Description
给定一个长度为n的正整数数列a[i]。
定义2个位置的f值为两者位置差与数值差的和,即f(x,y)=|x-y|+|a[x]-a[y]|。
你需要写一个程序支持2种操作(k都是正整数):
Modify x k:将第x个数的值修改为k。
Query x k:询问有几个i满足f(x,i)<=k。询问不仅要考虑当前数列,还要考虑任意历史版本,即统计任意位置上出现过的任意数值与当前的a[x]的f值<=k的对数。(某位置多次修改为同样的数值,按多次统计)
Main
令F(x,y)=|x-y|+|a[x]-a[y]|,每次可以将a[x]修改为k,或者查询满足f(x,i)≤k的个数。
Analysis
【二维线段树/树状数组】
看到题目这样的粗俗,笼统,简洁明了,便知道一定要用一个数据结构维护
我们可以将x抽象为x坐标,a[x]抽象为y坐标,那么f(x,y)的意思就显然了:表示x点(x,a[x])和y点(y,a[y])的曼哈顿距离。
但是这个曼哈顿距离比较蛋疼,不着急,画(截)个图看看。
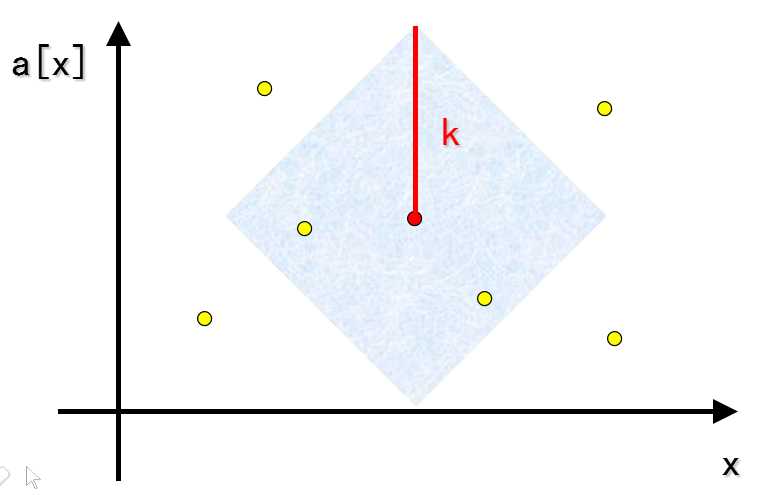
我们发现图片大概是这样的,发现这个可以取的范围是个菱形,旋转90°就变成了正方形。旋转就是使坐标(x,y)变成(x+y,x-y)
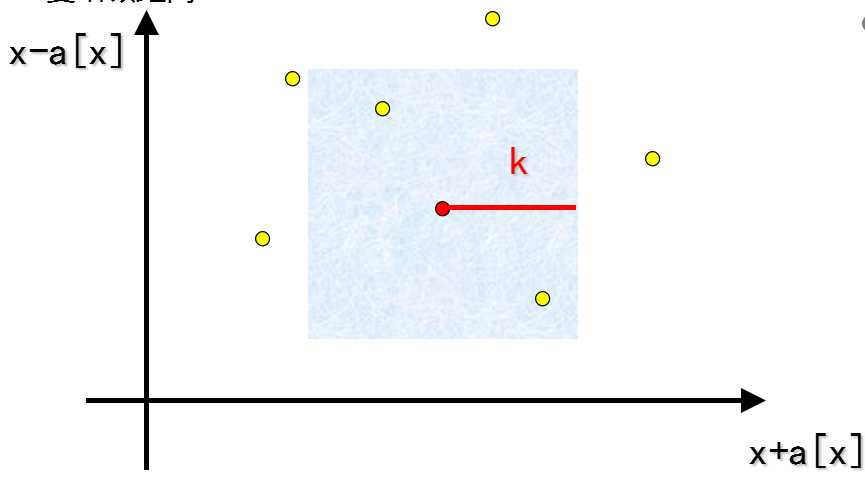
那么,问题就转化为每次可以加入一些点,求某个正方形内包含点的个数。
【K-Dtree】
。。。
【cbq分治+主席树】
...
