标签:des style blog http color io os java ar
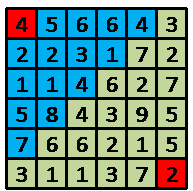
1 6 6 4 5 6 6 4 3 2 2 3 1 7 2 1 1 4 6 2 7 5 8 4 3 9 5 7 6 6 2 1 5 3 1 1 3 7 2
3948
这道题可以用如果用动态规划做,那就是初始化起始点方案数为1,每次枚举某一点能到达的位置,目标位置方案为能到达它的点方案数和。
如果是记忆化就是反过来做,终点位置方案数目为1,搜索过程记录搜到的每一点的方案数就好了。思路很清晰。
动态规划:
#include"stdio.h"
#include"string.h"
#define M 10000
#define N 110
int main()
{
int T,i,j,n,m,x,y,di,dj,t;
int a[N][N],dp[N][N];
scanf("%d",&T);
while(T--)
{
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
for(j=1;j<=m;j++)
{
scanf("%d",&a[i][j]);
}
}
memset(dp,0,sizeof(dp));
dp[1][1]=1;
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
for(j=1;j<=m;j++)
{
if(dp[i][j])
{
t=a[i][j];
for(x=0;x<=t;x++)
{
for(y=0;y<=t;y++)
{
if(x+y==0)
continue;
if(x+y>t)
break;
di=x+i;
dj=y+j;
if(di<=n&&dj<=m)
dp[di][dj]+=dp[i][j];
dp[di][dj]%=M;
}
}
}
}
}
printf("%d\n",dp[n][m]%M);
}
return 0;
}
记忆化搜索:
#include<iostream>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
#define N 105
const int mod=10000;
int n,m;
int a[N][N];
int mark[N][N];
int dfs(int x,int y)
{
if(mark[x][y]!=-1)
return mark[x][y];
int t,x1,y1,tmp;
tmp=0;
t=a[x][y];
for(x1=0;x1<=t;x1++)
{
if(x+x1>=n)
break;
for(y1=0;x1+y1<=t;y1++)
{
if(y+y1>=m)
break;
if(x1+y1!=0) //不能原地走
tmp+=dfs(x+x1,y+y1);
}
}
tmp%=mod;
return mark[x][y]=tmp;
}
int main()
{
int i,j,T;
scanf("%d",&T);
while(T--)
{
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<m;j++)
{
scanf("%d",&a[i][j]);
mark[i][j]=-1;
}
}
mark[n-1][m-1]=1;
printf("%d\n",dfs(0,0));
}
return 0;
}
hdu 1978 How many ways (动态规划、记忆化搜索)
标签:des style blog http color io os java ar
原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/u011721440/article/details/39576677