标签:算法 用户 create 基本 如何 因子 bool home 默认值
|
Hive数据类型 |
Java数据类型 |
长度 |
例子 |
|
TINYINT |
byte |
1byte有符号整数 |
20 |
|
SMALINT |
short |
2byte有符号整数 |
20 |
|
INT |
int |
4byte有符号整数 |
20 |
|
BIGINT |
long |
8byte有符号整数 |
20 |
|
BOOLEAN |
boolean |
布尔类型,true或者false |
TRUE FALSE |
|
FLOAT |
float |
单精度浮点数 |
3.14159 |
|
DOUBLE |
double |
双精度浮点数 |
3.14159 |
|
STRING |
string |
字符系列。可以指定字符集。可以使用单引号或者双引号。 |
‘now is the time’ “for all good men” |
|
TIMESTAMP |
|
时间类型 |
|
|
BINARY |
|
字节数组 |
|
对于Hive的String类型相当于数据库的varchar类型,该类型是一个可变的字符串,不过它不能声明其中最多能存储多少个字符,理论上它可以存储2GB的字符数。
|
数据类型 |
描述 |
语法示例 |
|
STRUCT |
和c语言中的struct类似,都可以通过“点”符号访问元素内容。例如,如果某个列的数据类型是STRUCT{first STRING, last STRING},那么第1个元素可以通过字段.first来引用。 |
struct() |
|
MAP |
MAP是一组键-值对元组集合,使用数组表示法可以访问数据。例如,如果某个列的数据类型是MAP,其中键->值对是’first’->’John’和’last’->’Doe’,那么可以通过字段名[‘last’]获取最后一个元素 |
map() |
|
ARRAY |
数组是一组具有相同类型和名称的变量的集合。这些变量称为数组的元素,每个数组元素都有一个编号,编号从零开始。例如,数组值为[‘John’, ‘Doe’],那么第2个元素可以通过数组名[1]进行引用。 |
Array() |
Hive有三种复杂数据类型ARRAY、MAP 和 STRUCT。ARRAY和MAP与Java中的Array和Map类似,而STRUCT与C语言中的Struct类似,它封装了一个命名字段集合,复杂数据类型允许任意层次的嵌套。
案例实操
1)假设某表有如下一行,我们用JSON格式来表示其数据结构。在Hive下访问的格式为
|
{ "name": "songsong", "friends": ["bingbing" , "lili"] , //列表Array, "children": { //键值Map, "xiao song": 18 , "xiaoxiao song": 19 } "address": { //结构Struct, "street": "hui long guan" , "city": "beijing" } } |
2)基于上述数据结构,我们在Hive里创建对应的表,并导入数据。
创建本地测试文件test.txt
|
songsong,bingbing_lili,xiao song:18_xiaoxiao song:19,hui long guan_beijing yangyang,caicai_susu,xiao yang:18_xiaoxiao yang:19,chao yang_beijing |
注意,MAP,STRUCT和ARRAY里的元素间关系都可以用同一个字符表示,这里用“_”。
3)Hive上创建测试表test
|
create table test( name string, friends array<string>, children map<string, int>, address struct<street:string, city:string> ) row format delimited fields terminated by ‘,‘ collection items terminated by ‘_‘ map keys terminated by ‘:‘ lines terminated by ‘\n‘; |
字段解释:
row format delimited fields terminated by ‘,‘ -- 列分隔符
collection items terminated by ‘_‘ --MAP STRUCT 和 ARRAY 的分隔符(数据分割符号)
map keys terminated by ‘:‘ -- MAP中的key与value的分隔符
lines terminated by ‘\n‘; -- 行分隔符
4)导入文本数据到测试表
|
hive (default)> load data local inpath ‘/opt/module/datas/test.txt‘ into table test; |
5)访问三种集合列里的数据,以下分别是ARRAY,MAP,STRUCT的访问方式
|
hive (default)> select friends[1],children[‘xiao song‘],address.city from test where name="songsong"; OK _c0 _c1 city lili 18 beijing Time taken: 0.076 seconds, Fetched: 1 row(s) |
Hive的原子数据类型是可以进行隐式转换的,类似于Java的类型转换,例如某表达式使用INT类型,TINYINT会自动转换为INT类型,但是Hive不会进行反向转化,例如,某表达式使用TINYINT类型,INT不会自动转换为TINYINT类型,它会返回错误,除非使用CAST 操作。
1)隐式类型转换规则如下。
(1)任何整数类型都可以隐式地转换为一个范围更广的类型,如TINYINT可以转换成INT,INT可以转换成BIGINT。
(2)所有整数类型、FLOAT和STRING类型都可以隐式地转换成DOUBLE。
(3)TINYINT、SMALLINT、INT都可以转换为FLOAT。
(4)BOOLEAN类型不可以转换为任何其它的类型。
2)可以使用CAST操作显示进行数据类型转换,例如CAST(‘1‘ AS INT)将把字符串‘1‘ 转换成整数1;如果强制类型转换失败,如执行CAST(‘X‘ AS INT),表达式返回空值 NULL。
1)创建一个数据库,数据库在HDFS上的默认存储路径是/user/hive/warehouse/*.db。
hive (default)> create database db_hive;
2)避免要创建的数据库已经存在错误,增加if not exists判断。(标准写法)
FAILED: Execution Error, return code 1 from org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.exec.DDLTask. Database db_hive already exi
sts
hive (default)> create database if not exists db_hive;
3)创建一个数据库,指定数据库在HDFS上存放的位置
hive (default)> create database db_hive2 location ‘/db_hive2.db‘;
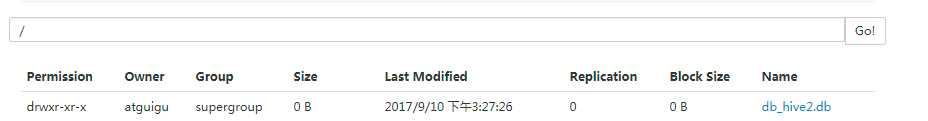

 用户可以使用ALTER DATABASE命令为某个数据库的DBPROPERTIES设置键-值对属性值,来描述这个数据库的属性信息。数据库的其他元数据信息都是不可更改的,包括数据库名和数据库所在的目录位置。
用户可以使用ALTER DATABASE命令为某个数据库的DBPROPERTIES设置键-值对属性值,来描述这个数据库的属性信息。数据库的其他元数据信息都是不可更改的,包括数据库名和数据库所在的目录位置。
hive (default)> alter database db_hive set dbproperties(‘createtime‘=‘20170830‘);
在mysql中查看修改结果
hive> desc database extended db_hive;
db_name comment location owner_name owner_type parameters
db_hive hdfs://hadoop102:8020/user/hive/warehouse/db_hive.db atguigu USER {createtime=20170830}
2.3.1 显示数据库
1)显示数据库
hive> show databases;
2)过滤显示查询的数据库
hive> show databases like ‘db_hive*‘;
hive> show databases like ‘db_hive*‘;
OK
db_hive
db_hive_1
2.3.2 查看数据库详情
1)显示数据库信息
hive> desc database db_hive;
OK
db_hive hdfs://hadoop102:8020/user/hive/warehouse/db_hive.db atguiguUSER
2)显示数据库详细信息,extended
hive> desc database extended db_hive;
OK
db_hive hdfs://hadoop102:8020/user/hive/warehouse/db_hive.db atguiguUSER
2.3.3 使用数据库
hive (default)> use db_hive;
1)删除空数据库
hive>drop database db_hive2;
2)如果删除的数据库不存在,最好采用 if exists判断数据库是否存在
hive> drop database db_hive2;
FAILED: SemanticException [Error 10072]: Database does not exist: db_hive
hive> drop database if exists db_hive2;
3)如果数据库不为空,可以采用cascade命令,强制删除
hive> drop database db_hive;
FAILED: Execution Error, return code 1 from org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.exec.DDLTask. InvalidOperationException(message:Database db_hive is not empty. One or more tables exist.)
