Django 自定义用户认证
Django附带的认证对于大多数常见情况来说已经足够了,但是如何在 Django 中使用自定义的数据表进行用户认证,有一种较为笨蛋的办法就是自定义好数据表后,使用OnetoOne来跟 Django 的表进行关联,类似于这样:
from django.contrib.auth.models import User
class UserProfile(models.Model):
"""
用户账号表
"""
user = models.OneToOneField(User)
name = models.CharField(max_length=32)
def __str__(self):
return self.name
class Meta:
verbose_name_plural = verbose_name = "用户账号"
ordering = [‘id‘]这样做虽然可以简单、快速的实现,但是有一个问题就是我们在自己的表中创建一个用户就必须再跟 admin 中的一个用户进行关联,这简直是不可以忍受的。
admin代替默认User model
- 写我们自定义的 models 类来创建用户数据表来代替默认的
User model,而不与django admin的进行关联,相关的官方文档在这里
??戳我
from django.db import models
from django.contrib.auth.models import User
from django.contrib.auth.models import (
BaseUserManager, AbstractBaseUser
)
class UserProfileManager(BaseUserManager):
def create_user(self, email, name, password=None):
"""
用户创建,需要提供 email、name、password
"""
if not email:
raise ValueError(‘Users must have an email address‘)
user = self.model(
email=self.normalize_email(email),
name=name,
)
user.set_password(password)
user.save(using=self._db)
return user
def create_superuser(self, email, name, password):
"""
超级用户创建,需要提供 email、name、password
"""
user = self.create_user(
email,
password=password,
name=name,
)
user.is_admin = True
user.is_active = True
user.save(using=self._db)
return user
class UserProfile(AbstractBaseUser):
# 在此处可以配置更多的自定义字段
email = models.EmailField(
verbose_name=‘email address‘,
max_length=255,
unique=True,
)
name = models.CharField(max_length=32, verbose_name="用户名称")
phone = models.IntegerField("电话")
is_active = models.BooleanField(default=True)
is_admin = models.BooleanField(default=False)
objects = UserProfileManager()
USERNAME_FIELD = ‘email‘ # 将email 作为登入用户名
REQUIRED_FIELDS = [‘name‘, ‘phone‘]
def __str__(self):
return self.email
def get_full_name(self):
# The user is identified by their email address
return self.email
def get_short_name(self):
# The user is identified by their email address
return self.email
def has_perm(self, perm, obj=None):
"Does the user have a specific permission?"
# Simplest possible answer: Yes, always
return True
def has_module_perms(self, app_label):
"Does the user have permissions to view the app `app_label`?"
# Simplest possible answer: Yes, always
return True
@property
def is_staff(self):
"Is the user a member of staff?"
# Simplest possible answer: All admins are staff
return self.is_adminadmin 配置
class UserCreationForm(forms.ModelForm):
"""A form for creating new users. Includes all the required
fields, plus a repeated password."""
password1 = forms.CharField(label=‘Password‘, widget=forms.PasswordInput)
password2 = forms.CharField(label=‘Password confirmation‘, widget=forms.PasswordInput)
class Meta:
model = models.UserProfile
fields = (‘email‘, ‘name‘)
def clean_password2(self):
password1 = self.cleaned_data.get("password1")
password2 = self.cleaned_data.get("password2")
if password1 and password2 and password1 != password2:
raise forms.ValidationError("Passwords don‘t match")
return password2
def save(self, commit=True):
user = super(UserCreationForm, self).save(commit=False)
user.set_password(self.cleaned_data["password1"])
if commit:
user.save()
return user
class UserChangeForm(forms.ModelForm):
"""A form for updating users. Includes all the fields on
the user, but replaces the password field with admin‘s
password hash display field.
