输入输出流(I/O)
通过数据流、序列化和文件系统提供输入和输出。输入和输出是相对于内存而言,将文件中的数据读取到内存中即为输入;将数据保存到文件中即为输出。
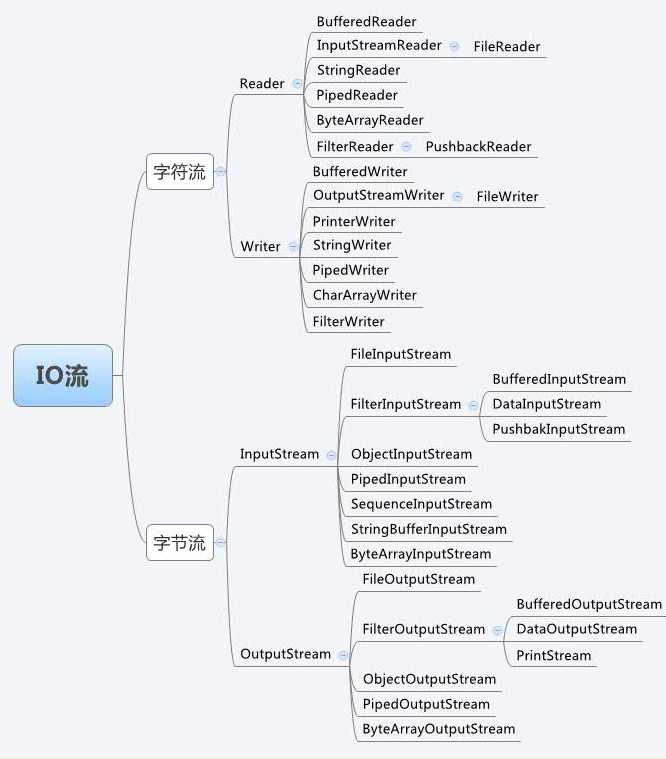
Java流操作有关的类或接口
|
File |
文件类 |
|
RandomAccessFile |
随机存取文件类 |
|
InputStream |
字节输入流 |
|
OutputStream |
字节输出流 |
|
Reader |
字符输入流 |
|
Writer |
字符输出流 |
Java流类图结构
File类
java.io.File
文件和目录路径名的抽象表示形式。
File类是IO包中唯一代表磁盘文件本身的对象。通过File类创建,删除,重命名文件。File类对象的主要作用就是用来获取文本本身的一些信息。如文本的所在的目录,文件的长度,读写权限等等。
路径字符串与抽象路径名之间的转换与系统有关。默认名称分隔符有系统属性File.separator定义。
构造方法
File(File parent, String child)
根据 parent 抽象路径名和 child 路径名字符串创建一个新 File 实例。
File(String pathname)
通过将给定路径名字符串转换为抽象路径名来创建一个新 File 实例。
File(String parent, String child)
根据 parent 路径名字符串和 child 路径名字符串创建一个新 File 实例。
方法
public boolean createNewFile(); //创建文件,如果存在这样的文件,就不创建了。
public boolean mkdir(); //创建文件夹,如果存在这样的,就不创建了。
public boolean delete(); //删除文件或者文件夹
public boolean isDirectory(); //判断是否是目录
public boolean isFile(); //判断是否是文件
public boolean exists(); //判断是否存在
public String[] list(); //获取指定目录下的所有文件或者文件夹的名称数组
public File[] listFiles(); //获取指定目标下的所有文件或者文件夹的File数组
程序示例:将一句话存入G盘的File文件夹中的Test.txt文件内
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
String str = "这是一句话";
String url = "G:"+File.separator+"File";
File f1 = new File(url);
//判断是否为目录,若不是则创建
if (!f1.isDirectory()) {
f1.mkdir();
}
File f2 = new File(url+File.separator+"Test.txt");
//判断是否存在此文件,若不存在则创建
if (!f2.exists()) {
f2.createNewFile();
}
//获得文件的输出流,后面的true表示文件后面可以追加
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(f2,true);
byte[] bs = str.getBytes();
out.write(bs);
out.close();
}
字节流FileInputStream和FileOutputStream
read()方法
int read();
从此输入流总读取下一个数据字节,返回一个0到255范围内的int字节值。如果到达末尾没有字节可读,则返回-1.
文件复制
public class Copy {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File f = new File("G:"+File.separator+"File"+File.separator+"Test.txt");
File f2 = new File("G:"+File.separator+"File"+File.separator+"复制.txt");
FileInputStream input = new FileInputStream(f);
FileOutputStream output = new FileOutputStream(f2);
int b;
while ((b = input.read()) != -1){
output.write(b);
}
input.close();
output.close();
System.out.println("复制完成");
}
}
高速缓冲流(BufferedInputStream和BufferedOutputStream)
BufferedInputStream中内置了一个缓冲区(数组),从BufferedInputStream中读取一个字节时,BufferedInputStream会一次性从文件中读取8192个,存在缓冲区中,返回给程序一个。程序再次读取时,就不用找文件了,直接从缓冲区中获取。直到缓冲区中所有的都被使用过,才重新从文件中读取8192个。
BufferedOutputStream也内置了一个缓冲区(数组),程序向流中写出字节时,不会直接写到文件,先写到缓冲区中,直到缓冲区写满,BufferedOutputStream才会把缓冲区中的数据一次性写到文件里。
public class Copy02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File f = new File("G:"+File.separator+"File"+File.separator+"Test.txt");
File f2 = new File("G:"+File.separator+"File"+File.separator+"复制.txt");
BufferedInputStream br = new BufferedInputStream (new FileReader(f));
BufferedOutputStream bw = new BufferedOutputStream (new FileWriter(f2));
int i;
while ((i=br.read())!= -1) {
bw.write(i);
}
br.close();
bw.close();
System.out.println("复制完成");
}
}
字符流FileReader和FileWriter
字符流可以直接读写字符
字符流读取字符,就要先读取到字节数据,然后转为字符。如果要写出字符,需要把字符转为字节再写出。
字符流不能拷贝非纯文本的文件,因为在读的时候会将字节转为字符,在转换过程中,可能找不到对应的字符,就会用?替代,写出的时候会将字符转换成字节写出去,如果是?,直接写出文件后就会乱码。
字符流同样也有高速缓冲流BufferedReader和BufferedWriter。
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File f = new File("G:"+File.separator+"File"+File.separator+"Test.txt");
File f2 = new File("G:"+File.separator+"File"+File.separator+"复制.txt");
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(f));
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(f2));
int i;
while ((i=br.read())!= -1) {
bw.write(i);
}
br.close();
bw.close();
System.out.println("复制完成");
}
字节流和字符流的区别选择
Stream结尾的都是字节流,reader和writer结尾都是字符流两者的区别就是读写的时候,一个按字节读写,一个按字符,实际上使用差不多。
在读写文件需要对内容按行处理,比如比较特定的字符,处理某一行数据的时候一般会选择字符流。只是读写文件,和文件内容无关的,一般选择字节流。
字符流 = 字节流 + 编码集
参考博客
[1] Java中IO流,输入输出流概述与总结
http://www.cnblogs.com/biehongli/p/6074713.html