hive> drop database db_hive cascade;
1)建表语法
|
CREATE [EXTERNAL] TABLE [IF NOT EXISTS] table_name [(col_name data_type [COMMENT col_comment], ...)] [COMMENT table_comment] [PARTITIONED BY (col_name data_type [COMMENT col_comment], ...)] [CLUSTERED BY (col_name, col_name, ...) [SORTED BY (col_name [ASC|DESC], ...)] INTO num_buckets BUCKETS] [ROW FORMAT row_format] [STORED AS file_format] [LOCATION hdfs_path] |
2)字段解释说明:
(1)CREATE TABLE 创建一个指定名字的表。如果相同名字的表已经存在,则抛出异常;用户可以用 IF NOT EXISTS 选项来忽略这个异常。
(2)EXTERNAL关键字可以让用户创建一个外部表,在建表的同时指定一个指向实际数据的路径(LOCATION),Hive创建内部表时,会将数据移动到数据仓库指向的路径;若创建外部表,仅记录数据所在的路径,不对数据的位置做任何改变。在删除表的时候,内部表的元数据和数据会被一起删除,而外部表只删除元数据,不删除数据。
(3)COMMENT:为表和列添加注释。
(4)PARTITIONED BY创建分区表
(5)CLUSTERED BY创建分桶表
(6)SORTED BY不常用
(7)ROW FORMAT
DELIMITED [FIELDS TERMINATED BY char] [COLLECTION ITEMS TERMINATED BY char]
[MAP KEYS TERMINATED BY char] [LINES TERMINATED BY char]
| SERDE serde_name [WITH SERDEPROPERTIES (property_name=property_value, property_name=property_value, ...)]
用户在建表的时候可以自定义SerDe或者使用自带的SerDe。如果没有指定ROW FORMAT 或者ROW FORMAT DELIMITED,将会使用自带的SerDe。在建表的时候,用户还需要为表指定列,用户在指定表的列的同时也会指定自定义的SerDe,Hive通过SerDe确定表的具体的列的数据。
(8)STORED AS 指定存储文件类型
常用的存储文件类型:SEQUENCEFILE(二进制序列文件)、TEXTFILE(文本)、RCFILE(列式存储格式文件)
如果文件数据是纯文本,可以使用STORED AS TEXTFILE。如果数据需要压缩,使用 STORED AS SEQUENCEFILE。
(9)LOCATION :指定表在HDFS上的存储位置。
(10)LIKE允许用户复制现有的表结构,但是不复制数据。
2.5.1 管理表
1)理论
默认创建的表都是所谓的管理表,有时也被称为内部表。因为这种表,Hive会(或多或少地)控制着数据的生命周期。Hive默认情况下会将这些表的数据存储在由配置项hive.metastore.warehouse.dir(例如,/user/hive/warehouse)所定义的目录的子目录下。 当我们删除一个管理表时,Hive也会删除这个表中数据。管理表不适合和其他工具共享数据。
2)案例实操
(1)普通创建表
create table if not exists student2(
id int, name string
)
row format delimited fields terminated by ‘\t‘
stored as textfile
location ‘/user/hive/warehouse/student2‘;
(2)根据查询结果创建表(查询的结果会添加到新创建的表中)
create table if not exists student3
as select id, name from student;
(3)根据已经存在的表结构创建表
create table if not exists student4 like student;
(4)查询表的类型
hive (default)> desc formatted student2;
Table Type: MANAGED_TABLE
2.5.2 外部表
1)理论
因为表是外部表,所有Hive并非认为其完全拥有这份数据。删除该表并不会删除掉这份数据,不过描述表的元数据信息会被删除掉。
2)管理表和外部表的使用场景:
每天将收集到的网站日志定期流入HDFS文本文件。在外部表(原始日志表)的基础上做大量的统计分析,用到的中间表、结果表使用内部表存储,数据通过SELECT+INSERT进入内部表。
3)案例实操
分别创建部门和员工外部表,并向表中导入数据。
(1)原始数据

10 ACCOUNTING 1700 20 RESEARCH 1800 30 SALES 1900 40 OPERATIONS 1700

7369 SMITH CLERK 7902 1980-12-17 800.00 20 7499 ALLEN SALESMAN 7698 1981-2-20 1600.00 300.00 30 7521 WARD SALESMAN 7698 1981-2-22 1250.00 500.00 30 7566 JONES MANAGER 7839 1981-4-2 2975.00 20 7654 MARTIN SALESMAN 7698 1981-9-28 1250.00 1400.00 30 7698 BLAKE MANAGER 7839 1981-5-1 2850.00 30 7782 CLARK MANAGER 7839 1981-6-9 2450.00 10 7788 SCOTT ANALYST 7566 1987-4-19 3000.00 20 7839 KING PRESIDENT 1981-11-17 5000.00 10 7844 TURNER SALESMAN 7698 1981-9-8 1500.00 0.00 30 7876 ADAMS CLERK 7788 1987-5-23 1100.00 20 7900 JAMES CLERK 7698 1981-12-3 950.00 30 7902 FORD ANALYST 7566 1981-12-3 3000.00 20 7934 MILLER CLERK 7782 1982-1-23 1300.00 10
(2)建表语句
创建部门表
create external table if not exists default.dept(
deptno int,
dname string,
loc int
)
row format delimited fields terminated by ‘\t‘;
创建员工表
create external table if not exists default.emp(
empno int,
ename string,
job string,
mgr int,
hiredate string,
sal double,
comm double,
deptno int)
row format delimited fields terminated by ‘\t‘;
(3)查看创建的表
hive (default)> show tables;
OK
tab_name
dept
emp
(4)向外部表中导入数据
导入数据
hive (default)> load data local inpath ‘/opt/module/datas/dept.txt‘ into table default.dept;
hive (default)> load data local inpath ‘/opt/module/datas/emp.txt‘ into table default.emp;
查询结果
hive (default)> select * from emp;
hive (default)> select * from dept;
(5)查看表格式化数据
hive (default)> desc formatted dept;
Table Type: EXTERNAL_TABLE
分区表实际上就是对应一个HDFS文件系统上的独立的文件夹,该文件夹下是该分区所有的数据文件。Hive中的分区就是分目录,把一个大的数据集根据业务需要分割成小的数据集。在查询时通过WHERE子句中的表达式选择查询所需要的指定的分区,这样的查询效率会提高很多。
2.6.1 分区表基本操作
1)引入分区表(需要根据日期对日志进行管理)
/user/hive/warehouse/log_partition/20170702/20170702.log
/user/hive/warehouse/log_partition/20170703/20170703.log