Solution
我们考虑用一个数据结构来维护,如二维线段树/树状数组。
每次相当于插入点(x+a[x],x-a[x])到图中,线段树/树状数组维护左下角为(x1,y1),右上角为(x2,y2)的矩阵信息,查询即可。
对于二维线段树,有两种实现方法。一种是划分为4个区域,第二种是划分为2个,根据长宽的大小来切。
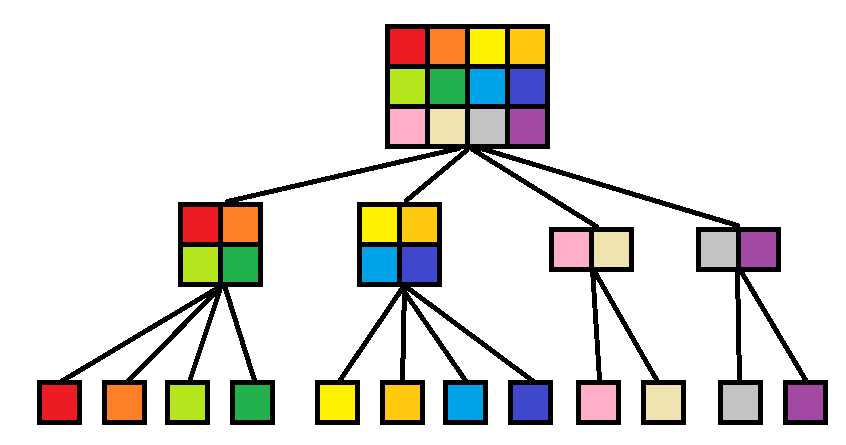
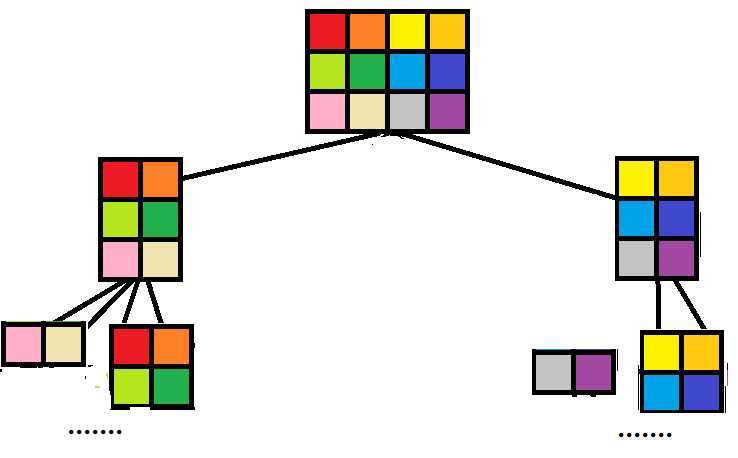
要动态开点。直接做会超时,要加优化:当前子树没有贡献,直接退出。
【K-Dtree】
。。。
【cbq分治+主席树】
...
Code
{$inline on} var ch,lala:char; n,m,i,x,y,tot,ans:longint; a:array[0..60000] of longint; tree:array[0..2500000] of longint; son:array[0..2500000,1..2] of longint; procedure dispose; inline; begin read(ch); lala:=‘1‘; while lala<>‘ ‘ do read(lala); readln(x,y); end; procedure fyj(x:longint); inline; begin if son[x,1]=0 then begin inc(tot); son[x,1]:=tot; inc(tot); son[x,2]:=tot; end; end; procedure change(root,x1,y1,x2,y2,fx,fy:longint); inline; var mid:longint; begin if (x1=x2) and (y1=y2) and (x1=fx) and (y1=fy) then begin inc(tree[root]); exit; end; fyj(root); if x2-x1>=y2-y1 then begin mid:=(x1+x2) shr 1; if fx<=mid then change(son[root,1],x1,y1,mid,y2,fx,fy) else change(son[root,2],mid+1,y1,x2,y2,fx,fy); end else begin mid:=(y1+y2) shr 1; if fy<=mid then change(son[root,1],x1,y1,x2,mid,fx,fy) else change(son[root,2],x1,mid+1,x2,y2,fx,fy); end; tree[root]:=tree[son[root,1]]+tree[son[root,2]]; end; procedure find(root,x1,y1,x2,y2,fx1,fy1,fx2,fy2:longint); inline; var mid:longint; begin if (x1=fx1) and (x2=fx2) and (y1=fy1) and (y2=fy2) then begin ans:=ans+tree[root]; exit; end; if son[root,1]=0 then exit; if x2-x1>=y2-y1 then begin mid:=(x1+x2) shr 1; if fx2<=mid then find(son[root,1],x1,y1,mid,y2,fx1,fy1,fx2,fy2) else if fx1>mid then find(son[root,2],mid+1,y1,x2,y2,fx1,fy1,fx2,fy2) else begin find(son[root,1],x1,y1,mid,y2,fx1,fy1,mid,fy2); find(son[root,2],mid+1,y1,x2,y2,mid+1,fy1,fx2,fy2); end; end else begin mid:=(y1+y2) shr 1; if fy2<=mid then find(son[root,1],x1,y1,x2,mid,fx1,fy1,fx2,fy2) else if fy1>mid then find(son[root,2],x1,mid+1,x2,y2,fx1,fy1,fx2,fy2) else begin find(son[root,1],x1,y1,x2,mid,fx1,fy1,fx2,mid); find(son[root,2],x1,mid+1,x2,y2,fx1,mid+1,fx2,fy2); end; end; end; begin readln(n,m); tot:=1; for i:=1 to n do begin read(a[i]); change(1,0,0,320000,280000,i+a[i]+100000,i-a[i]+100000); end; readln; for i:=1 to m do begin dispose; if ch=‘M‘ then begin change(1,0,0,320000,280000,x+y+100000,x-y+100000); a[x]:=y; end else begin ans:=0; find(1,0,0,320000,280000,x+a[x]-y+100000,x-a[x]-y+100000,x+a[x]+y+100000,x-a[x]+y+100000); writeln(ans); end; end; end.
