是,定义一个空的key ‘loggers‘: { ‘‘: { ‘handlers‘: [‘default‘, ‘console‘], ‘level‘: ‘DEBUG‘, ‘propagate‘: True, }, } 这样我们再取logger对象时 logging.getLogger(__name__),不同的文件__name__不同,这保证了打印日志时标识信息不同,但是拿着该名字去loggers里找key名时却发现找不到,于是默认使用key=‘‘的配置 !!!关于如何拿到logger对象的详细解释!!!
三 re模块
一:什么是正则?
正则就是用一些具有特殊含义的符号组合到一起(称为正则表达式)来描述字符或者字符串的方法。或者说:正则就是用来描述一类事物的规则。(在Python中)它内嵌在Python中,并通过 re 模块实现。正则表达式模式被编译成一系列的字节码,然后由用 C 编写的匹配引擎执行。
生活中处处都是正则:
比如我们描述:4条腿
你可能会想到的是四条腿的动物或者桌子,椅子等
继续描述:4条腿,活的
就只剩下四条腿的动物这一类了
二:常用匹配模式(元字符)
http://blog.csdn.net/yufenghyc/article/details/51078107
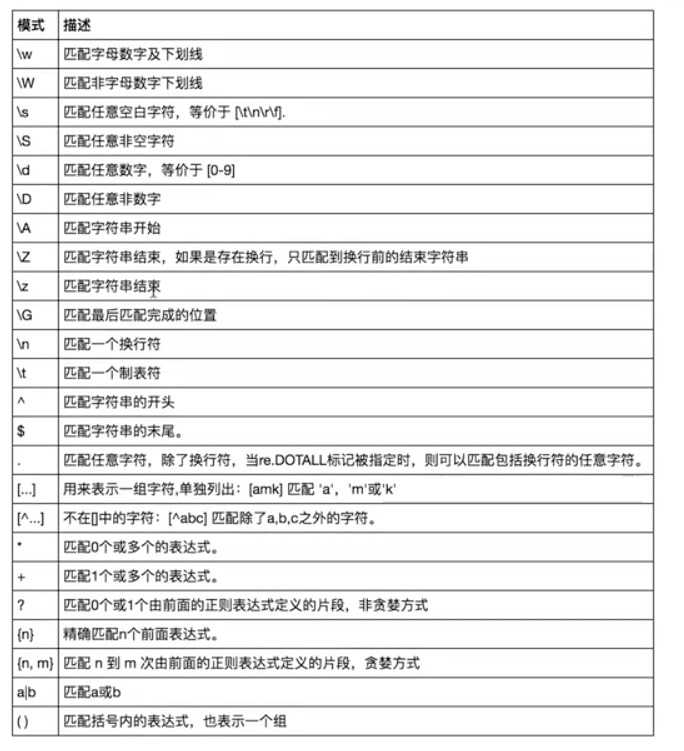
# =================================匹配模式=================================
#一对一的匹配
# ‘hello‘.replace(old,new)
# ‘hello‘.find(‘pattern‘)
#正则匹配
import re
#\w与\W
print(re.findall(‘\w‘,‘hello egon 123‘)) #[‘h‘, ‘e‘, ‘l‘, ‘l‘, ‘o‘, ‘e‘, ‘g‘, ‘o‘, ‘n‘, ‘1‘, ‘2‘, ‘3‘]
print(re.findall(‘\W‘,‘hello egon 123‘)) #[‘ ‘, ‘ ‘]
#\s与\S
print(re.findall(‘\s‘,‘hello egon 123‘)) #[‘ ‘, ‘ ‘, ‘ ‘, ‘ ‘]
print(re.findall(‘\S‘,‘hello egon 123‘)) #[‘h‘, ‘e‘, ‘l‘, ‘l‘, ‘o‘, ‘e‘, ‘g‘, ‘o‘, ‘n‘, ‘1‘, ‘2‘, ‘3‘]
#\n \t都是空,都可以被\s匹配
print(re.findall(‘\s‘,‘hello \n egon \t 123‘)) #[‘ ‘, ‘\n‘, ‘ ‘, ‘ ‘, ‘\t‘, ‘ ‘]
#\n与\t
print(re.findall(r‘\n‘,‘hello egon \n123‘)) #[‘\n‘]
print(re.findall(r‘\t‘,‘hello egon\t123‘)) #[‘\n‘]
#\d与\D
print(re.findall(‘\d‘,‘hello egon 123‘)) #[‘1‘, ‘2‘, ‘3‘]
print(re.findall(‘\D‘,‘hello egon 123‘)) #[‘h‘, ‘e‘, ‘l‘, ‘l‘, ‘o‘, ‘ ‘, ‘e‘, ‘g‘, ‘o‘, ‘n‘, ‘ ‘]
#\A与\Z
print(re.findall(‘\Ahe‘,‘hello egon 123‘)) #[‘he‘],\A==>^
print(re.findall(‘123\Z‘,‘hello egon 123‘)) #[‘he‘],\Z==>$
#^与$
print(re.findall(‘^h‘,‘hello egon 123‘)) #[‘h‘]
print(re.findall(‘3$‘,‘hello egon 123‘)) #[‘3‘]
# 重复匹配:| . | * | ? | .* | .*? | + | {n,m} |
#.