/user/hive/warehouse/log_partition/20170704/20170704.log
2)创建分区表语法
hive (default)> create table dept_partition(
deptno int, dname string, loc string
)
partitioned by (month string)
row format delimited fields terminated by ‘\t‘;
3)加载数据到分区表中
hive (default)> load data local inpath ‘/opt/module/datas/dept.txt‘ into table default.dept_partition partition(month=‘201709‘);
hive (default)> load data local inpath ‘/opt/module/datas/dept.txt‘ into table default.dept_partition partition(month=‘201708‘);
hive (default)> load data local inpath ‘/opt/module/datas/dept.txt‘ into table default.dept_partition partition(month=‘201707‘);
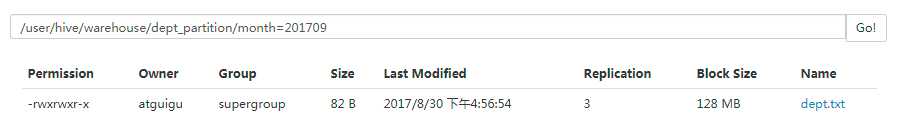

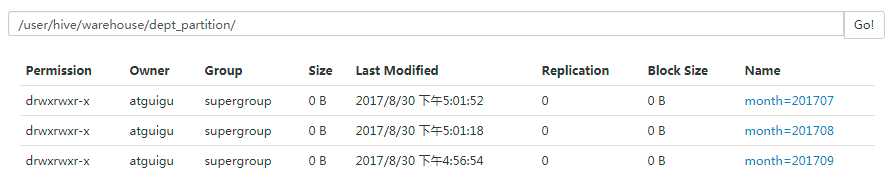

4)查询分区表中数据
单分区查询
hive (default)> select * from dept_partition where month=‘201709‘;
多分区联合查询
hive (default)> select * from dept_partition where month=‘201709‘
union
select * from dept_partition where month=‘201708‘
union
select * from dept_partition where month=‘201707‘;
_u3.deptno _u3.dname _u3.loc _u3.month
10 ACCOUNTING NEW YORK 201707
10 ACCOUNTING NEW YORK 201708
10 ACCOUNTING NEW YORK 201709
20 RESEARCH DALLAS 201707
20 RESEARCH DALLAS 201708
20 RESEARCH DALLAS 201709
30 SALES CHICAGO 201707
30 SALES CHICAGO 201708
30 SALES CHICAGO 201709
40 OPERATIONS BOSTON 201707
40 OPERATIONS BOSTON 201708
40 OPERATIONS BOSTON 201709
5)增加分区
创建单个分区
hive (default)> alter table dept_partition add partition(month=‘201706‘) ;
同时创建多个分区
hive (default)> alter table dept_partition add partition(month=‘201705‘) partition(month=‘201704‘);
6)删除分区
删除单个分区
hive (default)> alter table dept_partition drop partition (month=‘201704‘);
同时删除多个分区
hive (default)> alter table dept_partition drop partition (month=‘201705‘), partition (month=‘201706‘);
7)查看分区表有多少分区
hive>show partitions dept_partition;
8)查看分区表结构
hive>desc formatted dept_partition;
# Partition Information
# col_name data_type comment
month string
2.6.2 分区表注意事项
1)创建二级分区表
hive (default)> create table dept_partition2(
deptno int, dname string, loc string
)
partitioned by (month string, day string)
row format delimited fields terminated by ‘\t‘;2)正常的加载数据
(1)加载数据到二级分区表中
hive (default)> load data local inpath ‘/opt/module/datas/dept.txt‘ into table default.dept_partition2 partition(month=‘201709‘, day=‘13‘);
(2)查询分区数据
hive (default)> select * from dept_partition2 where month=‘201709‘ and day=‘13‘;
3)把数据直接上传到分区目录上,让分区表和数据产生关联的三种方式
(1)方式一:上传数据后修复
上传数据
hive (default)> dfs -mkdir -p /user/hive/warehouse/dept_partition2/month=201709/day=12;
hive (default)> dfs -put /opt/module/datas/dept.txt /user/hive/warehouse/dept_partition2/month=201709/day=12;
查询数据(老版本的hive,查询不到刚上传的数据)
hive (default)> select * from dept_partition2 where month=‘201709‘ and day=‘12‘;
执行修复命令
hive>msck repair table dept_partition2;
再次查询数据
hive (default)> select * from dept_partition2 where month=‘201709‘ and day=‘12‘;
(2)方式二:上传数据后添加分区
上传数据
hive (default)> dfs -mkdir -p /user/hive/warehouse/dept_partition2/month=201709/day=11;
hive (default)> dfs -put /opt/module/datas/dept.txt /user/hive/warehouse/dept_partition2/month=201709/day=11;
执行添加分区
hive (default)> alter table dept_partition2 add partition(month=‘201709‘, day=‘11‘);
查询数据
hive (default)> select * from dept_partition2 where month=‘201709‘ and day=‘11‘;
(3)方式三:上传数据后load数据到分区
创建目录
hive (default)> dfs -mkdir -p /user/hive/warehouse/dept_partition2/month=201709/day=10;
上传数据
hive (default)> load data local inpath ‘/opt/module/datas/dept.txt‘ into table dept_partition2 partition(month=‘201709‘,day=‘10‘);
查询数据
hive (default)> select * from dept_partition2 where month=‘201709‘ and day=‘10‘;
2.7.1 重命名表
1)语法
ALTER TABLE table_name RENAME TO new_table_name
(2)实操案例
hive (default)> alter table dept_partition2 rename to dept_partition3;
2.7.2 增加、修改和删除表分区
详见2.6.1分区表基本操作。
2.7.3 增加/修改/替换列信息
1)语法
更新列
ALTER TABLE table_name CHANGE [COLUMN] col_old_name col_new_name column_type [COMMENT col_comment] [FIRST|AFTER column_name]
增加和替换列
ALTER TABLE table_name ADD|REPLACE COLUMNS (col_name data_type [COMMENT col_comment], ...)
