标签:not syn mod 头部 font execution blog 生成 img
FutureTask是J.U.C中的类,是一个可删除的异步计算类。这个类提供了Future接口的的基本实现,使用相关方法启动和取消计算,查询计算是否完成,并检索计算结果。只有在计算完成时才能使用get方法检索结果;如果计算尚未完成,get方法将会阻塞。一旦计算完成,计算就不能重新启动或取消(除非使用runAndReset方法调用计算)。
通常实现一个线程我们会使用继承Thread的方式或者实现Runnable接口,这两种方式有一个共同的缺陷就是在执行完任务之后无法获取执行结果。从Java1.5之后就提供了Callable与Future,这两个接口就可以实现获取任务执行结果。
public interface RunnableFuture<V> extends Runnable, Future<V> { void run(); }
public interface Callable<V> { V call() throws Exception; }
Future接口提供了一系列方法用于控制线程执行计算,如下:
public interface Future<V> { boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning);//取消任务 boolean isCancelled();//是否被取消 boolean isDone();//计算是否完成 V get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException;//获取计算结果,在执行过程中任务被阻塞 V get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)//timeout等待时间、unit时间单位 throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException; }
使用方法:
public class FutureExample { static class MyCallable implements Callable<String> { @Override public String call() throws Exception { log.info("do something in callable"); Thread.sleep(5000); return "Done"; } } public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); Future<String> future = executorService.submit(new MyCallable());//线程池提交任务 log.info("do something in main"); Thread.sleep(1000); String result = future.get();//获取不到一直阻塞 log.info("result:{}", result); } }
运行结果:阻塞效果

Future实现了RunnableFuture接口,而RunnableFuture接口继承了Runnable与Future接口,所以它既可以作为Runnable被线程中执行,又可以作为callable获得返回值。
public class FutureTask<V> implements RunnableFuture<V> { ... } public interface RunnableFuture<V> extends Runnable, Future<V> { void run(); }
FutureTask支持两种参数类型,Callable和Runnable,在使用Runnable 时,还可以多指定一个返回结果类型。
public FutureTask(Callable<V> callable) { if (callable == null) throw new NullPointerException(); this.callable = callable; this.state = NEW; // ensure visibility of callable } public FutureTask(Runnable runnable, V result) { this.callable = Executors.callable(runnable, result); this.state = NEW; // ensure visibility of callable }
使用方法:
public class FutureTaskExample { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { FutureTask<String> futureTask = new FutureTask<String>(new Callable<String>() { @Override public String call() throws Exception { log.info("do something in callable"); Thread.sleep(5000); return "Done"; } }); new Thread(futureTask).start(); log.info("do something in main"); Thread.sleep(1000); String result = futureTask.get(); log.info("result:{}", result); } }
运行结果:
ForkJoin是Java7提供的一个并行执行任务的框架,是把大任务分割成若干个小任务,待小任务完成后将结果汇总成大任务结果的框架。主要采用的是工作窃取算法,工作窃取算法是指某个线程从其他队列里窃取任务来执行。
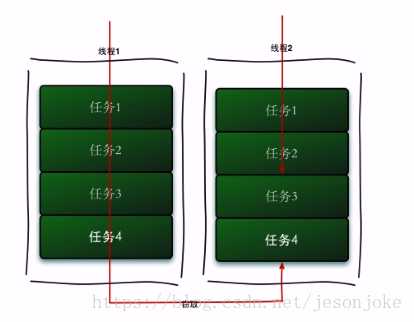
在窃取过程中两个线程会访问同一个队列,为了减少窃取任务线程和被窃取任务线程之间的竞争,通常我们会使用双端队列来实现工作窃取算法。被窃取任务的线程永远从队列的头部拿取任务,窃取任务的线程从队列尾部拿取任务。
1、任务只能使用fork和join作为同步机制,如果使用了其他同步机制,当他们在同步操作时,工作线程就不能执行其他任务了。比如在fork框架使任务进入了睡眠,那么在睡眠期间内在执行这个任务的线程将不会执行其他任务了。
2、我们所拆分的任务不应该去执行IO操作,如读和写数据文件。
3、任务不能抛出检查异常。必须通过必要的代码来处理他们。
核心有两个类:ForkJoinPool | ForkJoinTask
ForkJoinPool:负责来做实现,包括工作窃取算法、管理工作线程和提供关于任务的状态以及他们的执行信息。
ForkJoinTask:提供在任务中执行fork和join的机制。
@Slf4j public class ForkJoinTaskExample extends RecursiveTask<Integer> { public static final int threshold = 2;//设定不大于两个数相加就直接for循环,不适用框架 private int start; private int end; public ForkJoinTaskExample(int start, int end) { this.start = start; this.end = end; } @Override protected Integer compute() { int sum = 0; //如果任务足够小就计算任务 boolean canCompute = (end - start) <= threshold; if (canCompute) { for (int i = start; i <= end; i++) { sum += i; } } else { // 如果任务大于阈值,就分裂成两个子任务计算(分裂算法,可依情况调优) int middle = (start + end) / 2; ForkJoinTaskExample leftTask = new ForkJoinTaskExample(start, middle); ForkJoinTaskExample rightTask = new ForkJoinTaskExample(middle + 1, end); // 执行子任务 leftTask.fork(); rightTask.fork(); // 等待任务执行结束合并其结果 int leftResult = leftTask.join(); int rightResult = rightTask.join(); // 合并子任务 sum = leftResult + rightResult; } return sum; } public static void main(String[] args) { ForkJoinPool forkjoinPool = new ForkJoinPool(); //生成一个计算任务,计算1+2+3+4...100 ForkJoinTaskExample task = new ForkJoinTaskExample(1, 100); //执行一个任务 Future<Integer> result = forkjoinPool.submit(task); try { log.info("result:{}", result.get()); } catch (Exception e) { log.error("exception", e); } } }
主要应用场景:生产者消费者模型,是线程安全的
1、当队列满了进行入队操作
2、当队列空了的时候进行出队列操作
BlockingQueue提供了四套方法,分别来进行插入、移除、检查。每套方法在不能立刻执行时都有不同的反应。
public interface Delayed extends Comparable<Delayed> { long getDelay(TimeUnit unit); }
DalayQueue内部采用PriorityQueue与ReentrantLock实现。
public class DelayQueue<E extends Delayed> extends AbstractQueue<E> implements BlockingQueue<E> { private final transient ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(); private final PriorityQueue<E> q = new PriorityQueue<E>(); ... }
public LinkedBlockingQueue() { this(Integer.MAX_VALUE);//不指定大小,无边界采用默认值,最大整型值 }
public boolean add(E e) {//添加方法 return offer(e); } public boolean offer(E e) { if (e == null) throw new NullPointerException(); final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock; lock.lock(); int n, cap; Object[] array; while ((n = size) >= (cap = (array = queue).length)) tryGrow(array, cap); try { Comparator<? super E> cmp = comparator;//必须实现Comparator接口 if (cmp == null) siftUpComparable(n, e, array); else siftUpUsingComparator(n, e, array, cmp); size = n + 1; notEmpty.signal(); } finally { lock.unlock(); } return true; }
并发容器J.U.C --组件FutureTask、ForkJoin、BlockingQueue
标签:not syn mod 头部 font execution blog 生成 img
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/ktao/p/8985159.html