标签:targe 数据 tip inf gradient atp loss tran 0.00
iris二分类
# Linear Support Vector Machine: Soft Margin # ---------------------------------- # # This function shows how to use TensorFlow to # create a soft margin SVM # # We will use the iris data, specifically: # x1 = Sepal Length # x2 = Petal Width # Class 1 : I. setosa # Class -1: not I. setosa # # We know here that x and y are linearly seperable # for I. setosa classification. import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np import tensorflow as tf from sklearn import datasets from tensorflow.python.framework import ops ops.reset_default_graph() # Set random seeds np.random.seed(7) tf.set_random_seed(7) # Create graph sess = tf.Session() # Load the data # iris.data = [(Sepal Length, Sepal Width, Petal Length, Petal Width)] iris = datasets.load_iris() x_vals = np.array([[x[0], x[3]] for x in iris.data]) y_vals = np.array([1 if y == 0 else -1 for y in iris.target]) # Split data into train/test sets train_indices = np.random.choice(len(x_vals), round(len(x_vals)*0.9), replace=False) test_indices = np.array(list(set(range(len(x_vals))) - set(train_indices))) x_vals_train = x_vals[train_indices] x_vals_test = x_vals[test_indices] y_vals_train = y_vals[train_indices] y_vals_test = y_vals[test_indices] # Declare batch size batch_size = 135 # Initialize placeholders x_data = tf.placeholder(shape=[None, 2], dtype=tf.float32) y_target = tf.placeholder(shape=[None, 1], dtype=tf.float32) # Create variables for linear regression A = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal(shape=[2, 1])) b = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal(shape=[1, 1])) # Declare model operations model_output = tf.subtract(tf.matmul(x_data, A), b) # Declare vector L2 ‘norm‘ function squared l2_norm = tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(A)) # Declare loss function # Loss = max(0, 1-pred*actual) + alpha * L2_norm(A)^2 # L2 regularization parameter, alpha alpha = tf.constant([0.01]) # Margin term in loss classification_term = tf.reduce_mean(tf.maximum(0., tf.subtract(1., tf.multiply(model_output, y_target)))) # Put terms together loss = tf.add(classification_term, tf.multiply(alpha, l2_norm)) # Declare prediction function prediction = tf.sign(model_output) accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(tf.equal(prediction, y_target), tf.float32)) # Declare optimizer my_opt = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.01) train_step = my_opt.minimize(loss) # Initialize variables init = tf.global_variables_initializer() sess.run(init) # Training loop loss_vec = [] train_accuracy = [] test_accuracy = [] for i in range(500): rand_index = np.random.choice(len(x_vals_train), size=batch_size) rand_x = x_vals_train[rand_index] rand_y = np.transpose([y_vals_train[rand_index]]) sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={x_data: rand_x, y_target: rand_y}) temp_loss = sess.run(loss, feed_dict={x_data: rand_x, y_target: rand_y}) loss_vec.append(temp_loss) train_acc_temp = sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={ x_data: x_vals_train, y_target: np.transpose([y_vals_train])}) train_accuracy.append(train_acc_temp) test_acc_temp = sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={ x_data: x_vals_test, y_target: np.transpose([y_vals_test])}) test_accuracy.append(test_acc_temp) if (i + 1) % 100 == 0: print(‘Step #{} A = {}, b = {}‘.format( str(i+1), str(sess.run(A)), str(sess.run(b)) )) print(‘Loss = ‘ + str(temp_loss)) # Extract coefficients [[a1], [a2]] = sess.run(A) [[b]] = sess.run(b) slope = -a2/a1 y_intercept = b/a1 # Extract x1 and x2 vals x1_vals = [d[1] for d in x_vals] # Get best fit line best_fit = [] for i in x1_vals: best_fit.append(slope*i+y_intercept) # Separate I. setosa setosa_x = [d[1] for i, d in enumerate(x_vals) if y_vals[i] == 1] setosa_y = [d[0] for i, d in enumerate(x_vals) if y_vals[i] == 1] not_setosa_x = [d[1] for i, d in enumerate(x_vals) if y_vals[i] == -1] not_setosa_y = [d[0] for i, d in enumerate(x_vals) if y_vals[i] == -1] # Plot