注:ADD是代表新增一字段,字段位置在所有列后面(partition列前),REPLACE则是表示替换表中所有字段。
2)实操案例
(1)查询表结构
hive>desc dept_partition;
(2)添加列
hive (default)> alter table dept_partition add columns(deptdesc string);
(3)查询表结构
hive>desc dept_partition;
(4)更新列
hive (default)> alter table dept_partition change column deptdesc desc int;
(5)查询表结构
hive>desc dept_partition;
(6)替换列
hive (default)> alter table dept_partition replace columns(deptno string, dname string, loc string);
(7)查询表结构
hive>desc dept_partition;
hive (default)> drop table dept_partition;
3.1.1 向表中装载数据(Load)
1)语法
hive>load data [local] inpath ‘/opt/module/datas/student.txt‘ [overwrite] into table student [partition (partcol1=val1,…)];
(1)load data:表示加载数据
(2)local:表示从本地加载数据到hive表;否则从HDFS加载数据到hive表
(3)inpath:表示加载数据的路径
(4)into table:表示加载到哪张表
(5)student:表示具体的表
(6)overwrite:表示覆盖表中已有数据,否则表示追加
(7)partition:表示上传到指定分区
2)实操案例
(0)创建一张表
hive (default)> create table student(id string, name string) row format delimited fields terminated by ‘\t‘;
(1)加载本地文件到hive
hive (default)> load data local inpath ‘/opt/module/datas/student.txt‘ into table default.student;
(2)加载HDFS文件到hive中
上传文件到HDFS
hive (default)> dfs -put /opt/module/datas/student.txt /user/atguigu/hive;
加载HDFS上数据
hive (default)>load data inpath ‘/user/atguigu/hive/student.txt‘ into table default.student;
(3)加载数据覆盖表中已有的数据
上传文件到HDFS
hive (default)> dfs -put /opt/module/datas/student.txt /user/atguigu/hive;
加载数据覆盖表中已有的数据
hive (default)>load data inpath ‘/user/atguigu/hive/student.txt‘ overwrite into table default.student;
3.1.2 通过查询语句向表中插入数据(Insert)
1)创建一张分区表
hive (default)> create table student(id string, name string) partitioned by (month string) row format delimited fields terminated by ‘\t‘;
2)基本插入数据
hive (default)> insert into table student partition(month=‘201709‘) values(‘1004‘,‘wangwu‘);
3)基本模式插入(根据单张表查询结果)
hive (default)> insert overwrite table student partition(month=‘201708‘)
select id, name from student where month=‘201709‘;
4)多插入模式(根据多张表查询结果)
hive (default)> from student
insert overwrite table student partition(month=‘201707‘)
select id, name where month=‘201709‘
insert overwrite table student partition(month=‘201706‘)
select id, name where month=‘201709‘;
3.1.3 查询语句中创建表并加载数据(As Select)
根据查询结果创建表(查询的结果会添加到新创建的表中)
create table if not exists student3
as select id, name from student;
3.1.4 创建表时通过Location指定加载数据路径
1)创建表,并指定在hdfs上的位置
hive (default)> create table if not exists student5(
id int, name string
)
row format delimited fields terminated by ‘\t‘
location ‘/user/hive/warehouse/student5‘;
2)上传数据到hdfs上
hive (default)> dfs -put /opt/module/datas/student.txt /user/hive/warehouse/student5;
3)查询数据
hive (default)> select * from student5;
3.1.5 Import数据到指定Hive表中
先用export导出后,再将数据导入。
hive (default)> import table student2 partition(month=‘201709‘) from ‘/user/hive/warehouse/export/student‘;
3.2.1 Insert导出
1)将查询的结果导出到本地
hive (default)> insert overwrite local directory ‘/opt/module/datas/export/student‘
select * from student;
2)将查询的结果格式化导出到本地
hive (default)> insert overwrite local directory ‘/opt/module/datas/export/student1‘
ROW FORMAT DELIMITED FIELDS TERMINATED BY ‘\t‘ COLLECTION ITEMS TERMINATED BY ‘\n‘
select * from student;
3)将查询的结果导出到HDFS上(没有local)
hive (default)> insert overwrite directory ‘/user/atguigu/hive/warehouse/student2‘
ROW FORMAT DELIMITED FIELDS TERMINATED BY ‘\t‘ COLLECTION ITEMS TERMINATED BY ‘\n‘
select * from student;
3.2.2 Hadoop命令导出到本地
hive (default)> dfs -get /user/hive/warehouse/student/month=201709/000000_0 /opt/module/datas/export/student3.txt;
3.2.3 Hive Shell 命令导出
bin/hive -e ‘select * from default.student;‘ > /opt/module/datas/export/student4.txt;
3.2.4 Export导出到HDFS上
hive (default)> export table default.student to ‘/user/hive/warehouse/export/student‘;
3.2.5 Sqoop导出
hive (default)> truncate table student;
注意:Truncate只能删除管理表,不能删除外部表中数据
备注:官网地址:https://cwiki.apache.org/confluence/display/Hive/LanguageManual+Select

[WITH CommonTableExpression (, CommonTableExpression)*] (Note: Only available starting with Hive 0.13.0) SELECT [ALL | DISTINCT] select_expr, select_expr, ... FROM table_reference [WHERE where_condition] [GROUP BY col_list] [ORDER BY col_list] [CLUSTER BY col_list | [DISTRIBUTE BY col_list] [SORT BY col_list] ] [LIMIT number]
4.1.1 全表和特定字段查询
1)全表查询
hive (default)> select * from emp;
2)选择特定列查询
hive (default)> select empno, ename from emp;
注意:
(1)SQL 语言大小写不敏感。
(2)SQL 可以写在一行或者多行
(3)关键字不能被缩写也不能分行
(4)各子句一般要分行写。
(5)使用缩进提高语句的可读性。
4.1.2 列别名
1)重命名一个列。
2)便于计算。
3)紧跟列名,也可以在列名和别名之间加入关键字‘AS’
4)案例实操
(1)查询名称和部门
hive (default)> select ename AS name, deptno dn from emp;
4.1.3 算术运算符
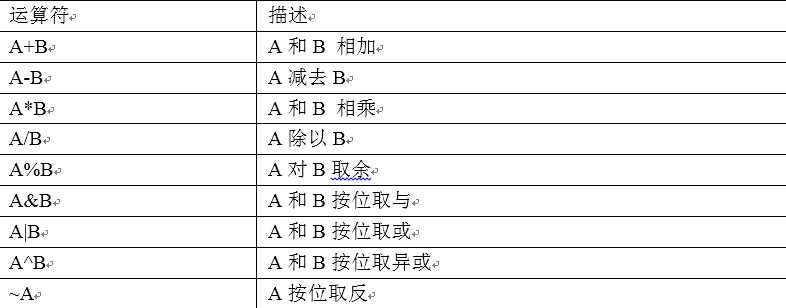
案例实操
hive (default)> select sal +1 from emp;
4.1.4 常用函数
1)求总行数(count)
hive (default)> select count(*) cnt from emp;
2)求工资的最大值(max)
