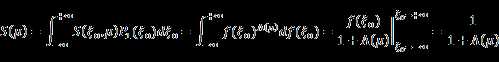Derivation for equation (8)
This equation tell us how to construct a macrosurface BRDF given microsurface ‘s D, G, F.
![]()
In this equation,
![]() is
incident vector.
is
incident vector.
![]() is outgoing
vector.
is outgoing
vector.
![]() is macrosurface
normal.
is macrosurface
normal.
![]() is microsurface
normal.
is microsurface
normal.
![]() is the
macrosurface BRDF.
is the
macrosurface BRDF.
![]() is the
microsurface BRDF.
is the
microsurface BRDF.
![]() is microfacet
distribution function.
is microfacet
distribution function.
![]() is
shadowing-masking function.
is
shadowing-masking function.
![]() is solid angle
in the hemisphere
is solid angle
in the hemisphere ![]() .
.
How can we get this equation? Please see the figure below.
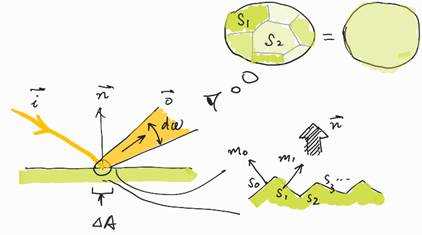
In this figure, the surface is illuminated
by a light source and an observer is looking at the surface. The observer has a
microscope so that he will see the microfacets s1, s2,
... . These microfacets have different colors because of their orientations are
different. When the observer look at the surface at the same location, but
without the microscope, he will no longer see the microfacets but a uniform color.
This time, he knows that it is colors from microfacets that mix together and
form the uniform color. Let‘s denote the colors from microfacets as ![]() and the
uniform color as
and the
uniform color as ![]() . Then we have:
. Then we have:
![]()
In this equation,
![]() is the
projected area of si . According to the definition of microfacet
distribution function, we have:
is the
projected area of si . According to the definition of microfacet
distribution function, we have:
![]()
In this equation,
![]() is the area of
macrosurface.
is the area of
macrosurface.
![]() is i-th microfacet‘s normal.
is i-th microfacet‘s normal.
![]() is a small
solid angle aligned with
is a small
solid angle aligned with ![]() .
.
![]() is microfacet
distribution function.
is microfacet
distribution function.
Combine these equations, we have:
![]()
We can
eliminate ![]() and using the equation
(3) in the paper:
and using the equation
(3) in the paper:
![]()
Convert sum to integral, then we get:
![]()
Now we
can see the term ![]() . Let‘s investigate
the term
. Let‘s investigate
the term![]() further:
further:
![]()
In this equation,
![]() is a small
solid angle of incident light over the hemisphere
is a small
solid angle of incident light over the hemisphere ![]() .
.
Finally, we have:
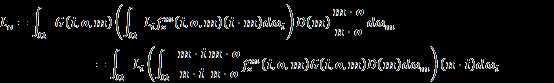
According to the rendering equation
![]()
We can
regard the inner integral ![]() as the
equivalent BRDF for macrosurface, so that we get:
as the
equivalent BRDF for macrosurface, so that we get:
![]()
Confirm equation (9)
According to the definition of radiance:
![]()
In this equation,
![]() is the
radiance in outgoing direction
is the
radiance in outgoing direction ![]()
![]() is luminous
flux
is luminous
flux
![]() is area of
macrofacet
is area of
macrofacet
So the outgoing irradiance is:
![]()
Put equation (9) in, we have:
![]()
According to equation (10),
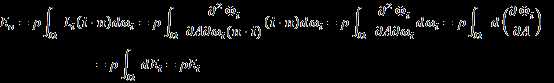
So According to equation (9), the overall
outgoing irradiance equals the incoming irradiance scaled by a factor ![]() , which is less than
1.
, which is less than
1.
Derivation for equation (20)
According to equation (8),
![]()
Put equation (15) in it, we have:
![]()
When ![]() ,
, ![]() , then according to
equation (10), we have:
, then according to
equation (10), we have:
![]()
Derivation for equation (42)
Let us take a careful look at the
definition of ![]() .
.
Suppose there is one point ![]() on surface
whose normal is
on surface
whose normal is ![]() , we construct a
plane
, we construct a
plane![]() perpendicular to
the normal and choose two perpendicular axes
perpendicular to
the normal and choose two perpendicular axes ![]() and
and ![]() . For a small patch
. For a small patch ![]() on the plane,
we denote the direction pointing from
on the plane,
we denote the direction pointing from ![]() to it
to it ![]() , and the small
solid angle it occupies
, and the small
solid angle it occupies ![]() .
.
