标签:范围 node opened pypy open bubuko ted == nbsp
一 shelve模块:
shelve模块比pickle模块简单,只有一个open函数,所以使用完之后要使用f.close关闭文件。返回类似字典的对象,可读可写;key必须为字符串,而值可以是python所支持的数据类型。
import shelve f=shelve.open(r‘sheve.txt‘) # f[‘stu1_info‘]={‘name‘:‘egon‘,‘age‘:18,‘hobby‘:[‘piao‘,‘smoking‘,‘drinking‘]} # f[‘stu2_info‘]={‘name‘:‘gangdan‘,‘age‘:53} # f[‘school_info‘]={‘website‘:‘http://www.pypy.org‘,‘city‘:‘beijing‘} print(f[‘stu1_info‘][‘hobby‘]) f.close() 复制代码
二 xml模块
xml是实现不同语言或程序之间进行数据交换的协议,跟json差不多,但json使用起来更简单。
xml使用〈〉来区别分数据结构:
xml协议在各个语言里的都 是支持的,在python中可以用以下模块操作xml:
# print(root.iter(‘year‘)) #搜索全部内容 # print(root.find(‘country‘)) #在root的子节点找,只找一个,也就是说找到一个country就停止。 # print(root.findall(‘country‘)) #在root的子节点找,找所有,将所有的country都找到。
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET new_xml = ET.Element("namelist") name = ET.SubElement(new_xml,"name",attrib={"enrolled":"yes"}) age = ET.SubElement(name,"age",attrib={"checked":"no"}) sex = ET.SubElement(name,"sex") sex.text = ‘33‘ name2 = ET.SubElement(new_xml,"name",attrib={"enrolled":"no"}) age = ET.SubElement(name2,"age") age.text = ‘19‘ et = ET.ElementTree(new_xml) #生成文档对象 et.write("test.xml", encoding="utf-8",xml_declaration=True) ET.dump(new_xml) #打印生成的格式
同样的xml可以对文件内容进行增,删,改,查:

import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET tree = ET.parse("xmltest.xml") root = tree.getroot() print(root.tag) #遍历xml文档 for child in root: print(‘========>‘,child.tag,child.attrib,child.attrib[‘name‘]) for i in child: print(i.tag,i.attrib,i.text) #只遍历year 节点 for node in root.iter(‘year‘): print(node.tag,node.text) #--------------------------------------- import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET tree = ET.parse("xmltest.xml") root = tree.getroot() #修改 for node in root.iter(‘year‘): new_year=int(node.text)+1 node.text=str(new_year) node.set(‘updated‘,‘yes‘) node.set(‘version‘,‘1.0‘) tree.write(‘test.xml‘) #删除node for country in root.findall(‘country‘): rank = int(country.find(‘rank‘).text) if rank > 50: root.remove(country) tree.write(‘output.xml‘) 复制代码 复制代码 #在country内添加(append)节点year2 import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET tree = ET.parse("a.xml") root=tree.getroot() for country in root.findall(‘country‘): for year in country.findall(‘year‘): if int(year.text) > 2000: year2=ET.Element(‘year2‘) year2.text=‘新年‘ year2.attrib={‘update‘:‘yes‘} country.append(year2) #往country节点下添加子节点 tree.write(‘a.xml.swap‘) 复制代码
