前面的话
这几天被redux折腾的够呛,看了很多视频,也看了很多资料。很多时候,感觉好像顿悟了,但实际上只是理解了其中的一个小概念而已。真正去做项目的时候,还是会卡壳。可能是学CSS和Javascript时花的时间太久了,学redux的时候有点浮躁。还有就是redux内容实在是不少,全部都看都理解,好像没什么必要。不看吧,用的时候总是有点力不从心。于是,决定把这些资料按自己的理解写成博客,方便自己回忆思路,也希望能帮助到需要的人
核心概念
redux专注于状态管理,把所有的状态都存在一个对象中。核心概念包括:store、state、action、reducer
【store】
store是保存数据的地方,redux提供createStore函数来生成 Store。函数参数是后面要介绍的reducer
import { createStore } from ‘redux‘
const store = createStore(reducer)
【state】
state是store的某个时刻的快照,可以通过store.getState()取得当前时刻的state
const state = store.getState()
【action】
action用来改变state。action是一个对象,其中的type属性是必须的,其他的属性一般用来设置改变state需要的数据
const action = { type: ‘ADD_ONE‘, num: 1 }
store.dispatch()是发出action的唯一方法
const action = { type: ‘ADD_ONE‘, num: 1 } store.dispatch(action)
【reducer】
reducer 是一个函数,它接受action和当前state作为参数,返回一个新的state
import { createStore } from ‘redux‘
const store = createStore(reducer)
const reducer = (state = 10, action) => { switch (action.type) { case ‘ADD_ONE‘: return state + action.num; default: return state; } };
当store.dispatch发送过来一个新的action,store就会自动调用reducer,得到新的state
简单实例
多余的概念不再介绍,下面用上面介绍的这四个核心概念实现一个简单的实例,将create-react-app中index.js文件内容更改如下,即可运行
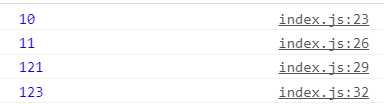
//第一步,创建action const addOne = { type: ‘ADD‘, num: 1 } const addTwo = { type: ‘ADD‘, num: 2 } const square = { type: ‘SQUARE‘ } //第二步,创建reducer let math = (state = 10, action) => { switch (action.type) { case ADD: return state + action.num case SQUARE: return state * state default: return state } } //第三步,创建store import { createStore } from ‘redux‘ const store = createStore(math) //第四步,测试,通过dispatch发出action,并通过getState()取得当前state值 console.log(store.getState()) //默认值为10 store.dispatch(addOne) //发起‘+1‘的action console.log(store.getState()) //当前值为10+1=11 store.dispatch(square) //发起‘乘方‘的action console.log(store.getState()) //当前值为11*11=121 store.dispatch(addTwo) //发起‘+2‘的action console.log(store.getState()) //当前值为121+2=123
结果如下
目录结构
下面对目录结构进行划分
1、一般地,将action.type设置为常量,这样在书写错误时,会得到报错提示
// constants/ActionTypes.js export const ADD = ‘ADD‘ export const SQUARE = ‘SQUARE‘
2、可以将addOne对象和addTwo对象整合成add函数的形式
// action/math.js import { ADD, SQUARE } from ‘../constants/ActionTypes‘ export const add = num => ({ type: ADD, num }) export const square = { type: SQUARE }
3、根据action.type的分类来拆分reducer,最终通过combineReducers方法将拆分的reducer合并起来。上例中的action类型都是数字运算,无需拆分,只需进行如下变化
// reducer/math.js import { ADD, SQUARE } from ‘../constants/ActionTypes‘ const math = (state = 10, action) => { switch (action.type) { case ADD: return state + action.num case SQUARE: return state * state default: return state } }
export default math
// reducer/index.js import { combineReducers } from ‘redux‘ import math from ‘./math‘ const rootReducer = combineReducers({ math }) export default rootReducer
4、将store存储到store/index.js文件中
// store/index.js import { createStore } from ‘redux‘ import rootReducer from ‘../reducer‘ export default createStore(rootReducer)
5、最终,根路径下的index.js内容如下所示
import store from ‘./store‘ import {add, square} from ‘./action/math‘ console.log(store.getState()) //默认值为10 store.dispatch(add(1)) //发起‘+1‘的action console.log(store.getState()) //当前值为10+1=11 store.dispatch(square) //发起‘乘方‘的action console.log(store.getState()) //当前值为11*11=121 store.dispatch(add(2)) //发起‘+2‘的action console.log(store.getState()) //当前值为121+2=123
最终目录路径如下所示
最终结果如下所示

UI层
前面的示例中,只是redux的状态改变,下面利用UI层来建立view和state的联系,将根目录下的index.js的内容更改如下
