一、运算符
1、算数运算
| 运算符 | 描述 | 实例 |
|---|---|---|
| + | 加-两个对象相加 | a+b 输出结果10 |
| - | 减-一个数减另一个数或是负数 | a-b 输出结果0 |
| * | 乘-两个数相乘或返回一个被重复若干次的字符串 | a*b 输出结果25 |
| / | 除-x除以y | x/y 输出结果 1 |
| % | 取模-返回除法的余数 | a%b 输出结果 0 |
| ** | 幂-返回x的y次幂 | a**b 输出结果 3125 |
| // | 取整除-返回商的整数部分 | 9//2 输出结果 4 9.0//2.0输出结果4.0 |
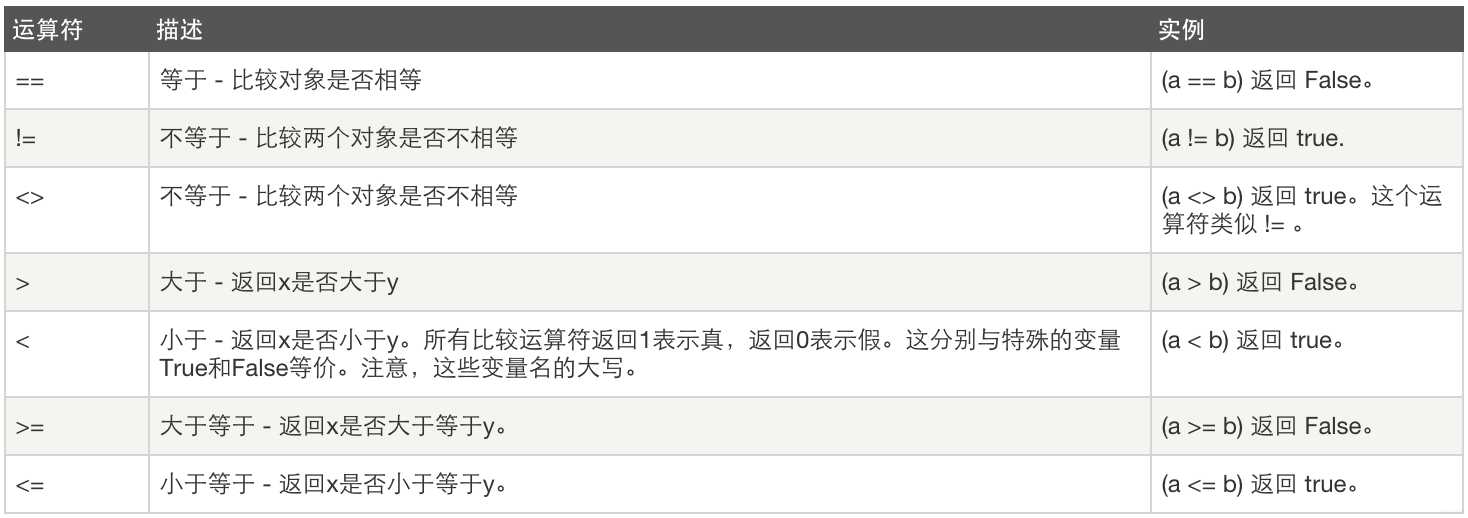
2、比较运算
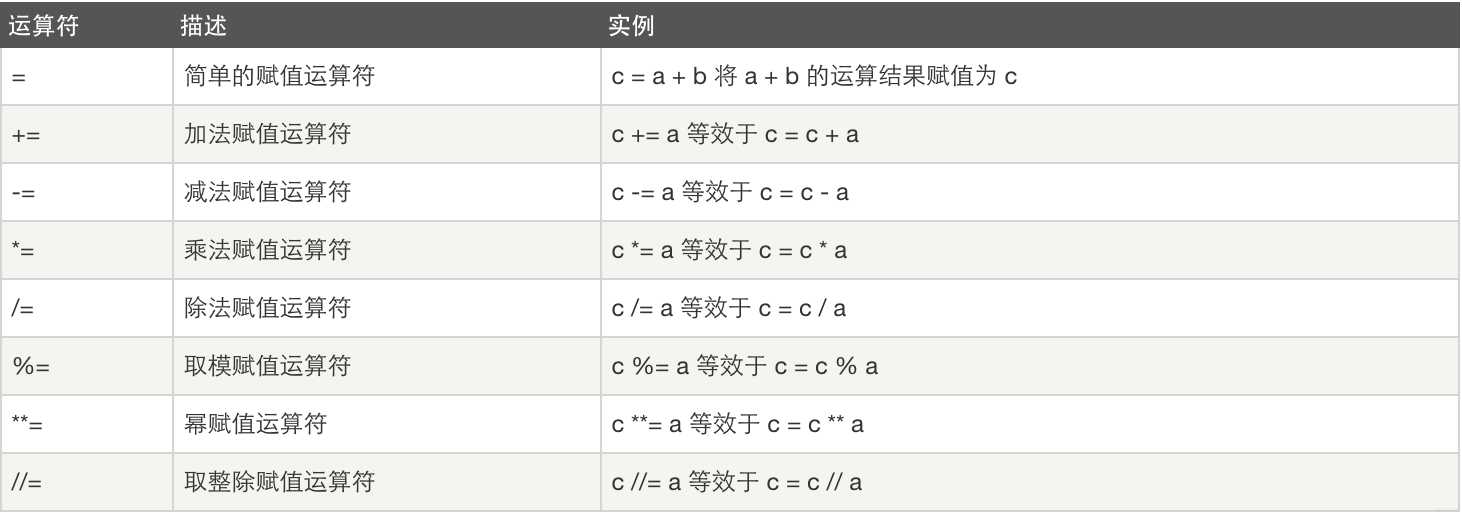
3、赋值运算
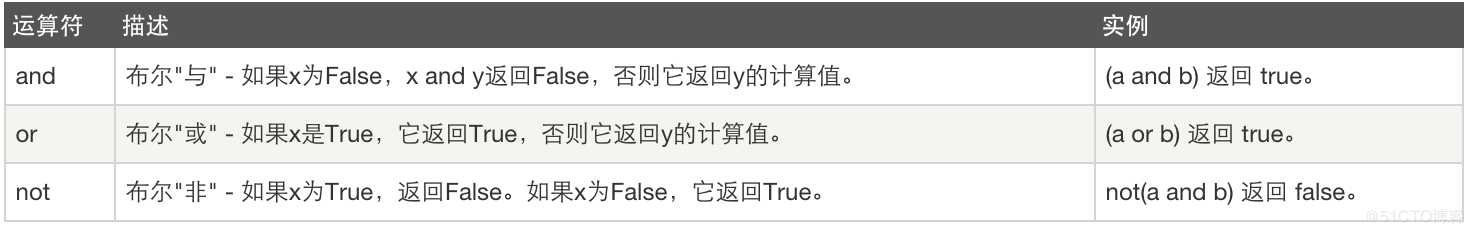
4、逻辑运算
5、成员运算
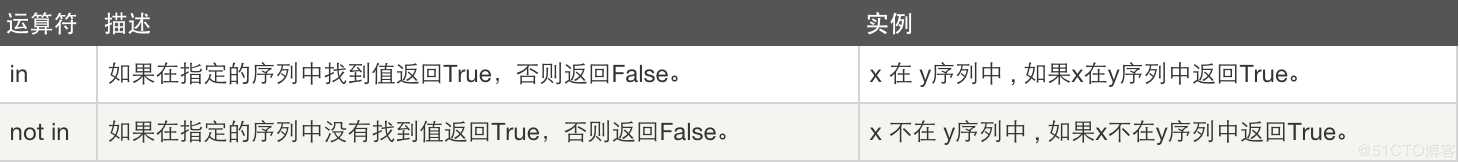
注意:注意:当有多个and or执行顺序:从前到后执行
例: user == "root" pwd == "123" v = user == "root" and pwd == "123" or 1==2 and pwd == "1234" True or ====> 直接得到结果为True True and ====> 继续向后走 False or ====> 继续向后走 False and ====> 直接得到结果为False
二、基本数据类型(1)
1、数字
python3中数字的类型都由int表示,python2中整形为int,长整型为long
(1)、转换
#int (1)将字符串转换为数字 #a = "123" #b = int(a) #print(type(b)) b的类型为数字 #print(type(a)) a的类型为字符串 #num = "c" c为16进制 #b = int(num,base=16) base=16 把num字符串以16进制转换为10进制 #print(b) #age = 10 #1 --> 01 二进制 #2 --> 10 #3 --> 11 #4 --> 100 #5 --> 101 #r = age.bit_length() #当前数字的2进制至少用几位来表示 #print(r)
2、字符串
#test = "alex" #v = test.capitalize()#首字母大写 #print(v) #test = "aLex" #v1 = test.casefold()#把大写变成小写casefold很多未知的对应关系也可以转换 #v2 = test.lower()#只能转换普通的字母 #print(v1,v2) #判断是否为小写 #test = "aLeX" #v = test.islower() 判断 #v1 = test.lower() 转换 #print(v,v1) #判断是否为大写 #v = test.isupper() 判断 #v1 = test.upper() 转换 #print(v,v1) #center #test = "alex" #def center(self(可以忽略), (设置宽度20,并将内容居中)width(必须带), (内容填充只能填一个字符)fillchar=None(带等于号的可带可不带)) #v = test.center(20,"*") #print(v) #ljust、rjust 与center做对比 #ljust将字符串放到左边右面为填充 #rjust将字符串放到右边左面为填充 #test = "alex" #v = test.ljust(20,"*") #v1 = test.rjust(20,"*") #print(v) #print(v1) #zfill 只用0填充,字符串放在右侧 #test = "alex" #v = test.zfill(20) #print(v) #count 统计这个字符或子序列出现的个数 #def count(self, sub, (从第几位开始)start=None,(到第几位结束) end=None) #test = "aLexalex" #v = test.count(‘l‘,5) #print(v) #endswith 以什么结尾 startswith 以什么什么开头 #test = "alex" #v = test.endswith(‘xle‘) #v1 = test.startswith(‘a‘) #print(v,v1) #从开始往后找,找到第一个之后获取其位置,找不到输出-1;第一位从0开始 #def find(self, sub, start=None, end=None) #test = "alexalex" #v = test.find(‘ex‘,5,7) #print(v) #index与find作对比,找到输出位置,找不到报错 #test = ‘alexalex‘ #v = test.index(‘e‘,3,7) #print(v) #format格式化,将一个字符串中的占位符替换成指定的值 #def format(self, *args, **kwargs): #test = ‘i am {name}, age {a}‘ #print(test) #v = test.format(name=‘alex‘,a=19) #print(v) #下面的用位置来替换 alex替换0的位置 19替换1的位置 #test = ‘i am {0}, age {1}‘ #print(test) #v = test.format(‘alex‘,19) #print(v) #另一类格式化传入的值( {"name":‘alex‘,"a":‘19‘} ) #test = ‘i am {name}, age {a}‘ #v = test.format_map( {"name":‘alex‘,"a":‘19‘} ) #index 找不到会报错 所以忽略这个魔法8代表取值范围8<=x #test = "alexalex" #v= test.index(‘ex‘,8) #print(v) #isalnum 判断字符串中是否只包含字母和数字 #test = "usaf890" #v = test.isalnum() #print(v) #expandtabs 断句20个一组,只要出现\t就会将前边的缺少的部分补齐,如果\t之前无字符那么\t会自己占用20个字符 #test = "username\temail\tpassword\nlaiying\t123@qq.com\t123\nlaiying\t123@qq.com\t123\nlaiying\t123@qq.com\t123" #v = test.expandtabs(20) #print(v) #是否是字母 是true 否false #test = "a2lex" #v = test.isalpha() #print(v) #isdigit 支持特殊的数字 #isdecimal 不支持特殊的数字 十进制小数 #上面两个都是判断是否是数字 #test = "②" #v1 = test.isdecimal() 只能判断数字2的类型 #v2 = test.isdigit() 可以判断特殊格式的② #v3 = test.isnumeric() 可以判断汉字二 #print(v1,v2) #大小写转换,大写变为小写,小写变为大写 #test = "aLex" #v = test.swapcase() #print(v) #是否存在不可见的不可显示的字符如**\t \n** 如果存在输出false否则为true #test = "asfuhafjfuasda" #v = test.isprintable() #print(v) #isspace 是否全部是空格 #test = " " #v = test.isspace() #print(v) #istitle 判断是否是标题;就是每个单词首字母是否大写;是输出true否则输出false #title 将字符串替换成标题的格式 #test = "Asfaf sd" #v1 = test.title() 输出Asfaf Sd #print(v1) #v = test.istitle() 输出false #print(v) #join 以前边的参数作为两个字符的链接符 将字符串中的每一个元素按照指定分隔符进行拼接 #test = "你是风儿我是沙" #print(test) #t = ‘ ‘ #v = t.join(test) #print(v) #去除左右空白 #去除\t \n #去除字符 #test = " alexalexxa " #test = " \talex " #test = " \nalex " #test1 = "alexalexxa" #v = test1.lstrip("a") 安装括号内匹配去除;将a去掉,输出lexalexxa,注意括号内会从左匹配到右,如果字符串中出现括号中没有的子集就停止。 #v = test.lstrip() 去除左 #v1 = test.rstrip() 去除右 #v2 = test.strip() 全部去除 #print(v2) #maketrans 与translate #test = "aeiou" #test1 = "45678" #m = str.maketrans("aeiou","45678") #创建对应关系 #v = "asfhjgasfauihqawjdsaaufka" #new_v = v.translate(m) #利用所创建的对应关系将aeiou替换成45678 #print(new_v) #partition、rpartition保存分割的元素、split、rsplit 不保存分割的元素 #test = ‘testadasafasfasf‘ #test.partition() 按照括号内的字符分割,找到第一个s就进行分割 从左向右;分割为三部分,只可以传递分割的参数 #v = test.partition(‘s‘) #print(v) #test.rpartition() 与partition应用相同,从右向左 #v = test.rpartition(‘s‘) #print(v) #test.split() 按照括号内的字符分割,将找到的分割符显示成逗号,后面可加参数,参数的意思为分几次,从左开始 #v = test.split(‘s‘,3) #print(v) #test.rsplit() 与split相同,从右开始 #v = test.rsplit(‘s‘,3) #print(v) #splitlines 按照换行符进行分割True 保存换行符 False不保存 #test = "asfasfaasf\nafsagsgg\nasfasfsaf" #v = test.splitlines(True) #print(v) ################7个基本方法##########################
join split strip upper lower find replace
###################################################
################高级方法##########################
# test = "alex" #[] 里面单个数字代表下表,索引 获取字符串中某一个字符 # v = test[0] # print(v) #0:1 代表范围 0<= x<1 切片 -号代表从最后开始最后一位可以为-1 # v = test[0:-2] # print(v) #python3中 len代表字符串中有几个字符 py2中一个汉字由3个字节组成 结果为9 # test = "张小华" # v = len(test) # print(v) #len 和join在其他数据类型也可用到 # test = "郑建文妹子有种冲我来" # a = 0 # while a < len(test): # v = test[a] # print(v) # a += 1 # print("end") #for循环 语法: for 变量名 in 字符串(代码块): #print(变量名) # 逐个打印 # for itm in test: # print(itm) # for循环 #len("asdadas") #索引 #切片 ####################12个数据方法##################### #后补充的方法 # replace 替换,源字符 ,新字符,替换几个(可加可不加 不加为全部替换) # test = "alexalexalex" # v = test.replace("ex","ccc",1) # print(v) # test = "郑建文妹子有种冲我来" # for item in test: # print(item) # break # for item in test: # print(item) # continue #py2 range(100)范围为0<=x<100 内存中立即创建0-99 py3中没有创建 #range 创建连续数字 也可以设置步长指定不连续 # v = range(0,100,5) # v = range(100) # for item in v: # print(item)
#test = "alex"