三 re模块
re模块就是我们说的正则:
那么正则就是用使用一些具有特殊意义的符号组合起来的,用来描述字符或则字符串的方法。
其中组合起来的特殊字符就叫做正则表达式。
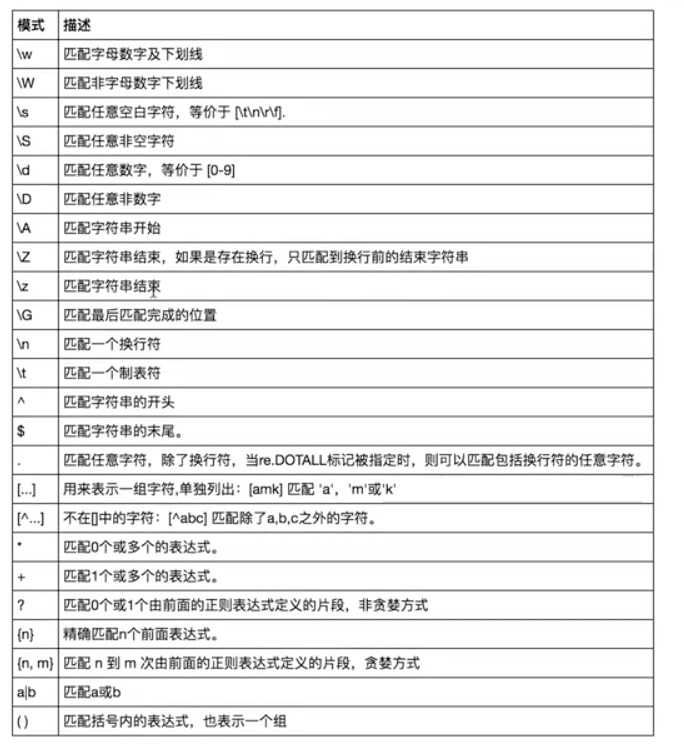
‘\w’:用来匹配字母数字以及下划线。
‘\W’:大写的W与小w是相反的,匹配非字母数字下划线。
‘\s’:匹配任意空白字符,[\t\n\r]或则一个空字符‘’
‘\S‘:匹配任意非空字符,除了空字符
‘\d‘:匹配任意数字,相当于匹配任意[0-9]的数字
‘\D‘:匹配任意非数字。
‘\n‘:匹配一个换行符
‘\t‘:匹配一个制表符
‘^‘:匹配字符串的开始字符
‘$‘:匹配字符串的结尾字符
‘.’:匹配任意字符,除了换行符,当我们在后面加上(re.Dotall时可以匹配任意字符包括换行符)
‘[...]‘:匹配一个指定范围的字符(这个字符来自于括号内),[]内只能代表一个。
‘[^...]’:对括号内的内容取反,当我们使用‘-’时,应将‘-’放左边或右边,不能放中间,放中间有其特殊意义。
‘*’:表示匹配0个或则无数个。
‘+’:表示匹配1个或者无数个
‘?’:匹配0个或者1个。
‘{m,n}’:匹配m到n个。

=================================匹配模式================================= #一对一的匹配 # ‘hello‘.replace(old,new) # ‘hello‘.find(‘pattern‘) #正则匹配 import re #\w与\W print(re.findall(‘\w‘,‘hello egon 123‘)) #[‘h‘, ‘e‘, ‘l‘, ‘l‘, ‘o‘, ‘e‘, ‘g‘, ‘o‘, ‘n‘, ‘1‘, ‘2‘, ‘3‘] print(re.findall(‘\W‘,‘hello egon 123‘)) #[‘ ‘, ‘ ‘] #\s与\S print(re.findall(‘\s‘,‘hello egon 123‘)) #[‘ ‘, ‘ ‘, ‘ ‘, ‘ ‘] print(re.findall(‘\S‘,‘hello egon 123‘)) #[‘h‘, ‘e‘, ‘l‘, ‘l‘, ‘o‘, ‘e‘, ‘g‘, ‘o‘, ‘n‘, ‘1‘, ‘2‘, ‘3‘] #\n \t都是空,都可以被\s匹配 print(re.findall(‘\s‘,‘hello \n egon \t 123‘)) #[‘ ‘, ‘\n‘, ‘ ‘, ‘ ‘, ‘\t‘, ‘ ‘] #\n与\t print(re.findall(r‘\n‘,‘hello egon \n123‘)) #[‘\n‘] print(re.findall(r‘\t‘,‘hello egon\t123‘)) #[‘\n‘] #\d与\D print(re.findall(‘\d‘,‘hello egon 123‘)) #[‘1‘, ‘2‘, ‘3‘] print(re.findall(‘\D‘,‘hello egon 123‘)) #[‘h‘, ‘e‘, ‘l‘, ‘l‘, ‘o‘, ‘ ‘, ‘e‘, ‘g‘, ‘o‘, ‘n‘, ‘ ‘] #\A与\Z print(re.findall(‘\Ahe‘,‘hello egon 123‘)) #[‘he‘],\A==>^ print(re.findall(‘123\Z‘,‘hello egon 123‘)) #[‘he‘],\Z==>$ #^与$ print(re.findall(‘^h‘,‘hello egon 123‘)) #[‘h‘] print(re.findall(‘3$‘,‘hello egon 123‘)) #[‘3‘] # 重复匹配:| . | * | ? | .* | .