import store from ‘./store‘ import React from ‘react‘ import ReactDOM from ‘react-dom‘ import { add, square } from ‘./action/math‘ ReactDOM.render( <div store={store}> <p>{store.getState().math}</p> <input type="button" onClick={() => store.dispatch(add(1))} value="+1" /> <input type="button" onClick={() => store.dispatch(add(2))} value="+2" /> <input type="button" onClick={() => store.dispatch(square)} value="乘方" /> </div>, document.getElementById(‘root‘) )
虽然可以显示数字,但是点击按钮时,却不能重新渲染页面
【store.subscribe()】
接下来介绍store.subscribe()方法了,该方法用来设置监听函数,一旦state发生变化,就自动执行这个函数。该方法的返回值是一个函数,调用这个函数可以解除监听
下面将示例代码更改如下
import store from ‘./store‘ import React from ‘react‘ import ReactDOM from ‘react-dom‘ import { add, square } from ‘./action/math‘ const render = () => ReactDOM.render( <div store={store}> <p>{store.getState().math}</p> <input type="button" onClick={() => store.dispatch(add(1))} value="+1" /> <input type="button" onClick={() => store.dispatch(add(2))} value="+2" /> <input type="button" onClick={() => store.dispatch(square)} value="乘方" /> </div>, document.getElementById(‘root‘) ) render() store.subscribe(render)
代码终于可以正常运行了
异步
redux默认只处理同步,对于API请求这样的异步任务则无能为力
接下来尝试使用axios的get方法来请求下面这个API
https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts/2
获取的数据如下
{ "userId": 1, "id": 2, "title": "qui est esse", "body": "est rerum tempore vitae\nsequi sint nihil reprehenderit dolor beatae ea dolores neque\nfugiat blanditiis voluptate porro vel nihil molestiae ut reiciendis\nqui aperiam non debitis possimus qui neque nisi nulla" }
然后,将其id值设置为state.math的值
代码修改如下
// constants/ActionTypes.js export const ADD = ‘ADD‘ export const SQUARE = ‘SQUARE‘ export const SET = ‘SET‘ // action/math.js import { ADD, SQUARE, SET } from ‘../constants/ActionTypes‘ export const add = num => ({ type: ADD, num }) export const square = { type: SQUARE } export const setNum = num => ({type: SET,num}) // reduce/math.js import { ADD, SQUARE,SET } from ‘../constants/ActionTypes‘ const math = (state = 10, action) => { switch (action.type) { case ADD: return state + action.num case SQUARE: return state * state case SET: return action.num default: return state } } export default math // index.js import store from ‘./store‘ import React from ‘react‘ import ReactDOM from ‘react-dom‘ import { add, square, setNum } from ‘./action/math‘ import axios from ‘axios‘ let uri = ‘https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts/2‘ const render = () => ReactDOM.render( <div store={store}> <p>{store.getState().math}</p> <input type="button" onClick={() => {axios.get(uri).then(res => {store.dispatch(store.dispatch(setNum(res.data.id)))})}} value="设置Num" /> <input type="button" onClick={() => store.dispatch(add(1))} value="+1" /> <input type="button" onClick={() => store.dispatch(add(2))} value="+2" /> <input type="button" onClick={() => store.dispatch(square)} value="乘方" /> </div>, document.getElementById(‘root‘) ) render() store.subscribe(render)
效果如下
但是,虽然API是异步操作,但store.dispatch并不是异步,而axios通过get方法请求回来数据后,store.dispatch在axios中的then方法中同步取得数据
【redux-thunk】
如果要使用真正的异步操作,即把axios方法封装到store.dispatch中,需要使用redux-thunk中间件
首先,使用npm进行安装
npm install --save redux-thunk
然后,使用applyMiddleware来使用thunk中间件
import { createStore, applyMiddleware } from ‘redux‘
import thunk from ‘redux-thunk‘
import rootReducer from ‘../reducer‘
export default createStore(rootReducer,applyMiddleware(thunk))
接着来定义setNum这个action creator,然后在index.js文件的DOM加载完成后就发出setNum
