标签:C++ static_cast const_cast reinterpret_cast dynamic_cast
我们之前在 C 语言进行类型转换是强制类型转换的,这样极易出 bug,还不易查找。格式如下:(Type)(Experssion) 或 Type(Experssion),我们来看个示例代码,看看 C 语言中的强制类型转换#include <stdio.h>
typedef void(PF)(int);
struct Point
{
int x;
int y;
};
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int v = 0x12345;
PF* pf = (PF*)v;
char c = char(v);
Point* p = (Point*)v;
pf(5);
printf("p->x = %d\n", p->x);
printf("p->y = %d\n", p->y);
return 0;
}编译结果如下
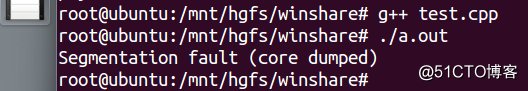
我们看到直接运行段错误,但是它编译是通过的,因此我们如果在大型的项目中是难以查找 bug 的。
在 C 方式的强制类型转换的过程中,它存在的问题:a> 过于粗暴:任意类型之间都可以进行转换,编译器很难判断其正确性;b> 难于定位:在源码中无法快速定位所有使用强制类型转换的语句。那么强制类型转换在实际工程中是很难完全避免的!如何进行更加安全可靠的转换呢?在 C++ 中出现了新式类型转换,C++ 将强制类型转换分为 4 中不同的类型:a> static_cast;b> const_cast;c> dynamic_cast;d> reinterpret_cast;用法是:xxx_cast<Type>(Expression)。下来我们分别来讲下这四种新式类型转换的特点及要求
A、static_cast 强制类型转换
用于基本类型间的转换;不能用于基本类型指针间的转换;用于有继承关系类对象之间的转换和类指针之间的转换。
B、const_cast 强制类型转换
用于去除变量的只读属性;强制转换的目标类型必须是指针或引用。
C、reinterpret_cast 强制类型转换
用于指针类型间的强制转换;用于整数和指针类型间的强制转换。
D、dynamic_cast 强制类型转换
用于有继承关系的类指针间的转换;用于有交叉关系的类指针间的转换;具有类型检查的功能;需要虚函数的支持。
关于上面讲到的有些概念,我们会在后面进行详细的介绍,下来我们以代码为例进行分析
#include <stdio.h>
void static_cast_demo()
{
int i = 0x12345;
char c = 'c';
int* pi = &i;
char* pc = &c;
c = static_cast<char>(i);
pc = static_cast<char*>(pi); // error
}
void const_cast_demo()
{
const int& j = 1;
int& k = const_cast<int&>(j);
const int x = 2;
int& y = const_cast<int&>(x);
int z = const_cast<int>(x); // error
k = 5;
printf("k = %d\n", k);
printf("j = %d\n", j);
y = 8;
printf("x = %d\n", x);
printf("y = %d\n", y);
printf("&x = %p\n", &x);
printf("&y = %p\n", &y);
}
void reinterpret_cast_demo()
{
int i = 0;
char c = 'c';
int* pi = &i;
char* pc = &c;
pc = reinterpret_cast<char*>(pi);
pi = reinterpret_cast<int*>(pc);
pi = reinterpret_cast<int*>(i);
c = reinterpret_cast<char>(i); // error
}
void dynamic_cast_demo()
{
int i = 0;
int* pi = &i;
char* pc = dynamic_cast<char*>(pi); // error
}
int main()
{
static_cast_demo();
const_cast_demo();
reinterpret_cast_demo();
dynamic_cast_demo();
return 0;
}我们来分析下这个代码,在 static_cast_demo 中,static_cast 不能用于指针间的转换,所以第 11 行会报错。在 const_cast_demo 中,第 16 行定义了一个具有只读属性的变量 j,我们还是可以通过 const_cast 来改变它的属性的。第 19 行定义了一个真正意义上的常量,它会进入到符号表中,但在栈上会为它分配 4 个字节的空间,所以第 20 行的也会成功。const_cast 强制转换的目标类型必须是指针或引用,所以第 22 行会报错。第 26 、 27 行会打印出 5、5;第 31 - 34 会打印出 2、8、后面两个地址是一样的。在 reinterpret_cast_demo 中,reinterpret_cast 用于指针类型间及整数和指针类型间的强制转换,所以第 47 行会报错。在 dynamic_cast_demo 中,第 54 行会报错。我们来看看编译结果
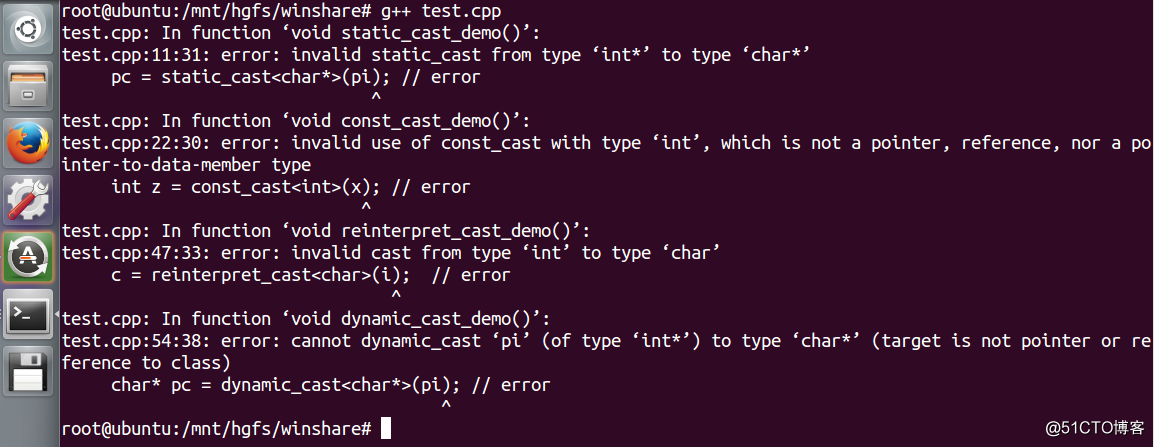
我们分别注释掉这几行,再来编译,看看结果是否如我们所分析的那样
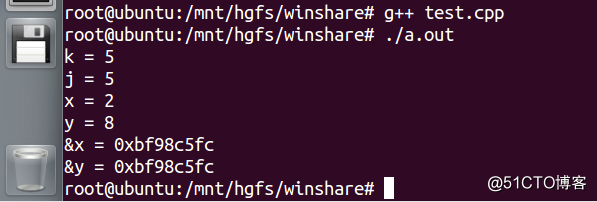
我们看到和我们所分析的是一致的。通过对强制类型转换的学习,总结如下:1、C 方式的强制类型转换:a> 过于粗暴。 b> 潜在的问题不易被发现。 c> 不易在代码中定位;2、新式类型转换以 C++ 关键字的方式出现:a> 编译器能帮助检查潜在的问题。 b> 非常方便的在代码中定位。 c> 支持动态类型识别(dynamic_cast)。
欢迎大家一起来学习 C++ 语言,可以加我QQ:243343083。
标签:C++ static_cast const_cast reinterpret_cast dynamic_cast
原文地址:http://blog.51cto.com/12810168/2113349