Arrays, Linked Lists, Stacks & Queues
Introduction
Efficiency is important
Focus on main memory data storage; data storage in secondary storage (e.g., hard disks and databases) is usually called indexing structures
Array
Array is a data structure that arranges items at equally spaced addresses in computer memory
int foo[7]
Unsorted Arrays
Pros:
- Array elements can be accessed by specifying the array name followed by the index in square brackets. Eg foo[2] is 8
- Efficient for insertion by appending a new element.
Cons:
- Have to scan through the whole array to determine for sure if an item is not there
Sorted Arrays
Pros:
- Efficient for searching
Cons:
- Have to move all items behind the point of insertion to make room for the new one
Linked Lists
A linked list is a data structure that allows both efficient searching and insertion/deletion.
A collection of items linked in a sequence:
![]()
Pros:
-
Easy to insert/delete items in the middle, provided we know where to insert/delete (a sorted linked list can easily be maintained.)
Cons:
-
Difficult to access the i-th item, given an arbitrary i
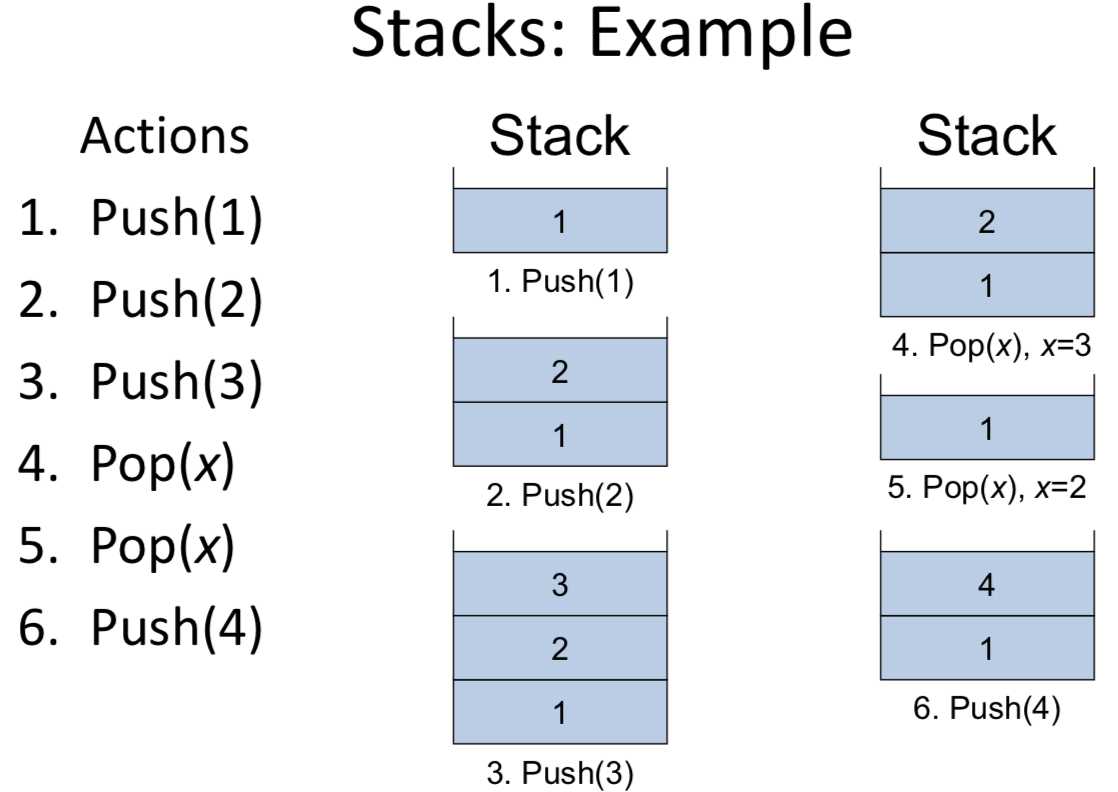
Stacks
A stack is a sequence of elements in which update can only happen at one end of the sequence, called the top.
Operations supported:
– push(x): add an element x to the top
– pop(x): remove the top element and return it in x, i.e., first-in-last-out (FILO)
Queues