print(re.findall(‘a.b‘,‘a1b‘)) #[‘a1b‘]
print(re.findall(‘a.b‘,‘a1b a*b a b aaab‘)) #[‘a1b‘, ‘a*b‘, ‘a b‘, ‘aab‘]
print(re.findall(‘a.b‘,‘a\nb‘)) #[]
print(re.findall(‘a.b‘,‘a\nb‘,re.S)) #[‘a\nb‘]
print(re.findall(‘a.b‘,‘a\nb‘,re.DOTALL)) #[‘a\nb‘]同上一条意思一样
#*
print(re.findall(‘ab*‘,‘bbbbbbb‘)) #[]
print(re.findall(‘ab*‘,‘a‘)) #[‘a‘]
print(re.findall(‘ab*‘,‘abbbb‘)) #[‘abbbb‘]
#?
print(re.findall(‘ab?‘,‘a‘)) #[‘a‘]
print(re.findall(‘ab?‘,‘abbb‘)) #[‘ab‘]
#匹配所有包含小数在内的数字
print(re.findall(‘\d+\.?\d*‘,"asdfasdf123as1.13dfa12adsf1asdf3")) #[‘123‘, ‘1.13‘, ‘12‘, ‘1‘, ‘3‘]
#.*默认为贪婪匹配
print(re.findall(‘a.*b‘,‘a1b22222222b‘)) #[‘a1b22222222b‘]
#.*?为非贪婪匹配:推荐使用
print(re.findall(‘a.*?b‘,‘a1b22222222b‘)) #[‘a1b‘]
#+
print(re.findall(‘ab+‘,‘a‘)) #[]
print(re.findall(‘ab+‘,‘abbb‘)) #[‘abbb‘]
#{n,m}
print(re.findall(‘ab{2}‘,‘abbb‘)) #[‘abb‘]
print(re.findall(‘ab{2,4}‘,‘abbb‘)) #[‘abb‘]
print(re.findall(‘ab{1,}‘,‘abbb‘)) #‘ab{1,}‘ ===> ‘ab+‘
print(re.findall(‘ab{0,}‘,‘abbb‘)) #‘ab{0,}‘ ===> ‘ab*‘
#[]
print(re.findall(‘a[1*-]b‘,‘a1b a*b a-b‘)) #[]内的都为普通字符了,且如果-没有被转意的话,应该放到[]的开头或结尾
print(re.findall(‘a[^1*-]b‘,‘a1b a*b a-b a=b‘)) #[]内的^代表的意思是取反,所以结果为[‘a=b‘]
print(re.findall(‘a[0-9]b‘,‘a1b a*b a-b a=b‘)) #[]内的^代表的意思是取反,所以结果为[‘a=b‘]
print(re.findall(‘a[a-z]b‘,‘a1b a*b a-b a=b aeb‘)) #[]内的^代表的意思是取反,所以结果为[‘a=b‘]
print(re.findall(‘a[a-zA-Z]b‘,‘a1b a*b a-b a=b aeb aEb‘)) #[]内的^代表的意思是取反,所以结果为[‘a=b‘]
#\# print(re.findall(‘a\\c‘,‘a\c‘)) #对于正则来说a\\c确实可以匹配到a\c,但是在python解释器读取a\\c时,会发生转义,然后交给re去执行,所以抛出异常
print(re.findall(r‘a\\c‘,‘a\c‘)) #r代表告诉解释器使用rawstring,即原生字符串,把我们正则内的所有符号都当普通字符处理,不要转义
print(re.findall(‘a\\\\c‘,‘a\c‘)) #同上面的意思一样,和上面的结果一样都是[‘a\\c‘]
#():分组
print(re.findall(‘ab+‘,‘ababab123‘)) #[‘ab‘, ‘ab‘, ‘ab‘]
print(re.findall(‘(ab)+123‘,‘ababab123‘)) #[‘ab‘],匹配到末尾的ab123中的ab
print(re.findall(‘(?:ab)+123‘,‘ababab123‘)) #findall的结果不是匹配的全部内容,而是组内的内容,?:可以让结果为匹配的全部内容
print(re.findall(‘href="(.*?)"‘,‘<a href="http://www.baidu.com">点击</a>‘))#[‘http://www.baidu.com‘]