data and line plt.plot(setosa_x, setosa_y, ‘o‘, label=‘I. setosa‘) plt.plot(not_setosa_x, not_setosa_y, ‘x‘, label=‘Non-setosa‘) plt.plot(x1_vals, best_fit, ‘r-‘, label=‘Linear Separator‘, linewidth=3) plt.ylim([0, 10]) plt.legend(loc=‘lower right‘) plt.title(‘Sepal Length vs Pedal Width‘) plt.xlabel(‘Pedal Width‘) plt.ylabel(‘Sepal Length‘) plt.show() # Plot train/test accuracies plt.plot(train_accuracy, ‘k-‘, label=‘Training Accuracy‘) plt.plot(test_accuracy, ‘r--‘, label=‘Test Accuracy‘) plt.title(‘Train and Test Set Accuracies‘) plt.xlabel(‘Generation‘) plt.ylabel(‘Accuracy‘) plt.legend(loc=‘lower right‘) plt.show() # Plot loss over time plt.plot(loss_vec, ‘k-‘) plt.title(‘Loss per Generation‘) plt.xlabel(‘Generation‘) plt.ylabel(‘Loss‘) plt.show()
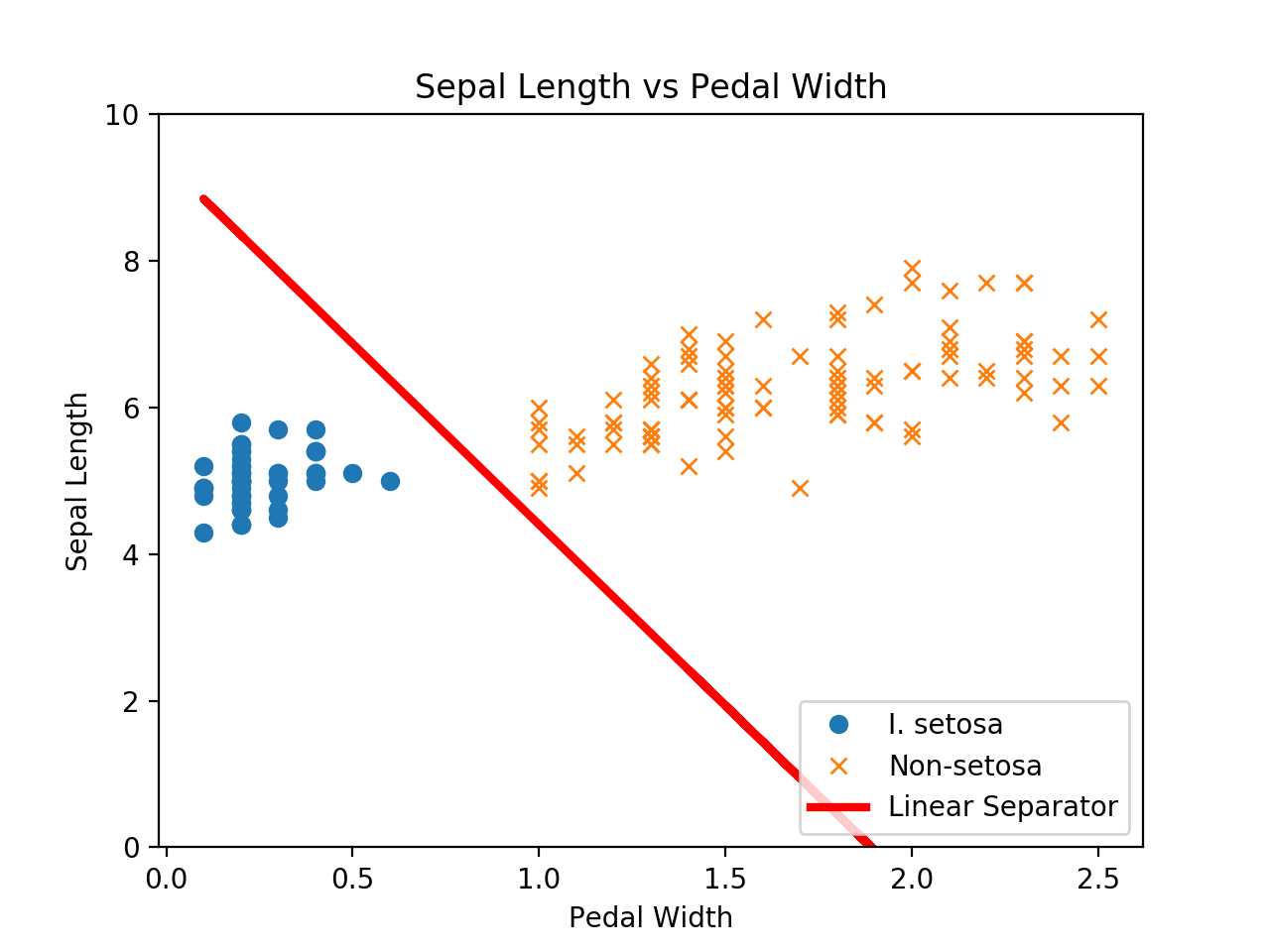
下面例子数据集可能更好看;
# SVM Regression
#----------------------------------
#
# This function shows how to use TensorFlow to
# solve support vector regression. We are going
# to find the line that has the maximum margin
# which INCLUDES as many points as possible
#
# We will use the iris data, specifically:
# y = Sepal Length
# x = Pedal Width
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from sklearn import datasets
from tensorflow.python.framework import ops
ops.reset_default_graph()
# Create graph
sess = tf.Session()
# Load the data
# iris.data = [(Sepal Length, Sepal Width, Petal Length, Petal Width)]
iris = datasets.load_iris()
x_vals = np.array([x[3] for x in iris.data])
y_vals = np.array([y[0] for y in iris.data])
# Split data into train/test sets
train_indices = np.random.choice(len(x_vals), round(len(x_vals)*0.8), replace=False)
test_indices = np.array(list(set(range(len(x_vals))) - set(train_indices)))
x_vals_train = x_vals[train_indices]
x_vals_test = x_vals[test_indices]
y_vals_train = y_vals[train_indices]
y_vals_test = y_vals[test_indices]
# Declare batch size
batch_size = 50
# Initialize placeholders
x_data = tf.placeholder(shape=[None, 1], dtype=tf.float32)
