Wooden Sticks
There is a pile of n wooden sticks. The length and weight of each stick are known in advance. The sticks are to be processed by a woodworking machine in one by one fashion. It needs some time, called setup time, for the machine to prepare processing a stick. The setup times are associated with cleaning operations and changing tools and shapes in the machine. The setup times of the woodworking machine are given as follows:
(a) The setup time for the first wooden stick is 1 minute.
(b) Right after processing a stick of length l and weight w , the machine will need no setup time for a stick of length l‘ and weight w‘ if l<=l‘ and w<=w‘. Otherwise, it will need 1 minute for setup.
You are to find the minimum setup time to process a given pile of n wooden sticks. For example, if you have five sticks whose pairs of length and weight are (4,9), (5,2), (2,1), (3,5), and (1,4), then the minimum setup time should be 2 minutes since there is a sequence of pairs (1,4), (3,5), (4,9), (2,1), (5,2).
Input
The input consists of T test cases. The number of test cases (T) is given in the first line of the input file. Each test case consists of two lines: The first line has an integer n , 1<=n<=5000, that represents the number of wooden sticks in the test case, and the second line contains n 2 positive integers l1, w1, l2, w2, ..., ln, wn, each of magnitude at most 10000 , where li and wi are the length and weight of the i th wooden stick, respectively. The 2n integers are delimited by one or more spaces.
Output
The output should contain the minimum setup time in minutes, one per line.
Sample Input
3
5
4 9 5 2 2 1 3 5 1 4
3
2 2 1 1 2 2
3
1 3 2 2 3 1
Sample Output
2
1
3
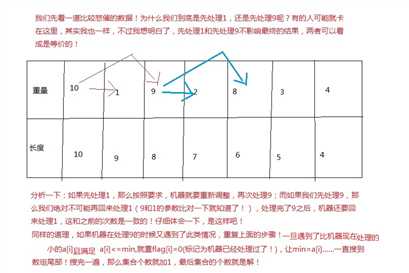
题解:
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<cstdlib> 3 #include<cstdio> 4 #include<cstring> 5 #include<cmath> 6 #include<algorithm> 7 #include<vector> 8 using namespace std; 9 struct wooden{ 10 int l,w; 11 }; 12 wooden my[5010]; 13 bool comp(wooden a,wooden b){ 14 if(a.l>b.l)return 1; 15 else if(a.l==b.l) 16 return a.w>b.w; 17 else return 0; 18 } 19 int main() 20 { 21 int t; 22 scanf("%d",&t); 23 while(t--){ 24 int n; 25 scanf("%d",&n); 26 int i=0,j; 27 while(i<n) 28 { 29 scanf("%d %d",&my[++i].l,&my[i].w); 30 } 31 sort(my,my+n,comp); 32 int out=n; 33 for(i=1;i<n;i++) 34 for(j=0;j<=i-1;j++){ 35 if(my[j].l>=my[i].l&&my[j].w>=my[i].w){ 36 out--; 37 my[j].l=my[i].l; 38 my[j].w=my[i].w; 39 my[i].l=0; 40 my[i].w=0; 41 break; 42 } 43 } 44 printf("%d\n",out); 45 } 46 return 0; 47 }