"""
password = ReadOnlyPasswordHashField()
class Meta:
model = models.UserProfile
fields = (‘email‘, ‘password‘, ‘name‘, ‘is_active‘, ‘is_admin‘)
def clean_password(self):
return self.initial["password"]
class UserProfileAdmin(BaseUserAdmin):
form = UserChangeForm
add_form = UserCreationForm
list_display = (‘email‘, ‘name‘, ‘is_admin‘, ‘is_staff‘)
list_filter = (‘is_admin‘,)
fieldsets = (
(None, {‘fields‘: (‘email‘, ‘password‘)}),
(‘Personal info‘, {‘fields‘: (‘name‘,)}),
(‘Permissions‘, {‘fields‘: (‘is_admin‘, ‘is_active‘, ‘roles‘, ‘user_permissions‘, ‘groups‘)}),
)
add_fieldsets = (
(None, {
‘classes‘: (‘wide‘,),
‘fields‘: (‘email‘, ‘name‘, ‘password1‘, ‘password2‘)}
),
)
search_fields = (‘email‘,)
ordering = (‘email‘,)
filter_horizontal = (‘groups‘, ‘user_permissions‘,‘roles‘)2.Django允许您通过AUTH_USER_MODEL配置来引用自定义的model设置来覆盖默认User模型,这个配置的配置方法为在 settings 中加入:AUTH_USER_MODEL = "APP.model_class",例如本例中我们需要在 setting 中加入以下配置:
AUTH_USER_MODEL = "app1.UserProfile"3.部署
python manage.py makemigrations
python manage.py migrate创建一个新用户,此时我们就可以用这个用户来登录 admin 后台了
python manage.py createsuperuser
效果如下:
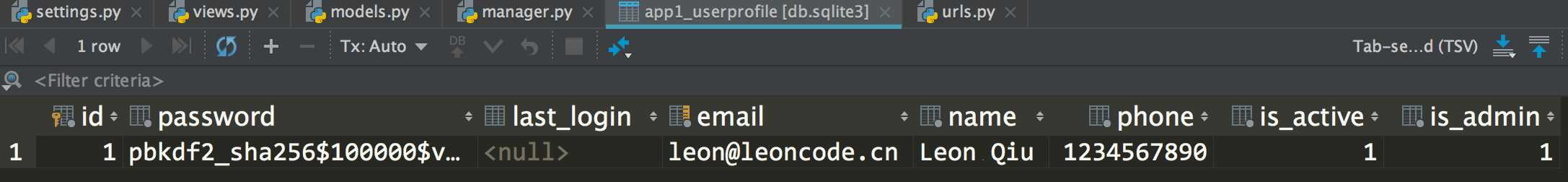
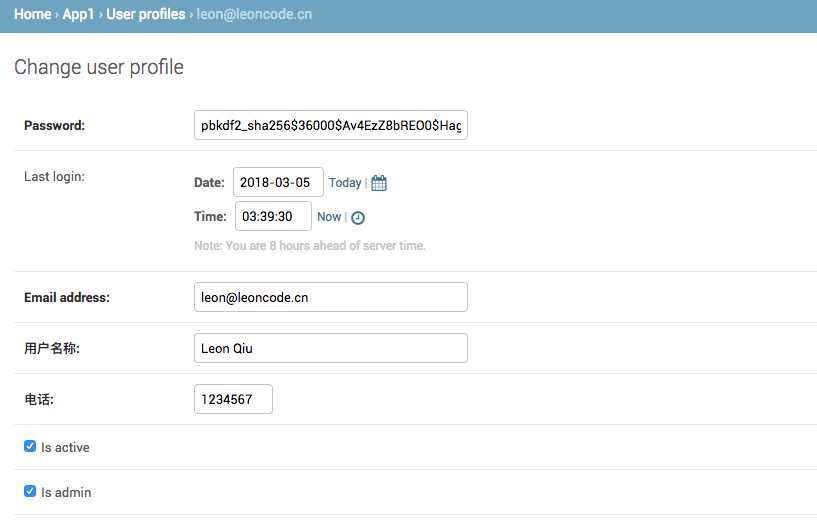
自定义认证
那如果我们需要使用我们自己的认证系统呢,假如我们有一个 login 页面和一个 home 页面:
from django.shortcuts import render, HttpResponse, redirect
from django.contrib.auth import authenticate,login,logout
from app1 import models
from django.contrib.auth.decorators import login_required
def auth_required(auth_type):
# 认证装饰器
def wapper(func):
def inner(request, *args, **kwargs):
if auth_type == ‘admin‘:
ck = request.COOKIES.get("login") # 获取当前登录的用户
if request.user.is_authenticated() and ck:
return func(request, *args, **kwargs)
else:
return redirect("/app1/login/")
return inner
return wapper
def login_auth(request):
# 认证
if request.method == "GET":
return render(request, ‘login.html‘)
elif request.method == "POST":
username = request.POST.get(‘username‘, None)
password = request.POST.get(‘password‘, None)
user = authenticate(username=username, password=password)
if user is not None:
if user.is_active:
login(request, user)
_next = request.GET.get("next",‘/crm‘)
return redirect(‘_next‘)
else:
return redirect(‘/app1/login/‘)
else:
return redirect(‘/app1/login/‘)
else:
pass
def my_logout(request):
# 注销
if request.method == ‘GET‘:
logout(request)
return redirect(‘/app1/login/‘)
@login_required
def home(request):
# home page
path1, path2 = "Home", ‘主页‘
if request.method == "GET":
return render(request, ‘home.html‘, locals())
elif request.method == "POST":
pass