http://www.lydsy.com/JudgeOnline/problem.php?id=2655
f[i][j] 表示[1,i]里选严格递增的j个数,序列值之和
那么ans=f[A][n] * n!
A太大,那么用拉格朗日插值法
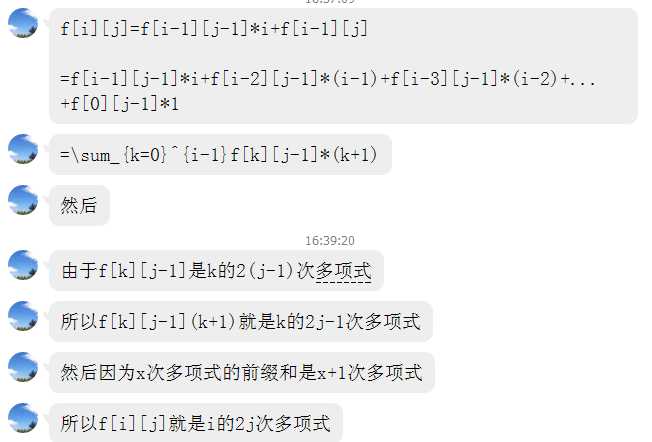
f[i][j] 是关于i的2j次多项式,证明如下:
%%%rqy
#include<cstdio> using namespace std; int mod; int f[1510][501]; int x[1005],y[1005],tot; int Pow(int a,int b) { int res=1; for(;b;a=1LL*a*a%mod,b>>=1) if(b&1) res=1LL*res*a%mod; return res; } int Langrange(int n) { int fz=1; for(int i=1;i<=tot;++i) fz=1LL*fz*(n-x[i])%mod; int fm; int ans=0; for(int i=1;i<=tot;++i) { fm=n-x[i]; for(int j=1;j<=tot;++j) if(i!=j) fm=1LL*fm*(x[i]-x[j])%mod; ans=(ans+1LL*fz*y[i]%mod*Pow(fm,mod-2)%mod)%mod; } if(ans<0) ans+=mod; return ans; } int main() { int A,n; scanf("%d%d%d",&A,&n,&mod); f[0][0]=1; int m=3*n+10; f[0][0]=1; for(int i=1;i<=m;++i) { f[i][0]=1; for(int j=1;j<=i;++j) f[i][j]=(1LL*f[i-1][j-1]*i%mod+f[i-1][j])%mod; } for(int i=1;i<=m && tot<2*n+1;++i) if(f[i][n] && i!=A) x[++tot]=i,y[tot]=f[i][n]; int fac=1; for(int i=2;i<=n;++i) fac=1LL*fac*i%mod; printf("%d",1LL*Langrange(A)*fac%mod); }
