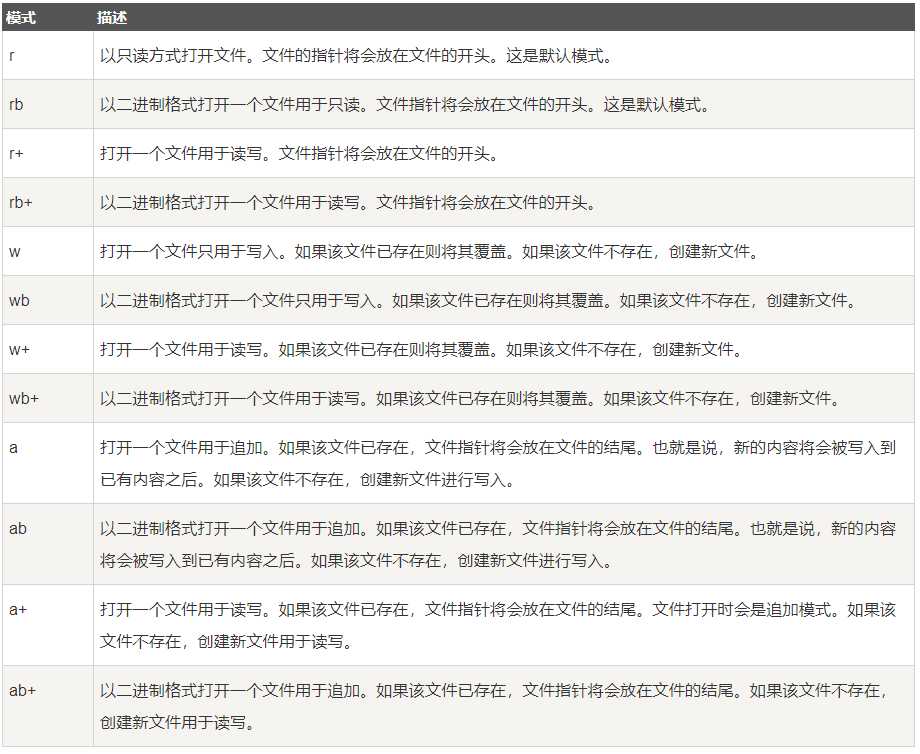
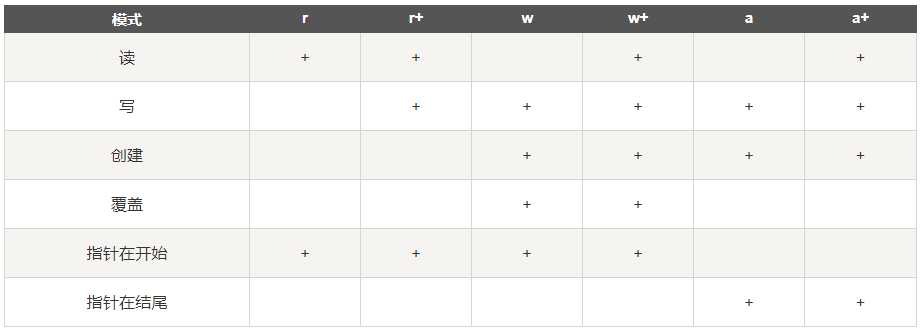
读写文件是最常见的IO操作。Python内置了读写文件的函数,用法和C是兼容的
写文件
#打开data.txt,创建一个实例f f = open(‘data.txt‘,‘w‘) #向文件中写内容 f.write(‘I miss the taste of a sweeter life\n‘) f.writelines(‘I miss the conversation\n‘) #写入一行自动添加换行符 f.write(‘I\‘m searching for a song tonight\n‘) f.flush() #立即写入缓冲区 #关闭文件 f.close()
读文件
读取data.txt的全部文件
f = open(‘data.txt‘,‘r‘) #效率最高的循环方式 for line in f: print(line) f.close()
如果怕遗忘关闭文件,还可以用下面的方法读写:
with open(‘data.txt‘,‘r‘) as f: for line in f: print(line) #效果和上面的代码相同
文件定位
其实可以把文件读写的过程看作写word,可以通过控制文件光标来读任意位置的文件
我们以上面写文件创建的data.txt文件为例子
I miss the taste of a sweeter life I miss the conversation I‘m searching for a song tonight
f = open(‘data.txt‘,‘r‘) print(f.readline()) print(f.tell()) #返回当前文件指针的位置36 f.seek(47) print(f.read(6)) #打印50个字符后10个文字 f.close() """ 结果: I miss the taste of a sweeter life 36 conver """
文件其他操作方法