1: 为系统添加操作用户,并授予sudo权限
[root@localhost ~]# groupadd cai [root@localhost ~]# useradd cai -g cai [root@localhost ~]# passwd cai 更改用户 cai 的密码 。 新的 密码: 无效的密码: 过于简单化/系统化 无效的密码: 过于简单 重新输入新的 密码: passwd: 所有的身份验证令牌已经成功更新。 [root@localhost ~]# su - cai
sudo的配置文件在/etc/sudoers下面,不过是只读文件。想要修改使用“visudo”命令。
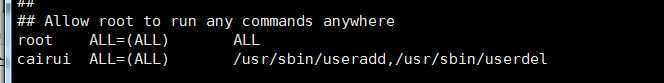
用户名 可登录的终端 具体命令(使用绝对路径,which查看)
cairui ALL=(ALL) /usr/sbin/useradd
2: 配置Yum源为国内源(在我的其他博客中专门有一篇介绍,此处不写了)
3: 关闭防火墙(iptables)和Selinux
(1)因为防火墙和selinux的设置很麻烦,而且需要大量的时间去搞,所以索性就关掉。
临时关闭防火墙:(可以查看状态,重启,关闭,打开)
[root@localhost ~]# /etc/init.d/iptables
Usage: iptables {start|stop|reload|restart|condrestart|status|panic|save}
永久关闭防火墙:(关闭开机自启)
[root@localhost ~]# chkconfig iptables off
查看iptables开机状态:
[root@localhost ~]# chkconfig --list | grep iptables iptables 0:关闭 1:关闭 2:关闭 3:关闭 4:关闭 5:关闭 6:关闭
(2)关闭selinux
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/selinux/config # This file controls the state of SELinux on the system. # SELINUX= can take one of these three values: # enforcing - SELinux security policy is enforced. # permissive - SELinux prints warnings instead of enforcing. # disabled - No SELinux policy is loaded. #SELINUX=enforcing SELINUX=disabled 修改为disabled # SELINUXTYPE= can take one of these two values: # targeted - Targeted processes are protected, # mls - Multi Level Security protection. SELINUXTYPE=targeted
4: 修改ssh服务的默认配置
修改之前先备份默认的配置:
[root@localhost ~]# cp /etc/ssh/sshd_config /etc/ssh/sshd_config.backup
再修改
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/ssh/sshd_config # $OpenBSD: sshd_config,v 1.80 2008/07/02 02:24:18 djm Exp $ # This is the sshd server system-wide configuration file. See # sshd_config(5) for more information. # This sshd was compiled with PATH=/usr/local/bin:/bin:/usr/bin # The strategy used for options in the default sshd_config shipped with # OpenSSH is to specify options with their default value where # possible, but leave them commented. Uncommented options change a # default value. #Port 22 Port 52000 修改Linux默认连接端口 #AddressFamily any #ListenAddress 0.0.0.0 #ListenAddress :: # Disable legacy (protocol version 1) support in the server for new # installations. In future the default will change to require explicit # activation of protocol 1 Protocol 2 # HostKey for protocol version 1 #HostKey /etc/ssh/ssh_host_key # HostKeys for protocol version 2 #HostKey /etc/ssh/ssh_host_rsa_key #HostKey /etc/ssh/ssh_host_dsa_key # Lifetime and size of ephemeral version 1 server key #KeyRegenerationInterval 1h #ServerKeyBits 1024 # Logging # obsoletes QuietMode and FascistLogging #SyslogFacility AUTH SyslogFacility AUTHPRIV #LogLevel INFO # Authentication: #LoginGraceTime 2m #PermitRootLogin yes PermitRootLogin no #不允许root用户登录(因为每个人都知道root能够登录) #StrictModes yes #MaxAuthTries 6 #MaxSessions 10 #RSAAuthentication yes #PubkeyAuthentication yes #AuthorizedKeysFile .ssh/authorized_keys #AuthorizedKeysCommand none #AuthorizedKeysCommandRunAs nobody # For this to work you will also need host keys in /etc/ssh/ssh_known_hosts #RhostsRSAAuthentication no # similar for protocol version 2 #HostbasedAuthentication no # Change to yes if you don‘t trust ~/.ssh/known_hosts for # RhostsRSAAuthentication and HostbasedAuthentication #IgnoreUserKnownHosts no # Don‘t read the user‘s ~/.rhosts and ~/.shosts files #IgnoreRhosts yes # To disable tunneled clear text passwords, change to no here! #PasswordAuthentication yes #PermitEmptyPasswords no PasswordAuthentication yes # Change to no to disable s/key passwords #ChallengeResponseAuthentication yes ChallengeResponseAuthentication no # Kerberos options #KerberosAuthentication