数据集的合并或连接运算是通过一个或多个键将行链接起来的,而pandas的merge函数是对数据应用这些算法的主要切入点。
一对多:df1的数据有多个被标记为a和b的行,而df2中key列的每个值则仅对应一行。
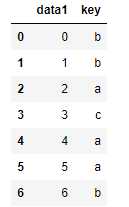
df1 = DataFrame({‘key‘: [‘b‘, ‘b‘, ‘a‘, ‘c‘, ‘a‘, ‘a‘, ‘b‘],
‘data1‘: range(7)})
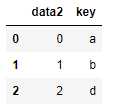
df2 = DataFrame({‘key‘: [‘a‘, ‘b‘, ‘d‘],
‘data2‘: range(3)})
  |
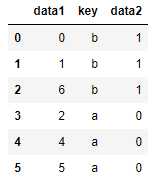
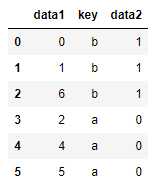
注意:若没有指定哪个列进行连接,则默认将重叠列的列名当作键。
pd.merge(df1, df2) pd.merge(df1, df2, on=‘key‘)
  |
若两个对象的列名不同,也可以分别进行指定:
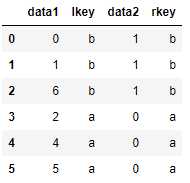
df3 = DataFrame({‘lkey‘: [‘b‘, ‘b‘, ‘a‘, ‘c‘, ‘a‘, ‘a‘, ‘b‘],
‘data1‘: range(7)})
df4 = DataFrame({‘rkey‘: [‘a‘, ‘b‘, ‘d‘],
‘data2‘: range(3)})
pd.merge(df3, df4, left_on=‘lkey‘, right_on=‘rkey‘)
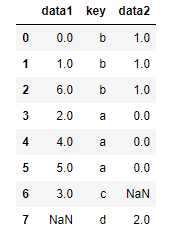
#默认merge做的事inner连接,结果是键的交集,其他方式有left、right、outer
pd.merge(df1, df2, how=‘outer‘)
  |
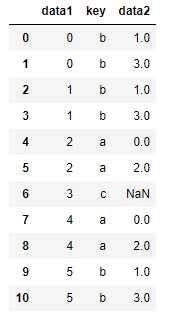
多对多:
df1 = DataFrame({‘key‘: [‘b‘, ‘b‘, ‘a‘, ‘c‘, ‘a‘, ‘b‘],
‘data1‘: range(6)})
df2 = DataFrame({‘key‘: [‘a‘, ‘b‘, ‘a‘, ‘b‘, ‘d‘],
‘data2‘: range(5)})
#多对多产生的是行的笛卡尔积 left
pd.merge(df1, df2, on=‘key‘, how=‘left‘)
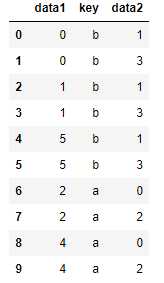
#连接方式只影响出现在结果中的键 inner
pd.merge(df1, df2, how=‘inner‘)
  |
若要根据多个键进行合并,需传入一个由列名组成的列表:
left = DataFrame({‘key1‘: [‘foo‘, ‘foo‘, ‘bar‘],
‘key2‘: [‘one‘, ‘two‘, ‘one‘],
‘lval‘: [1, 2, 3]})
right = DataFrame({‘key1‘: [‘foo‘, ‘foo‘, ‘bar‘, ‘bar‘],
‘key2‘: [‘one‘, ‘one‘, ‘one‘, ‘two‘],
‘rval‘: [4, 5, 6, 7]})
pd.merge(left, right, on=[‘key1‘, ‘key2‘], how=‘outer‘)
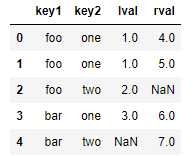 |
对于合并运算需要考虑的最后一个问题是对重复列名的处理。而merge的suffixes选项,正用于指定附加到左右两个dataframe对象的重复列名上的字符串:
pd.merge(left, right, on=‘key1‘) pd.merge(left, right, on=‘key1‘, suffixes=(‘_left‘, ‘_right‘))
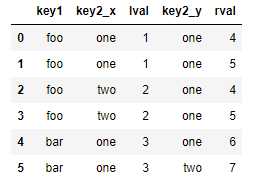 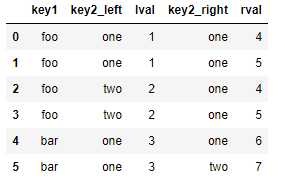 |
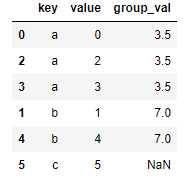
索引的合并:有时候连接键位于其索引中,则可以传入left_index=True或right_index=True以说明索引应该被用作连接键。
left1 = DataFrame({‘key‘: [‘a‘, ‘b‘, ‘a‘, ‘a‘, ‘b‘, ‘c‘],
‘value‘: range(6)})
right1 = DataFrame({‘group_val‘: [3.5, 7]}, index=[‘a‘, ‘b‘])
pd.merge(left1, right1, left_on=‘key‘, right_index=True)
#外连接
pd.merge(left1, right1, left_on=‘key‘, right_index=True, how=‘outer‘)
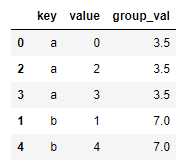  |
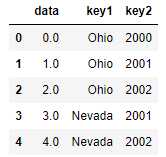
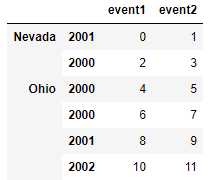
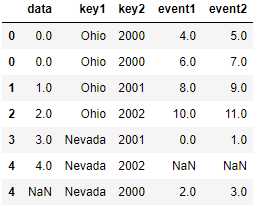
层次化索引数据,必须以列表的形式指明用作合并键的多个列
