tip: 1)这些属性写在子元素中,作用于子元素(父元素中应设置display:flex)
2)作用是子元素如何分配父元素的空间
3)
flex-grow 是扩展比率,当子元素宽度总和小于父元素宽度时起作用,会按比例分配父元素剩余空间(按比例自适应)
flex-shrink 是收缩比率,当子元素宽度总和大于父元素宽度时起作用,会按比例收缩空间(按比例自适应)
flex-basis 伸缩基准值,子元素本来宽度
举例:flex:1 1 300px;
<template> <div class="test"> <div class="top">头部</div> <div class="main">中间</div> <div class="bottom">底部</div> </div> </template> <style lang="scss"> .test{ display: flex; display: -webkit-flex; justify-content: center; align-items: center; border: 1px solid red; box-sizing: border-box;
overflow: hidden;
width: 100%; height: 500px; .top{ border: 1px solid blue; // 子元素可以随父元素自由伸缩 -webkit-flex: 1 1 300px; -ms-flex: 1 1 300px; flex: 1 1 300px; // width: 200px; height: 200px; } .main{ border: 1px solid green; // 子元素可以随父元素自由伸缩 flex: 1 1 300px; // width: 200px; height: 200px; } .bottom{ border: 1px solid black; // 子元素可以随父元素自由伸缩 flex: 1 1 300px; // width: 200px; height: 200px; } } </style>
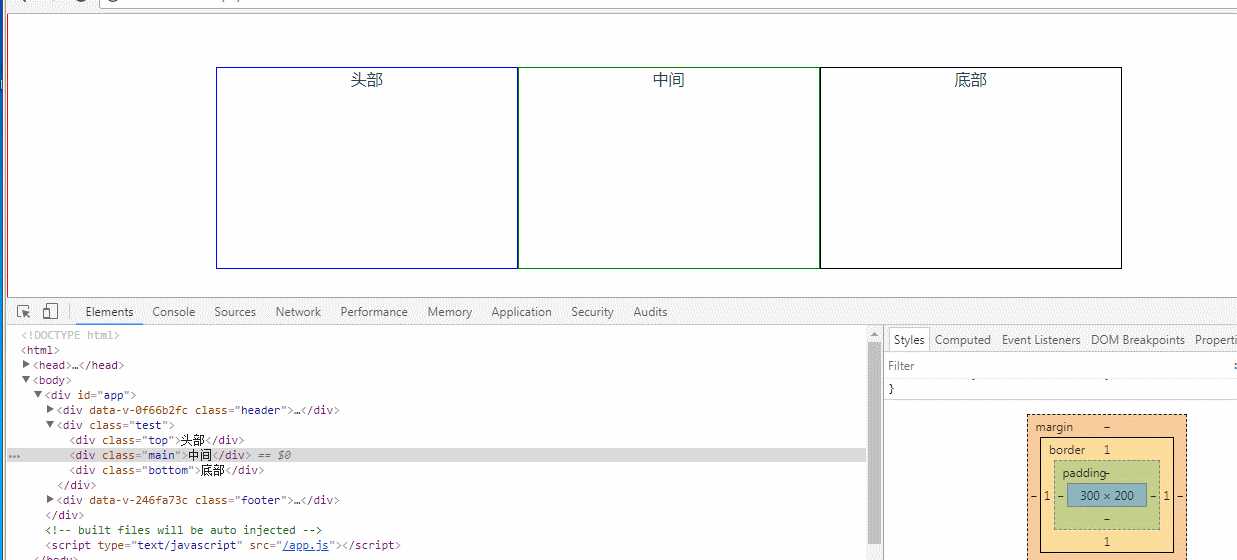
不管子元素宽度总和(300px+300px+300px)是否大于或小于父元素宽度,都会都会自适应父元素宽度

flex: 1 0 300px;扩张起作用;当父元素宽度大于900px(300px+300px+300px)时起作用,反之,不起作用
<template> <div class="test"> <div class="top">头部</div> <div class="main">中间</div> <div class="bottom">底部</div> </div> </template> <style lang="scss"> .test{ display: flex; display: -webkit-flex; justify-content: center; align-items: center; border: 1px solid red; box-sizing: border-box;
overflow: hidden;
width: 100%; height: 500px; .top{ border: 1px solid blue; -webkit-flex: 1 0 300px; -ms-flex: 1 0 300px; flex: 1 0 300px; // width: 200px; height: 200px; } .main{ border: 1px solid green; flex: 1 0 300px; // width: 200px; height: 200px; } .bottom{ border: 1px solid black; flex: 1 0 300px; // width: 200px; height: 200px; } } </style>
