标签:linux
十五周五次课18.6 负载均衡集群介绍
18.7 LVS介绍
18.8 LVS调度算法
18.9/18.10 LVS NAT模式搭建
18.6 负载均衡集群介绍
主流开源软件LVS、keepalived、haproxy、nginx等
其中LVS属于4层(网络OSI 7层模型),nginx属于7层,haproxy既可以认为是4层,也可以当做7层使用
keepalived的负载均衡功能其实就是lvs,lvs是keepalived内置的
lvs这种4层的负载均衡是可以分发TCP协议,web服务是80端口,除了分发80端口,还有其他的端口通信的,比如MySQL的负载均衡,就可以用LVS实现,而nginx仅仅支持http,https,mail,haproxy;haproxy也支持MySQL这种TCP负载均衡的
7层有限制,不过有些更高级的功能,nginx可以通过站点目录,去区分网站服务器之前,LVS4层的就不支持
相比较来说,LVS这种4层的更稳定,能承受更多的请求,承载的并发量更高,而nginx这种7层的更加灵活,能实现更多的个性化需求
18.7 LVS介绍
LVS是由国人章文嵩开发
流行度不亚于apache的httpd,基于TCP/IP做的路由和转发,稳定性和效率很高
LVS最新版本基于Linux内核2.6,有好多年不更新了
LVS有三种常见的模式:NAT、DR、IP Tunnel
LVS架构中有一个核心角色叫做分发器(Load balance),它用来分发用户的请求,还有诸多处理用户请求的服务器(Real Server,简称rs)
LVS NAT模式,借助iptables的nat表来实现
用户的请求到分发器后,通过预设的iptables规则,把请求的数据包转发到后端的rs上去
rs需要设定网关为分发器的内网ip
用户请求的数据包和返回给用户的数据包全部经过分发器,所以分发器成为瓶颈
在nat模式中,只需要分发器有公网ip即可,所以比较节省公网ip资源
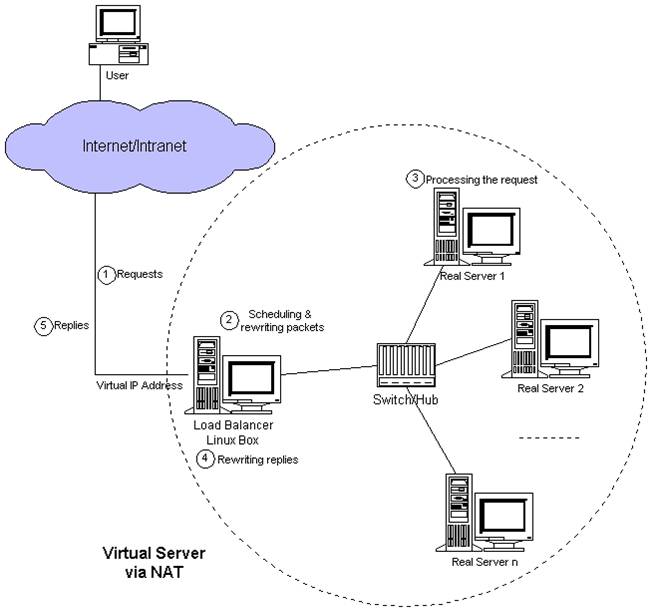
原理图解释:
Load Balancer,就是一个分发器;把用户的请求,分发给后端的Real Server ,Real Server这些服务器接收到请求以后,处理好用户请求以后,就重新丢回给Load Balancer;最后Load Balancer再返回给用户;
这个模式的弊端,当访问量、请求量、反馈量大的时候,Load Balancer的压力很大
LVS规模,一般规模最多支持10来台服务器,超过10台的话就会有力不从心;
nat模式这个结构,只需要有一个公网IP,其他real server服务器全部在内网就可以实现。优点,节省很多的资源
LVS IP Tunnel模式,需要有一个公共的IP配置在分发器和所有rs上,我们把它叫做vip
客户端请求的目标IP为vip,分发器接收到请求数据包后,会对数据包做一个加工,会把目标IP改为rs的IP,这样数据包就到了rs上
rs接收数据包后,会还原原始数据包,这样目标IP为vip,因为所有rs上配置了这个vip,所以它会认为是它自己
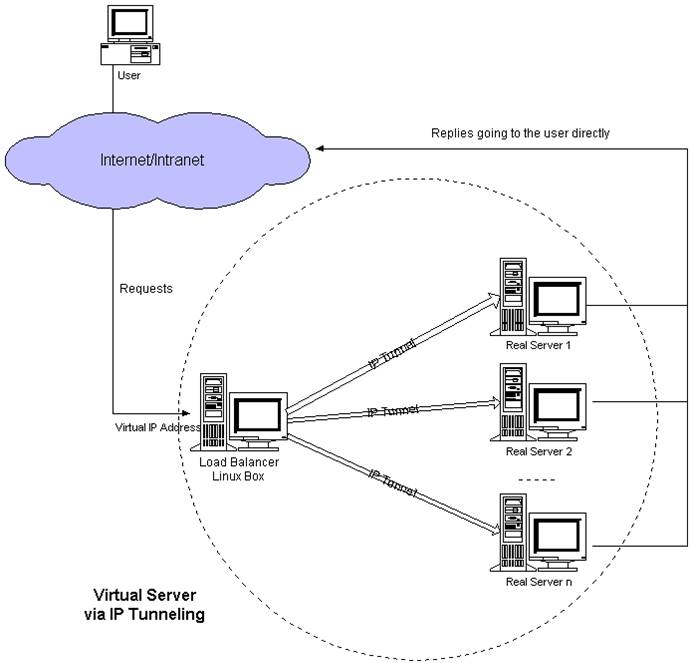
原理图解释:
在load balancer与real server之间建立了虚拟通道,叫做 ip tunnel ;实际上是更改了数据包目的IP;请求过来通过load balancer,通过在real server上配置的VIP;用户请求的时候,数据包里面包好的目的IP,当数据包到达load balancer的时候,load balancer会进行一个数据包目的IP的更改,然后发送到具体的real server上,通过lvs的自己的算法,进行实现到底传输到哪个real server上;然后real server再解包处理,再通过一个VIP直接返回到用户,这就省略数据回到load balancer分发器的过程,这样就load balancer就没有瓶颈
LVS DR模式,也需要有一个公共的IP配置在分发器和所有rs上,也就是vip
和IP Tunnel不同的是,它会把数据包的MAC地址修改为rs的MAC地址
rs接收数据包后,会还原原始数据包,这样目标IP为vip,因为所有rs上配置了这个vip,所以它会认为是它自己
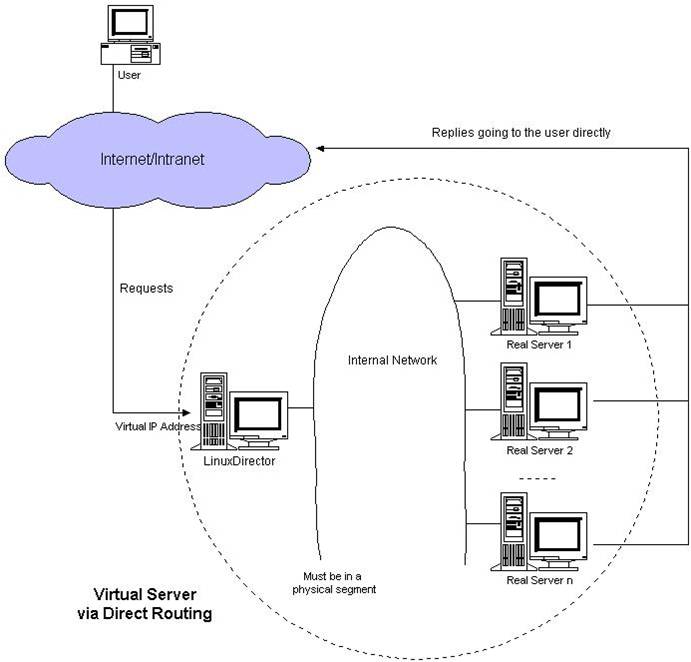
18.8 LVS调度算法
轮询 Round-Robin 简称:rr 最简单的也是最容易理解
用户请求过来,均衡的分发到rs上
加权轮询 Weight Round-Robin 简称:wrr
带权重的轮询,可以对机器单独设置权重,对高权重的机器发送的请求会多一些
最小连接 Least-Connection 简称: lc
把请求发送到请求数量小的rs上
加权最小连接 Weight Least-Connection 简称: wlc
