NMS(non maximum suppression)应用:边缘检测、目标检测等。
背景:
绝大多数人脸检测器的核心是分类器,即给定一个尺寸固定的图片,分类器判断是否为人脸;
而分类器晋升为检测器的关键是: 常用滑动窗口在原始图像上从多个尺度产生窗口,并resize到固定尺寸,然后送给分类器做判断,如下图所示:
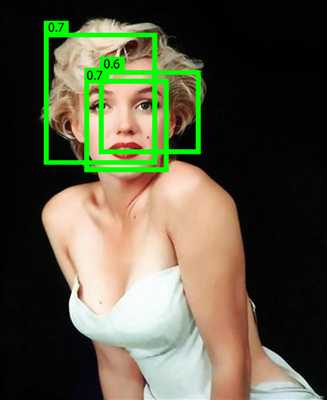
目标:
一个对象只保留一个最优的框 ,用非极大值抑制,来抑制那些冗余的框: 抑制的过程是一个迭代-遍历-消除的过程。
NMS 算法的核心:
1.将所有框的得分排序,选中置信度最高的一个boundingbox(bbox)框作为目标
2.遍历其余的框,如果和目标bbox 最高分框的重叠面积(IOU)大于一定阈值,我们就在剩下的bbox中去除该bbox(即使该bbox的置信度与目标bbox的置信度一样)
3.从未处理的框中继续选一个得分最高的(第二置信度),重复上述1、2过程。
def nms(dets, thresh): ‘‘‘ NMS非极大值抑制算法 ‘‘‘ x1 = dets[:, 0] y1 = dets[:, 1] x2 = dets[:, 2] y2 = dets[:, 3] scores = dets[:, 4] # confidence # 每个boundingbox的面积 areas = (x2 - x1 + 1) * (y2 - y1 + 1) # boundingbox的置信度排序 order = scores.argsort()[::-1] # 用来保存最后留下来的boundingbox keep = [] while order.size > 0: i = order[0] # 置信度最高的boundingbox的index keep.append(i) # 添加本次置信度最高的boundingbox的index # 当前bbox和剩下bbox之间的交叉区域; 选择大于x1,y1和小于x2,y2的区域 xx1 = np.maximum(x1[i], x1[order[1:]]) yy1 = np.maximum(y1[i], y1[order[1:]]) xx2 = np.minimum(x2[i], x2[order[1:]]) yy2 = np.minimum(y2[i], y2[order[1:]]) # 当前bbox和其他剩下bbox之间交叉区域的面积 w = np.maximum(0.0, xx2 - xx1 + 1) h = np.maximum(0.0, yy2 - yy1 + 1) inter = w * h # 交叉区域面积 / (bbox + 某区域面积 - 交叉区域面积) ovr = inter / (areas[i] + areas[order[1:]] - inter) # 保留交集小于一定阈值的boundingbox inds = np.where(ovr <= thresh)[0] order = order[inds + 1] return keep if __name__ == "__main__": dets = np.array([ [204, 102, 358, 250, 0.5], [257, 118, 380, 250, 0.7], [280, 135, 400, 250, 0.6], [255, 118, 360, 235, 0.7]]) thresh = 0.4 print "最大bbox:", nms(dets, thresh)
