上一篇主要介绍了图像拼接的一些原理和方法,这一篇将主要介绍步骤和例程:
接上一篇:
基于特征的接拼方法,分为四个步骤
1、特征检测:从图像中检测出显著且独特的图像特征,诸如:闭合区域,直线段,边缘,轮廓,点等。
2、特征匹配:从相似度确定图像之间特征的对应关系,又分为如下几类:
2.1:使用空域关系的方法
2.2:使用不变描述符的方法
2.3:松弛方法
2.4:金字塔和小波方法
3、变换模型的估计:变换函数选择和函数参数估计
4、图像变换和重采样:可以通过前向或后向的方式来实现,插值的方法有最近邻插值、双线性插值、双三次函数插值、二次样条插值、三次B样条插值、高阶B样条插值。
基于特征的方法普遍适用于局部结构信息更显著的情况,能够处理图像之间复杂变形的情况,不足之处是特征检测困难且不稳定,最关键的一点是需要有一种判断力很强的、鲁棒性能好的且对图像之间变化保持不变的特征匹配算法。
下面是Halcon自带例程,如何拼接图像
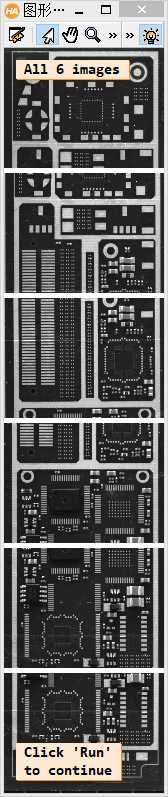
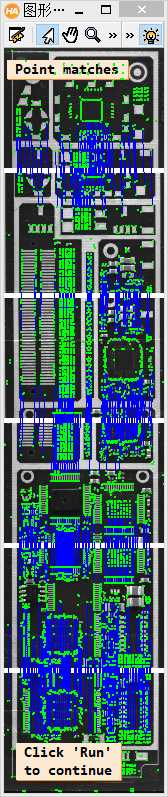
1 **此例程讲解了如何将几张局部的PCB图像拼接居一张大的马赛克PCB图像。 2 **此例程使用算子proj_match_points_ransac和算子 gen_projective_masaic完成上述工作。 3 **请注意:这个PCB图像有一几处看起来像拼接逢合线的破损点,为了更好的区分真正的缝合线,例程呈现逢合线。 4 dev_update_off () 5 dev_close_window () 6 dev_open_window (0, 0, 640, 480, ‘white‘, WindowHandle) 7 dev_set_color (‘green‘) 8 set_display_font (WindowHandle, 14, ‘mono‘, ‘true‘, ‘false‘) 9 **一张一张的读取图像。 10 gen_empty_obj (Images) 11 for J := 1 to 6 by 1 12 read_image (Image, ‘mosaic/pcb_‘ + J$‘02‘) 13 concat_obj (Images, Image, Images) 14 dev_display (Image) 15 disp_message (WindowHandle, ‘Image ‘ + J$‘d‘, ‘image‘, -1, -1, ‘black‘, ‘true‘) 16 wait_seconds (1) 17 endfor 18 disp_continue_message (WindowHandle, ‘black‘, ‘true‘) 19 stop () 20 * To show the point matches that are used to compute the projective 21 * transformation between the images, we will show all images in a large 22 * tiled image with some space between the images so that the extents 23 * of the images are easily visible. 24 dev_set_window_extents (-1, -1, 640 / 4, 2980 / 4) 25 tile_images_offset (Images, TiledImage, [0,500,1000,1500,2000,2500], [0,0,0,0,0,0], [-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1], [-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1], [-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1], [-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1], 640, 2980) 26 dev_clear_window () 27 dev_display (TiledImage) 28 disp_message (WindowHandle, ‘All 6 images‘, ‘window‘, 12, 12, ‘black‘, ‘true‘) 29 disp_message (WindowHandle, ‘Click \‘Run\‘\nto continue‘, ‘window‘, 2980 / 4 - 50, 12, ‘black‘, ‘true‘) 30 stop () 31 * Now we compute point matches between the five pairs of images and with this 32 * the projective transformation between the image pairs. Note that the code 33 * below calls the point operator for each image pair. Since the images form 34 * a strip, with a little book keeping we could make the process a little more 35 * efficient by saving the points from the last iteration (ImageT in pair J will 36 * be identical to ImageF in pair J+1). This is not done here because such an 37 * optimization would be quite cumbersome in the general case where the images 38 * can lie in a general configuration that cannot be represented by a strip. 