对请求数量小的rs,加上一个权重,使他优先
基于局部性的最小连接 Locality-Based Least Connections 简称: lblc
带复制的基于局部性最小连接 Locality-Based Least Connections with Replication 简称: lblcr
目标地址散列调度 Destination Hashing 简称:dh
源地址散列调度 Source Hashing 简称: sh
18.9/18.10 LVS NAT模式搭建
LVS NAT模式搭建
NAT模式搭建 – 准备工作
内网:133.133,设置网关为133.130
内网:133.132,设置网关为133.130
内网:133.130,外网:147.144(vmware仅主机模式)
三台机器
分发器,也叫调度器(简写为dir)
rs1
rs2
三台机器上都执行执行
systemctl stop firewalld; systemc disable firewalld
systemctl start iptables-services; iptables -F; service iptables save
NAT模式搭建
在dir上安装ipvsadm
yum install -y ipvsdam
在dir上编写脚本,vim /usr/local/sbin/lvs_nat.sh//内容如下
#! /bin/bash # director 服务器上开启路由转发功能 echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward # 关闭icmp的重定向 echo 0 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/conf/all/send_redirectsecho 0 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/conf/default/send_redirects # 注意区分网卡名字,阿铭的两个网卡分别为ens33和ens37 echo 0 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/conf/ens33/send_redirects echo 0 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/conf/ens37/send_redirects # director 设置nat防火墙 iptables -t nat -F iptables -t nat -X iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -s 192.168.133.0/24 -j MASQUERADE # director设置ipvsadm IPVSADM='/usr/sbin/ipvsadm' $IPVSADM -C$IPVSADM -A -t 192.168.147.144:80 -s wlc -p 3 $IPVSADM -a -t 192.168.147.144:80 -r 192.168.133.132:80 -m -w 1 $IPVSADM -a -t 192.168.147.144:80 -r 192.168.133.133:80 -m -w 1
NAT模式效果测试
两台rs上都安装nginx
设置两台rs的主页,做一个区分,也就是说直接curl两台rs的ip时,得到不同的结果
浏览器里访问192.168.142.147,多访问几次看结果差异
NAT模式是通过iptables实现的,所以必须配置一些iptables规则
1.在配置前准备三台机器,一台作为分发器,也叫做调度器,简称 dir,另外两台就是real server,用来处理用户请求的服务器,rs1、rs2(克隆虚拟机步骤)克隆或者重新装一台机器都可以
A机器IP为192.168.23.130、B机器IP为192.168.23.129,网关为23.130;C机器IP为192.168.23.128,网关为23.130
A机器增加一块网卡,并启动查看网段为192.168.38.0(根据自己机器来设置),设置新的网卡IP为192.168.38.147,并在物理机访问这个IP地址,看是否正常通信
增加新的网卡需要更改IP,然后重启网卡,并重启网络服务。增加网卡注意点
[root@tianqi-01 ~]# cd /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/
[root@tianqi-01 network-scripts]# ls
