标签:zookeeper 理论 测试 ISE 初始 方便 异步 zook 分布式事务
目前几乎很多大型网站及应用都是分布式部署的,分布式场景中的数据一致性问题一直是一个比较重要的话题。分布式的CAP理论告诉我们“任何一个分布式系统都无法同时满足一致性(Consistency)、可用性(Availability)和分区容错性(Partition tolerance),最多只能同时满足两项。”所以,很多系统在设计之初就要对这三者做出取舍。在互联网领域的绝大多数的场景中,都需要牺牲强一致性来换取系统的高可用性,系统往往只需要保证“最终一致性”,只要这个最终时间是在用户可以接受的范围内即可。
在很多场景中,我们为了保证数据的最终一致性,需要很多的技术方案来支持,比如分布式事务、分布式锁等。
在此就不介绍Redis的安装了,具体在Linux和Windows中的安装可以查看我前面的博客。
http://www.cnblogs.com/liuyang0/p/6504826.html
SETNX
SETNX key val
当且仅当key不存在时,set一个key为val的字符串,返回1;若key存在,则什么都不做,返回0。
expire
expire key timeout
为key设置一个超时时间,单位为second,超过这个时间锁会自动释放,避免死锁。
delete
delete key
删除key
在使用Redis实现分布式锁的时候,主要就会使用到这三个命令。
使用的是jedis来连接Redis。
实现思想
分布式锁的核心代码如下:
1 package com.distribute; 2 3 import redis.clients.jedis.Jedis; 4 import redis.clients.jedis.JedisPool; 5 import redis.clients.jedis.Transaction; 6 import redis.clients.jedis.exceptions.JedisException; 7 8 import java.util.List; 9 import java.util.UUID; 10 11 /** 12 * Created by liuyang on 2017/4/20. 13 */ 14 public class DistributedLock { 15 private final JedisPool jedisPool; 16 17 public DistributedLock(JedisPool jedisPool) { 18 this.jedisPool = jedisPool; 19 } 20 21 /** 22 * 加锁 23 * 24 * @param locaName 锁的key 25 * @param acquireTimeout 获取超时时间 26 * @param timeout 锁的超时时间 27 * @return 锁标识 28 */ 29 public String lockWithTimeout(String locaName, long acquireTimeout, long timeout) { 30 Jedis conn = null; 31 String retIdentifier = null; 32 try { 33 // 获取连接 34 conn = jedisPool.getResource(); 35 // 随机生成一个value 36 String identifier = UUID.randomUUID().toString(); 37 // 锁名,即key值 38 String lockKey = "lock:" + locaName; 39 // 超时时间,上锁后超过此时间则自动释放锁 40 int lockExpire = (int) (timeout / 1000); 41 42 // 获取锁的超时时间,超过这个时间则放弃获取锁 43 long end = System.currentTimeMillis() + acquireTimeout; 44 while (System.currentTimeMillis() < end) { 45 if (conn.setnx(lockKey, identifier) == 1) { 46 conn.expire(lockKey, lockExpire); 47 // 返回value值,用于释放锁时间确认 48 retIdentifier = identifier; 49 return retIdentifier; 50 } 51 // 返回-1代表key没有设置超时时间,为key设置一个超时时间 52 if (conn.ttl(lockKey) == -1) { 53 conn.expire(lockKey, lockExpire); 54 } 55 56 try { 57 Thread.sleep(10); 58 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 59 Thread.currentThread().interrupt(); 60 } 61 } 62 } catch (JedisException e) { 63 e.printStackTrace(); 64 } finally { 65 if (conn != null) { 66 conn.close(); 67 } 68 } 69 return retIdentifier; 70 } 71 72 /** 73 * 释放锁 74 * 75 * @param lockName 锁的key 76 * @param identifier 释放锁的标识 77 * @return 78 */ 79 public boolean releaseLock(String lockName, String identifier) { 80 Jedis conn = null; 81 String lockKey = "lock:" + lockName; 82 boolean retFlag = false; 83 try { 84 conn = jedisPool.getResource(); 85 while (true) { 86 // 监视lock,准备开始事务 87 