public String[][] build(String[][] total, int subject_num, int num_range) { // 生成算式
int[] so_count = new int[subject_num]; // 记录单运算符的下标
for (int i = 0; i < subject_num; i++) {
int operator_num = rd.nextInt(3) + 1;// 随机生成1-3个运算符个数
int flag = rd.nextInt(2); // 分数标志
先存放首个运算数,再以运算符+运算数的形式存放
*************************
int factor = rd.nextInt(num_range - 1) + 1;// 先存放首个数字字符
String str = String.valueOf(factor);
total[i][0] = str;
for (int j = 1; j < operator_num * 2; j = j + 2) {
if (operator_num == 1)
so_count[i] = i;
total[i][j] = getOperator(operator); // 再存放一组运算符加数字字符
if (flag == 1) { // 生成分数
int factor1 = rd.nextInt(num_range - 1) + 1;
int factor2 = rd.nextInt(num_range - 1) + 1;
if (factor1 > factor2) {
int temp = factor2;
factor2 = factor1;
factor1 = temp;
}
String str1 = String.valueOf(factor1);
String str2 = String.valueOf(factor2);
total[i][j + 1] = str1 + "/" + str2;
fraction_count.add(i);
} else { // 无分数
factor = rd.nextInt(num_range - 1) + 1;
str = String.valueOf(factor);
total[i][j + 1] = str;
}
}
}
********************************
生成括号
for (int i = 0; i < subject_num; i++) { // 生成括号
for (int k = 0; k < subject_num; k++) {
if (so_count[k] == i)
i++;
}
int flag_bracket = rd.nextInt(4);
if (flag_bracket == 0) {
for (int j = 9; j > 0; j--) {
total[i][j] = total[i][j - 1];
}
total[i][0] = "(";
for (int j = 9; j > 4; j--) {
total[i][j] = total[i][j - 1];
}
total[i][4] = ")";
}
if (flag_bracket == 1) {
for (int j = 9; j > 2; j--) {
total[i][j] = total[i][j - 1];
}
total[i][2] = "(";
for (int j = 9; j > 6; j--) {
total[i][j] = total[i][j - 1];
}
total[i][6] = ")";
}
}
return total;
}
*********************
2.进行分类的sort方法:
public void sort(String[][] total, int subject_num) {
把之前定义的fraction_count数组排除重复元素,生成的fraction_counts数组用于存放分式的下标
LinkedHashSet<Integer> set = new LinkedHashSet<Integer>(fraction_count);
ArrayList<Integer> fraction_counts = new ArrayList<Integer>(set); // 删除重复后的分数组,用来区分算法
********************
String[][] inter = new String[subject_num][15]; // 存放整数算式
String[][] fraction = new String[subject_num][15]; // 存放分数算式
int inter_i = 0; // 整式下标计数
int fraction_i = 0; // 分式下标计数
int flag = 0; // 判断标志
for (int i = 0; i < subject_num; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < fraction_counts.size(); j++) {
if (fraction_counts.get(j) != i)
flag++;
else
flag--;
}
如果当前下标的值与fraction_counts数组中任意匹配时,说明为分式,进行划分
if (flag == fraction_counts.size()) {
inter[inter_i] = total[i];
inter_i++;
} else {
fraction[fraction_i] = total[i];
fraction_i++;
}
flag = 0;
}
3.分数计算calculate2方法:
先计算括号的内容,把结果放入sum_count中
for (int i = 0; i < fraction.length; i++) { // 先算括号
for (int j = 0; j < 15; j++) {
if (fraction[i][j] == "(") {
if (fraction[i][j + 2] == "+")
sum_count[i] = fracAdd(compute[i][j + 1], compute[i][j + 2], compute[i][j + 3],
compute[i][j + 4]);
if (fraction[i][j + 2] == "-")
sum_count[i] = fracSub(compute[i][j + 1], compute[i][j + 2], compute[i][j + 3],
compute[i][j + 4]);
if (fraction[i][j + 2] == "x")
sum_count[i] = fracMul(compute[i][j + 1], compute[i][j + 2], compute[i][j + 3],
compute[i][j + 4]);
if (fraction[i][j + 2] == "÷")
sum_count[i] = fracDiv(compute[i][j + 1], compute[i][j + 2], compute[i][j + 3],
compute[i][j + 4]);
}
}
}
********************************
分数的加法,输入运算的分子分母,输出结果的分子和分母
// 分数相加
public static int[] fracAdd(int first_numerator, int first_denominator, int second_numrator,
int second_denominator) {
// 以下代码能够在控制台上显示结果
// 需要调用求最大公约数的函数
// 需要调用求最小公倍数的函数
int a = lcm(first_denominator, second_denominator);
int numerator, denominator;
numerator = first_numerator * (a / first_denominator) + second_numrator * (a / second_denominator);
denominator = a;
int b = gcd(numerator, denominator);
numerator = numerator / b;
denominator = denominator / b;
int[] sum = new int[2];
sum[0] = numerator;
sum[1] = denominator;
return sum;
}
*************************
六、测试运行
输入题目数与数值范围:

生成题目(有分数和整式以及混合式):

结果:
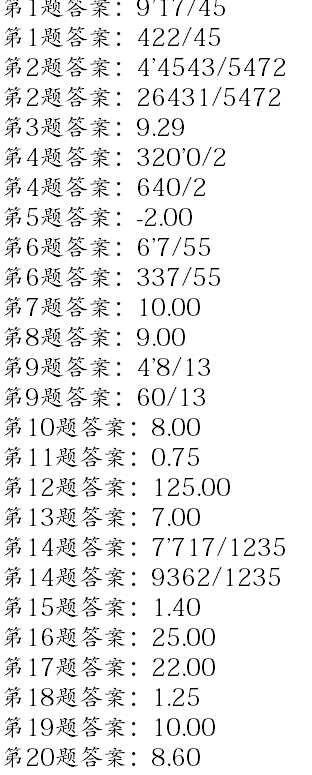
七、小结
本次四则运算的练习还是做得不够完善,运用的方法比较笨重,以后考虑二叉树的形式,目前还未完成查重、写入文件、答题与批改等功能,此系统还会继续完善下去。
通过此次作业的练习可以从前期的需求分析开始逐步对系统进行完善和改进,对于了解整个软件的体系结构和面向对象的概念有很好的帮助,需求分析是每一个软件项目都
必须完成的。所以今后在进行软件开发的时候一定要注意前期的准备和设计阶段,这些步骤不能大意和忽视。
项目链接:https://gitee.com/laoxu10086/four_operations/tree/master