39 dev_clear_window () 40 dev_display (TiledImage) 41 disp_message (WindowHandle, ‘Point matches‘, ‘window‘, 12, 3, ‘black‘, ‘true‘) 42 * We define the image pairs, i.e., which image should be mapped to which image. 43 From := [1,2,3,4,5] 44 To := [2,3,4,5,6] 45 Num := |From| 46 * We need a variable to accumulate the projective transformation matrices. 47 ProjMatrices := [] 48 * Furthermore, since we want to create a rigid mosaic below we need to 49 * accumulate all the point correspondences and the number of matches per 50 * image pair. 51 Rows1 := [] 52 Cols1 := [] 53 Rows2 := [] 54 Cols2 := [] 55 NumMatches := [] 56 * Now we can determine the transformations between the five image pairs. 57 for J := 0 to Num - 1 by 1 58 F := From[J] 59 T := To[J] 60 select_obj (Images, ImageF, F) 61 select_obj (Images, ImageT, T) 62 * Extract the points in both images. 63 points_foerstner (ImageF, 1, 2, 3, 200, 0.3, ‘gauss‘, ‘false‘, RowJunctionsF, ColJunctionsF, CoRRJunctionsF, CoRCJunctionsF, CoCCJunctionsF, RowAreaF, ColAreaF, CoRRAreaF, CoRCAreaF, CoCCAreaF) 64 points_foerstner (ImageT, 1, 2, 3, 200, 0.3, ‘gauss‘, ‘false‘, RowJunctionsT, ColJunctionsT, CoRRJunctionsT, CoRCJunctionsT, CoCCJunctionsT, RowAreaT, ColAreaT, CoRRAreaT, CoRCAreaT, CoCCAreaT) 65 * Determine the point matches and the transformation for the current 66 * image pair. 67 proj_match_points_ransac (ImageF, ImageT, RowJunctionsF, ColJunctionsF, RowJunctionsT, ColJunctionsT, ‘ncc‘, 21, 0, 0, 480, 640, 0, 0.5, ‘gold_standard‘, 1, 4364537, ProjMatrix, Points1, Points2) 68 * Accumulate the transformation matrix. 69 ProjMatrices := [ProjMatrices,ProjMatrix] 70 * Accumulate the point matches and number of point matches. 71 Rows1 := [Rows1,subset(RowJunctionsF,Points1)] 72 Cols1 := [Cols1,subset(ColJunctionsF,Points1)] 73 Rows2 := [Rows2,subset(RowJunctionsT,Points2)] 74 Cols2 := [Cols2,subset(ColJunctionsT,Points2)] 75 NumMatches := [NumMatches,|Points1|] 76 * Generate crosses that represent the extracted points in the tiled image. 77 * Note that we have to take the row offsets of the images in the tiled image 78 * into account. 79 gen_cross_contour_xld (PointsF, RowJunctionsF + (F - 1) * 500, ColJunctionsF, 6, rad(45)) 80 gen_cross_contour_xld (PointsT, RowJunctionsT + (T - 1) * 500, ColJunctionsT, 6, rad(45)) 81 * Generate a representation of the matched point pairs as lines. We create 82 * XLD contours from the lines so that we can zoom into the graphics window 83 * to take a closer look at the matches. 