一,为什么session.commit()可以引起事务的提交?
进入commit()方法查看源码
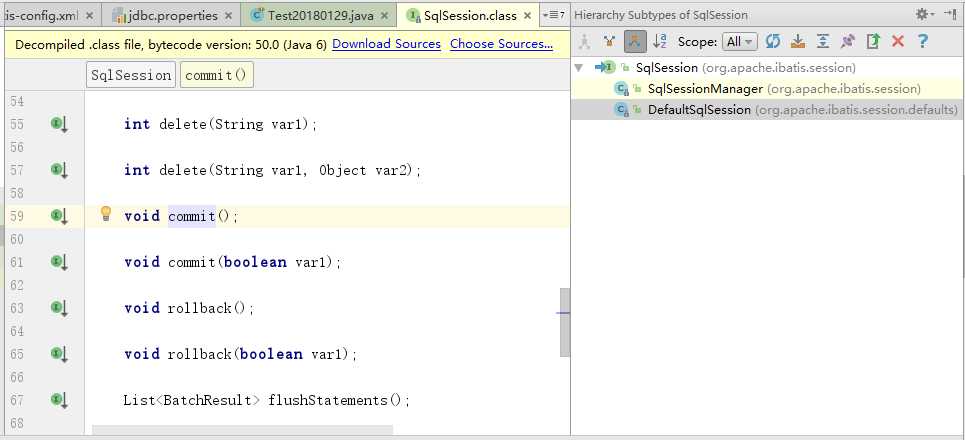
进入SqlSession.class文件之后,Ctrl+H弹出右边的框,选择DeFaultSqlSession
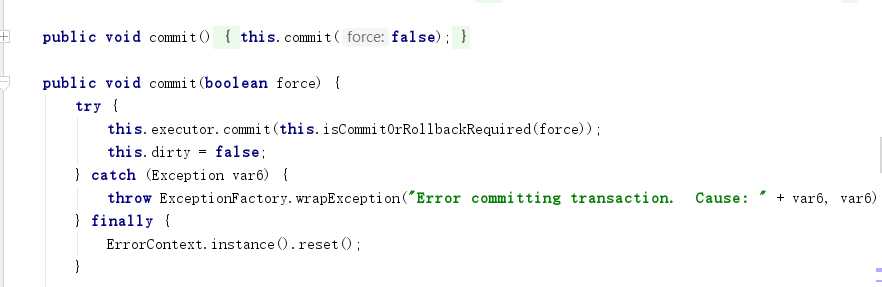
找到COMMIt()方法的重载,ctrl+左键进入源码进行下一步的剖析
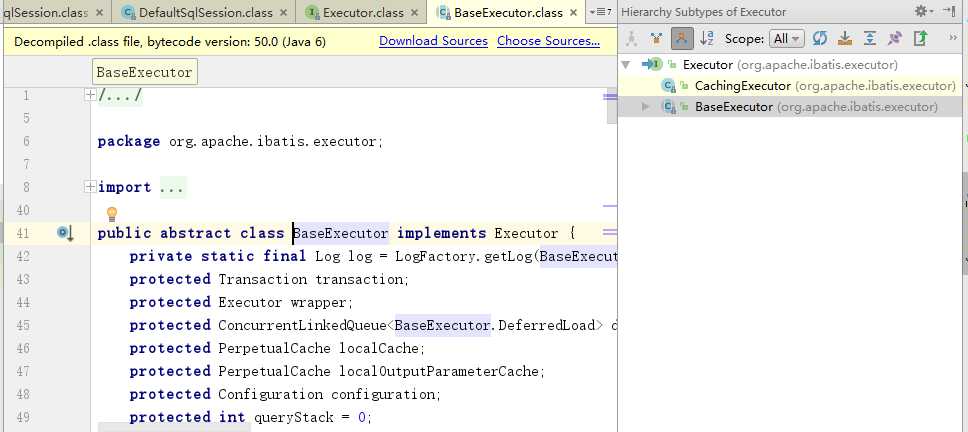
在最底层的commit()方法里边进行了事务的提交,所以SqlSession.commit()方法可以引起事务的提交

二,ResultMap的结果映射
注意:ResultMap不可以和ResultType共存
为什么使用ResultMap?