注意看中间框的大小变化,还有右下角样式变化当父元素小于900px时,子元素宽度一直保持300px
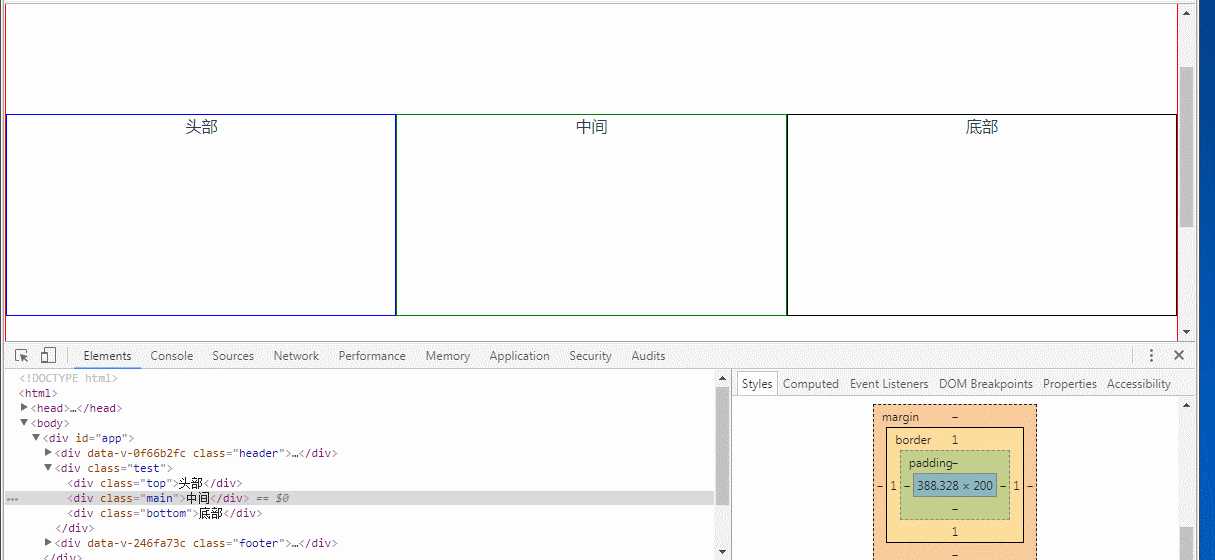
flex:0 1 300px; 收缩起作用;注意看父元素小于900px时,子元素宽度变化
<template> <div class="test"> <div class="top">头部</div> <div class="main">中间</div> <div class="bottom">底部</div> </div> </template> <style lang="scss"> .test{ display: flex; display: -webkit-flex; justify-content: center; align-items: center; border: 1px solid red; box-sizing: border-box; overflow: hidden; width: 100%; height: 500px; .top{ border: 1px solid blue; -webkit-flex: 0 1 300px; -ms-flex: 0 1 300px; flex: 0 1 300px; // width: 200px; height: 200px; } .main{ border: 1px solid green; flex: 0 1 300px; // width: 200px; height: 200px; } .bottom{ border: 1px solid black; flex: 0 1 300px; // width: 200px; height: 200px; } } </style>
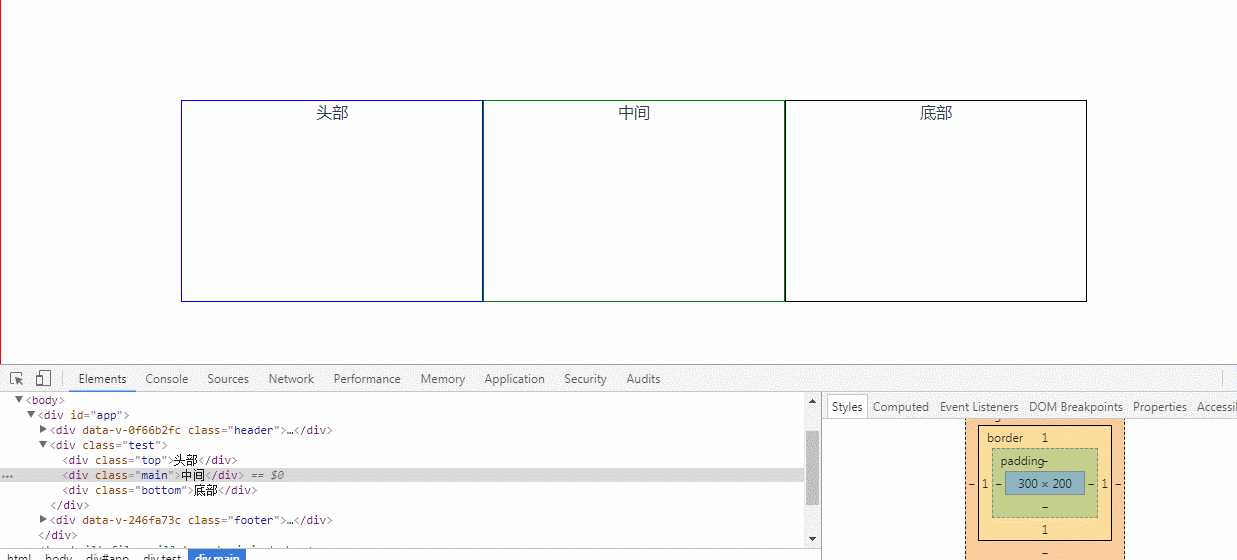
flex: 0 0 auto; width: 300px;不管子元素总和是否大于父元素,都不会随父元素大小而变化
<template> <div class="test"> <div class="top">头部</div> <div class="main">中间</div> <div class="bottom">底部</div> </div> </template> <style lang="scss"> .test{ display: flex; display: -webkit-flex; justify-content: center; align-items: center; border: 1px solid red; box-sizing: border-box; overflow: hidden; width: 100%; height: 500px; .top{ border: 1px solid blue; -webkit-flex: 0 0 auto; -ms-flex: 0 0 auto; flex: 0 0 auto; width: 300px; height: 200px; } .main{ border: 1px solid green; flex: 0 0 auto; width: 300px; height: 200px; } .bottom{ border: 1px solid black; flex: 0 0 auto; width: 300px; height: 200px; } } </style>
flex主要是父元素对子元素的布局用的,要结合display: flex; justify-content: center; align-items: center;使用。
如果对display: flex; justify-content: center; align-items: center不了解的可以查看我的另一片文章