[注意]如果action是一个对象,则它就是一个action,如果action是一个函数,则它是一个action creator,即action制造器
修改的代码如下
// action/math.js import { ADD, SQUARE, SET } from ‘../constants/ActionTypes‘ import axios from ‘axios‘ const uri = ‘https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts/2‘ export const add = num => ({ type: ADD, num }) export const square = { type: SQUARE } export const setNum = () => (dispatch, getState) => { return axios.get(uri).then(res => { dispatch({ type: SET, num: res.data.id }) }) } // index.js import store from ‘./store‘ import React from ‘react‘ import ReactDOM from ‘react-dom‘ import { add, square, setNum } from ‘./action/math‘ const render = () => ReactDOM.render( <div store={store}> <p>{store.getState().math}</p> <input type="button" onClick={() => store.dispatch(setNum())} value="设置Num" /> <input type="button" onClick={() => store.dispatch(add(1))} value="+1" /> <input type="button" onClick={() => store.dispatch(add(2))} value="+2" /> <input type="button" onClick={() => store.dispatch(square)} value="乘方" /> </div>, document.getElementById(‘root‘) ) render() store.subscribe(render)
效果如下
【提示信息】
如果做的更完备一点,应该把异步请求时的提示信息也加上。增加一个fetch的action,用于控制fetch过程的提示信息及显示隐藏情况
代码更改如下
// action/fetch.js import { SET_FETCH_MESSAGE, HIDE_FETCH_MESSAGE } from ‘../constants/ActionTypes‘ export const startFetch = { type: SET_FETCH_MESSAGE,message: ‘开始发送异步请求‘ } export const successFetch = { type: SET_FETCH_MESSAGE, message: ‘成功接收数据‘ } export const failFetch = { type: SET_FETCH_MESSAGE, message: ‘接收数据失败‘ } export const hideFetchMessage = { type: HIDE_FETCH_MESSAGE }
// action/math.js import { ADD, SQUARE, SET } from ‘../constants/ActionTypes‘ import { startFetch, successFetch, failFetch, hideFetchMessage } from ‘./fetch‘ import axios from ‘axios‘ const uri = ‘https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts/2‘ export const add = num => ({ type: ADD, num }) export const square = { type: SQUARE } export const setNum = () => (dispatch, getState) => { dispatch(startFetch) setTimeout(() => { dispatch(hideFetchMessage) }, 500) return axios .get(uri) .then(res => { setTimeout(() => { dispatch(successFetch) setTimeout(() => { dispatch(hideFetchMessage) }, 500) dispatch({ type: SET, num: res.data.id }) }, 1000) }) .catch(err => { dispatch(failFetch) setTimeout(() => { dispatch(hideFetchMessage) }, 500) }) }
// constants/ActionTypes.js export const ADD = ‘ADD‘ export const SQUARE = ‘SQUARE‘ export const SET = ‘SET‘ export const SET_FETCH_MESSAGE = ‘SET_FETCH_MESSAGE‘ export const HIDE_FETCH_MESSAGE = ‘HIDE_FETCH_MESSAGE‘
// reduce/fetch.js import { SET_FETCH_MESSAGE,HIDE_FETCH_MESSAGE } from ‘../constants/ActionTypes‘ const initState = { message:‘‘, isShow:false } const fetch = (state = initState, action) => { switch (action.type) { case SET_FETCH_MESSAGE: return {isShow: true, message: action.message} case HIDE_FETCH_MESSAGE: return { isShow: false, message: ‘‘ } default: return state } } export default fetch
// index.js import store from ‘./store‘ import React from ‘react‘ import ReactDOM from ‘react-dom‘ import { add, square, setNum } from ‘./action/math‘ const render = () => ReactDOM.render( <div store={store}> <p>{store.getState().math}</p> <input type="button" onClick={() => store.dispatch(setNum())} value="设置Num" /> <input type="button" onClick={() => store.dispatch(add(1))} value="+1" /> <input type="button" onClick={() => store.dispatch(add(2))} value="+2" /> <input type="button" onClick={() => store.dispatch(square)} value="乘方" /> {store.getState().fetch.isShow && <p>{store.getState().fetch.message}</p>} </div>, document.getElementById(‘root‘) ) render() store.subscribe(render)