ifcfg-ens33 ifdown-bnep ifdown-isdn ifdown-sit ifup ifup-ippp ifup-plusb ifup-sit ifup-wireless
ifcfg-ens33:0 ifdown-eth ifdown-post ifdown-Team ifup-aliases ifup-ipv6 ifup-post ifup-Team init.ipv6-global
ifcfg-lo ifdown-ippp ifdown-ppp ifdown-TeamPort ifup-bnep ifup-isdn ifup-ppp ifup-TeamPort network-functions
ifdown ifdown-ipv6 ifdown-routes ifdown-tunnel ifup-eth ifup-plip ifup-routes ifup-tunnel network-functions-ipv6
[root@tianqi-01 network-scripts]# cp ifcfg-ens33 ifcfg-ens37
[root@tianqi-01 network-scripts]# ls
ifcfg-ens33 ifdown-bnep ifdown-post ifdown-TeamPort ifup-eth ifup-plusb ifup-Team network-functions
ifcfg-ens33:0 ifdown-eth ifdown-ppp ifdown-tunnel ifup-ippp ifup-post ifup-TeamPort network-functions-ipv6
ifcfg-ens37 ifdown-ippp ifdown-routes ifup ifup-ipv6 ifup-ppp ifup-tunnel
ifcfg-lo ifdown-ipv6 ifdown-sit ifup-aliases ifup-isdn ifup-routes ifup-wireless
ifdown ifdown-isdn ifdown-Team ifup-bnep ifup-plip ifup-sit init.ipv6-global
[root@tianqi-01 network-scripts]# vim ifcfg-ens37
TYPE=Ethernet
PROXY_METHOD=none
BROWSER_ONLY=no
BOOTPROTO=static
DEFROUTE=yes
IPV4_FAILURE_FATAL=no
IPV6INIT=yes
IPV6_AUTOCONF=yes
IPV6_DEFROUTE=yes
IPV6_FAILURE_FATAL=no
IPV6_ADDR_GEN_MODE=stable-privacy
NAME=ens37
#UUID=bd1e1864-e75b-4f5f-bc63-9b1b0d64feff
DEVICE=ens37
ONBOOT=yes
IPADDR=192.168.38.147
#NETMASK=255.255.255.0
#GATEWAY=192.168.23.2
#DNS1=119.29.29.29
保存退出
重启ens37网卡
[root@tianqi-01 network-scripts]# ifdown ens37 && ifup ens37
Device 'ens37' successfully disconnected.
Connection successfully activated (D-Bus active path: /org/freedesktop/NetworkManager/ActiveConnection/3)
[root@tianqi-01 network-scripts]# ifconfig
ens33: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
inet 192.168.23.130 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.23.255
inet6 fe80::1eb9:8f9e:264a:7159 prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20<link>
ether 00:0c:29:25:28:af txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet)
RX packets 584 bytes 48043 (46.9 KiB)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 334 bytes 59127 (57.7 KiB)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
