Decorator模式就是不断地为对象添加装饰的设计模式。以蛋糕为例,程序中的对象就相当于蛋糕,然后像不断地装饰蛋糕一样地不断地对其增加功能,它就变成了使用目的更加明确的对象。
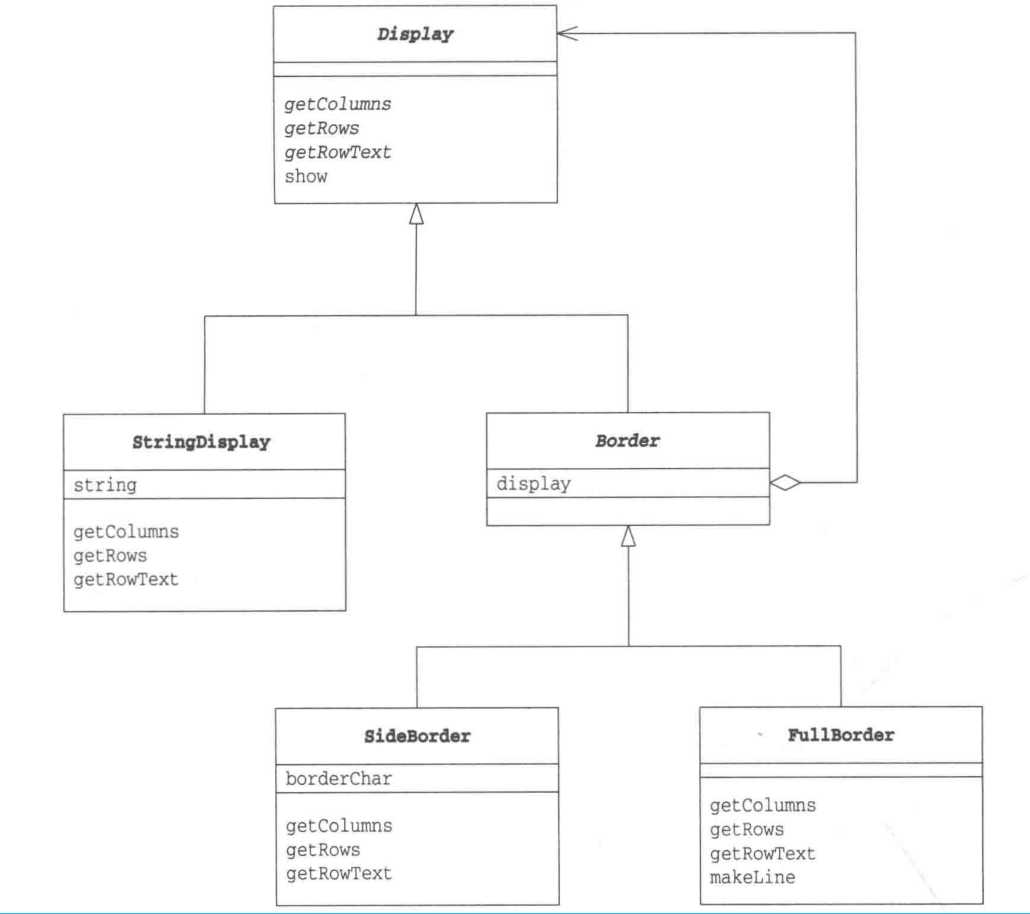
首先看示例程序的类图。
然后看示例程序代码。
1 package bigjunoba.bjtu.decorator; 2 3 public abstract class Display { 4 5 public abstract int getColumns(); 6 public abstract int getRows(); 7 public abstract String getRowText(int row); 8 public final void show() { 9 for (int i = 0; i < getRows(); i++) { 10 System.out.println(getRowText(i)); 11 } 12 } 13 }
Display类是可以显示多行字符串的抽象类。getColumns方法用来获取横向行数,getRows方法用来获取纵向行数,getRowText方法用于获取指定的某一行的字符串,show方法是用来显示所有行字符串,首先获得行数,然后循环打印每一行的字符串。
1 package bigjunoba.bjtu.decorator; 2 3 public class StringDisplay extends Display{ 4 5 private String string; 6 7 public StringDisplay(String string) { 8 this.string = string; 9 } 10 11 @Override 12 public int getColumns() { 13 return string.getBytes().length; 14 } 15 16 @Override 17 public int getRows() { 18 return 1; 19 } 20 21 @Override 22 public String getRowText(int row) { 23 if (row == 0) { 24 return string; 25 } else { 26 return null; 27 } 28 } 29 30 }
StringDisplay类用于显示单行字符串。string字段中保存的是要显示的字符串,由于StringDisplay类显示的是单行字符串,因此getColumns方法就是返回字符串的长度,而getRows方法返回的行数就是1,由于返回的是单行字符串,所以getRowText方法只有在传入的参数是0时才会返回字符串。StringDisplay类就相当于生日蛋糕中的核心蛋糕。
1 package bigjunoba.bjtu.decorator; 2 3 public abstract class Border extends Display { 4 5 protected Display display; 6 protected Border(Display display) { 7 this.display = display; 8 } 9 }
Border类继承了Display类,但它是装饰边框的抽象类。这里有一些疑惑。装饰边框与装饰物具有了相同的方法,因此也就具有了一致性。
还需要注意的是,Border类中的display字段,表示的是被装饰物,也就是说,只要是display类的子类,都可以传递进来保存在display字段中。更有趣的是,当然可以把Border类的子类传递进来,这样Border类的子类表示的装饰边框类中又有一个display字段,又可以传递进去一个边框或装饰物,反复循环。可以理解为实现了不断增加新的装饰物。
1 package bigjunoba.bjtu.decorator; 2 3 public class SideBorder extends Border { 4 5 private char borderChar; 6 7 protected SideBorder(Display display, char ch) { 8 super(display); 9 this.borderChar = ch; 10 // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub 11 } 12 13 @Override 14 public int getColumns() { 15 return 1 + display.getColumns(); 16 } 17 18 @Override 19 public int getRows() { 20 return display.getRows(); 21 } 22 23 @Override 24 public String getRowText(int row) { 25 return borderChar + display.getRowText(row) + borderChar; 26 } 27 28 }
SideBorder类可以用指定的字符来装饰字符串的左右两侧。borderChar字段用来保存指定的字符。首先通过调用父类的构造器指定display和ch。然后通过调用被装饰物display的相关方法来实现这一装饰目的。