hive (default)> select max(sal) max_sal from emp;
3)求工资的最小值(min)
hive (default)> select min(sal) min_sal from emp;
4)求工资的总和(sum)
hive (default)> select sum(sal) sum_sal from emp;
5)求工资的平均值(avg)
hive (default)> select avg(sal) avg_sal from emp;
4.1.5 Limit语句
典型的查询会返回多行数据。LIMIT子句用于限制返回的行数。
hive (default)> select * from emp limit 5;
介绍
1)使用WHERE 子句,将不满足条件的行过滤掉。
2)WHERE 子句紧随 FROM 子句。
3)案例实操
查询出薪水大于1000的所有员工
hive (default)> select * from emp where sal >1000;
4.2.1 比较运算符(Between/In/ Is Null)
1)下面表中描述了谓词操作符,这些操作符同样可以用于JOIN…ON和HAVING语句中。
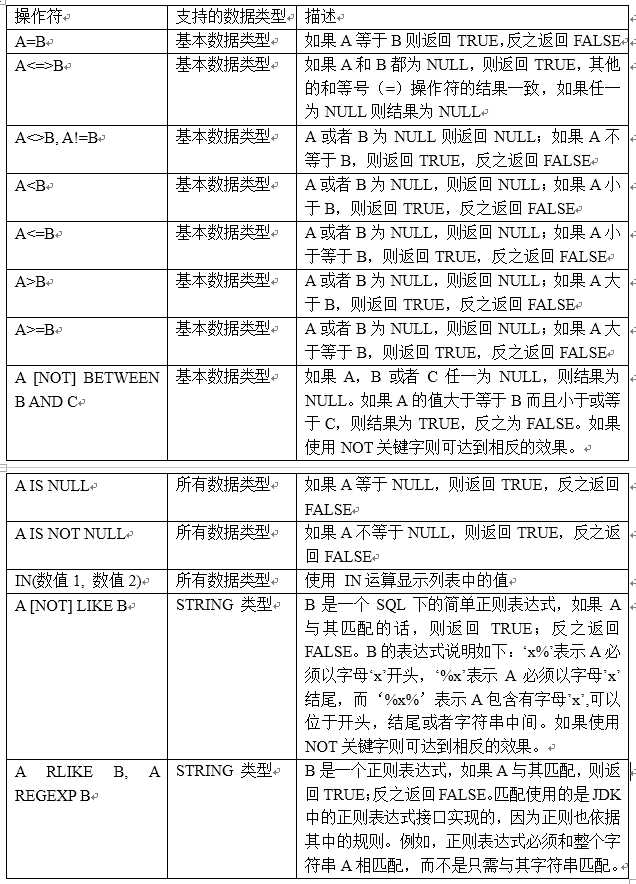
2)案例实操
(1)查询出薪水等于5000的所有员工
hive (default)> select * from emp where sal =5000;
(2)查询工资在500到1000的员工信息
hive (default)> select * from emp where sal between 500 and 1000;
(3)查询comm为空的所有员工信息
hive (default)> select * from emp where comm is null;
(4)查询工资是1500和5000的员工信息
hive (default)> select * from emp where sal IN (1500, 5000);
4.2.2 Like和RLike
1)使用LIKE运算选择类似的值
2)选择条件可以包含字符或数字:
% 代表零个或多个字符(任意个字符)。
_ 代表一个字符。
3)RLIKE子句是Hive中这个功能的一个扩展,其可以通过Java的正则表达式这个更强大的语言来指定匹配条件。
4)案例实操
(1)查找以2开头薪水的员工信息
hive (default)> select * from emp where sal LIKE ‘2%‘;
(2)查找第二个数值为2的薪水的员工信息
hive (default)> select * from emp where sal LIKE ‘_2%‘;
3)查找薪水中含有2的员工信息
hive (default)> select * from emp where sal RLIKE ‘[2]‘;
4.2.3 逻辑运算符(And/Or/Not)
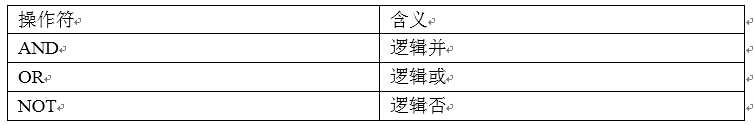
案例实操
(1)查询薪水大于1000,部门是30
hive (default)> select * from emp where sal>1000 and deptno=30;
(2)查询薪水大于1000,或者部门是30
hive (default)> select * from emp where sal>1000 or deptno=30;
(3)查询除了20部门和30部门以外的员工信息
hive (default)> select * from emp where deptno not IN(30, 20);
4.3.1 Group By语句
GROUP BY语句通常会和聚合函数一起使用,按照一个或者多个列队结果进行分组,然后对每个组执行聚合操作。
案例实操:
(1)计算emp表每个部门的平均工资
hive (default)> select t.deptno, avg(t.sal) avg_sal from emp t group by t.deptno;
(2)计算emp每个部门中每个岗位的最高薪水
hive (default)> select t.deptno, t.job, max(t.sal) max_sal from emp t group by t.deptno, t.job;
4.3.2 Having语句
1)having与where不同点
(1)where针对表中的列发挥作用,查询数据;having针对查询结果中的列发挥作用,筛选数据。
(2)where后面不能写分组函数,而having后面可以使用分组函数。
(3)having只用于group by分组统计语句。
2)案例实操:
(1)求每个部门的平均薪水大于2000的部门
求每个部门的平均工资
hive (default)> select deptno, avg(sal) from emp group by deptno;
求每个部门的平均薪水大于2000的部门
hive (default)> select deptno, avg(sal) avg_sal from emp group by deptno having avg_sal > 2000;
4.4.1 等值Join
Hive支持通常的SQL JOIN语句,但是只支持等值连接,不支持非等值连接。
案例操作
(1)根据员工表和部门表中的部门编号相等,查询员工编号、员工名称和部门编号;
hive (default)> select e.empno, e.ename, d.deptno, d.dname from emp e join dept d on e.deptno = d.deptno;
4.4.2 表的别名
1)好处
(1)使用别名可以简化查询。
(2)使用表名前缀可以提高执行效率。
2)案例实操
合并员工表和部门表
hive (default)> select e.empno, e.ename, d.deptno from emp e join dept d on e.deptno = d.deptno;
4.4.3 内连接
内连接:只有进行连接的两个表中都存在与连接条件相匹配的数据才会被保留下来。
hive (default)> select e.empno, e.ename, d.deptno from emp e join dept d on e.deptno = d.deptno;
4.4.4 左外连接
左外连接:JOIN操作符左边表中符合WHERE子句的所有记录将会被返回。
hive (default)> select e.empno, e.ename, d.deptno from emp e left join dept d on e.deptno = d.deptno;
4.4.5 右外连接
右外连接:JOIN操作符右边表中符合WHERE子句的所有记录将会被返回。
hive (default)> select e.empno, e.ename, d.deptno from emp e right join dept d on e.deptno = d.deptno;
4.4.6 满外链接
满外连接:将会返回所有表中符合WHERE语句条件的所有记录。如果任一表的指定字段没有符合条件的值的话,那么就使用NULL值替代。
hive (default)> select e.empno, e.ename, d.deptno from emp e full join dept d on e.deptno = d.deptno;
4.4.7 多表连接
注意:连接 n个表,至少需要n-1个连接条件。例如:连接三个表,至少需要两个连接条件。
0)数据准备

1700 Beijing 1800 London 1900 Tokyo
1)创建位置表
create table if not exists default.location(
loc int,
loc_name string
)
row format delimited fields terminated by ‘\t‘;
2)导入数据
hive (default)> load data local inpath ‘/opt/module/datas/location.txt‘ into table default.location;
3)多表连接查询
hive (default)>SELECT e.ename, d.deptno, l. loc_name
FROM emp e
JOIN dept d
ON d.deptno = e.deptno
JOIN location l
ON d.loc = l.loc;
大多数情况下,Hive会对每对JOIN连接对象启动一个MapReduce任务。本例中会首先启动一个MapReduce job对表e和表d进行连接操作,然后会再启动一个MapReduce job将第一个MapReduce job的输出和表l;进行连接操作。
注意:为什么不是表d和表l先进行连接操作呢?这是因为Hive总是按照从左到右的顺序执行的。
4.4.8 笛卡尔积 JOIN
1)笛卡尔集会在下面条件下产生:
(1)省略连接条件
(2)连接条件无效
(3)所有表中的所有行互相连接
2)案例实操
hive (default)> select empno, deptno from emp, dept;
FAILED: SemanticException Column deptno Found in more than One Tables/Subqueries
4.5.1 全局排序(Order By)
Order By:全局排序,一个MapReduce
1)使用 ORDER BY 子句排序
ASC(ascend): 升序(默认)
DESC(descend): 降序
2)ORDER BY 子句在SELECT语句的结尾。
3)案例实操
(1)查询员工信息按工资升序排列
hive (default)> select * from emp order by sal;
(2)查询员工信息按工资降序排列
hive (default)> select * from emp order by sal desc;
4.5.2 按照别名排序
按照员工薪水的2倍排序
hive (default)> select ename, sal*2 twosal from emp order by twosal;
4.5.3 多个列排序
按照部门和工资升序排序
hive (default)> select ename, deptno, sal from emp order by deptno, sal ;
4.5.4 每个MapReduce内部排序(Sort By)
Sort By:每个MapReduce内部进行排序,对全局结果集来说不是排序
1)设置reduce个数
hive (default)> set mapreduce.job.reduces=3;
2)查看设置reduce个数