主要解决数据表中的列名和数据库实体类的属性名不一致的问题
ResultMap的使用步骤:
在映射文件中,创建一个节点
 这里的property对应的是实体类的属性名,column对应的是数据表中的列名
这里的property对应的是实体类的属性名,column对应的是数据表中的列名
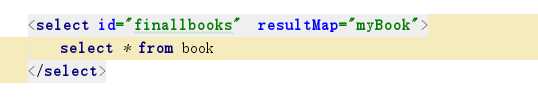
在select节点中,将ResultType改为ResultMap并将值改为创建好的节点的id属性值
三,多条件查询
1.普通的多条件查询
//多条件查询 public List<book> selectMultMap(Map<String,Object> map);
<!--多条件查询-->
<select id="selectMultMap" resultMap="myBook">
select * from book where bookName like ‘%‘ #{bookName} ‘%‘ and bookprice>#{bookprice}
</select>
@Test public void test4(){ SqlSession sqlSession= MyBatisUtil.getSession(); IBookDao mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(IBookDao.class); Map<String,Object> map=new HashMap<String,Object>(); map.put("bookName","大"); map.put("bookprice",100); List<book> books = mapper.selectMultMap(map); for(book item:books){ System.out.println(item.getBookName()); } sqlSession.close(); }
2.多条件索引查询
//多条件索引查询 public List<book> selectMultIndex(String bookname,Integer bookprice);
<!--多条件索引查询-->
<select id="selectMultIndex" resultMap="myBook">
select * from book where bookName like ‘%‘ #{0} ‘%‘ and bookprice>#{1}
</select>
@Test public void test5(){ SqlSession sqlSession= MyBatisUtil.getSession(); IBookDao mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(IBookDao.class); List<book> list = mapper.selectMultIndex("大", 300); for(book item:list){ System.out.println(item.getBookName()); } sqlSession.close(); }e[‘
四,添加后返回自增列的值
当我们需要拿到新添加的列的主键Id的时候:
在<insert>节点中,在书写一个<selectKey>节点
!!!需要注意的是:由于主键Id是自增的,在Sql语句中我们是不用添加的,所以这里声明的keyProperty的作用就是将其赋给Id

五,工具类、
将一些重复性很大的代码放在一个类中,调用时直接通过类的方法来调用,减少代码的书写量
例如:将这几行代封装在一个类,以后需要用到时就不需要在进行书写,直接调用
String path="mybatis-config.xml"; InputStream is= Resources.getResourceAsStream(path); SqlSessionFactory factory=new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(is); SqlSession sqlSession =factory.openSession();
public class MyBatisUtil { static String path="mybatis-config.xml"; static InputStream is; static SqlSessionFactory factory; static { try { is= Resources.getResourceAsStream(path); factory=new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(is); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public static SqlSession getSession(){ return factory.openSession(true); } }
六,智能标签
智能标签分为:
if where foreaachArray[数组类型] foreachList<包装类型Integer> foreachList<自定义类型>
//智能标签if查询 public List<book> selectIf(book bok); //foreach array public List<book> foreachArray(int[] ids); //foreach List public List<book> foreachArrayList(List<Integer> list); //foreach 自定义类型 public List<book> foreachArrayBook(List<book> list);
if where
<select id="selectIf" resultMap="myBook"> SELECT * from book <where> <if test="bookName!=null"> and bookName like ‘%‘ #{bookName} ‘%‘ </if> <if test="bookprice!=null"> and bookprice>#{bookprice} </if> </where> </select>
foreaachArray[数组类型] foreachList<包装类型Integer> foreachList<自定义类型>
<!--数组-->
<select id="foreachArray" resultMap="myBook">
SELECT * from book
<where>
bookId IN
<foreach collection="array" open="(" close=")" separator="," item="myid">
#{myid}
</foreach>
</where>
</select>
<!--List集合-->
<select id="foreachArrayList" resultMap="myBook">
SELECT * from book
<where>
bookId IN
<foreach collection="list" open="(" close=")" separator="," item="myid">
#{myid}
</foreach>
</where>
</select>
<!--自定义类型的List集合-->
<select id="foreachArrayBook" resultMap="myBook">
SELECT * from book
<where>
bookId IN
<foreach collection="list" open="(" close=")" separator="," item="books">
#{books.bookId}
</foreach>
</where>
</select>
