标签:style bubuko inf second iterator include pop file 方式
相信大家看到swap这个词都一定不会感到陌生,就是简单的元素交换。但swap在C++ STL中散发着无穷的魅力。下面将详细的说明泛型算法swap和容器中的swap成员函数的使用!
swap的函数原型:
template <class T> void swap ( T& a, T& b ) { T c(a); a=b; b=c; }
vect中swap成员函数实现源码:
void swap(vector<_Tp, _Alloc>& __x) { __STD::swap(_M_start, __x._M_start); __STD::swap(_M_finish, __x._M_finish); __STD::swap(_M_end_of_storage, __x._M_end_of_storage); }
仅仅是交换了指向的首尾指针和容量指针
用法示例:
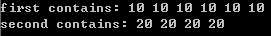
/******************************************************************* * Copyright (C) Jerry Jiang * * File Name : swap.cpp * Author : Jerry Jiang * Create Time : 2012-3-24 4:19:31 * Mail : jbiaojerry@gmail.com * Blog : http://blog.csdn.net/jerryjbiao * * Description : 简单的程序诠释C++ STL算法系列之十五 * 变易算法 : 元素交换swap * ******************************************************************/ #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #include <vector> #include <iterator> using namespace std; int main () { int x = 10, y = 20; // x:10 y:20 swap(x, y); // x:20 y:10 vector<int> first (4, x), second (6, y); // first:4x20 second:6x10 swap(first, second); // first:6x10 second:4x20 cout << "first contains:"; //使用一般的iterator方式输出first for (vector<int>::iterator it=first.begin(); it != first.end(); ++it) { cout << " " << *it; } cout << endl; cout << "second contains: "; //使用copy()来实现second的输出 copy(second.begin(), second.end(), ostream_iterator<int>(cout, " ")); cout << endl; return 0; }
在容器vector中,其内存占用的空间是只增不减的,比如说首先分配了10,000个字节,然后erase掉后面9,999个,则虽然有效元素只有一个,但是内存占用仍为10,000个。所有内存空间在vector析构时回收。
一般,我们都会通过vector中成员函数clear进行一些清除操作,但它清除的是所有的元素,使vector的大小减少至0,却不能减小vector占用的内存。要避免vector持有它不再需要的内存,这就需要一种方法来使得它从曾经的容量减少至它现在需要的容量,这样减少容量的方法被称为“收缩到合适(shrink to fit)”。(节选自《Effective STL》)如果做到“收缩到合适”呢,就要全仰仗“Swap大侠”啦,即通过如下代码进行释放过剩的容量:
vector< T >().swap(X)
示例:
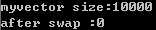
#include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #include <vector> #include <iterator> using namespace std; int main () { int x = 10; vector<int> myvector(10000, x); //这里打印仅仅是元素的个数不是内存大小 cout << "myvector size:" << myvector.size() << endl; //swap交换函数释放内存:vector<T>().swap(X); //T:int ; myvertor代表X vector<int>().swap(myvector); //两个输出仅用来表示swap前后的变化 cout << "after swap :" << myvector.size() << endl; return 0; }
swap交换技巧实现内存释放思想:vector()使用vector的默认构造函数建立临时vector对象,再在该临时对象上调用swap成员,swap调用之后对象myvector占用的空间就等于一个默认构造的对象的大小,临时对象就具有原来对象v的大小,而该临时对象随即就会被析构,从而其占用的空间也被释放。
std::vector<T>().swap(X) // 作用相当于: { std::vector<T> temp(X); temp.swap(X); }
以用类似的方法实现vector和string的适当收缩:
vector<int> vec(100000, 0); for (int i = 0; i < 100000-2; ++i) vec.pop_back(); cout << vec.capacity() <<endl; vector<int>(vec).swap(vec); cout << vec.capacity() << endl;
注意:并不是所有的STL容器的clear成员函数的行为都和vector一样。事实上,其他容器的clear成员函数都会释放其内存。比如另一个和vector类似的顺序容器deque。
标签:style bubuko inf second iterator include pop file 方式
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/xiaobingqianrui/p/9092051.html