ens33:0: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
inet 192.168.11.139 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.11.255
ether 00:0c:29:25:28:af txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet)
ens37: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
inet 192.168.38.147 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.38.255
inet6 fe80::8926:30a4:c44a:4412 prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20<link>
ether 00:0c:29:25:28:b9 txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet)
RX packets 4 bytes 618 (618.0 B)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 25 bytes 2338 (2.2 KiB)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
lo: flags=73<UP,LOOPBACK,RUNNING> mtu 65536
inet 127.0.0.1 netmask 255.0.0.0
inet6 ::1 prefixlen 128 scopeid 0x10<host>
loop txqueuelen 1 (Local Loopback)
RX packets 2 bytes 196 (196.0 B)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 2 bytes 196 (196.0 B)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
[root@tianqi-01 network-scripts]#
PS:网关最后设置,否则包无法下载

B机器和C机器的网关必须设置成分发器(即A机器)的内网IP,若不设置成它的网关,是没法通信的
这时B、C机器就无法上网了
2.三台机器设置完成后,关闭三台机器的防火墙
关闭firewalld服务
systemctl stop firewalld
使firewalld服务不再开机启动
systemctl disable firewalld
3.机器B、机器C 下载安装iptables-services 包
[root@tianqi-02 ~]# yum install -y iptables-services
[root@localhost ~]# yum install -y iptables-services
有时下载包的时候特别慢,就是epel.repo源的原因导致的,这里可以临时关闭,就是直接更改名字即可(因为epel.repo源是国外的资源,所以很慢)
4.机器B、机器C 启动iptables服务
systemctl start iptables
机器B
[root@tianqi-02 ~]# systemctl start iptables
[root@tianqi-02 ~]#
机器C
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl start iptables
[root@localhost ~]#
5.机器B、机器C 设置开机启动
systemctl enable iptables
systemctl enable iptables
iptables -F
service iptables save
机器B
[root@tianqi-02 ~]# systemctl start iptables
[root@tianqi-02 ~]# systemctl enable iptables
Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/basic.target.wants/iptables.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/iptables.service.