*? | + | {n,m} | #. print(re.findall(‘a.b‘,‘a1b‘)) #[‘a1b‘] print(re.findall(‘a.b‘,‘a1b a*b a b aaab‘)) #[‘a1b‘, ‘a*b‘, ‘a b‘, ‘aab‘] print(re.findall(‘a.b‘,‘a\nb‘)) #[] print(re.findall(‘a.b‘,‘a\nb‘,re.S)) #[‘a\nb‘] print(re.findall(‘a.b‘,‘a\nb‘,re.DOTALL)) #[‘a\nb‘]同上一条意思一样 #* print(re.findall(‘ab*‘,‘bbbbbbb‘)) #[] print(re.findall(‘ab*‘,‘a‘)) #[‘a‘] print(re.findall(‘ab*‘,‘abbbb‘)) #[‘abbbb‘] #? print(re.findall(‘ab?‘,‘a‘)) #[‘a‘] print(re.findall(‘ab?‘,‘abbb‘)) #[‘ab‘] #匹配所有包含小数在内的数字 print(re.findall(‘\d+\.?\d*‘,"asdfasdf123as1.13dfa12adsf1asdf3")) #[‘123‘, ‘1.13‘, ‘12‘, ‘1‘, ‘3‘] #.*默认为贪婪匹配 print(re.findall(‘a.*b‘,‘a1b22222222b‘)) #[‘a1b22222222b‘] #.*?为非贪婪匹配:推荐使用 print(re.findall(‘a.*?b‘,‘a1b22222222b‘)) #[‘a1b‘] #+ print(re.findall(‘ab+‘,‘a‘)) #[] print(re.findall(‘ab+‘,‘abbb‘)) #[‘abbb‘] #{n,m} print(re.findall(‘ab{2}‘,‘abbb‘)) #[‘abb‘] print(re.findall(‘ab{2,4}‘,‘abbb‘)) #[‘abb‘] print(re.findall(‘ab{1,}‘,‘abbb‘)) #‘ab{1,}‘ ===> ‘ab+‘ print(re.findall(‘ab{0,}‘,‘abbb‘)) #‘ab{0,}‘ ===> ‘ab*‘ #[] print(re.findall(‘a[1*-]b‘,‘a1b a*b a-b‘)) #[]内的都为普通字符了,且如果-没有被转意的话,应该放到[]的开头或结尾 print(re.findall(‘a[^1*-]b‘,‘a1b a*b a-b a=b‘)) #[]内的^代表的意思是取反,所以结果为[‘a=b‘] print(re.findall(‘a[0-9]b‘,‘a1b a*b a-b a=b‘)) #[]内的^代表的意思是取反,所以结果为[‘a=b‘] print(re.findall(‘a[a-z]b‘,‘a1b a*b a-b a=b aeb‘)) #[]内的^代表的意思是取反,所以结果为[‘a=b‘] print(re.findall(‘a[a-zA-Z]b‘,‘a1b a*b a-b a=b aeb aEb‘)) #[]内的^代表的意思是取反,所以结果为[‘a=b‘] #\# print(re.findall(‘a\\c‘,‘a\c‘)) #对于正则来说a\\c确实可以匹配到a\c,但是在python解释器读取a\\c时,会发生转义,然后交给re去执行,所以抛出异常 print(re.findall(r‘a\\c‘,‘a\c‘)) #r代表告诉解释器使用rawstring,即原生字符串,把我们正则内的所有符号都当普通字符处理,不要转义 print(re.findall(‘a\\\\c‘,‘a\c‘)) #同上面的意思一样,和上面的结果一样都是[‘a\\c‘] #():分组 print(re.findall(‘ab+‘,‘ababab123‘)) #[‘ab‘, ‘ab‘, ‘ab‘] print(re.findall(‘(ab)+123‘,‘ababab123‘)) #[‘ab‘],匹配到末尾的ab123中的ab print(re.findall(‘(?:ab)+123‘,‘ababab123‘)) #findall的结果不是匹配的全部内容,而是组内的内容,?:可以让结果为匹配的全部内容 print(re.findall(‘href="(.*?)"‘,‘<a href="http://www.baidu.com">点击</a>‘))#[‘http://www.baidu.com‘] print(re.findall(‘href="(?:.*?)"‘,‘<a href="http://www.baidu.com">点击</a>‘))#[‘href="http://www.baidu.com"‘] #| print(re.findall(‘compan(?:y|ies)‘,‘Too many companies have gone bankrupt, and the next one is my company‘)) 复制代码
标签:范围 node opened pypy open bubuko ted == nbsp
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/zhangsanfeng/p/8761365.html