一、平衡二叉树的定义
平衡二叉树(AVL 树)仍然是一棵二叉查找树,只是在其基础上增加了“平衡”的要求。所谓平衡是指,对 AVL 树的任意结点来说,其左子树与右子树的高度之差的绝对值不超过 1,其中左子树与右子树的高度之差称为该结点的平衡因子。
由于需要对每个结点都得到平衡因子,因此需要在树的结构中加入一个变量 height,用来记录以当前结点为根结点的子树的高度:
1 // 平衡二叉树结构体 2 struct node { 3 int v, height; // v 为结点权值, height 为当前子树高度 4 node *lchild, *rchild; // 左右孩子结点地址 5 };
在这种定义下,如果需要新建一个结点,就可以采用如下写法:
1 // 平衡二叉树新建结点 2 node* newNode(int v) { 3 node* Node = (node*)malloc(sizeof(node)); // 申请地址空间 4 Node->v = v; // 结点权值为 v 5 Node->height = 1; // 结点高度初始为 1 6 Node->lchild = Node->rchild = NULL; // 初始状态下没有左右孩子 7 return Node; 8 }
可通过下面的函数获取结点 root 所在子树的当前高度:
// 获取以 root 为根结点的子树的当前高度 int getHeight(node* root) { if(root == NULL) return 0; // 空树高度为 0 return root->height; }
于是根据定义,可以通过下面的函数计算平衡因子:
// 计算结点 root 的平衡因子 int getBalanceFactor(node* root) { // 左子树高度减右子树高度 return getHeight(root->lchild) - getHeight(root->rchild); }
显然,结点 root 所在子树的 height 等于其左子树的 height 与右子树的 height 的较大值加 1,因此可通过下面的函数来更新 height:
1 // 更新结点 root 的高度 2 void updateHeight(node* root) { 3 // 根结点高度为左右子树高度较大值 +1 4 int lHeight = getHeight(root->lchild), rHeight = getHeight(root->rchild); 5 int max = lHeight > rHeight ? lHeight : rHeight; 6 root->height = max + 1; 7 }