[root@tianqi-02 ~]# iptables -nvL
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
72 5204 ACCEPT all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 state RELATED,ESTABLISHED
0 0 ACCEPT icmp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
0 0 ACCEPT all -- lo * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
0 0 ACCEPT tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 state NEW tcp dpt:22
0 0 REJECT all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 reject-with icmp-host-prohibited
Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
0 0 REJECT all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 reject-with icmp-host-prohibited
Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 49 packets, 4508 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
[root@tianqi-02 ~]# iptables -F //清空表的规则,以便后续实验
[root@tianqi-02 ~]# service iptables save
iptables: Saving firewall rules to /etc/sysconfig/iptables:[ OK ]
[root@tianqi-02 ~]#
机器C同上
6.清空并查看机器A的规则
[root@tianqi-01 network-scripts]# iptables -nvL
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 63 packets, 4614 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 40 packets, 3560 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
[root@tianqi-01 network-scripts]#
7.关闭机器机器A,机器B,机器C,三台机器的selinux
setenforce 0 //临时关闭selinux
getenforce //查看selinux是否关闭
为了保险起见,在配置文件中永久关闭selinux
vi /etc/selinux/config
SELINUX=enforcing更改为SELINUX=disabled
NAT模式搭建
1.首先在分发器dir上(即A机器),安装ipvsadm ,这个是实现 lvs 的一个重要的工具,缺少这个工具,将没有办法实现 lvs 的功能
[root@tianqi-01 ~]# yum install -y ipvsadm
2.在分发器(A机器)上编写一个脚本(LVS全都是以脚本的方式去执行的,这样比较方便进行维护不用一条命令一条命令的进行操作)
[root@tianqi-01 ~]# vim /usr/local/sbin/lvs_nat.sh
#! /bin/bash
# director 服务器上开启路由转发功能
echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward //对内核参数修改,打开路由转发
# 关闭icmp的重定向
echo 0 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/conf/all/send_redirects //伪装操作,不然不能转发rs的数据
echo 0 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/conf/default/send_redirects //伪装操作,不然不能转发rs的数据
# 注意区分网卡名字,阿铭的两个网卡分别为ens33和ens37
echo 0 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/conf/ens33/send_redirects
echo 0 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/conf/ens37/send_redirects
# director 设置nat防火墙
iptables -t nat -F
iptables -t nat -X
iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -s 192.168.23.0/24 -j MASQUERADE //MASQUERADE实现同网段的机器去上网,路由器使用的就是这个功能
# director设置ipvsadm
IPVSADM='/usr/sbin/ipvsadm' //设置一个变量,方便下面命令引用
$IPVSADM -C //清空规则
$IPVSADM -A -t 192.168.38.147:80 -s rr //用来定义lvs 的模式;wlc为算法,可以按需求选择 lvs 里面适合的算法
$IPVSADM -a -t 192.168.38.147:80 -r 192.168.23.128:80 -m -w 1 //小规则,-r 指定dir机器IP,-m 指定nat模式,-w指定rs权重
$IPVSADM -a -t 192.168.38.147:80 -r 192.168.23.129:80 -m -w 1 //小规则,-r 指定dir机器IP,-m 指定nat模式,-w指定rs权重