1 package bigjunoba.bjtu.decorator; 2 3 public class FullBorder extends Border{ 4 5 protected FullBorder(Display display) { 6 super(display); 7 } 8 9 @Override 10 public int getColumns() { 11 return 1 + display.getColumns() + 1; 12 } 13 14 @Override 15 public int getRows() { 16 return 1 + display.getRows() + 1; 17 } 18 19 @Override 20 public String getRowText(int row) { 21 if (row ==0) { 22 return "[" + makeLine(‘@‘, display.getColumns()) + "]"; 23 } else if (row == display.getRows() + 1) { 24 return "[" + makeLine(‘@‘, display.getColumns()) + "]"; 25 } else { 26 return "|" + display.getRowText(row - 1) + "|"; 27 } 28 29 } 30 31 private String makeLine(char ch, int count) { 32 StringBuffer stringBuffer = new StringBuffer(); 33 for (int i = 0; i < count + 1; i++) { 34 stringBuffer.append(ch); 35 } 36 return stringBuffer.toString(); 37 } 38 39 }
FullBorder类在字符串的上下左右都加上装饰边框。这里需要理解一下这些方法。getColumns方法获得的列数,也就是字符数为被装饰物的字符数加上两侧边框字符数。getRows方法获得的行数是被装饰物的行数加上上下边框的行数
makeLine方法是连续地显示count次指定的字符ch,声明为private是因为防止被FullBorder以外的类使用。getRowText用于生成指定那一行的字符串,例如,row ==0表示下边框,row == display.getRows() + 1表示上边框。
1 package bigjunoba.bjtu.decorator; 2 3 public class Main { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 Display display1 = new StringDisplay("Lianjiang"); 7 Display display2 = new SideBorder(display1, ‘*‘); 8 Display display3 = new FullBorder(display2); 9 Display display4 = 10 new SideBorder( 11 new FullBorder( 12 new FullBorder( 13 new SideBorder( 14 new FullBorder(new StringDisplay("Lianjiang")),‘*‘ 15 ) 16 ) 17 ),‘!‘ 18 ); 19 System.out.println("这是display1的输出:"); 20 display1.show(); 21 System.out.println(); 22 23 System.out.println("这是display2的输出:"); 24 display2.show(); 25 System.out.println(); 26 27 System.out.println("这是display3的输出:"); 28 display3.show(); 29 System.out.println(); 30 31 System.out.println("这是display4的输出:"); 32 display4.show(); 33 } 34 }
这是测试类。
这是display1的输出: Lianjiang 这是display2的输出: *Lianjiang* 这是display3的输出: [@@@@@@@@@@@] |*Lianjiang*| [@@@@@@@@@@@] 这是display4的输出: ![@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@]! !|[@@@@@@@@@@@@@]|! !||*[@@@@@@@@@]*||! !||*|Lianjiang|*||! !||*[@@@@@@@@@]*||! !|[@@@@@@@@@@@@@]|! ![@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@]!
测试结果如图所示。结合测试类来分析,1的装饰边框是2,然后得到完全体后2的装饰框是3,最后4是组合装饰,也就是多重边框。