no #KerberosOrLocalPasswd yes #KerberosTicketCleanup yes #KerberosGetAFSToken no #KerberosUseKuserok yes # GSSAPI options #GSSAPIAuthentication no GSSAPIAuthentication yes #GSSAPICleanupCredentials yes GSSAPICleanupCredentials yes #GSSAPIStrictAcceptorCheck yes #GSSAPIKeyExchange no # Set this to ‘yes‘ to enable PAM authentication, account processing, # and session processing. If this is enabled, PAM authentication will # be allowed through the ChallengeResponseAuthentication and # PasswordAuthentication. Depending on your PAM configuration, # PAM authentication via ChallengeResponseAuthentication may bypass # the setting of "PermitRootLogin without-password". # If you just want the PAM account and session checks to run without # PAM authentication, then enable this but set PasswordAuthentication # and ChallengeResponseAuthentication to ‘no‘. #UsePAM no UsePAM yes # Accept locale-related environment variables AcceptEnv LANG LC_CTYPE LC_NUMERIC LC_TIME LC_COLLATE LC_MONETARY LC_MESSAGES AcceptEnv LC_PAPER LC_NAME LC_ADDRESS LC_TELEPHONE LC_MEASUREMENT AcceptEnv LC_IDENTIFICATION LC_ALL LANGUAGE AcceptEnv XMODIFIERS #AllowAgentForwarding yes #AllowTcpForwarding yes #GatewayPorts no #X11Forwarding no X11Forwarding yes #X11DisplayOffset 10 #X11UseLocalhost yes #PrintMotd yes #PrintLastLog yes #TCPKeepAlive yes #UseLogin no #UsePrivilegeSeparation yes #PermitUserEnvironment no #Compression delayed #ClientAliveInterval 0 #ClientAliveCountMax 3 #ShowPatchLevel no #UseDNS yes UseDNS no #不使用DNS #PidFile /var/run/sshd.pid #MaxStartups 10:30:100 #PermitTunnel no #ChrootDirectory none # no default banner path #Banner none # override default of no subsystems Subsystem sftp /usr/libexec/openssh/sftp-server # Example of overriding settings on a per-user basis #Match User anoncvs # X11Forwarding no # AllowTcpForwarding no # ForceCommand cvs server
修改完之后重启:
[root@localhost ~]# /etc/init.d/sshd
用法: /etc/init.d/sshd {start|stop|restart|reload|force-reload|condrestart|try-restart|status}
5: 系统内核优化
[root@localhost ~]# cat /etc/sysctl.conf # Kernel sysctl configuration file for Red Hat Linux # # For binary values, 0 is disabled, 1 is enabled. See sysctl(8) and # sysctl.conf(5) for more details. # # Use ‘/sbin/sysctl -a‘ to list all possible parameters. # Controls IP packet forwarding net.ipv4.ip_forward = 0 # Controls source route verification net.ipv4.conf.default.rp_filter = 1 # Do not accept source routing net.ipv4.conf.default.accept_source_route = 0 # Controls the System Request debugging functionality of the kernel kernel.sysrq = 0 # Controls whether core dumps will append the PID to the core filename. # Useful for debugging multi-threaded applications. kernel.core_uses_pid = 1 # Controls the use of TCP syncookies net.ipv4.tcp_syncookies = 1 # Controls the default maxmimum size of a mesage queue kernel.msgmnb = 65536 # Controls the maximum size of a message, in bytes kernel.msgmax = 65536 # Controls the maximum shared segment size, in bytes kernel.shmmax = 68719476736 # Controls the maximum number of shared memory segments, in pages kernel.shmall = 4294967296 # 下面是内核调优参数 net.ipv4.tcp_syn_retries = 1 net.ipv4.tcp_synack_retries = 1 net.ipv4.tcp_keepalive_time = 600 net.ipv4.tcp_keepalive_probes = 3 net.ipv4.tcp_keepalive_intvl =15 net.ipv4.tcp_retries2 = 5 net.ipv4.tcp_fin_timeout = 2 net.ipv4.tcp_max_tw_buckets = 36000 net.ipv4.tcp_tw_recycle = 1 net.ipv4.tcp_tw_reuse = 1 net.ipv4.tcp_max_orphans = 32768 net.ipv4.tcp_syncookies = 1 net.ipv4.tcp_max_syn_backlog = 16384 net.ipv4.tcp_wmem = 8192 131072 16777216 net.ipv4.tcp_rmem = 32768 131072 16777216 net.ipv4.tcp_mem = 786432 1048576 1572864 net.ipv4.ip_local_port_range = 1024 65000 net.ipv4.ip_conntrack_max = 65536 net.ipv4.netfilter.ip_conntrack_max=65536 net.ipv4.netfilter.ip_conntrack_tcp_timeout_established=180 net.core.somaxconn = 16384 net.core.netdev_max_backlog = 16384
