标签:ali 重要 parent ons post 结果 中序遍历 start app
树的遍历是树的一种重要的运算。所谓遍历是指对树中所有结点的信息的访问,即依次对树中每个结点访问一次且仅访问一次,我们把这种对所有节点的访问称为遍历(traversal)。那么树的两种重要的遍历模式是深度优先遍历和广度优先遍历,深度优先一般用递归,广度优先一般用队列。一般情况下能用递归实现的算法大部分也能用堆栈来实现。
对于一颗二叉树,深度优先搜索(Depth First Search)是沿着树的深度遍历树的节点,尽可能深的搜索树的分支。
那么深度遍历有重要的三种方法。这三种方式常被用于访问树的节点,它们之间的不同在于访问每个节点的次序不同。这三种遍历分别叫做先序遍历(preorder),中序遍历(inorder)和后序遍历(postorder)。我们来给出它们的详细定义,然后举例看看它们的应用。
def preorder(self, root):
"""递归实现先序遍历"""
if root == None:
return
print root.elem
self.preorder(root.lchild)
self.preorder(root.rchild)
def inorder(self, root):
"""递归实现中序遍历"""
if root == None:
return
self.inorder(root.lchild)
print root.elem
self.inorder(root.rchild)
def postorder(self, root):
"""递归实现后续遍历"""
if root == None:
return
self.postorder(root.lchild)
self.postorder(root.rchild)
print root.elem
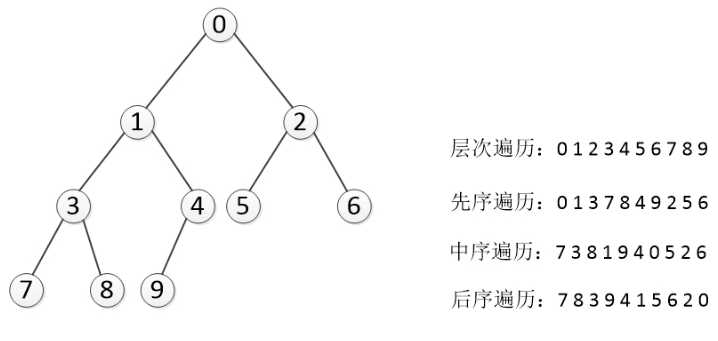
课堂练习: 按照如图树的结构写出三种遍历的顺序:
结果:
先序:a b c d e f g h
中序:b d c e a f h g
后序:d e c b h g f a
思考:哪两种遍历方式能够唯一的确定一颗树???
从树的root开始,从上到下从从左到右遍历整个树的节点
def breadth_travel(self, root):
"""利用队列实现树的层次遍历"""
if root == None:
return
queue = []
queue.append(root)
while queue:
node = queue.pop(0)
print node.elem,
if node.lchild != None:
queue.append(node.lchild)
if node.rchild != None:
queue.append(node.rchild)标签:ali 重要 parent ons post 结果 中序遍历 start app
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/amou/p/9058396.html