题目描述
Cows are such finicky eaters. Each cow has a preference for certain foods and drinks, and she will consume no others.
Farmer John has cooked fabulous meals for his cows, but he forgot to check his menu against their preferences. Although he might not be able to stuff everybody, he wants to give a complete meal of both food and drink to as many cows as possible.
Farmer John has cooked F (1 ≤ F ≤ 100) types of foods and prepared D (1 ≤ D ≤ 100) types of drinks. Each of his N (1 ≤ N ≤ 100) cows has decided whether she is willing to eat a particular food or drink a particular drink. Farmer John must assign a food type and a drink type to each cow to maximize the number of cows who get both.
Each dish or drink can only be consumed by one cow (i.e., once food type 2 is assigned to a cow, no other cow can be assigned food type 2).
有F种食物和D种饮料,每种食物或饮料只能供一头牛享用,且每头牛只享用一种食物和一种饮料。现在有n头牛,每头牛都有自己喜欢的食物种类列表和饮料种类列表,问最多能使几头牛同时享用到自己喜欢的食物和饮料。(1 <= f <= 100, 1 <= d <= 100, 1 <= n <= 100)
输入输出格式
输入格式:
Line 1: Three space-separated integers: N, F, and D
Lines 2..N+1: Each line i starts with a two integers Fi and Di, the number of dishes that cow i likes and the number of drinks that cow i likes. The next Fi integers denote the dishes that cow i will eat, and the Di integers following that denote the drinks that cow i will drink.
输出格式:
Line 1: A single integer that is the maximum number of cows that can be fed both food and drink that conform to their wishes
输入输出样例
说明
One way to satisfy three cows is:
Cow 1: no meal
Cow 2: Food #2, Drink #2
Cow 3: Food #1, Drink #1
Cow 4: Food #3, Drink #3
The pigeon-hole principle tells us we can do no better since there are only three kinds of food or drink. Other test data sets are more challenging, of course.
最大流问题。
一个比较容易想到的思路就是
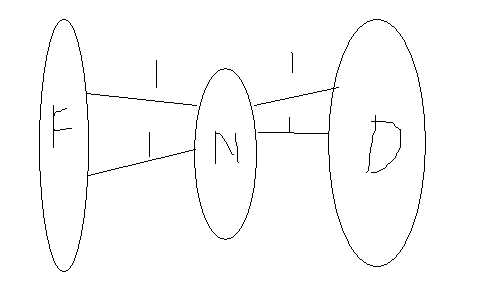
但是这样可能出现左边有两个流量经过中间同一个点的情况
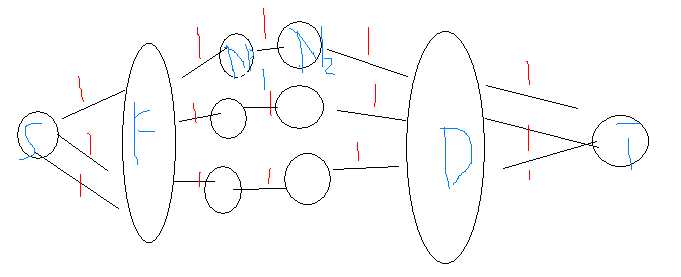
所以我们把中间的点拆开
最终的图应该是这样的
#include<cstdio> #include<cstring> #include<queue> using namespace std; const int MAXN=801,INF=5*1e8+10; inline char nc() { static char buf[MAXN],*p1=buf,*p2=buf; return p1==p2&&(p2=(p1=buf)+fread(buf,1,MAXN,stdin),p1==p2)?EOF:*p1++; } inline int read() { char c=nc();int x=0,f=1; while(c<‘0‘||c>‘9‘){if(c==‘-‘)f=-1;c=nc();} while(c>=‘0‘&&c<=‘9‘){x=x*10+c-‘0‘;c=nc();} return x*f; } int S=0,T=301; struct node { int u,v,flow,nxt; }edge[MAXN*20]; int head[MAXN],cur[MAXN],num=0; inline void add_edge(int x,int y,int z) { edge[num].u=x; edge[num].v=y; edge[num].flow=z; edge[num].nxt=head[x]; head[x]=num++; } inline void AddEdge(int x,int y,int z) { add_edge(x,y,z); add_edge(y,x,0); }int deep[MAXN]; inline bool BFS() { memset(deep,0,sizeof(deep)); deep[S]=1; queue<int>q; q.push(S); while(q.size()!=0) { int p=q.front(); q.pop(); for(int i=head[p];i!=-1;i=edge[i].nxt) if(!deep[edge[i].v]&&edge[i].flow) { deep[edge[i].v]=deep[p]+1;q.push(edge[i].v); if(edge[i].v==T) return 1; } } return deep[T]; } int DFS(int now,int nowflow) { if(now==T||nowflow<=0) return nowflow; int totflow=0; for(int &i=cur[now];i!=-1;i=edge[i].nxt) { if(deep[edge[i].v]==deep[now]+1&&edge[i].flow) { int canflow=DFS(edge[i].v,min(nowflow,edge[i].flow)); edge[i].flow-=canflow;edge[i^1].flow+=canflow; totflow+=canflow; nowflow-=canflow; if(nowflow<=0) break; } } return totflow; } int Dinic() { int ans=0; while(BFS()) { memcpy(cur,head,sizeof(head)); ans+=DFS(S,INF); } return ans; } int N,F,D; int main() { #ifdef WIN32 freopen("a.in","r",stdin); #else #endif memset(head,-1,sizeof(head)); N=read();F=read();D=read(); for(int i=1;i<=N;i++) { int Fnum=read(),Dnum=read(); AddEdge(F+i,F+N+i,1); for(int j=1;j<=Fnum;j++){int P=read();AddEdge(P,F+i,1);} for(int j=1;j<=Dnum;j++){int P=read();AddEdge(F+N+i,2*N+F+P,1);}; } for(int i=1;i<=F;i++) AddEdge(S,i,1); for(int i=1;i<=D;i++) AddEdge(2*N+F+i,T,1); printf("%d",Dinic()); return 0; }