lefth = DataFrame({‘key1‘: [‘Ohio‘, ‘Ohio‘, ‘Ohio‘, ‘Nevada‘, ‘Nevada‘],
‘key2‘: [2000, 2001, 2002, 2001, 2002],
‘data‘: np.arange(5.)})
righth = DataFrame(np.arange(12).reshape((6, 2)),
index=[[‘Nevada‘, ‘Nevada‘, ‘Ohio‘, ‘Ohio‘, ‘Ohio‘, ‘Ohio‘],
[2001, 2000, 2000, 2000, 2001, 2002]],
columns=[‘event1‘, ‘event2‘])
  |
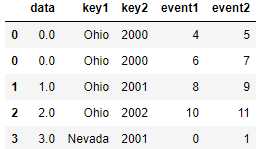
pd.merge(lefth, righth, left_on=[‘key1‘, ‘key2‘], right_index=True) pd.merge(lefth, righth, left_on=[‘key1‘, ‘key2‘], right_index=True, how=‘outer‘)
  |
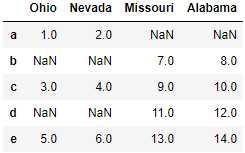
直接合并双方的索引也可以:
left2 = DataFrame([[1., 2.], [3., 4.], [5., 6.]], index=[‘a‘, ‘c‘, ‘e‘], columns=[‘Ohio‘, ‘Nevada‘]) right2 = DataFrame([[7., 8.], [9., 10.], [11., 12.], [13, 14]], index=[‘b‘, ‘c‘, ‘d‘, ‘e‘], columns=[‘Missouri‘, ‘Alabama‘])
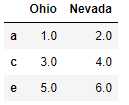 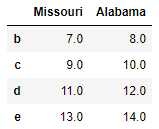 |
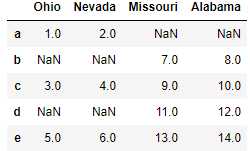
pd.merge(left2, right2, how=‘outer‘, left_index=True, right_index=True) #join实例方法,更为方便地按索引合并 left2.join(right2, how=‘outer‘)
  |
轴向连接:pd.concatenation 简单数据连接
arr = np.arange(12).reshape((3, 4)) ‘‘‘ array([[ 0, 1, 2, 3], [ 4, 5, 6, 7], [ 8, 9, 10, 11]]) ‘‘‘ np.concatenate([arr, arr], axis=1) ‘‘‘ array([[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 0, 1, 2, 3], [ 4, 5, 6, 7, 4, 5, 6, 7], [ 8, 9, 10, 11, 8, 9, 10, 11]]) ‘‘‘
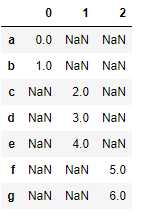
pandas的concat函数提供了一种能够轴向连接的方式。
s1 = Series([0, 1], index=[‘a‘, ‘b‘]) s2 = Series([2, 3, 4], index=[‘c‘, ‘d‘, ‘e‘]) s3 = Series([5, 6], index=[‘f‘, ‘g‘]) pd.concat([s1, s2, s3]) #默认concat的axis=0返回Series对象,而axis=1则返回dataframe对象 pd.concat([s1, s2, s3], axis=1)
  |
| 参数 | 说明 |
| objs | 参与连接的pandas对象的列表或者字典,唯一的必须参数 |
| axis | 指明连接的轴向,默认0 |
| join | 选项包括inner(交集)、outer(并集) |
| join_axes | 指明用于其他(n-1)条轴的索引,不执行并集或交集运算 |
| keys | 与连接对象有关的值,用于形成连接轴向上的层次化索引。可以是任意值的列表或数组 |
| levels | 指定用作层次化索引各级别上的索引(若设置了keys的话) |
| names | 用于创建分层级别的名称(若设置了keys和levels的话) |
| verify_integrity | 检查结果对象新轴上的重复情况,若发现则异常,默认允许重复(false) |
| ignore_index | 不保留连接轴上的索引,产生一组新索引 |
合并重叠数据:Series中combine_first方法,dataframe也可以使用
a = Series([np.nan, 2.5, np.nan, 3.5, 4.5, np.nan], index=[‘f‘, ‘e‘, ‘d‘, ‘c‘, ‘b‘, ‘a‘]) b = Series(np.arange(len(a), dtype=np.float64), index=[‘f‘, ‘e‘, ‘d‘, ‘c‘, ‘b‘, ‘a‘]) #np.where方法 np.where(pd.isnull(a), b, a) ‘‘‘ array([ 0. , 2.5, 2. , 3.5, 4.5, nan]) ‘‘‘ #combine_first方法 b[:-2].combine_first(a[2:]) ‘‘‘ a NaN b 4.5 c 3.0 d 2.0 e 1.0 f 0.0 dtype: float64 ‘‘‘