保存退出
IPVSADM -A -t 192.168.38.147:80 -s lc -p 3 : -A增加一个规则,-t 制定lvs 模式,之后IP 就是dir的IP,-s 指定算法;-p 指定超时时间(数据包转发超时时间)
超时时间解释:
用户1访问的是a机器,-p 的意思就是在同一个时间,一直在同一台机器上进行请求
3.执行脚本,若是没输出,表示脚本没有错误
[root@tianqi-01 ~]# sh /usr/local/sbin/lvs_nat.sh
[root@tianqi-01 ~]#
NAT模式效果测试
两台rs上都安装nginx
设置两台rs的主页,做一个区分,也就是说直接curl两台rs的ip时,得到不同的结果
浏览器里访问192.168.142.147,多访问几次看结果差异
1.首先查看B机器和C机器上的nginx服务是否开启
B机器
[root@tianqi-02 ~]# ps aux |grep nginx
root 1318 0.0 0.0 112660 976 pts/0 S+ 01:13 0:00 grep --color=auto nginx
[root@tianqi-02 ~]# systemctl start nginx
[root@tianqi-02 ~]# ps aux |grep nginx
root 1334 0.0 0.1 122908 2104 ? Ss 01:14 0:00 nginx: master process /usr/sbin/nginx
nginx 1335 0.0 0.1 123292 3136 ? S 01:14 0:00 nginx: worker process
nginx 1336 0.0 0.1 123292 3136 ? S 01:14 0:00 nginx: worker process
root 1338 0.0 0.0 112660 976 pts/0 S+ 01:14 0:00 grep --color=auto nginx
[root@tianqi-02 ~]#
C机器
[root@localhost ~]# ps aux |grep nginx
root 2154 0.0 0.0 112644 952 pts/0 R+ 17:05 0:00 grep --color=auto nginx
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl start nginx
[root@localhost ~]# ps aux |grep nginx
root 2167 0.0 0.2 122864 2104 ? Ss 17:06 0:00 nginx: master process /usr/sbin/nginx
nginx 2168 0.0 0.3 123248 3120 ? S 17:06 0:00 nginx: worker process
root 2170 0.0 0.0 112644 948 pts/0 R+ 17:06 0:00 grep --color=auto nginx
[root@localhost ~]#
2设置两台rs的主页,做一个区分,也就是说直接curl两台rs的ip时,得到不同的结果
编辑B机器的索引页
[root@localhost ~]# curl localhost
backup backup.
[root@localhost ~]# vim /usr/share/nginx/html/index.html
aming02.
保存退出
[root@localhost ~]# curl localhost
aming02.
[root@localhost ~]#
编辑C机器的索引页
[root@tianqi-02 ~]# vim /usr/share/nginx/html/index.html
aming03.
保存退出
[root@tianqi-02 ~]# curl localhost
aming03.
[root@tianqi-02 ~]#
3.这时浏览器访问模拟的公网IP,即192.168.204.1,若是浏览器访问不成功,可用curl测试
[root@tianqi-01 ~]# curl 192.168.38.147
aming02.
[root@tianqi-01 ~]# curl 192.168.38.147
aming02.
4.查看A机器上的nat规则
[root@tianqi-01 ~]# iptables -t nat -nvL
Chain PREROUTING (policy ACCEPT 29 packets, 1560 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 2 packets, 156 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 4 packets, 240 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
Chain POSTROUTING (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
0 0 MASQUERADE all -- * * 192.168.23.0/24 0.0.0.0/0
[root@tianqi-01 ~]#
5.查看 ipvsadm 规则
[root@tianqi-01 ~]# ipvsadm -ln
IP Virtual Server version 1.2.1 (size=4096)
Prot LocalAddress:Port Scheduler Flags
-> RemoteAddress:Port Forward Weight ActiveConn InActConn
TCP 192.168.38.147:80 lc persistent 3
-> 192.168.23.128:80 Masq 1 0 0
-> 192.168.23.129:80 Masq 1 0 0
[root@tianqi-01 ~]#
友情链接:http://www.apelearn.com阿铭linux
标签:linux
原文地址:http://blog.51cto.com/13184900/2097200