[root@localhost ~]# sysctl -p #配置生效 net.ipv4.ip_forward = 0 net.ipv4.conf.default.rp_filter = 1 net.ipv4.conf.default.accept_source_route = 0 kernel.sysrq = 0 kernel.core_uses_pid = 1 net.ipv4.tcp_syncookies = 1 kernel.msgmnb = 65536 kernel.msgmax = 65536 kernel.shmmax = 68719476736 kernel.shmall = 4294967296 net.ipv4.tcp_syn_retries = 1 net.ipv4.tcp_synack_retries = 1 net.ipv4.tcp_keepalive_time = 600 net.ipv4.tcp_keepalive_probes = 3 net.ipv4.tcp_keepalive_intvl = 15 net.ipv4.tcp_retries2 = 5 net.ipv4.tcp_fin_timeout = 2 net.ipv4.tcp_max_tw_buckets = 36000 net.ipv4.tcp_tw_recycle = 1 net.ipv4.tcp_tw_reuse = 1 net.ipv4.tcp_max_orphans = 32768 net.ipv4.tcp_syncookies = 1 net.ipv4.tcp_max_syn_backlog = 16384 net.ipv4.tcp_wmem = 8192 131072 16777216 net.ipv4.tcp_rmem = 32768 131072 16777216 net.ipv4.tcp_mem = 786432 1048576 1572864 net.ipv4.ip_local_port_range = 1024 65000 error: "net.ipv4.ip_conntrack_max" is an unknown key error: "net.ipv4.netfilter.ip_conntrack_max" is an unknown key error: "net.ipv4.netfilter.ip_conntrack_tcp_timeout_established" is an unknown key net.core.somaxconn = 16384 net.core.netdev_max_backlog = 16384
6: 超时设置(timeout)
为了系统的安全,设置无操作超时自动退出登录设置
临时生效:
[root@centos6 ~]# export TMOUT=5 [root@centos6 ~]# timed out waiting for input: auto-logout
永久配置生效:
[root@centos6 ~]# echo "export TMOUT=300" >>/etc/profile 实际生产环境 5 分钟 [root@centos6 ~]# source / etc/profile
7: 加大文件描述符
文件描述符是由无符号整数表示的句柄(一般使用范围0~65535),进程使用它来标识打开的文件。文件描述符与包括相关信息(如文件的打开模式、文件的位置类型、文件的初始类型等)的对象想关联,这些信息称为文件的上下文。
对于内核而言,所有打开的文件都是通过文件描述符引用的。当打开一个现有文件或者创建一个新文件时,内核向进程返回一个文件描述符。
按照惯例,UNIX系统shell使用0-》标准输入,1-》标准输出,2-》标准错误
查看系统默认的文件描述符大小: [root@centos6 ~]# ulimit -n 1024 [root@centos6 ~]# echo "* - nofile 65535">>/etc/security/limits.conf 退出重新登录,才会生效 [root@centos6 ~]# ulimit -n 65535
8: 隐藏系统版本消息
[cairui@localhost ~]$ cat /etc/issue CentOS release 6.8 (Final) Kernel \r on an \m [cairui@localhost ~]$ cat /etc/issue.net CentOS release 6.8 (Final) Kernel \r on an \m
只需要清空上述的文件内容,就可以隐藏信息。
9: 给grub引导菜单加密码保护(因为grub能进入看到root密码)
[root@localhost ~]# /sbin/grub-md5-crypt Password: Retype password: $1$kpiKh/$..jTvOdnHGnMsqqs5OWlM/ [root@localhost ~]# vi /etc/grub.conf [root@localhost ~]# cat /etc/grub.conf # grub.conf generated by anaconda # # Note that you do not have to rerun grub after making changes to this file # NOTICE: You have a /boot partition. This means that # all kernel and initrd paths are relative to /boot/, eg. # root (hd0,0) # kernel /vmlinuz-version ro root=/dev/sda3 # initrd /initrd-[generic-]version.img #boot=/dev/sda default=0 timeout=5 splashimage=(hd0,0)/grub/splash.xpm.gz hiddenmenu password --md5 $1$hv58gkgk9G995885/JG0orl4m #后来添加的 title CentOS 6 (2.6.32-642.el6.x86_64) root (hd0,0) kernel /vmlinuz-2.6.32-642.el6.x86_64 ro root=UUID=57e48303-c321-4c12-8ac4-7596c31f55ef rd_NO_LUKS KEYBOARDTYPE=pc KEYTABLE=us rd_NO_MD crashkernel=auto LANG=zh_CN.UTF-8 rd_NO_LVM rd_NO_DM rhgb quiet initrd /initramfs-2.6.32-642.el6.x86_64.img
10: 调整字符集
[root@centos6 ssh]# echo $LANG en_US.UTF-8 [root@centos6 ssh]# cat /etc/sysconfig/i18n LANG="en_US.UTF-8" SYSFONT="latarcyrheb-sun16" [root@centos6 ssh]# cp /etc/sysconfig/i18n /etc/sysconfig/i18n.2016.12.21 [root@centos6 ssh]# sed -i ‘s#LANG="en_US.UTF-8"#LANG="zh_CN.UTF-8"#g‘ /etc/sysconfig/i18n [root@centos6 ssh]# source /etc/sysconfig/i18n [root@centos6 ssh]# echo $LANG zh_CN.UTF-8