84 RowF := subset(RowJunctionsF,Points1) + (F - 1) * 500 85 ColF := subset(ColJunctionsF,Points1) 86 RowT := subset(RowJunctionsT,Points2) + (T - 1) * 500 87 ColT := subset(ColJunctionsT,Points2) 88 gen_empty_obj (Matches) 89 for K := 0 to |RowF| - 1 by 1 90 gen_contour_polygon_xld (Match, [RowF[K],RowT[K]], [ColF[K],ColT[K]]) 91 concat_obj (Matches, Match, Matches) 92 endfor 93 * Now display the extracted data. 94 dev_set_color (‘blue‘) 95 dev_display (Matches) 96 dev_set_color (‘green‘) 97 dev_display (PointsF) 98 dev_display (PointsT) 99 endfor 100 disp_message (WindowHandle, ‘Click \‘Run\‘\nto continue‘, ‘window‘, 2980 / 4 - 50, 12, ‘black‘, ‘true‘) 101 stop () 102 * Finally, we can generate the mosaic image from the projective transformations. 103 gen_projective_mosaic (Images, MosaicImage, 2, From, To, ProjMatrices, ‘default‘, ‘false‘, MosaicMatrices2D) 104 get_image_size (MosaicImage, Width, Height) 105 dev_set_window_extents (-1, -1, Width / 3, Height / 3) 106 dev_clear_window () 107 dev_display (MosaicImage) 108 disp_message (WindowHandle, ‘Projective mosaic‘, ‘window‘, 12, 12, ‘black‘, ‘true‘) 109 disp_message (WindowHandle, ‘Click \‘Run\‘\nto continue‘, ‘window‘, Height / 3 - 50, 12, ‘black‘, ‘true‘) 110 stop () 111 * To show more clearly that the folds visible in the image do not result from the 112 * mosaicking, we display the seams between the images in the mosaic image. 113 * This can be done most easily by creating an image that contains the border 114 * of the images, generating a mosaic from it, and segmenting the resulting 115 * mosaic image. 116 get_image_size (Image, Width, Height) 117 gen_image_const (ImageBlank, ‘byte‘, Width, Height) 118 gen_rectangle1 (Rectangle, 0, 0, Height - 1, Width - 1) 119 paint_region (Rectangle, ImageBlank, ImageBorder, 255, ‘margin‘) 120 gen_empty_obj (ImagesBorder) 121 for J := 1 to 6 by 1 122 concat_obj (ImagesBorder, ImageBorder, ImagesBorder) 123 endfor 124 gen_projective_mosaic (ImagesBorder, MosaicImageBorder, 2, From, To, ProjMatrices, ‘default‘, ‘false‘, MosaicMatrices2D) 125 threshold (MosaicImageBorder, Seams, 128, 255) 126 dev_clear_window () 127 dev_display (MosaicImage) 128 disp_message (WindowHandle, ‘Seams between the\nimages‘, ‘window‘, 12, 12, ‘black‘, ‘true‘) 129 dev_set_color (‘yellow‘) 130 dev_display (Seams) 131 disp_message (WindowHandle, ‘Click \‘Run\‘\nto continue‘, ‘window‘, 550, 12, ‘black‘, ‘true‘) 132 stop () 133 * If you look very closely at the projective mosaic above, you may note that 134 * there is a very slight projective distortion in the mosaic. This happens 135 * because the transformations cannot be determined with perfect accuracy 136 * because of very small errors in the point coordinates due to noise. Because 137 * of the strip configuration, essentially the overlapping area between the image 138 * pairs can act like a hinge around which the images may rotate out of the image 139 * plane. In this example, we know that the mapping between the images must 140 * be a rigid transformation. If we want to force the transformation to be rigid 141 * we can simply use bundle_adjust_mosaic. 