y_target = tf.placeholder(shape=[None, 1], dtype=tf.float32)
# Create variables for linear regression
A = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal(shape=[1,1]))
b = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal(shape=[1,1]))
# Declare model operations
model_output = tf.add(tf.matmul(x_data, A), b)
# Declare loss function
# = max(0, abs(target - predicted) + epsilon)
# 1/2 margin width parameter = epsilon
epsilon = tf.constant([0.5])
# Margin term in loss
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.maximum(0., tf.subtract(tf.abs(tf.subtract(model_output, y_target)), epsilon)))
# Declare optimizer
my_opt = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.075)
train_step = my_opt.minimize(loss)
# Initialize variables
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess.run(init)
# Training loop
train_loss = []
test_loss = []
for i in range(200):
rand_index = np.random.choice(len(x_vals_train), size=batch_size)
rand_x = np.transpose([x_vals_train[rand_index]])
rand_y = np.transpose([y_vals_train[rand_index]])
sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={x_data: rand_x, y_target: rand_y})
temp_train_loss = sess.run(loss, feed_dict={x_data: np.transpose([x_vals_train]), y_target: np.transpose([y_vals_train])})
train_loss.append(temp_train_loss)
temp_test_loss = sess.run(loss, feed_dict={x_data: np.transpose([x_vals_test]), y_target: np.transpose([y_vals_test])})
test_loss.append(temp_test_loss)
if (i+1)%50==0:
print(‘-----------‘)
print(‘Generation: ‘ + str(i+1))
print(‘A = ‘ + str(sess.run(A)) + ‘ b = ‘ + str(sess.run(b)))
print(‘Train Loss = ‘ + str(temp_train_loss))
print(‘Test Loss = ‘ + str(temp_test_loss))
# Extract Coefficients
[[slope]] = sess.run(A)
[[y_intercept]] = sess.run(b)
[width] = sess.run(epsilon)
# Get best fit line
best_fit = []
best_fit_upper = []
best_fit_lower = []
for i in x_vals:
best_fit.append(slope*i+y_intercept)
best_fit_upper.append(slope*i+y_intercept+width)
best_fit_lower.append(slope*i+y_intercept-width)