效果如下
展示和容器
下面来介绍react-redux。前面的代码中,我们是通过store.subscribe()方法监控state状态的变化来更新UI层的。而使用react-redux,可以让组件动态订阅状态树。状态树一旦被修改,组件能自动刷新显示最新数据
react-redux将所有组件分成两大类:展示组件和容器组件。展示组件只负责UI呈现,所有数据由参数props提供;容器组件则负责管理数据和业务逻辑,带有内部状态,可使用redux的API。要使用react-redux,就要遵守它的组件拆分规范
【provider】
react-redux提供Provider组件,可以让容器组件默认可以拿到state,而不用当容器组件层级很深时,一级级将state传下去
将index.js文件更改如下
// index.js import React from ‘react‘ import ReactDOM from ‘react-dom‘ import store from ‘./store‘ import MathContainer from ‘./container/MathContainer‘ import { Provider } from ‘react-redux‘ ReactDOM.render( <Provider store={store}> <MathContainer /> </Provider>, document.getElementById(‘root‘) )
按照组件拆分规范,将原来index.js中相关代码,分拆到container/MathContainer和component/Math这两个组件中
【connect】
react-redux提供connect方法,用于从展示组件生成容器组件。connect的意思就是将这两种组件连接起来
import { connect } from ‘react-redux‘
const MathContainer = connect()(Math);
Math是展示组件,MathContainer就是由React-redux通过connect方法自动生成的容器组件
为了定义业务逻辑,需要给出下面两方面的信息
1、输入逻辑:外部的数据(即state对象)如何转换为展示组件的参数
2、输出逻辑:用户发出的动作如何变为Action对象,从展示组件传出去
因此,connect方法的完整API如下
import {connect} from ‘react-redux‘
const MathContainer= connect(
mapStateToProps,
mapDispatchToProps
)(Math)
上面代码中,connect方法接受两个参数:mapStateToProps和mapDispatchToProps。它们定义了展示组件的业务逻辑。前者负责输入逻辑,即将state映射到UI组件的参数(props),后者负责输出逻辑,即将用户对展示组件的操作映射成Action
【mapStateToProps()】
mapStateToProps建立一个从外部的state对象到展示组件的props对象的映射关系。作为参数,mapStateToProps执行后应该返回一个对象,里面的每一个键值对就是一个映射。
const mapStateToProps = (state) => { return { num: getNum(state) } }
mapStateToProps的第一个参数总是state对象,还可以使用第二个参数,代表容器组件的props对象。使用ownProps作为参数后,如果容器组件的参数发生变化,也会引发展示组件重新渲染
const mapStateToProps = (state,ownProps) => { return { num: getNum(state) } }
mapStateToProps会订阅Store,每当state更新的时候,就会自动执行,重新计算展示组件的参数,从而触发展示组件的重新渲染。connect方法可以省略mapStateToProps参数,那样,展示组件就不会订阅Store,就是说Store的更新不会引起展示组件的更新
【mapDispatchToProps】
mapDispatchToProps是connect函数的第二个参数,用来建立展示组件的参数到store.dispatch方法的映射。也就是说,它定义了用户的哪些操作应该当作action,传给Store。它可以是一个函数,也可以是一个对象
如果mapDispatchToProps是一个函数,会得到dispatch和ownProps(容器组件的props对象)两个参数
const mapDispatchToProps = (dispatch,ownProps) => { return { onSetNumClick: () => dispatch(setNum()) } }
mapDispatchToProps作为函数,应该返回一个对象,该对象的每个键值对都是一个映射,定义了展示组件的参数怎样发出action
如果mapDispatchToProps是一个对象,它的每个键名也是对应展示组件的同名参数,键值应该是一个函数,会被当作action creator,返回的action会由redux自动发出
因此,上面的写法简写如下所示
const mapDispatchToProps = { onsetNumClick: () => setNum() }
最终结构
由于store目录中,只能一个index.js文件,且不会有内容扩展,将其更改为根目录下的store.js文件
将其他的目录都变成复数形式,最终的目录结构如下所示
效果如下
详细代码如下所示,且可访问github线上地址
【components】
// components/Math.js import React from ‘react‘ const Math = ({ num, isShow, fetchMessage, onSetNumClick, onAddOneClick, onAddTwoClick, onSqureClick }) => ( <section> <p>{num}</p> <input type="button" onClick={onSetNumClick} value="设置Num" /> <input type="button" onClick={onAddOneClick} value="+1" /> <input type="button" onClick={onAddTwoClick} value="+2" /> <input type="button" onClick={onSqureClick} value="乘方" /> {isShow && <p>{fetchMessage}</p>} </section> ) export default Math
【containers】
