本笔记是从onenote写的,然后导成word发布在这里。自己记的相对随意,没有多花时间编辑因此也有内容重点不很突出、中英文混杂等的缺点,请见谅。
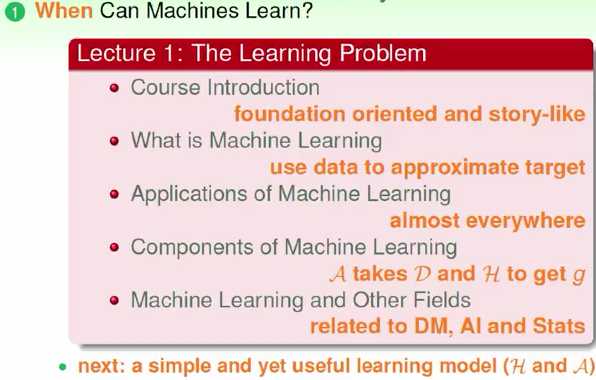
一 Course Introduction

方式:从基础的角度切入
story-like:
·When Can Machine Learn? (illustrative + technical)
·Why Can Machine Learn? (theoretical + illustrative)
·How Can Machine Learn? (technical + practical)
·How Can Machine Learn Better? (practical + theoretical)
二 What Is Machine Learning
1 What Is Learning
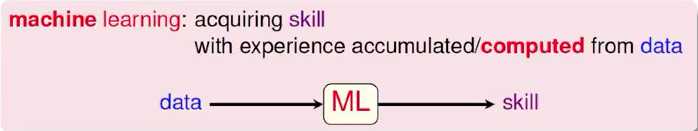
学习的一个共通性是从观察出发,听觉是一种观察,视觉也是一种观察。从这些观察出发,然后经过脑袋的转化过程,最后变成有用的技巧,这是一种学习的过程。

机器学习就是在模仿人类学习的过程。机器学习的主体从人转变成计算机。电脑观察到的东西(我们主动给电脑的东西或者电脑想办法获取到的东西)称为资料。电脑将资料拿来,经过一番处理,最后变成对电脑来说有用的技能。
2 What Is Skill
技巧是用来增进某一方面的表现。比如学习了数学,计算可以变得更准确。

3 Machine Learning
机器学习的过程是从资料出发,然后经过电脑的计算,最终得到某种表现的增进。
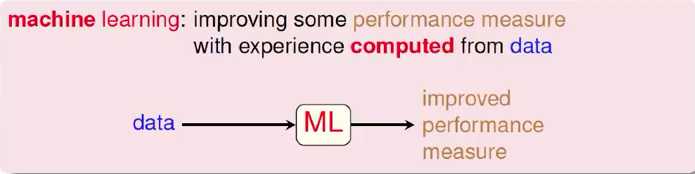
4 Why Use Machine Learning
The Machine Learning: an alternative route to build complicated systems

5 Key Essence of Machine Learning
什么情况下可以使用机器学习呢?如果问题有下面三个关键,可能可以使用机器学习。

三 Applications of Machine Learning (略看)
机器学习在我们日常生活中的衣食住行育乐都有应用。以下为几个方面的例子,了解一下就好。
衣食住行:
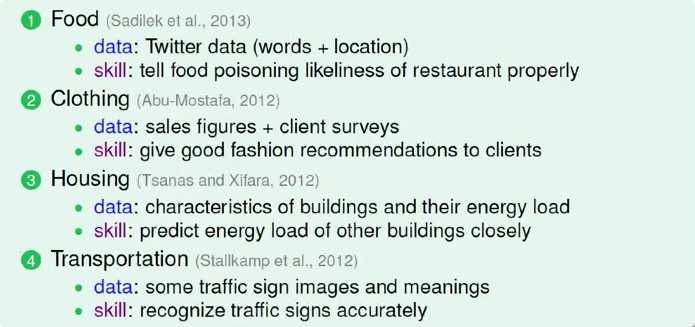
教育:
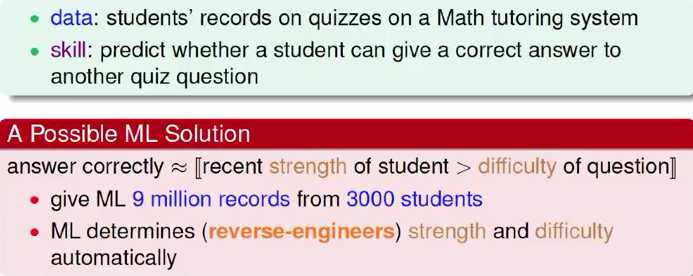
娱乐:

四 Components of Machine Learning (重点!!!)
1 Formalize of Learning Problem
·输入(Input):xX(银行掌握的用户信息)
·输出(Output):yY(是否发卡给用户)
·未知的函数,即目标函数(target function): f: X→Y(理想的信用卡发放公式)
·资料(data),即训练样本(training examples):D={(x1, y1), (x2, y2),…, (xN, yN)} (银行的历史记录)
·假说(hypothesis),即能增进表现的技能(skill): g:X→Y (学习到的公式)

2 Learning Flow
学习的简单流程:
学习的详细流程:
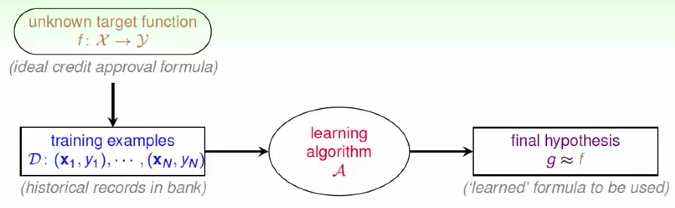
在上图中注意两点:
(1)target f unknown
(i.e. no programmable definition)
(2)hypothesis g hopefully ≈ f
but possibly different from f
(perfection ‘impossible‘ when f unknown)
3 The Learning Model
这里的流程图与2中不同。可能的假说公式有很多种,这些总合起来放到假设集合(hypothesis set,符号为H)中,有好的假设也有坏的假设。这是ML被详细的定义为机器学习算法(learning algorithm),它从看到的资料里面,去假设集合里选一个最好的出来。
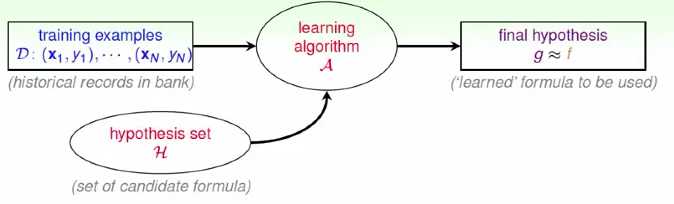
注意:
(1)assume g∈H={hk}, i.e. approving if
·h1: annual salary > NTD 800,000
·h2: debt > NTD 100,000 (really?)
·h3: year in job <= 2 (really?)
(2)hypothesis set H:
·can contain good or bad hypotheses
·up to A to pick the ‘best‘ one as g
模型:

4 Practical Definition of Machine Learning
现在可以对机器学习进行更完整的定义:

五 Machine Learning and Other Fields
1 Machine Learning and Data Mining
Machine Learning:
use data to compute hypothesis g that approximates target f
Data Mining:
use (huge) to find property that is interesting
·if ‘interesting property‘ same as ‘hypothesis that approximate target‘
--ML = DM (usually what KDDCup does)
·if ‘interesting property‘ related to ‘hypothesis that approximate target‘
-- DM can help ML, and vice versa (often, but not always)
·traditional DM also focuses on efficient computation in large database
In general, it‘s difficult to distinguish ML and DM in reality
2 Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence
Machine Learning:
use data to compute hypothesis g that approximates target f
Artificial Intelligence:
compute something that shows intelligent behavior
·g≈f is something that shows intelligent behavior
-- ML can realize AI, among other routes
·e.g. chess playing
traditional AI: game tree
ML for AI: ‘learning from board data‘
ML is one possible route to realize AI
3 Machine Learning and Statistics
Machine Learning:
use data to compute hypothesis g that approximates target f
Statistics:
use data to make inference about an unknown process
·g is an inference outcome; f is something unknown
--statistics can be used to achieve ML
·traditional statistics also focus on provable results with math assumptions,
and care less about computation
statistics: many useful tools for ML
4 Summary