print(re.findall(‘href="(?:.*?)"‘,‘<a href="http://www.baidu.com">点击</a>‘))#[‘href="http://www.baidu.com"‘]
#|
print(re.findall(‘compan(?:y|ies)‘,‘Too many companies have gone bankrupt, and the next one is my company‘))
# ===========================re模块提供的方法介绍===========================
import re
#1
print(re.findall(‘e‘,‘alex make love‘) ) #[‘e‘, ‘e‘, ‘e‘],返回所有满足匹配条件的结果,放在列表里
#2
print(re.search(‘e‘,‘alex make love‘).group()) #e,只到找到第一个匹配然后返回一个包含匹配信息的对象,该对象可以通过调用group()方法得到匹配的字符串,如果字符串没有匹配,则返回None。
#3
print(re.match(‘e‘,‘alex make love‘)) #None,同search,不过在字符串开始处进行匹配,完全可以用search+^代替match
#4
print(re.split(‘[ab]‘,‘abcd‘)) #[‘‘, ‘‘, ‘cd‘],先按‘a‘分割得到‘‘和‘bcd‘,再对‘‘和‘bcd‘分别按‘b‘分割
#5
print(‘===>‘,re.sub(‘a‘,‘A‘,‘alex make love‘)) #===> Alex mAke love,不指定n,默认替换所有
print(‘===>‘,re.sub(‘a‘,‘A‘,‘alex make love‘,1)) #===> Alex make love
print(‘===>‘,re.sub(‘a‘,‘A‘,‘alex make love‘,2)) #===> Alex mAke love
print(‘===>‘,re.sub(‘^(\w+)(.*?\s)(\w+)(.*?\s)(\w+)(.*?)$‘,r‘\5\2\3\4\1‘,‘alex make love‘)) #===> love make alex
print(‘===>‘,re.subn(‘a‘,‘A‘,‘alex make love‘)) #===> (‘Alex mAke love‘, 2),结果带有总共替换的个数
#6
obj=re.compile(‘\d{2}‘)
print(obj.search(‘abc123eeee‘).group()) #12
print(obj.findall(‘abc123eeee‘)) #[‘12‘],重用了obj

import re print(re.findall("<(?P<tag_name>\w+)>\w+</(?P=tag_name)>","<h1>hello</h1>")) #[‘h1‘] print(re.search("<(?P<tag_name>\w+)>\w+</(?P=tag_name)>","<h1>hello</h1>").group()) #<h1>hello</h1> print(re.search("<(?P<tag_name>\w+)>\w+</(?P=tag_name)>","<h1>hello</h1>").groupdict()) #<h1>hello</h1> print(re.search(r"<(\w+)>\w+</(\w+)>","<h1>hello</h1>").group()) print(re.search(r"<(\w+)>\w+</\1>","<h1>hello</h1>").group()) 补充一

import re print(re.findall(r‘-?\d+\.?\d*‘,"1-12*(60+(-40.35/5)-(-4*3))")) #找出所有数字[‘1‘, ‘-12‘, ‘60‘, ‘-40.35‘, ‘5‘, ‘-4‘, ‘3‘] #使用|,先匹配的先生效,|左边是匹配小数,而findall最终结果是查看分组,所有即使匹配成功小数也不会存入结果 #而不是小数时,就去匹配(-?\d+),匹配到的自然就是,非小数的数,在此处即整数 print(re.findall(r"-?\d+\.\d*|(-?\d+)","1-2*(60+(-40.35/5)-(-4*3))")) #找出所有整数[‘1‘, ‘-2‘, ‘60‘, ‘‘, ‘5‘, ‘-4‘, ‘3‘] 补充二