hive (default)> set mapreduce.job.reduces;
3)根据部门降序查看员工信息
hive (default)> select * from emp sort by empno desc;
4)将查询结果导入到文件中(按照部门编号降序排序)
hive (default)> insert overwrite local directory ‘/opt/module/datas/sortby-result‘ select * from emp sort by deptno desc;
4.5.5 分区排序(Distribute By)
Distribute By:类似MR中partition,进行分区,结合sort by使用。
注意,Hive要求DISTRIBUTE BY语句要写在SORT BY语句之前。
案例实操:
(1)先按照部门编号分区,再按照员工编号降序排序。
hive (default)> insert overwrite local directory ‘/opt/module/datas/distby-desc‘ select * from emp distribute by deptno sort by empno desc;
4.5.6 Cluster By
当distribute by和sorts by字段相同时,可以使用cluster by方式。
cluster by除了具有distribute by的功能外还兼具sort by的功能。但是排序只能是倒序排序,不能指定排序规则为ASC或者DESC。
1)以下两种写法等价
select * from emp cluster by deptno;
select * from emp distribute by deptno sort by deptno;
注意:按照部门编号分区,不一定就是固定死的数值,可以是20号和30号部门分到一个分区里面去。
4.6.1 分桶表数据存储
分区针对的是数据的存储路径;分桶针对的是数据文件。
分区提供一个隔离数据和优化查询的便利方式。不过,并非所有的数据集都可形成合理的分区,特别是之前所提到过的要确定合适的划分大小这个疑虑。
分桶是将数据集分解成更容易管理的若干部分的另一个技术。
1)先创建分桶表,通过直接导入数据文件的方式
(0)数据准备

1001 ss1 1002 ss2 1003 ss3 1004 ss4 1005 ss5 1006 ss6 1007 ss7 1008 ss8 1009 ss9 1010 ss10 1011 ss11 1012 ss12 1013 ss13 1014 ss14 1015 ss15 1016 ss16
(1)创建分桶表
create table stu_buck(id int, name string)
clustered by(id)
into 4 buckets
row format delimited fields terminated by ‘\t‘
(2)查看表结构
hive (default)> desc formatted stu_buck;
Num Buckets: 4
(3)导入数据到分桶表中
hive (default)> load data local inpath ‘/opt/module/datas/student.txt‘ into table stu_buck;
(4)查看创建的分桶表中是否分成4个桶
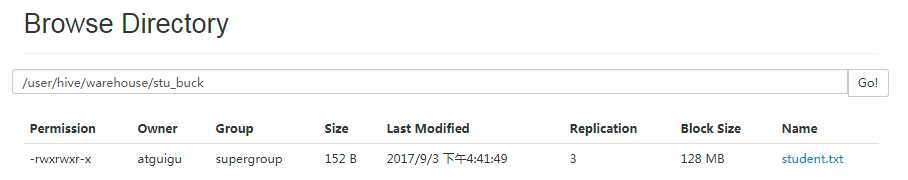
发现并没有分成4个桶。是什么原因呢?
2)创建分桶表时,数据通过子查询的方式导入
(1)先建一个普通的stu表
create table stu(id int, name string)
row format delimited fields terminated by ‘\t‘;
(2)向普通的stu表中导入数据
load data local inpath ‘/opt/module/datas/student.txt‘ into table stu;
(3)清空stu_buck表中数据
truncate table stu_buck;
select * from stu_buck;
(4)导入数据到分桶表,通过子查询的方式
insert into table stu_buck
select id, name from stu cluster by(id);
(5)发现还是只有一个分桶
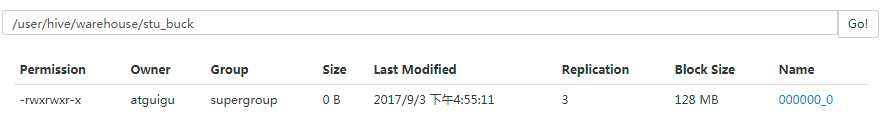
(6)需要设置一个属性
hive (default)>set hive.enforce.bucketing=true;
hive (default)> set mapreduce.job.reduces=-1;
hive (default)>insert into table stu_buck
select id, name from stu cluster by(id);
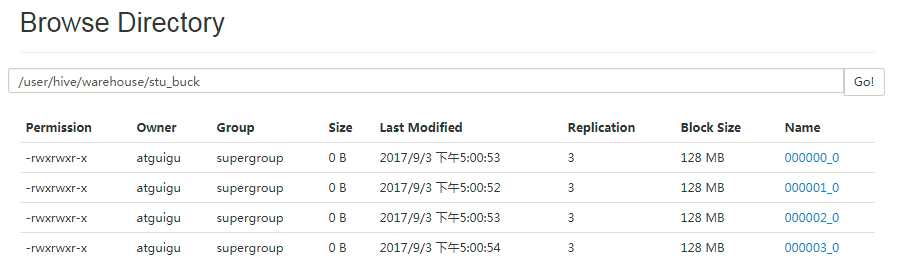
 (7)查询分桶的数据
(7)查询分桶的数据
hive (default)> select * from stu_buck;
OK

stu_buck.id stu_buck.name 1001 ss1 1005 ss5 1009 ss9 1012 ss12 1016 ss16 1002 ss2 1006 ss6 1013 ss13 1003 ss3 1007 ss7 1010 ss10 1014 ss14 1004 ss4 1008 ss8 1011 ss11 1015 ss15
4.6.2 分桶抽样查询
对于非常大的数据集,有时用户需要使用的是一个具有代表性的查询结果而不是全部结果。Hive可以通过对表进行抽样来满足这个需求。
查询6.6.1中表stu_buck的数据。
hive (default)> select * from stu_buck TABLESAMPLE(bucket 1 out of 4 on id);
注:tablesample是抽样语句,语法:TABLESAMPLE(BUCKET x OUT OF y) 。
y必须是table总bucket数的倍数或者因子。hive根据y的大小,决定抽样的比例。例如,table总共分了4份,当y=2时,抽取(4/2=)2个bucket的数据,当y=8时,抽取(4/8=)1/2个bucket的数据。
x表示从哪个bucket开始抽取。例如,table总bucket数为4,tablesample(bucket 4 out of 4),表示总共抽取(4/4=)1个bucket的数据,抽取第4个bucket的数据。
注意:x的值必须小于等于y的值,否则
FAILED: SemanticException [Error 10061]: Numerator should not be bigger than denominator in sample clause for table stu_buck
4.6.3 数据块抽样
Hive提供了另外一种按照百分比进行抽样的方式,这种事基于行数的,按照输入路径下的数据块百分比进行的抽样。
hive (default)> select * from stu tablesample(0.1 percent);
提示:这种抽样方式不一定适用于所有的文件格式。另外,这种抽样的最小抽样单元是一个HDFS数据块。因此,如果表的数据大小小于普通的块大小128M的话,那么将会返回所有行。
1)查看系统自带的函数
hive> show functions;
2)显示自带的函数的用法
hive> desc function upper;
3)详细显示自带的函数的用法
hive> desc function extended upper;
1)Hive 自带了一些函数,比如:max/min等,但是数量有限,自己可以通过自定义UDF来方便的扩展。
2)当Hive提供的内置函数无法满足你的业务处理需要时,此时就可以考虑使用用户自定义函数(UDF:user-defined function)。
3)根据用户自定义函数类别分为以下三种:
(1)UDF(User-Defined-Function)
一进一出
(2)UDAF(User-Defined Aggregation Function)
聚集函数,多进一出
类似于:count/max/min
(3)UDTF(User-Defined Table-Generating Functions)
一进多出
如lateral view explore()
4)官方文档地址
https://cwiki.apache.org/confluence/display/Hive/HivePlugins
5)编程步骤:
(1)继承org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.UDF
(2)需要实现evaluate函数;evaluate函数支持重载;
6)注意事项
(1)UDF必须要有返回类型,可以返回null,但是返回类型不能为void;
(2)UDF中常用Text/LongWritable等类型,不推荐使用java类型;
1)创建一个java工程,并创建一个lib文件夹
2)将hive的jar包解压后,将apache-hive-1.2.1-bin\lib文件下的jar包都拷贝到java工程中。
3)创建一个类
|
package com.atguigu.hive; import org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.exec.UDF;
public class Lower extends UDF {
public String convert(final String s) {
if (s == null) { return null; }
return s.toString().toLowerCase(); } } |
4)打成jar包上传到服务器/opt/module/jars/udf.jar
5)将jar包添加到hive的classpath
hive (default)> add jar /opt/module/jars/udf.jar;
6)创建临时函数与开发好的java class关联
hive (default)> create temporary function my_lower as "com.atguigu.hive.Lower";
7)即可在hql中使用自定义的函数strip
hive (default)> select ename, my_lower(ename) lowername from emp;