// containers/MathContainer.js import { connect } from ‘react-redux‘ import Math from ‘../components/Math‘ import { getNum } from ‘../selectors/math‘ import { getFetchMessage, getFetchIsShow } from ‘../selectors/fetch‘ import { setNum, add, square } from ‘../actions/math‘ const mapStateToProps = state => { return { num: getNum(state), fetchMessage: getFetchMessage(state), isShow: getFetchIsShow(state) } } const mapDispatchToProps = { onSetNumClick: () => setNum(), onAddOneClick: () => add(1), onAddTwoClick: () => add(2), onSqureClick: () => square } const MathContainer = connect(mapStateToProps, mapDispatchToProps)(Math) export default MathContainer
【actions】
// actions/fetch.js import { SET_FETCH_MESSAGE, HIDE_FETCH_MESSAGE } from ‘../constants/ActionTypes‘ export const startFetch = { type: SET_FETCH_MESSAGE,message: ‘开始发送异步请求‘ } export const successFetch = { type: SET_FETCH_MESSAGE, message: ‘成功接收数据‘ } export const failFetch = { type: SET_FETCH_MESSAGE, message: ‘接收数据失败‘ } export const hideFetchMessage = { type: HIDE_FETCH_MESSAGE }
// actions/math.js import { ADD, SQUARE, SET } from ‘../constants/ActionTypes‘ import { startFetch, successFetch, failFetch, hideFetchMessage } from ‘./fetch‘ import axios from ‘axios‘ const uri = ‘https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts/2‘ export const add = num => ({ type: ADD, num }) export const square = { type: SQUARE } export const setNum = () => (dispatch, getState) => { dispatch(startFetch) setTimeout(() => {dispatch(hideFetchMessage)}, 300) return axios .get(uri) .then(res => { dispatch(successFetch) setTimeout(() => {dispatch(hideFetchMessage)}, 300) dispatch({ type: SET, num: res.data.id }) }) .catch(err => { dispatch(failFetch) setTimeout(() => {dispatch(hideFetchMessage)}, 300) }) }
【constants】
// constants/ActionTypes.js export const ADD = ‘ADD‘ export const SQUARE = ‘SQUARE‘ export const SET = ‘SET‘ export const SET_FETCH_MESSAGE = ‘SET_FETCH_MESSAGE‘ export const HIDE_FETCH_MESSAGE = ‘HIDE_FETCH_MESSAGE‘
【reducers】
// reducers/fetch.js import { SET_FETCH_MESSAGE,HIDE_FETCH_MESSAGE } from ‘../constants/ActionTypes‘ const initState = { message:‘‘, isShow:false } const fetch = (state = initState, action) => { switch (action.type) { case SET_FETCH_MESSAGE: return {isShow: true, message: action.message} case HIDE_FETCH_MESSAGE: return { isShow: false, message: ‘‘ } default: return state } } export default fetch
// reducers/index.js import { combineReducers } from ‘redux‘ import math from ‘./math‘ import fetch from ‘./fetch‘ const rootReducer = combineReducers({ math, fetch }) export default rootReducer
// reduces/math.js import { ADD, SQUARE,SET } from ‘../constants/ActionTypes‘ const math = (state = 10, action) => { switch (action.type) { case ADD: return state + action.num case SQUARE: return state * state case SET: return action.num default: return state } } export default math
【selectors】
// selectors/fetch.js export const getFetchMessage = state => state.fetch.message export const getFetchIsShow = state => state.fetch.isShow
// selectors/math.js export const getNum = state => state.math
【根目录】
// index.js import React from ‘react‘ import ReactDOM from ‘react-dom‘ import store from ‘./store‘ import MathContainer from ‘./containers/MathContainer‘ import { Provider } from ‘react-redux‘ ReactDOM.render( <Provider store={store}> <MathContainer /> </Provider>, document.getElementById(‘root‘) )
// store.js import { createStore, applyMiddleware } from ‘redux‘ import thunk from ‘redux-thunk‘ import rootReducer from ‘./reducers‘ export default createStore(rootReducer,applyMiddleware(thunk))