#v = test.capitalize()#首字母大写
#print(v)
#test = "aLex"
#v1 = test.casefold()#把大写变成小写casefold很多未知的对应关系也可以转换
#v2 = test.lower()#只能转换普通的字母
#print(v1,v2)
#判断是否为小写
#test = "aLeX"
#v = test.islower() 判断
#v1 = test.lower() 转换
#print(v,v1)
#判断是否为大写
#v = test.isupper() 判断
#v1 = test.upper() 转换
#print(v,v1)
#center
#test = "alex"
#def center(self(可以忽略), (设置宽度20,并将内容居中)width(必须带), (内容填充只能填一个字符)fillchar=None(带等于号的可带可不带))
#v = test.center(20,"*")
#print(v)
#ljust、rjust 与center做对比
#ljust将字符串放到左边右面为填充
#rjust将字符串放到右边左面为填充
#test = "alex"
#v = test.ljust(20,"*")
#v1 = test.rjust(20,"*")
#print(v)
#print(v1)
#zfill 只用0填充,字符串放在右侧
#test = "alex"
#v = test.zfill(20)
#print(v)
#count 统计这个字符或子序列出现的个数
#def count(self, sub, (从第几位开始)start=None,(到第几位结束) end=None)
#test = "aLexalex"
#v = test.count(‘l‘,5)
#print(v)
#endswith 以什么结尾 startswith 以什么什么开头
#test = "alex"
#v = test.endswith(‘xle‘)
#v1 = test.startswith(‘a‘)
#print(v,v1)
#从开始往后找,找到第一个之后获取其位置,找不到输出-1;第一位从0开始
#def find(self, sub, start=None, end=None)
#test = "alexalex"
#v = test.find(‘ex‘,5,7)
#print(v)
#index与find作对比,找到输出位置,找不到报错
#test = ‘alexalex‘
#v = test.index(‘e‘,3,7)
#print(v)
#format格式化,将一个字符串中的占位符替换成指定的值
#def format(self, *args, **kwargs):
#test = ‘i am {name}, age {a}‘
#print(test)
#v = test.format(name=‘alex‘,a=19)
#print(v)
#下面的用位置来替换 alex替换0的位置 19替换1的位置
#test = ‘i am {0}, age {1}‘
#print(test)
#v = test.format(‘alex‘,19)
#print(v)
#另一类格式化传入的值( {"name":‘alex‘,"a":‘19‘} )
#test = ‘i am {name}, age {a}‘
#v = test.format_map( {"name":‘alex‘,"a":‘19‘} )
#index 找不到会报错 所以忽略这个魔法8代表取值范围8<=x
#test = "alexalex"
#v= test.index(‘ex‘,8)
#print(v)
#isalnum 判断字符串中是否只包含字母和数字
#test = "usaf890"
#v = test.isalnum()
#print(v)
#expandtabs 断句20个一组,只要出现\t就会将前边的缺少的部分补齐,如果\t之前无字符那么\t会自己占用20个字符
#test = "username\temail\tpassword\nlaiying\t123@qq.com\t123\nlaiying\t123@qq.com\t123\nlaiying\t123@qq.com\t123"