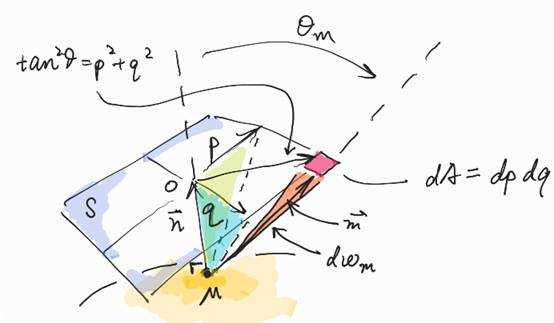
According to equation (4), which is
![]()
We can consider ![]() as the probability
as the probability ![]() of finding a
microfacet whose normal
of finding a
microfacet whose normal ![]() is inside
is inside ![]() , so that we
have
, so that we
have

That‘s exactly what ![]() is.
is.
Derivation for equation (45)
Break the ray into many short segments,
each with projected length ![]() . According to the
paper, the probability that the ray is first blocked in segment
. According to the
paper, the probability that the ray is first blocked in segment ![]() is
is ![]() , so the probability
that ray is always unblocked is:
, so the probability
that ray is always unblocked is:
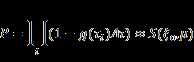
Then we have:
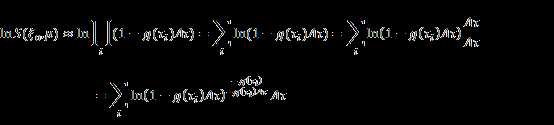
From calculus we know:
![]()
So
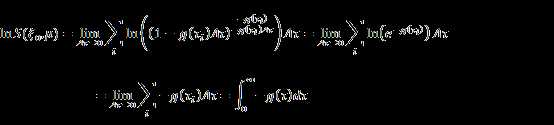
So that
![]()
Derivation for equation (46)
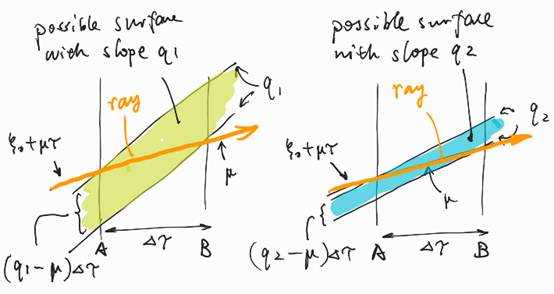
Let‘s consider the situation that a ray
intersects with an short and straight surface segment ![]() . In order to do
that, the surface height should below the ray at
. In order to do
that, the surface height should below the ray at ![]() and above the
ray at
and above the
ray at ![]() . For a given slope
. For a given slope ![]() , there exist a set
of surface segments that fulfill this condition, which are in the shaded areas
in the figures below.
, there exist a set
of surface segments that fulfill this condition, which are in the shaded areas
in the figures below.
It‘s easy to note that the possible surface
height at ![]() varies from
varies from ![]() to
to ![]() . So given a surface
with slope
. So given a surface
with slope ![]() , the probability
that it intersects with a ray
, the probability
that it intersects with a ray ![]() is
is
![]()
In this equation,
![]() is the probability
density that surface height reaches
is the probability
density that surface height reaches ![]() at point
at point ![]() .
.
Also we know that the probability that a
surface segment has slope ![]() is
is
![]()
Combine them, then we get the probability
for finding a surface segment with slope ![]() as well as
intersecting with the ray:
as well as
intersecting with the ray:
![]()
Consider all possible surface slope ![]() , the probability
that they intersect with the ray is:
, the probability
that they intersect with the ray is:
![]()
Among all surface segments with slope ![]() , the probability
that a surface segment below the ray is:
, the probability
that a surface segment below the ray is:
![]()
Consider all possible surface slope ![]() , the probability
that they below the ray is:
, the probability
that they below the ray is:
![]()
Assume ![]() is independent
from
is independent
from ![]() , we have:
, we have:
![]()
So the probability that a ray first
intersects with surface in ![]() is:
is:
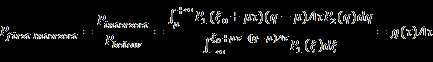
Let ![]() , so
, so
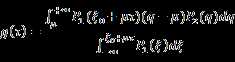
Derivation for equation (49)
From equation (48), we have:
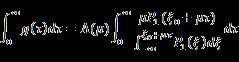
Note that
![]()
So
![]()
Then
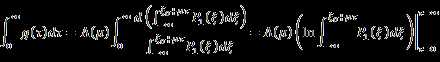
![]()
![]()
Put it in equation (45):
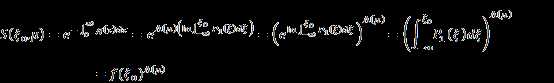
Derivation for equation (50)