# Plot fit with data
plt.plot(x_vals, y_vals, ‘o‘, label=‘Data Points‘)
plt.plot(x_vals, best_fit, ‘r-‘, label=‘SVM Regression Line‘, linewidth=3)
plt.plot(x_vals, best_fit_upper, ‘r--‘, linewidth=2)
plt.plot(x_vals, best_fit_lower, ‘r--‘, linewidth=2)
plt.ylim([0, 10])
plt.legend(loc=‘lower right‘)
plt.title(‘Sepal Length vs Pedal Width‘)
plt.xlabel(‘Pedal Width‘)
plt.ylabel(‘Sepal Length‘)
plt.show()
# Plot loss over time
plt.plot(train_loss, ‘k-‘, label=‘Train Set Loss‘)
plt.plot(test_loss, ‘r--‘, label=‘Test Set Loss‘)
plt.title(‘L2 Loss per Generation‘)
plt.xlabel(‘Generation‘)
plt.ylabel(‘L2 Loss‘)
plt.legend(loc=‘upper right‘)
plt.show()
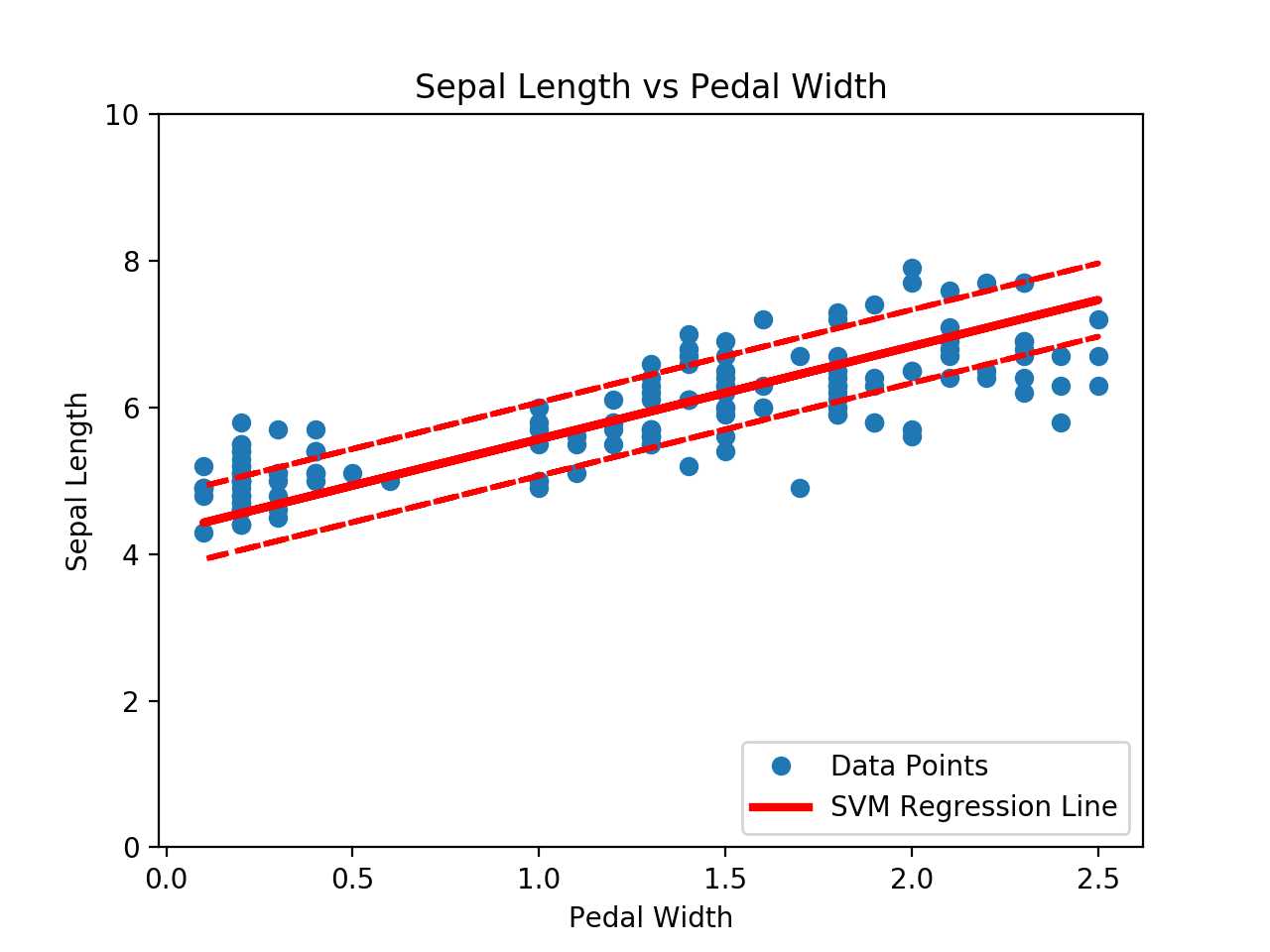
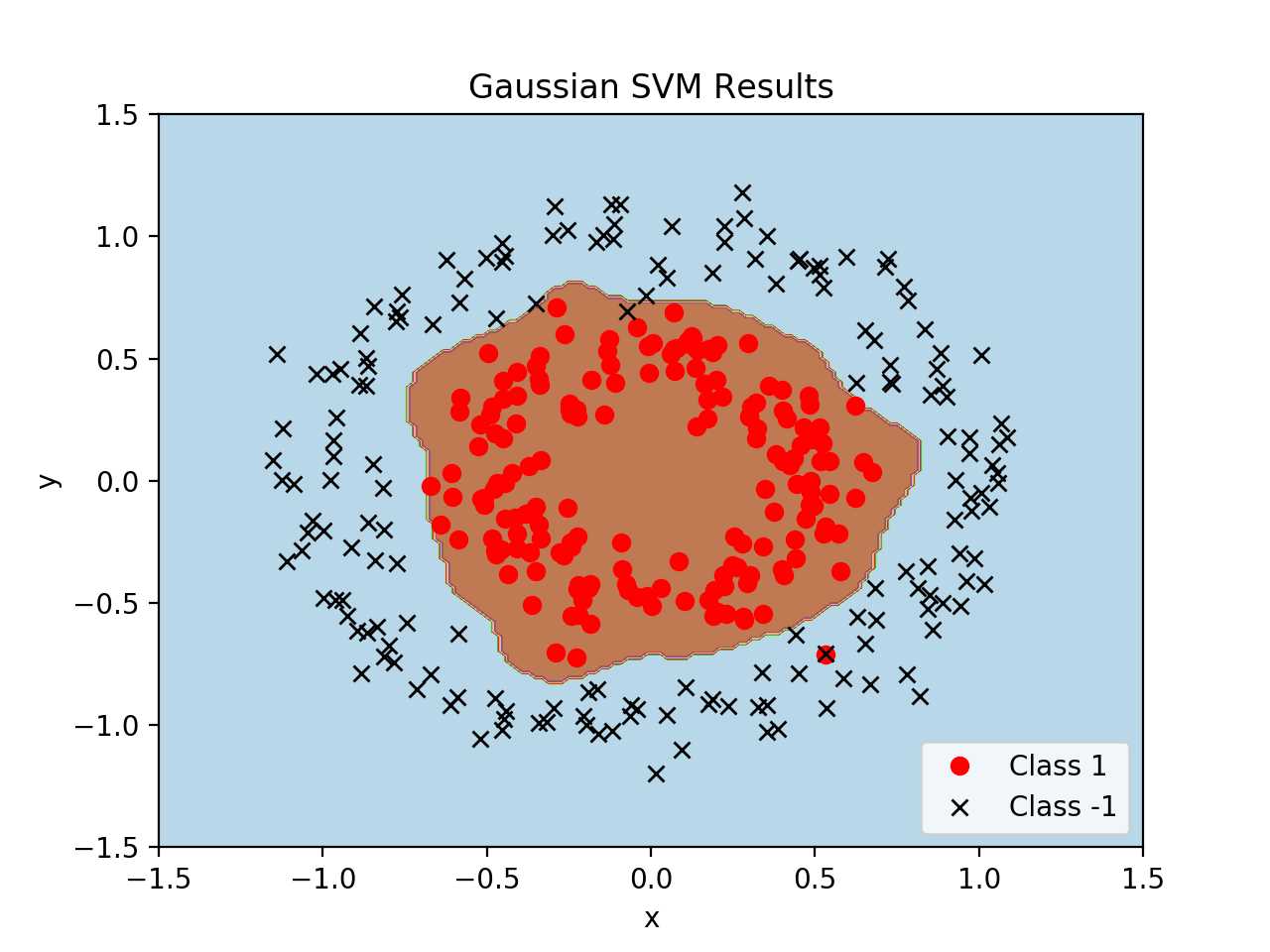
高斯核函数的应用,其实也可以自定义很多核函数:
# Illustration of Various Kernels
#----------------------------------
#
# This function wll illustrate how to
# implement various kernels in TensorFlow.
#
# Linear Kernel:
# K(x1, x2) = t(x1) * x2
#
# Gaussian Kernel (RBF):
# K(x1, x2) = exp(-gamma * abs(x1 - x2)^2)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from sklearn import datasets
from tensorflow.python.framework import ops
ops.reset_default_graph()
# Create graph
sess = tf.Session()
# Generate non-lnear data
(x_vals, y_vals) = datasets.make_circles(n_samples=350, factor=.5, noise=.1)
y_vals = np.array([1 if y==1 else -1 for y in y_vals])
class1_x = [x[0] for i,x in enumerate(x_vals) if y_vals[i]==1]
class1_y = [x[1] for i,x in enumerate(x_vals) if y_vals[i]==1]
class2_x = [x[0] for i,x in enumerate(x_vals) if y_vals[i]==-1]
class2_y = [x[1] for i,x in enumerate(x_vals) if y_vals[i]==-1]
# Declare batch size
batch_size = 350
# Initialize placeholders
x_data = tf.placeholder(shape=[None, 2], dtype=tf.float32)
y_target = tf.placeholder(shape=[None, 1], dtype=tf.float32)
prediction_grid = tf.placeholder(shape=[None, 2], dtype=tf.float32)
# Create variables for svm
b = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal(shape=[1,batch_size]))
