标签:line efficient session linear idt ram end new time
线性拟合??叶子的长宽:
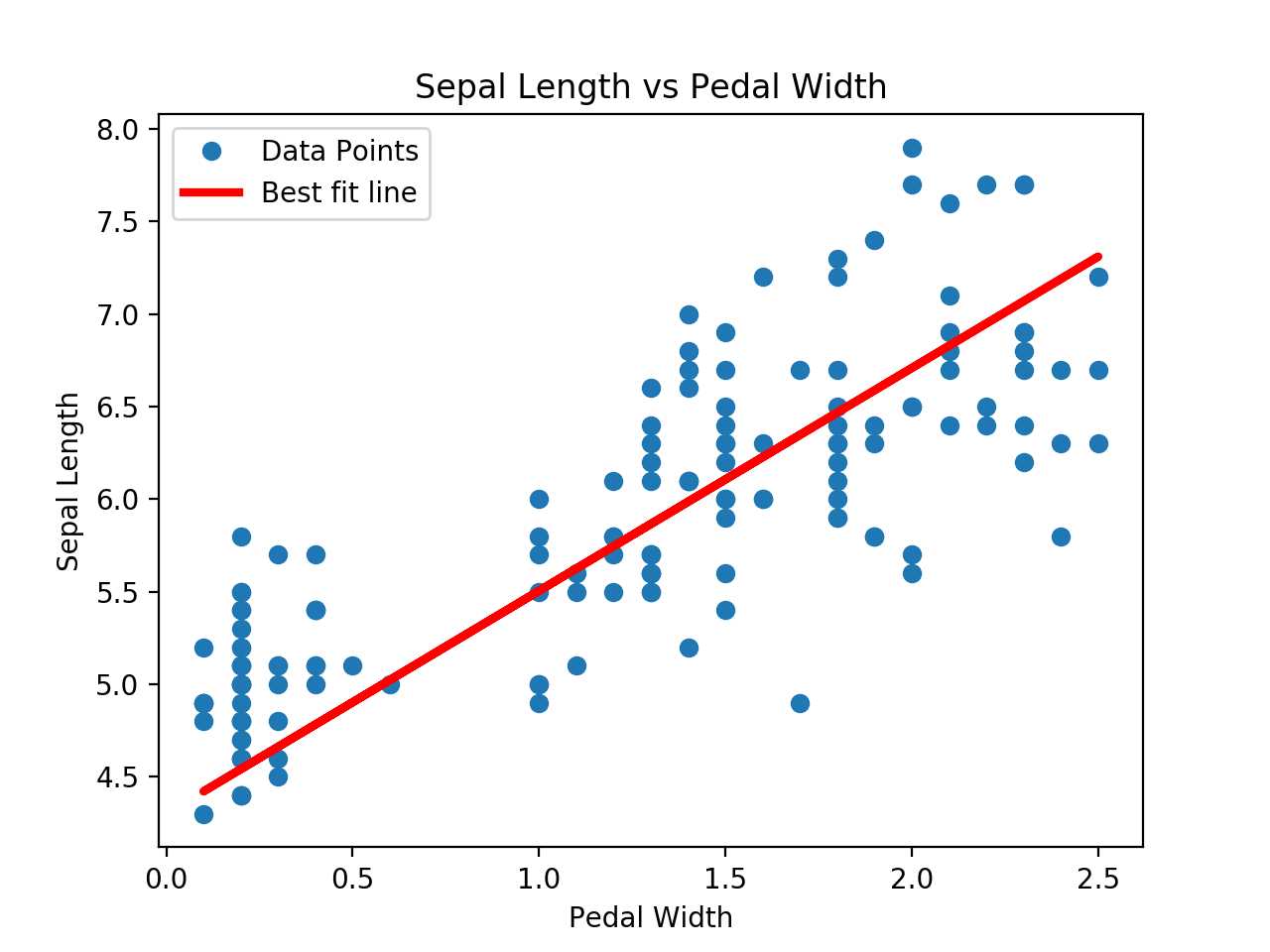
# Linear Regression: TensorFlow Way #---------------------------------- # # This function shows how to use TensorFlow to # solve linear regression. # y = Ax + b # # We will use the iris data, specifically: # y = Sepal Length # x = Petal Width import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np import tensorflow as tf from sklearn import datasets from tensorflow.python.framework import ops ops.reset_default_graph() # Create graph sess = tf.Session() # Load the data # iris.data = [(Sepal Length, Sepal Width, Petal Length, Petal Width)] iris = datasets.load_iris() x_vals = np.array([x[3] for x in iris.data]) y_vals = np.array([y[0] for y in iris.data]) # Declare batch size batch_size = 25 # Initialize placeholders x_data = tf.placeholder(shape=[None, 1], dtype=tf.float32) y_target = tf.placeholder(shape=[None, 1], dtype=tf.float32) # Create variables for linear regression A = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal(shape=[1,1])) b = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal(shape=[1,1])) # Declare model operations model_output = tf.add(tf.matmul(x_data, A), b) # Declare loss function (L2 loss) loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y_target - model_output)) # Declare optimizer my_opt = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.05) train_step = my_opt.minimize(loss) # Initialize variables init = tf.global_variables_initializer() sess.run(init) # Training loop loss_vec = [] for i in range(100): rand_index = np.random.choice(len(x_vals), size=batch_size) rand_x = np.transpose([x_vals[rand_index]]) rand_y = np.transpose([y_vals[rand_index]]) sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={x_data: rand_x, y_target: rand_y}) temp_loss = sess.run(loss, feed_dict={x_data: rand_x, y_target: rand_y}) loss_vec.append(temp_loss) if (i+1)%25==0: print(‘Step #‘ + str(i+1) + ‘ A = ‘ + str(sess.run(A)) + ‘ b = ‘ + str(sess.run(b))) print(‘Loss = ‘ + str(temp_loss)) # Get the optimal coefficients [slope] = sess.run(A) [y_intercept] = sess.run(b) # Get best fit line best_fit = [] for i in x_vals: best_fit.append(slope*i+y_intercept) # Plot the result plt.plot(x_vals, y_vals, ‘o‘, label=‘Data Points‘) plt.plot(x_vals, best_fit, ‘r-‘, label=‘Best fit line‘, linewidth=3) plt.legend(loc=‘upper left‘) plt.title(‘Sepal Length vs Pedal Width‘) plt.xlabel(‘Pedal Width‘) plt.ylabel(‘Sepal Length‘) plt.show() # Plot loss over time plt.plot(loss_vec, ‘k-‘) plt.title(‘L2 Loss per Generation‘) plt.xlabel(‘Generation‘) plt.ylabel(‘L2 Loss‘) plt.show()
标签:line efficient session linear idt ram end new time
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/bonelee/p/8996380.html