二、平衡二叉树的基本操作
和二叉查找树相同,AVL 树的基本操作有查找、插入、建树以及删除,由于删除操作较为复杂,因此主要介绍 AVL 树的查找、插入和建立。
1. 查找操作
由于 AVL 树是一棵二叉查找树,因此其查找操作的做法与二叉查找树相同。代码如下:
1 // 查找平衡二叉树中数据域为 x 的结点 2 void search(node* root, int x) { 3 if(root == NULL) { // 空树,查找失败 4 printf("search failed\n"); 5 return; 6 } 7 if(x == root->v) { // 查找成功,访问之 8 printf("search success %d\n", root->v); 9 } else if(x < root->v) { // x 比根结点的数据域小,往左子树查找 10 search(root->lchild, x); 11 } else { 12 search(root->rchild, x); // x 比根结点的数据域大,往右子树查找 13 } 14 }
2. 插入操作
先来看一下几个插入问题需要用到的几个操作。
左旋,调整步骤如下:
- 让 B 的左子树 ? 成为 A 的右子树。
- 让 A 成为 B 的左子树
- 将根结点设定为结点 B
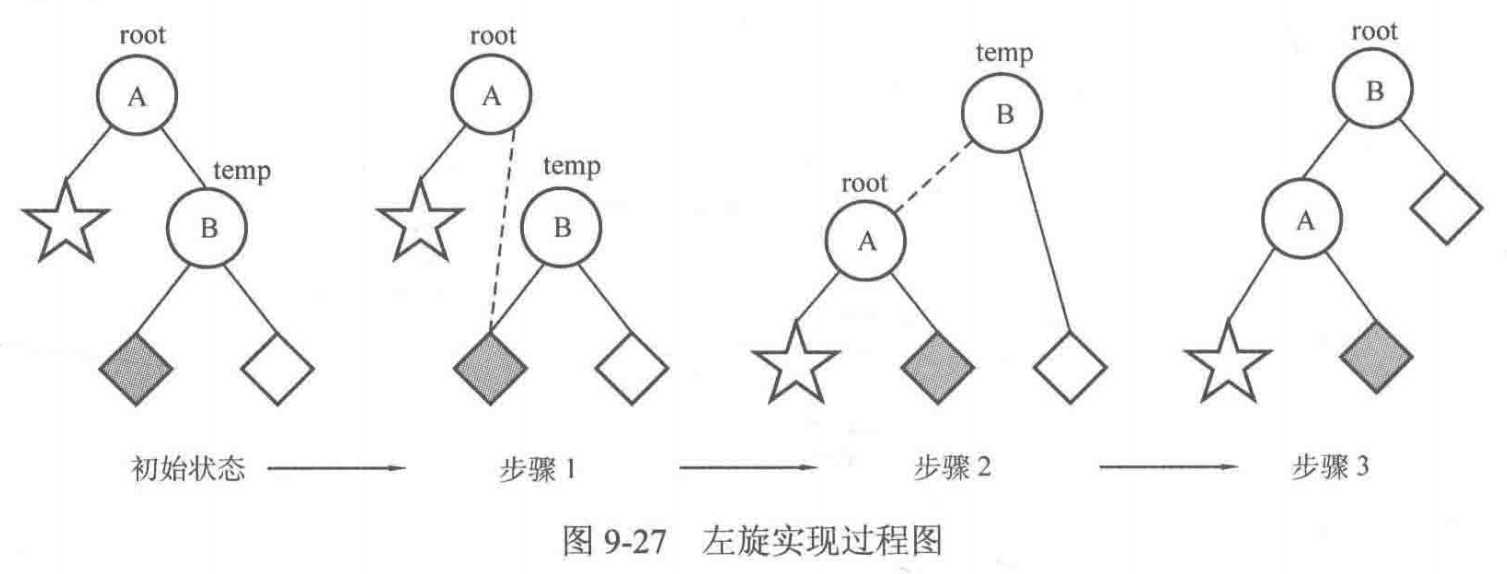
对应的代码如下:
1 // 左旋 2 void L(node** root) { 3 node* temp = (*root)->rchild; // root指向A,temp指向B 4 (*root)->rchild = temp->lchild; // 步骤 1 5 temp->lchild = *root; // 步骤 2 6 updateHeight(*root); // 更新高度 7 updateHeight(temp); 8 (*root) = temp; // 步骤 3 9 }
右旋的实现步骤和左旋基本相同:
- 让 A 的右子树 ? 成为 B 的左子树。
- 让 B 成为 A 的右子树。
- 将根结点设定为结点 A。
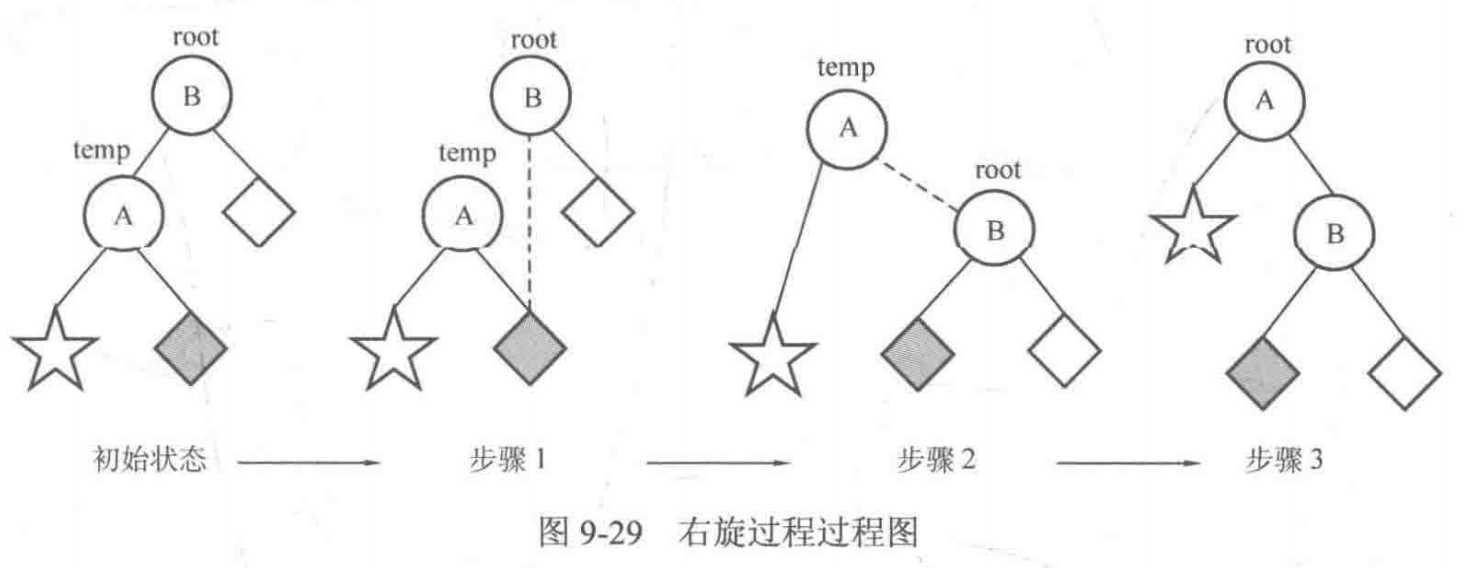
代码如下:
1 // 右旋 2 void R(node** root) { 3 node* temp = (*root)->lchild; // root指向A,temp指向B 4 (*root)->lchild = temp->rchild; // 步骤 1 5 temp->rchild = *root; // 步骤 2 6 updateHeight(*root); // 更新高度 7 updateHeight(temp); 8 (*root) = temp; // 步骤 3 9 }
关于旋转的讨论到此为止,接下来开始讨论 AVL 树的插入操作。
显然,只有在从根结点到该插入结点的路径上的结点才可能发生平衡因子变化,因此只需对这条路径上失衡的结点进行调整。可以证明,只要把最靠近插入结点的失衡结点调整到正常,路径上的所有结点就都会平衡。
假设最靠近插入结点的失衡结点是 A,显然它的平衡因子只可能是 2 或者 -2。很容易发现这两种情况完全对称,因此主要讨论结点 A 的平衡因子是 2 的情形。
于是以结点 A 为根结点的子树一定是下图的两种形态 LL 型与 LR 型之一。
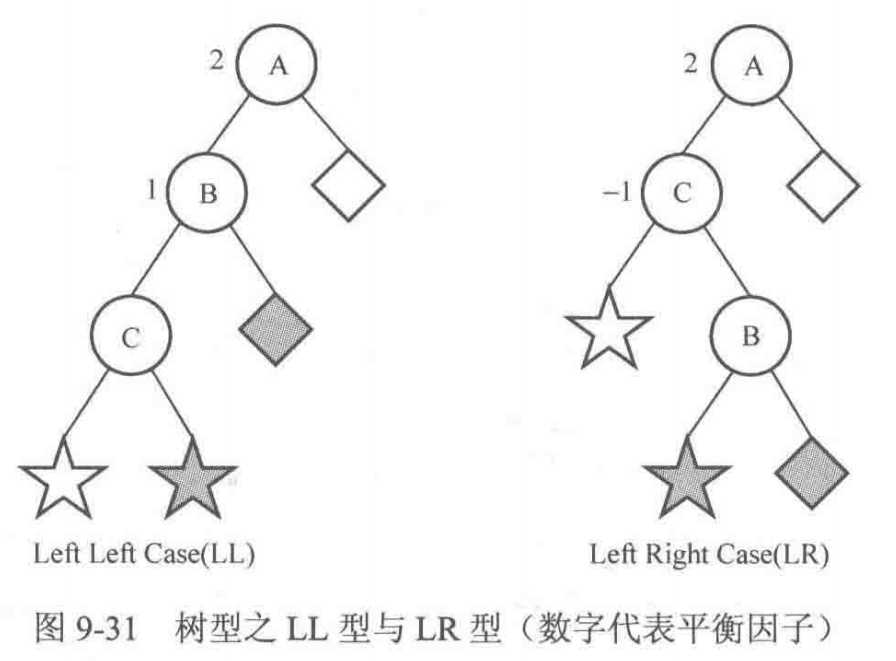
现在考虑怎样调整这两种树型,才能使树平衡。
先考虑 LL 型。可以把以 C 为根结点的子树看作一个整体,然后以结点 A 作为 root 进行右旋,便可以达到平衡,如下图:
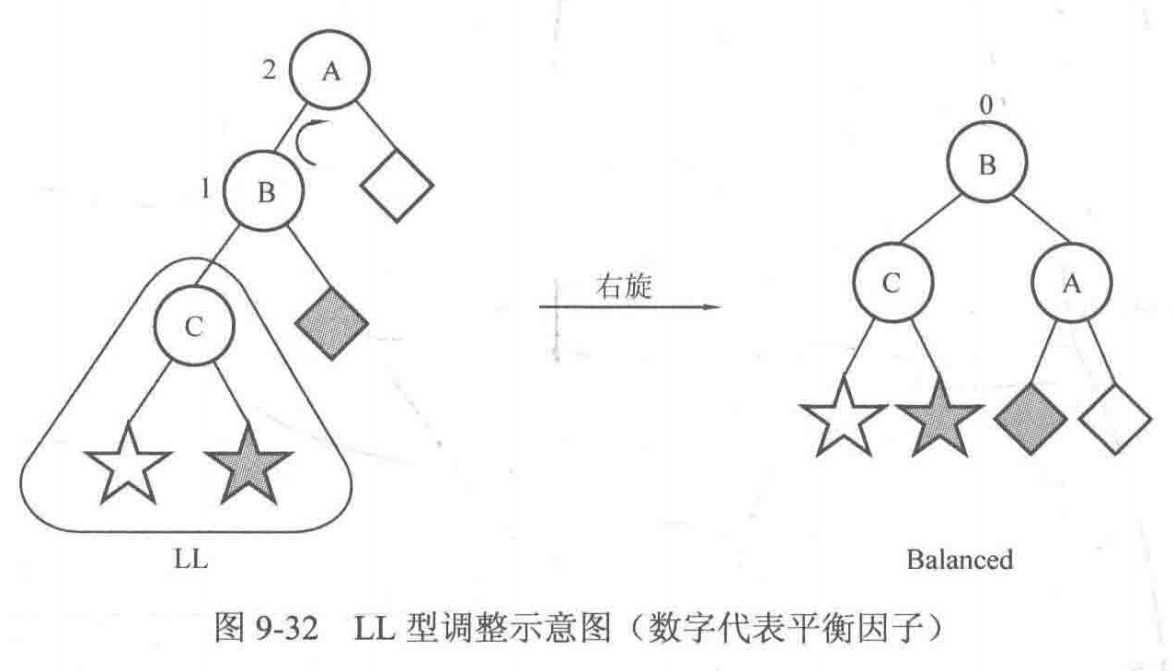
然后考虑 LR 型,可以先忽略结点 A,以结点 C 为 root 进行左旋,就可以把情况转化为 LL 型,然后按上面 LL 型的做法进行一次右旋即可,如下图所示:
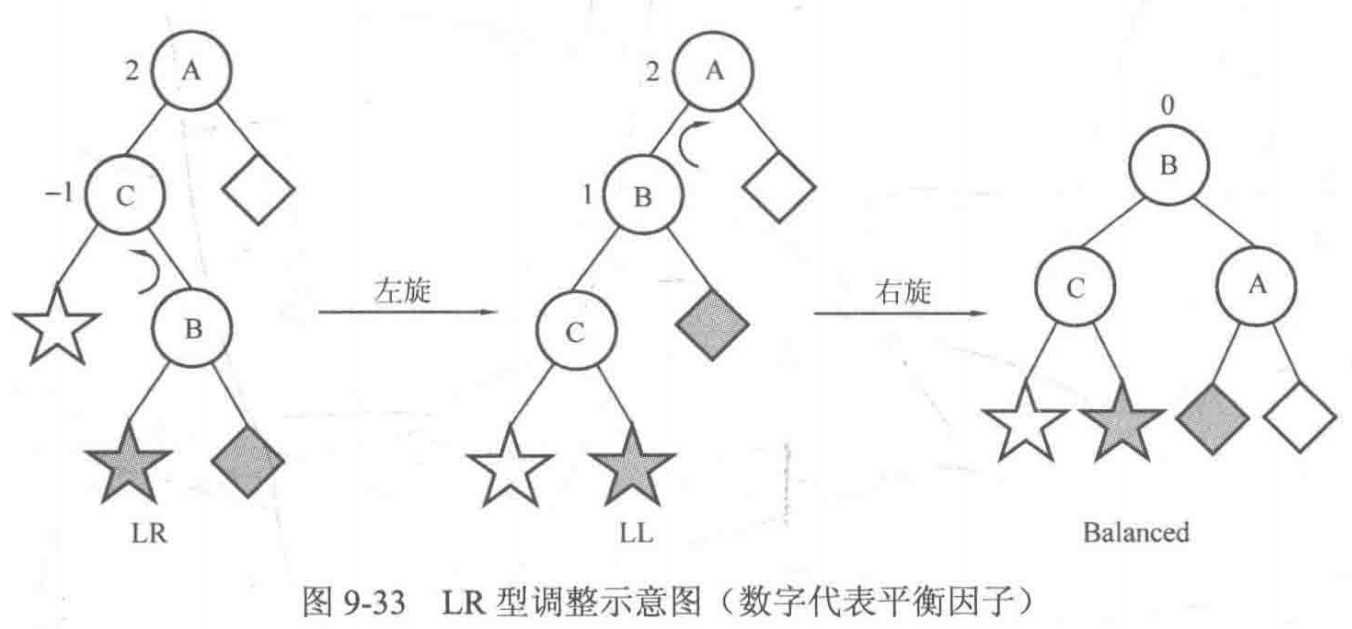
至此,结点 A 的平衡因子是 2 的情况已经讨论清楚,平衡因子是 -2 的情况完全对称。
对 LL 型、LR 型、RR型、RL型的调整方法汇总如下:
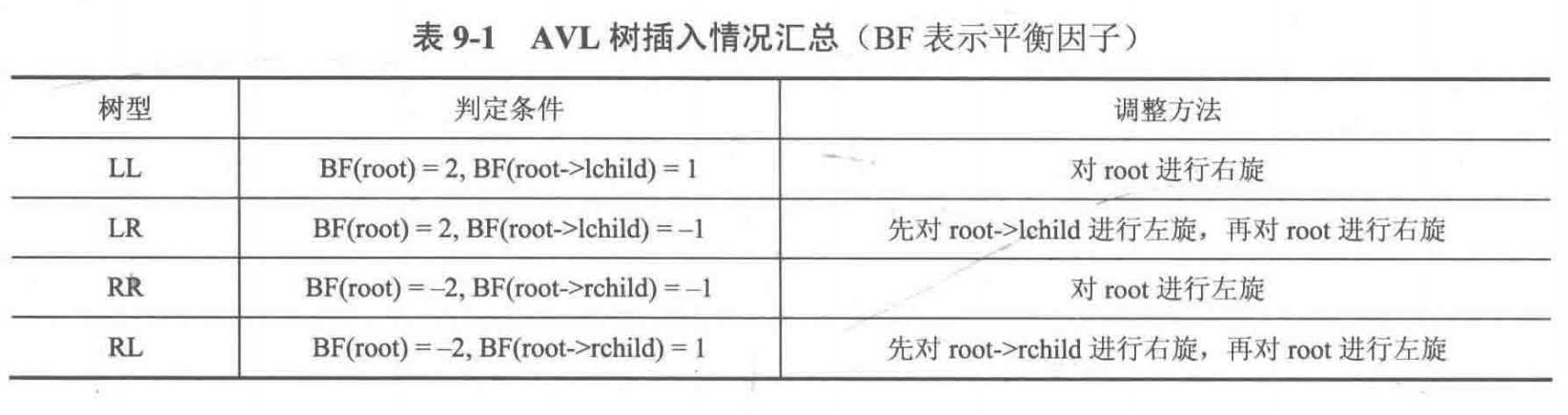
由于需要从插入的结点开始从下往上判断是否失衡,因此需要在每个 insert 函数之后更新当前子树的高度,并在之后根据树型进行平衡操作,代码如下:
1 // 插入权值为 v 的结点 2 void insert(node** root, int v) { 3 if((*root) == NULL) { // 到达插入位置 4 (*root) = newNode(v); 5 return; 6 } 7 if(v < (*root)->v) { // v 比根结点权值小 8 insert(&(*root)->lchild, v); // 往左子树插入 9 updateHeight(*root); // 更新树高 10 if(getBalanceFactor(*root) == 2) { 11 if(getBalanceFactor((*root)->lchild) == 1) { // LL 型 12 R(*root); 13 } else if(getBalanceFactor((*root)->lchild) == -1) { // LR 型 14 L(&(*root)->lchild); 15 R(root); 16 } 17 } 18 } else { // v 比根结点权值大 19 insert(&(*root)->rchild, v); // 往右子树插入 20 updateHeight(*root); // 更新树高 21 if(getBalanceFactor(*root) == -2) { 22 if(getBalanceFactor((*root)->rchild) == -1) { // RR 型 23 L(root); 24 } else if(getBalanceFactor((*root)->rchild) == 1) { // RL 型 25 R(&(*root)->rchild); 26 L(root); 27 } 28 } 29 } 30 }
3. AVL 树的建立
有了上面插入操作的基础,AVL 树的建立就非常简单了,因此只需依次插入 n 个结点即可。代码如下:
1 // AVL 树的建立 2 node* create(int data[], int n) { 3 node* root = NULL; // 新建根结点 root 4 int i; 5 for(i=0; i<n; ++i) { 6 insert(&root, data[i]); // 将 data 中数据依次插入AVL树 7 } 8 return root; // 返回根结点 9 }
完整的测试代码如下:

1 /* 2 平衡二叉树 3 */ 4 5 #include <stdio.h> 6 #include <string.h> 7 #include <math.h> 8 #include <stdlib.h> 9 #include <time.h> 10 #include <stdbool.h> 11 12 // 平衡二叉树结构体 13 typedef struct _node { 14 int v, height; // v 为结点权值, height 为当前子树高度 15 struct _node *lchild, *rchild; // 左右孩子结点地址 16 } node; 17 18 // 平衡二叉树新建结点 19 node* newNode(int v) { 20 node* Node = (node*)malloc(sizeof(node)); // 申请地址空间 21 Node->v = v; // 结点权值为 v 22 Node->height = 1; // 结点高度初始为 1 23 Node->lchild = Node->rchild = NULL; // 初始状态下没有左右孩子 24 return Node; 25 } 26 27 // 获取以 root 为根结点的子树的当前高度 28 int getHeight(node* root) { 29 if(root == NULL) return 0; // 空树高度为 0 30 return root->height; 31 } 32 33 // 计算结点 root 的平衡因子 34 int getBalanceFactor(node* root) { 35 // 左子树高度减右子树高度 36 return getHeight(root->lchild) - getHeight(root->rchild); 37 } 38 39 // 更新结点 root 的高度 40 void updateHeight(node* root) { 41 // 根结点高度为左右子树高度较大值 +1 42 int lHeight = getHeight(root->lchild), rHeight = getHeight(root->rchild); 43 int max = lHeight > rHeight ? lHeight : rHeight; 44 root->height = max + 1; 45 } 46 47 // 查找平衡二叉树中数据域为 x 的结点 48 void search(node* root, int x) { 49 if(root == NULL) { // 空树,查找失败 50 printf("search failed\n"); 51 return; 52 } 53 if(x == root->v) { // 查找成功,访问之 54 printf("search