conn.watch(lockKey); 88 // 通过前面返回的value值判断是不是该锁,若是该锁,则删除,释放锁 89 if (identifier.equals(conn.get(lockKey))) { 90 Transaction transaction = conn.multi(); 91 transaction.del(lockKey); 92 List<Object> results = transaction.exec(); 93 if (results == null) { 94 continue; 95 } 96 retFlag = true; 97 } 98 conn.unwatch(); 99 break; 100 } 101 } catch (JedisException e) { 102 e.printStackTrace(); 103 } finally { 104 if (conn != null) { 105 conn.close(); 106 } 107 } 108 return retFlag; 109 } 110 }
测试
下面就用一个简单的例子测试刚才实现的分布式锁。
例子中使用50个线程模拟秒杀一个商品,使用--运算符来实现商品减少,从结果有序性就可以看出是否为加锁状态。
模拟秒杀服务,在其中配置了jedis线程池,在初始化的时候传给分布式锁,供其使用。
1 import redis.clients.jedis.JedisPool; 2 import redis.clients.jedis.JedisPoolConfig; 3 4 /** 5 * Created by liuyang on 2017/4/20. 6 */ 7 public class Service { 8 private static JedisPool pool = null; 9 10 static { 11 JedisPoolConfig config = new JedisPoolConfig(); 12 // 设置最大连接数 13 config.setMaxTotal(200); 14 // 设置最大空闲数 15 config.setMaxIdle(8); 16 // 设置最大等待时间 17 config.setMaxWaitMillis(1000 * 100); 18 // 在borrow一个jedis实例时,是否需要验证,若为true,则所有jedis实例均是可用的 19 config.setTestOnBorrow(true); 20 pool = new JedisPool(config, "127.0.0.1", 6379, 3000); 21 } 22 23 DistributedLock lock = new DistributedLock(pool); 24 25 int n = 500; 26 27 public void seckill() { 28 // 返回锁的value值,供释放锁时候进行判断 29 String indentifier = lock.lockWithTimeout("resource", 5000, 1000); 30 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "获得了锁"); 31 System.out.println(--n); 32 lock.releaseLock("resource", indentifier); 33 } 34 }
// 模拟线程进行秒杀服务
1 public class ThreadA extends Thread { 2 private Service service; 3 4 public ThreadA(Service service) { 5 this.service = service; 6 } 7 8 @Override 9 public void run() { 10 service.seckill(); 11 } 12 } 13 14 public class Test { 15 public static void main(String[] args) { 16 Service service = new Service(); 17 for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++) { 18 ThreadA threadA = new ThreadA(service); 19 threadA.start(); 20 } 21 } 22 }
结果如下,结果为有序的。
1 public void seckill() { 2 // 返回锁的value值,供释放锁时候进行判断 3 //String indentifier = lock.lockWithTimeout("resource", 5000, 1000); 4 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "获得了锁"); 5 System.out.println(--n); 6 //lock.releaseLock("resource", indentifier); 7 }
从结果可以看出,有一些是异步进行的。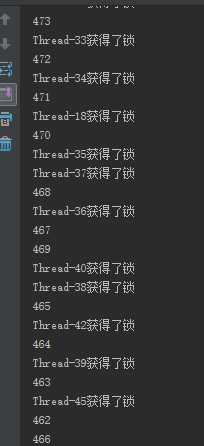
在分布式环境中,对资源进行上锁有时候是很重要的,比如抢购某一资源,这时候使用分布式锁就可以很好地控制资源。
当然,在具体使用中,还需要考虑很多因素,比如超时时间的选取,获取锁时间的选取对并发量都有很大的影响,上述实现的分布式锁也只是一种简单的实现,主要是一种思想。
下一次我会使用zookeeper实现分布式锁,使用zookeeper的可靠性是要大于使用redis实现的分布式锁的,但是相比而言,redis的性能更好。
上面的代码可以在我的GitHub中进行查看,地址如下:
https://github.com/yangliu0/DistributedLock
标签:zookeeper 理论 测试 ISE 初始 方便 异步 zook 分布式事务
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/cxxjohnson/p/9077946.html