bin/hive -help usage: hive -d,--define <key=value> Variable subsitution to apply to hive commands. e.g. -d A=B or --define A=B --database <databasename> Specify the database to use -e <quoted-query-string> SQL from command line -f <filename> SQL from files -H,--help Print help information --hiveconf <property=value> Use value for given property --hivevar <key=value> Variable subsitution to apply to hive commands. e.g. --hivevar A=B -i <filename> Initialization SQL file -S,--silent Silent mode in interactive shell -v,--verbose Verbose mode (echo executed SQL to the console)
1)“-e”不进入hive的交互窗口执行sql语句
bin/hive -e "select id from default.student;"
2)“-f”执行脚本中sql语句
(1)在/opt/module/datas目录下创建hivef.sql文件
touch hivef.sql
文件中写入正确的sql语句
select *from student;
(2)执行文件中的sql语句
bin/hive -f /opt/module/datas/hivef.sql
(3)执行文件中的sql语句并将结果写入文件中
bin/hive -f /opt/module/datas/hivef.sql > /opt/module/datas/hive_result.txt
1)退出hive窗口:
在新版的oracle中没区别了,在以前的版本是有的:
exit:先隐性提交数据,再退出; quit:不提交数据,退出;hive(default)>exit;
hive(default)>quit;
2)在hive cli命令窗口中如何查看hdfs文件系统
hive(default)>dfs -ls /;
3)在hive cli命令窗口中如何查看hdfs本地系统
hive(default)>! ls /opt/module/datas;
4)查看在hive中输入的所有历史命令
(1)进入到当前用户的根目录/root或/home/atguigu
(2)查看. hivehistory文件
cat .hivehistory
7.1.1 前期准备工作
1)CentOS联网
[root@hadoop101 桌面]# vi /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0
|
DEVICE=eth0 HWADDR=00:0c:29:ca:6e:ec TYPE=Ethernet UUID=9e008bf7-44f6-4e72-8ead-71b8ea7a9b5b ONBOOT=yes NM_CONTROLLED=yes BOOTPROTO=dhcp |
[root@hadoop101 桌面]# service network restart
注意:采用root角色编译,减少文件夹权限出现问题
2)jar包准备(hadoop源码、JDK7 、 maven、 ant 、protobuf)
(1)hadoop-2.7.2-src.tar.gz
(2)jdk-7u79-linux-x64.gz
(3)snappy-1.1.3.tar.gz
(4)apache-maven-3.0.5-bin.tar.gz
(5)protobuf-2.5.0.tar.gz
7.1.2 jar包安装
0)注意:所有操作必须在root用户下完成
1)JDK解压、配置环境变量 JAVA_HOME和PATH,验证java-version(如下都需要验证是否配置成功)
[root@hadoop101 software] # tar -zxf jdk-7u79-linux-x64.gz -C /opt/module/
[root@hadoop101 software]# vi /etc/profile
|
#JAVA_HOME export JAVA_HOME=/opt/module/jdk1.7.0_79 export PATH=$PATH:$JAVA_HOME/bin |
[root@hadoop101 software]#source /etc/profile
验证命令:java -version
2)Maven解压、配置 MAVEN_HOME和PATH。
[root@hadoop101 software]# tar -zxvf apache-maven-3.0.5-bin.tar.gz -C /opt/module/
[root@hadoop101 apache-maven-3.0.5]# vi /etc/profile
|
#MAVEN_HOME export MAVEN_HOME=/opt/module/apache-maven-3.0.5 export PATH=$PATH:$MAVEN_HOME/bin |
[root@hadoop101 software]#source /etc/profile
验证命令:mvn -version
7.1.3 编译源码
1)准备编译环境
[root@hadoop101 software]# yum install svn
[root@hadoop101 software]# yum install autoconf automake libtool cmake
[root@hadoop101 software]# yum install ncurses-devel
[root@hadoop101 software]# yum install openssl-devel
[root@hadoop101 software]# yum install gcc*
2)编译安装snappy
[root@hadoop101 software]# tar -zxvf snappy-1.1.3.tar.gz -C /opt/module/
[root@hadoop101 module]# cd snappy-1.1.3/
[root@hadoop101 snappy-1.1.3]# ./configure
[root@hadoop101 snappy-1.1.3]# make
[root@hadoop101 snappy-1.1.3]# make install
# 查看snappy库文件
[root@hadoop101 snappy-1.1.3]# ls -lh /usr/local/lib |grep snappy
3)编译安装protobuf
[root@hadoop101 software]# tar -zxvf protobuf-2.5.0.tar.gz -C /opt/module/
[root@hadoop101 module]# cd protobuf-2.5.0/
[root@hadoop101 protobuf-2.5.0]# ./configure
[root@hadoop101 protobuf-2.5.0]# make
[root@hadoop101 protobuf-2.5.0]# make install
# 查看protobuf版本以测试是否安装成功
[root@hadoop101 protobuf-2.5.0]# protoc --version
4)编译hadoop native
[root@hadoop101 software]# tar -zxvf hadoop-2.7.2-src.tar.gz
[root@hadoop101 software]# cd hadoop-2.7.2-src/
[root@hadoop101 software]# mvn clean package -DskipTests -Pdist,native -Dtar -Dsnappy.lib=/usr/local/lib -Dbundle.snappy
执行成功后,/opt/software/hadoop-2.7.2-src/hadoop-dist/target/hadoop-2.7.2.tar.gz即为新生成的支持snappy压缩的二进制安装包。
7.2.1 MR支持的压缩编码
|
压缩格式 |
工具 |
算法 |
文件扩展名 |
是否可切分 |
|
DEFAULT |
无 |
DEFAULT |
.deflate |
否 |
|
Gzip |
gzip |
DEFAULT |
.gz |
否 |
|
bzip2 |
bzip2 |
bzip2 |
.bz2 |
是 |
|
LZO |
lzop |
LZO |
.lzo |
否 |
|
LZ4 |
无 |
LZ4 |
.lz4 |
否 |
|
Snappy |
无 |
Snappy |
.snappy |
否 |
为了支持多种压缩/解压缩算法,Hadoop引入了编码/解码器,如下表所示
|
压缩格式 |
对应的编码/解码器 |
|
DEFLATE |
org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.DefaultCodec |
|
gzip |
org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.GzipCodec |
|
bzip2 |
org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.BZip2Codec |
|
LZO |
com.hadoop.compression.lzo.LzopCodec |
|
LZ4 |
org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.Lz4Codec |
|
Snappy |
org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.SnappyCodec |
压缩性能的比较
|
压缩算法 |
原始文件大小 |
压缩文件大小 |
压缩速度 |
解压速度 |
|
gzip |
8.3GB |
1.8GB |
17.5MB/s |
58MB/s |
|
bzip2 |
8.3GB |
1.1GB |
2.4MB/s |
9.5MB/s |
|
LZO |
8.3GB |
2.9GB |
49.3MB/s |
74.6MB/s |
http://google.github.io/snappy/
On a single core of a Core i7 processor in 64-bit mode, Snappy compresses at about 250 MB/sec or more and decompresses at about 500 MB/sec or more.