success %d\n", root->v); 55 } else if(x < root->v) { // x 比根结点的数据域小,往左子树查找 56 search(root->lchild, x); 57 } else { 58 search(root->rchild, x); // x 比根结点的数据域大,往右子树查找 59 } 60 } 61 62 // 左旋 63 void L(node** root) { 64 node* temp = (*root)->rchild; // root指向A,temp指向B 65 (*root)->rchild = temp->lchild; // 步骤 1 66 temp->lchild = *root; // 步骤 2 67 updateHeight(*root); // 更新高度 68 updateHeight(temp); 69 (*root) = temp; // 步骤 3 70 } 71 72 // 右旋 73 void R(node** root) { 74 node* temp = (*root)->lchild; // root指向A,temp指向B 75 (*root)->lchild = temp->rchild; // 步骤 1 76 temp->rchild = *root; // 步骤 2 77 updateHeight(*root); // 更新高度 78 updateHeight(temp); 79 (*root) = temp; // 步骤 3 80 } 81 82 // 插入权值为 v 的结点 83 void insert(node** root, int v) { 84 if((*root) == NULL) { // 到达插入位置 85 (*root) = newNode(v); 86 return; 87 } 88 if(v < (*root)->v) { // v 比根结点权值小 89 insert(&(*root)->lchild, v); // 往左子树插入 90 updateHeight(*root); // 更新树高 91 if(getBalanceFactor(*root) == 2) { 92 if(getBalanceFactor((*root)->lchild) == 1) { // LL 型 93 R(*root); 94 } else if(getBalanceFactor((*root)->lchild) == -1) { // LR 