# Apply kernel
# Linear Kernel
# my_kernel = tf.matmul(x_data, tf.transpose(x_data))
# Gaussian (RBF) kernel
gamma = tf.constant(-50.0)
dist = tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(x_data), 1)
dist = tf.reshape(dist, [-1,1])
sq_dists = tf.add(tf.subtract(dist, tf.multiply(2., tf.matmul(x_data, tf.transpose(x_data)))), tf.transpose(dist))
my_kernel = tf.exp(tf.multiply(gamma, tf.abs(sq_dists)))
# Compute SVM Model
first_term = tf.reduce_sum(b)
b_vec_cross = tf.matmul(tf.transpose(b), b)
y_target_cross = tf.matmul(y_target, tf.transpose(y_target))
second_term = tf.reduce_sum(tf.multiply(my_kernel, tf.multiply(b_vec_cross, y_target_cross)))
loss = tf.negative(tf.subtract(first_term, second_term))
# Create Prediction Kernel
# Linear prediction kernel
# my_kernel = tf.matmul(x_data, tf.transpose(prediction_grid))
# Gaussian (RBF) prediction kernel
rA = tf.reshape(tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(x_data), 1),[-1,1])
rB = tf.reshape(tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(prediction_grid), 1),[-1,1])
pred_sq_dist = tf.add(tf.subtract(rA, tf.multiply(2., tf.matmul(x_data, tf.transpose(prediction_grid)))), tf.transpose(rB))
pred_kernel = tf.exp(tf.multiply(gamma, tf.abs(pred_sq_dist)))
prediction_output = tf.matmul(tf.multiply(tf.transpose(y_target),b), pred_kernel)
prediction = tf.sign(prediction_output-tf.reduce_mean(prediction_output))
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(tf.equal(tf.squeeze(prediction), tf.squeeze(y_target)), tf.float32))
# Declare optimizer
my_opt = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.002)
train_step = my_opt.minimize(loss)
# Initialize variables
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess.run(init)
# Training loop
loss_vec = []
batch_accuracy = []
for i in range(1000):
rand_index = np.random.choice(len(x_vals), size=batch_size)
rand_x = x_vals[rand_index]
rand_y = np.transpose([y_vals[rand_index]])
sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={x_data: rand_x, y_target: rand_y})
temp_loss = sess.run(loss, feed_dict={x_data: rand_x, y_target: rand_y})