142 bundle_adjust_mosaic (6, 1, From, To, ProjMatrices, Rows1, Cols1, Rows2, Cols2, NumMatches, ‘rigid‘, MosaicMatrices2D, Rows, Cols, Error) 143 * Now, we can generate the mosaic image from the rigid transformations. 144 gen_bundle_adjusted_mosaic (Images, MosaicImageRigid, MosaicMatrices2D, ‘default‘, ‘false‘, TransMatrix2D) 145 get_image_size (MosaicImageRigid, Width, Height) 146 dev_set_window_extents (-1, -1, Width / 3, Height / 3) 147 dev_clear_window () 148 dev_display (MosaicImageRigid) 149 disp_message (WindowHandle, ‘Rigid mosaic‘, ‘window‘, 12, 12, ‘black‘, ‘true‘)
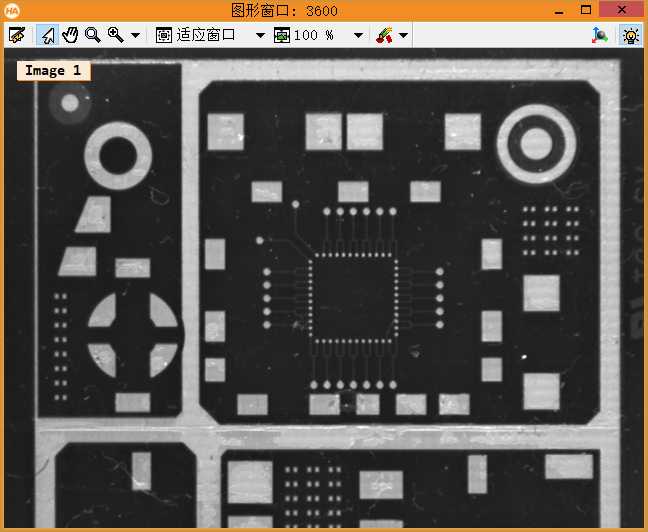
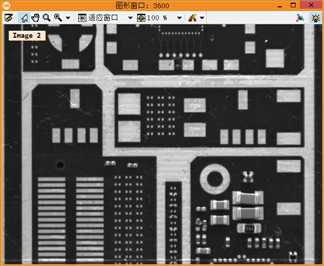
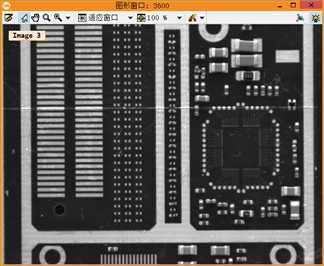
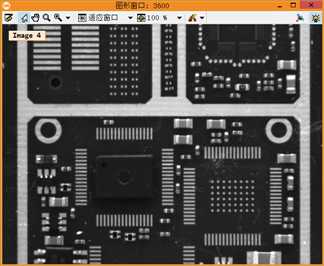
带逢合线的图像 找定位点
最终图像:
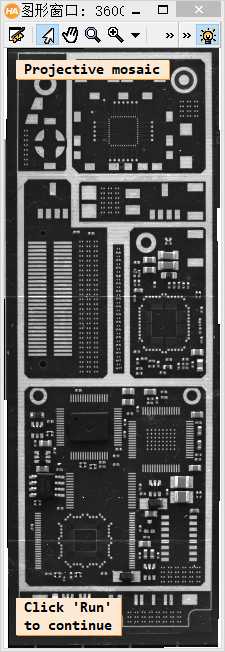
下面我们看一下另一个例程:
这个例程使用proj_match_points_ransac_guided 和 gen_projective_mosaic
主要介绍如何使用金字塔算法快速获取两个图像的特征点进行拼接。
1 * This example program shows how images can be combined 2 * into a mosaic image using proj_match_points_ransac_guided 3 * and gen_projective_mosaic. 4 * It is shown how the calculation of the projection between two 5 * images can be accelerated using an image pyramid. 6 * 7 * Initializations 8 ImgPath := ‘3d_machine_vision/mosaic/‘ 9 ImgName := ‘bga_r_‘ 10 Times := [] 11 Colors := [‘red‘,‘coral‘,‘yellow‘,‘lime green‘] 12 read_image (Images, ImgPath + ImgName + [‘01‘,‘06‘]) 13 dev_update_off () 14 dev_close_window () 15 dev_open_window_fit_size (0, 0, 640, 980, 320, 490, WindowHandle) 16 dev_open_window_fit_size (0, 330, 490, 490, 1000, 490, WindowHandle1) 17 set_display_font (WindowHandle, 14, ‘mono‘, ‘true‘, ‘false‘) 18 set_display_font (WindowHandle1, 14, ‘mono‘, ‘true‘, ‘false‘) 19 * The internal camera parameters of the used camera 20 * (necessary to eliminate radial distortions) 21 CamParam := [0.0121693,-2675.63,7.40046e-006,7.4e-006,290.491,258.887,640,480] 22 change_radial_distortion_cam_par (‘adaptive‘, CamParam, 0, CamParOut) 23 change_radial_distortion_image (Images, Images, Images, CamParam, CamParOut) 24 * To show the point matches that are used to compute the 25 * transformation between the images, we will show both images in a 26 * tiled image with some space between the images so that the extents 27 * of the images are easily visible. 28 tile_images_offset (Images, TiledImage, [0,500], [0,0], [-1,-1], [-1,-1], [-1,-1], [-1,-1], 640, 980) 29 * 30 * Now we can determine the transformations between the image pairs. 