标签:for head sub 一个 http put doctype val def
def transfer(request):
if request.method ==‘POST‘:
from_ =request.POST.get(‘from‘)
to_ =request.POST.get(‘to‘)
money =request.POST.get(‘money‘)
print(‘{} 给{} 转了{} 钱‘.format(from_,to_,money))
return HttpResponse(‘转账成功!‘)
return render(request, ‘transfer.html‘)
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <h1>正经的网站</h1> <form action="/transfer/" method="post"> {% csrf_token %} <p> 转出: <input type="text" name="from"> </p> <p> 转入: <input type="text" name="to"> </p> <p> 金额: <input type="text" name="money"> </p> <p> <input type="submit" value="提交"> </p> </form> </body> </html>
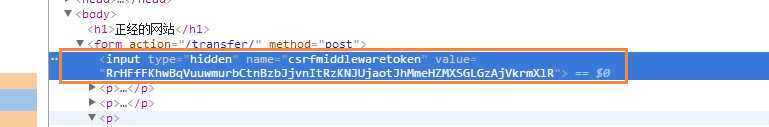

Django中内置了一个专门的处理csrf问题的中间件
django.middleware.csrf.csrfviewmiddleware
这个中间件做的事情:
1. 在rander返回页面的时候,在页面中塞了一个隐藏的input标签
我们在form 表单里写上 {%csrf -token%}
2. 在提交post数据的时候,它帮你做校验,如果校验不通过,就拒绝这次请求

标签:for head sub 一个 http put doctype val def
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/mengbin0546/p/9048010.html