历史:
Angular是Google推出的Web前端开发框架,从12年发布起就受到了强烈的关注,他首次提出了双向绑定的概念,让人耳目一新。

Angular 2特性
就在2016年9月中旬,时隔4年,Google正式发布了Angular的第二代开发框架Angular 2,2017年3月推出了Angular4。Angular 5 出来了,不过你也不用太过担心,因为不论是Angular 4 还是Angular 5,其内核依然是Angular 2。


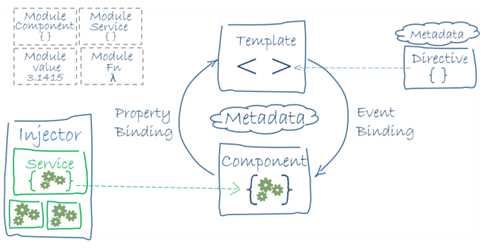
这个架构图展现了 Angular 应用中的 8 个主要构造块:
- 模块 (module)
- 组件 (component)
- 模板 (template)
- 元数据 (metadata)
- 数据绑定 (data binding)
- 指令 (directive)
- 服务 (service)
- 依赖注入 (dependency injection)
- 1. 模块 (module)
Angular 应用是模块化的,并且 Angular 有自己的模块系统,它被称为 Angular 模块或 NgModules。
Angular 或者 Ionic 新建的项目,都会存在一个根模块,默认名是 AppModule。如果你使用了模块化来创建应用,包括 AppModule,每个都会存在一个 @NgModule 装饰器的类(很像 java 中的注解,但官方命名叫装饰器)。新建的页面,如果不使用懒加载,都要在 @NgModule 中先声明后使用。
//app.module.ts
import { NgModule } from ‘@angular/core‘;
import { BrowserModule } from ‘@angular/platform-browser‘;
@NgModule({
imports: [ BrowserModule ],
providers: [ Logger ],
declarations: [ AppComponent ],
exports: [ AppComponent ],
bootstrap: [ AppComponent ]
})
export class AppModule { }
- imports 本模块声明的组件模板需要的类所在的其它模块。
- providers 服务的创建者,并加入到全局服务列表中,可用于应用任何部分。
- declarations 声明本模块中拥有的视图类。Angular 有三种视图类:组件、指令和管道。
- exports declarations 的子集,可用于其它模块的组件模板。
- bootstrap 指定应用的主视图(称为根组件),它是所有其它视图的宿主。只有根模块才能设置 bootstrap 属性。
- 2. 组件 (component)、模板 (template)、元数据 (metadata)
//hero-list.component.ts @Component({ selector: ‘hero-list‘, templateUrl: ‘./hero-list.component.html‘, providers: [ HeroService ] }) export class HeroListComponent implements OnInit { /* . . . */ }
组件就是一个类,是Angular的核心。@Component 是组件元数据装饰器,用来修饰一个组件,他能接受一个配置对象, Angular 会基于这些信息创建和展示组件及其视图。
- selector:CSS 选择器,它告诉 Angular 在父级 HTML 中查找 <hero-list> 标签,创建并插入该组件。
- templateUrl:组件 HTML 模板的模块相对地址,如果使用 template 来写的话是用“`”这个符号来直接编写 HTML 代码。
- providers:组件所需服务的依赖注入。
metadata
元数据装饰器用类似的方式来指导
Angular 的行为。 例如 @Input、@Output、@Injectable 等是一些最常用的装饰器。
- 1. 数据绑定 (data binding)
这里一共展示四种数据绑定,看一下示例代码:
1)//插值表达式 显示组件的hero.name属性的值
<li>{{hero.name}}</li>
2)//属性绑定 把父组件selectedHero的值传到子组件的hero属性中,也可以把组件中的属性绑定到模板中元素的dom属性上。
<hero-detail [hero]="selectedHero"></hero-detail>
3)//事件绑定 用户点击英雄的名字时调用组件的selectHero方法
<li (click)="selectHero(hero)"></li>
4)//双向绑定 数据属性值通过属性绑定从组件流到输入框。用户的修改通过事件绑定流回组件,把属性值设置为最新的值
<input [(ngModel)]="hero.name">
- 4. 指令 (directive)
严格来说组件就是一个指令,但是组件非常独特,并在 Angular 中位于中心地位,所以在架构概览中,我们把组件从指令中独立了出来。
我们这里提到的指令有两种类型:
结构型 structural 指令和属性
attribute 型指令。
1) 结构型指令是 ngFor、ngIf 这种的,通过在 DOM 中添加、移除和替换元素来修改布局。
2) 属性型指令是 ngModel 这种的,用来修改一个现有元素的外观或行为。
Angular 还有少量指令,它们或者修改结构布局(例如 ngSwitch ), 或者修改 DOM 元素和组件的各个方面(例如 ngStyle 和 ngClass)。
- 5. 服务 (service)
服务是用来封装可重用的业务逻辑
- 6. 依赖注入 (dependency injection)
依赖注入是提供类的新实例的一种方式,还负责处理类所需的全部依赖。大多数依赖都是服务。 Angular 使用依赖注入来提供新组件以及组件所需的服务。
比如我们要给某组件导入HeroService这个服务,看这段代码:
constructor(private service: HeroService) {
...
}
这个constructor就是构造函数,依赖注入在 constructor 中进行。前面写上 private、public(在构造函数内写上public会自动创建类的成员变量),这是 TypeScript 语法。
当 Angular 创建组件时,会首先为组件所需的服务请求一个注入器 injector。我们必须先用注入器 injector 为 HeroService 注册一个提供商 provider(服务)。
看一下下面的代码,意思就是我们必须在 providers 写上才能用(如果不在组件中注册,则需要在模块中注册)
@Component({ selector: ‘hero-list‘, templateUrl: ‘./hero-list.component.html‘, providers: [ HeroService ] })
依赖注入主要用来导入服务。