loss_vec.append(temp_loss)
acc_temp = sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={x_data: rand_x,
y_target: rand_y,
prediction_grid:rand_x})
batch_accuracy.append(acc_temp)
if (i+1)%250==0:
print(‘Step #‘ + str(i+1))
print(‘Loss = ‘ + str(temp_loss))
# Create a mesh to plot points in
x_min, x_max = x_vals[:, 0].min() - 1, x_vals[:, 0].max() + 1
y_min, y_max = x_vals[:, 1].min() - 1, x_vals[:, 1].max() + 1
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min, x_max, 0.02),
np.arange(y_min, y_max, 0.02))
grid_points = np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()]
[grid_predictions] = sess.run(prediction, feed_dict={x_data: rand_x,
y_target: rand_y,
prediction_grid: grid_points})
grid_predictions = grid_predictions.reshape(xx.shape)
# Plot points and grid
plt.contourf(xx, yy, grid_predictions, cmap=plt.cm.Paired, alpha=0.8)
plt.plot(class1_x, class1_y, ‘ro‘, label=‘Class 1‘)
plt.plot(class2_x, class2_y, ‘kx‘, label=‘Class -1‘)
plt.title(‘Gaussian SVM Results‘)
plt.xlabel(‘x‘)
plt.ylabel(‘y‘)
plt.legend(loc=‘lower right‘)
plt.ylim([-1.5, 1.5])
plt.xlim([-1.5, 1.5])
plt.show()
# Plot batch accuracy
plt.plot(batch_accuracy, ‘k-‘, label=‘Accuracy‘)
plt.title(‘Batch Accuracy‘)
plt.xlabel(‘Generation‘)
plt.ylabel(‘Accuracy‘)
plt.legend(loc=‘lower right‘)
plt.show()
# Plot loss over time
plt.plot(loss_vec, ‘k-‘)
plt.title(‘Loss per Generation‘)
plt.xlabel(‘Generation‘)
plt.ylabel(‘Loss‘)
plt.show()
# Evaluate on new/unseen data points
# New data points:
new_points = np.array([(-0.75, -0.75),
(-0.5, -0.5),
(-0.25, -0.25),
(0.25, 0.25),
(0.5, 0.5),
(0.75, 0.75)])
[evaluations] = sess.run(prediction, feed_dict={x_data: x_vals,
y_target: np.transpose([y_vals]),
prediction_grid: new_points})
for ix, p in enumerate(new_points):
print(‘{} : class={}‘.format(p, evaluations[ix]))
tensorflow实现svm iris二分类——本质上在使用梯度下降法求解线性回归(loss是定制的而已)
标签:targe 数据 tip inf gradient atp loss tran 0.00
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/bonelee/p/8996567.html