型 95 L(&(*root)->lchild); 96 R(root); 97 } 98 } 99 } else { // v 比根结点权值大 100 insert(&(*root)->rchild, v); // 往右子树插入 101 updateHeight(*root); // 更新树高 102 if(getBalanceFactor(*root) == -2) { 103 if(getBalanceFactor((*root)->rchild) == -1) { // RR 型 104 L(root); 105 } else if(getBalanceFactor((*root)->rchild) == 1) { // RL 型 106 R(&(*root)->rchild); 107 L(root); 108 } 109 } 110 } 111 } 112 113 // AVL 树的建立 114 node* create(int data[], int n) { 115 node* root = NULL; // 新建根结点 root 116 int i; 117 for(i=0; i<n; ++i) { 118 insert(&root, data[i]); // 将 data 中数据依次插入AVL树 119 } 120 return root; // 返回根结点 121 } 122 123 // 先序遍历 124 void preorder(node* root) { 125 if(root == NULL) { 126 return; // 空树,递归边界 127 } 128 printf("%d\n", root->v); // 访问该结点 129 preorder(root->lchild); // 访问左子树 130 preorder(root->rchild); // 访问右子树 131 } 132 133 int main() { 134 int data[10] = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9}; 135 node* root = NULL; 136 root = create(data, 10); // 创建 AVL 树 137 preorder(root); // 先序遍历 138 search(root, 10); // 在 root 中查找 10 139 return 0; 140 }