31 From := 1 32 To := 2 33 select_obj (Images, ImageF, From) 34 select_obj (Images, ImageT, To) 35 * 36 * Repeat the calculation 4 times with a different number of pyramid levels 37 for NumLevels := 1 to 4 by 1 38 * 39 dev_clear_window () 40 dev_set_window (WindowHandle) 41 dev_clear_window () 42 dev_display (TiledImage) 43 disp_message (WindowHandle, [‘Calculate point matches‘,‘with ‘ + NumLevels + ‘ pyramid levels‘,‘Please wait ...‘], ‘window‘, 20, 10, ‘black‘, ‘true‘) 44 * 45 * Calculate the projection between the two images 46 * Check the procedure‘s comments for details 47 count_seconds (S1) 48 proj_match_points_ransac_pyramid (ImageF, ImageT, NumLevels, RowFAll, ColFAll, RowTAll, ColTAll, ProjMatrix, Points1, Points2) 49 count_seconds (S2) 50 Times := [Times,S2 - S1] 51 * 52 * Display point correspondences 53 gen_cross_contour_xld (PointsF, RowFAll, ColFAll, 6, rad(45)) 54 gen_cross_contour_xld (PointsT, RowTAll + 500, ColTAll, 6, rad(45)) 55 RowF := subset(RowFAll,Points1) 56 ColF := subset(ColFAll,Points1) 57 RowT := subset(RowTAll,Points2) + 500 58 ColT := subset(ColTAll,Points2) 59 gen_empty_obj (Matches) 60 for K := 0 to |RowF| - 1 by 1 61 gen_contour_polygon_xld (Match, [RowF[K],RowT[K]], [ColF[K],ColT[K]]) 62 concat_obj (Matches, Match, Matches) 63 endfor 64 dev_display (TiledImage) 65 dev_set_color (‘blue‘) 66 dev_display (Matches) 67 dev_set_color (‘green‘) 68 dev_display (PointsF) 69 dev_display (PointsT) 70 disp_message (WindowHandle, [|RowF| + ‘ point matches‘,‘Time used: ‘ + (S2 - S1)$‘.3‘ + ‘ s‘], ‘window‘, 20, 10, ‘black‘, ‘true‘) 71 * 72 * Generate the mosaic image 73 gen_projective_mosaic (Images, MosaicImage, 1, From, To, ProjMatrix, [2,1], ‘false‘, MosaicMatrices2D) 74 * 75 * Display mosaic image 76 get_image_size (MosaicImage, Width, Height) 77 dev_set_window (WindowHandle1) 78 dev_resize_window_fit_image (MosaicImage, 0, 330, [400,700], 700) 79 dev_clear_window () 80 dev_display (MosaicImage) 81 disp_message (WindowHandle1, ‘Projective mosaic (used ‘ + NumLevels + ‘ pyramid levels)‘, ‘window‘, 20, 10, ‘black‘, ‘true‘) 82 disp_continue_message (WindowHandle1, ‘black‘, ‘true‘) 83 stop () 84 endfor 85 * 86 * Display execution times 87 dev_set_window (WindowHandle) 88 dev_close_window () 89 MaxTime := max(Times) 90 BaseRow := 380 91 RectHeight := 300 92 disp_message (WindowHandle1, [‘Time in s:‘,‘(#levels used)‘], ‘image‘, BaseRow + 20, 10, ‘black‘, ‘true‘) 93 for Index := 0 to |Times| - 1 by 1 94 gen_rectangle1 (Rectangle, BaseRow - RectHeight * Times[Index] / MaxTime, 200 + Index * 100, BaseRow, 280 + Index * 100) 95 disp_message (WindowHandle1, [Times[Index]$‘.3‘,‘(‘ + (Index + 1) + ‘)‘], ‘image‘, BaseRow + 20, 200 + 100 * Index, ‘black‘, ‘true‘) 96 dev_set_color (Colors[Index]) 97 dev_set_draw (‘fill‘) 98 dev_display (Rectangle) 99 endfor 100 disp_finished_message (WindowHandle1, ‘black‘, ‘true‘)