#v = test.expandtabs(20)
#print(v)
#是否是字母 是true 否false
#test = "a2lex"
#v = test.isalpha()
#print(v)
#isdigit 支持特殊的数字
#isdecimal 不支持特殊的数字 十进制小数
#上面两个都是判断是否是数字
#test = "②"
#v1 = test.isdecimal() 只能判断数字2的类型
#v2 = test.isdigit() 可以判断特殊格式的②
#v3 = test.isnumeric() 可以判断汉字二
#print(v1,v2)
#大小写转换,大写变为小写,小写变为大写
#test = "aLex"
#v = test.swapcase()
#print(v)
#是否存在不可见的不可显示的字符如**\t \n** 如果存在输出false否则为true
#test = "asfuhafjfuasda"
#v = test.isprintable()
#print(v)
#isspace 是否全部是空格
#test = " "
#v = test.isspace()
#print(v)
#istitle 判断是否是标题;就是每个单词首字母是否大写;是输出true否则输出false
#title 将字符串替换成标题的格式
#test = "Asfaf sd"
#v1 = test.title() 输出Asfaf Sd
#print(v1)
#v = test.istitle() 输出false
#print(v)
#join 以前边的参数作为两个字符的链接符 将字符串中的每一个元素按照指定分隔符进行拼接
#test = "你是风儿我是沙"
#print(test)
#t = ‘ ‘
#v = t.join(test)
#print(v)
#去除左右空白
#去除\t \n
#去除字符
#test = " alexalexxa "
#test = " \talex "
#test = " \nalex "
#test1 = "alexalexxa"
#v = test1.lstrip("a") 安装括号内匹配去除;将a去掉,输出lexalexxa,注意括号内会从左匹配到右,如果字符串中出现括号中没有的子集就停止。
#v = test.lstrip() 去除左
#v1 = test.rstrip() 去除右
#v2 = test.strip() 全部去除
#print(v2)
#maketrans 与translate
#test = "aeiou"
#test1 = "45678"
#m = str.maketrans("aeiou","45678") #创建对应关系
#v = "asfhjgasfauihqawjdsaaufka"
#new_v = v.translate(m) #利用所创建的对应关系将aeiou替换成45678
#print(new_v)
#partition、rpartition保存分割的元素、split、rsplit 不保存分割的元素
#test = ‘testadasafasfasf‘
#test.partition() 按照括号内的字符分割,找到第一个s就进行分割 从左向右;分割为三部分,只可以传递分割的参数
#v = test.partition(‘s‘)
#print(v)
#test.rpartition() 与partition应用相同,从右向左
#v = test.rpartition(‘s‘)
#print(v)
#test.split() 按照括号内的字符分割,将找到的分割符显示成逗号,后面可加参数,参数的意思为分几次,从左开始
#v = test.split(‘s‘,3)
#print(v)
#test.rsplit() 与split相同,从右开始
#v = test.rsplit(‘s‘,3)
#print(v)
#splitlines 按照换行符进行分割True 保存换行符 False不保存
#test = "asfasfaasf\nafsagsgg\nasfasfsaf"
#v = test.splitlines(True)
#print(v)
#startswith 以什么什么开头
#endswith 以什么什么结尾
#test = "backend 1.1.1.1"
#v = test.startswith("aa")
#v = test.endswith(‘.1‘)
#print(v)