7.2.2 压缩配置参数
要在Hadoop中启用压缩,可以配置如下参数(mapred-site.xml文件中):
|
参数 |
默认值 |
阶段 |
建议 |
|
io.compression.codecs (在core-site.xml中配置) |
org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.DefaultCodec, org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.GzipCodec, org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.BZip2Codec, org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.Lz4Codec |
输入压缩 |
Hadoop使用文件扩展名判断是否支持某种编解码器 |
|
mapreduce.map.output.compress |
false |
mapper输出 |
这个参数设为true启用压缩 |
|
mapreduce.map.output.compress.codec |
org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.DefaultCodec |
mapper输出 |
使用LZO、LZ4或snappy编解码器在此阶段压缩数据 |
|
mapreduce.output.fileoutputformat.compress |
false |
reducer输出 |
这个参数设为true启用压缩 |
|
mapreduce.output.fileoutputformat.compress.codec |
org.apache.hadoop.io.compress. DefaultCodec |
reducer输出 |
使用标准工具或者编解码器,如gzip和bzip2 |
|
mapreduce.output.fileoutputformat.compress.type |
RECORD |
reducer输出 |
SequenceFile输出使用的压缩类型:NONE和BLOCK |
开启map输出阶段压缩可以减少job中map和Reduce task间数据传输量。具体配置如下:
案例实操:
1)开启hive中间传输数据压缩功能
hive (default)>set hive.exec.compress.intermediate=true;
2)开启mapreduce中map输出压缩功能
hive (default)>set mapreduce.map.output.compress=true;
3)设置mapreduce中map输出数据的压缩方式
hive (default)>set mapreduce.map.output.compress.codec= org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.SnappyCodec;
4)执行查询语句
hive (default)> select count(ename) name from emp;
当Hive将输出写入到表中时,输出内容同样可以进行压缩。属性hive.exec.compress.output控制着这个功能。用户可能需要保持默认设置文件中的默认值false,这样默认的输出就是非压缩的纯文本文件了。用户可以通过在查询语句或执行脚本中设置这个值为true,来开启输出结果压缩功能。
案例实操:
1)开启hive最终输出数据压缩功能
hive (default)>set hive.exec.compress.output=true;
2)开启mapreduce最终输出数据压缩
hive (default)>set mapreduce.output.fileoutputformat.compress=true;
3)设置mapreduce最终数据输出压缩方式
hive (default)> set mapreduce.output.fileoutputformat.compress.codec = org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.SnappyCodec;
4)设置mapreduce最终数据输出压缩为块压缩
hive (default)> set mapreduce.output.fileoutputformat.compress.type=BLOCK;
5)测试一下输出结果是否是压缩文件
hive (default)> insert overwrite local directory ‘/opt/module/datas/distribute-result‘ select * from emp distribute by deptno sort by empno desc;
Hive支持的存储数的格式主要有:TEXTFILE 、SEQUENCEFILE、ORC、PARQUET。
7.5.1 列式存储和行式存储
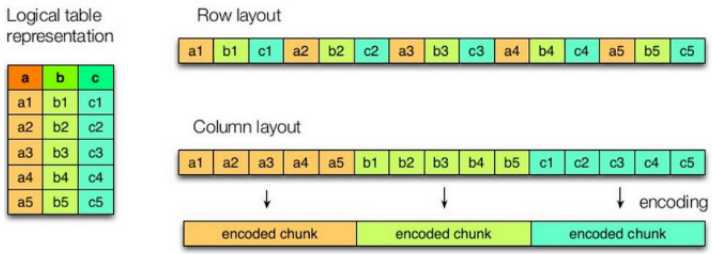
上图左边为逻辑表,右边第一个为行式存储,第二个为列式存储。
行存储的特点: 查询满足条件的一整行数据的时候,列存储则需要去每个聚集的字段找到对应的每个列的值,行存储只需要找到其中一个值,其余的值都在相邻地方,所以此时行存储查询的速度更快。
列存储的特点: 因为每个字段的数据聚集存储,在查询只需要少数几个字段的时候,能大大减少读取的数据量;每个字段的数据类型一定是相同的,列式存储可以针对性的设计更好的设计压缩算法。
TEXTFILE和SEQUENCEFILE的存储格式都是基于行存储的;
ORC和PARQUET是基于列式存储的。
7.5.2 TEXTFILE格式
默认格式,数据不做压缩,磁盘开销大,数据解析开销大。可结合Gzip、Bzip2使用(系统自动检查,执行查询时自动解压),但使用这种方式,hive不会对数据进行切分,从而无法对数据进行并行操作。
7.5.3 ORC格式
Orc (Optimized Row Columnar)是hive 0.11版里引入的新的存储格式。
可以看到每个Orc文件由1个或多个stripe组成,每个stripe250MB大小,这个Stripe实际相当于RowGroup概念,不过大小由4MB->250MB,这样应该能提升顺序读的吞吐率。每个Stripe里有三部分组成,分别是Index Data,Row Data,Stripe Footer:
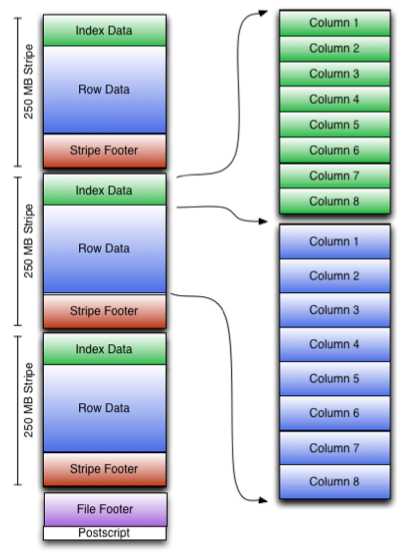
1)Index Data:一个轻量级的index,默认是每隔1W行做一个索引。这里做的索引应该只是记录某行的各字段在Row Data中的offset。
2)Row Data:存的是具体的数据,先取部分行,然后对这些行按列进行存储。对每个列进行了编码,分成多个Stream来存储。
3)Stripe Footer:存的是各个Stream的类型,长度等信息。
每个文件有一个File Footer,这里面存的是每个Stripe的行数,每个Column的数据类型信息等;每个文件的尾部是一个PostScript,这里面记录了整个文件的压缩类型以及FileFooter的长度信息等。在读取文件时,会seek到文件尾部读PostScript,从里面解析到File Footer长度,再读FileFooter,从里面解析到各个Stripe信息,再读各个Stripe,即从后往前读。
7.5.4 PARQUET格式
Parquet是面向分析型业务的列式存储格式,由Twitter和Cloudera合作开发,2015年5月从Apache的孵化器里毕业成为Apache顶级项目。
Parquet文件是以二进制方式存储的,所以是不可以直接读取的,文件中包括该文件的数据和元数据,因此Parquet格式文件是自解析的。
通常情况下,在存储Parquet数据的时候会按照Block大小设置行组的大小,由于一般情况下每一个Mapper任务处理数据的最小单位是一个Block,这样可以把每一个行组由一个Mapper任务处理,增大任务执行并行度。Parquet文件的格式如下图所示。
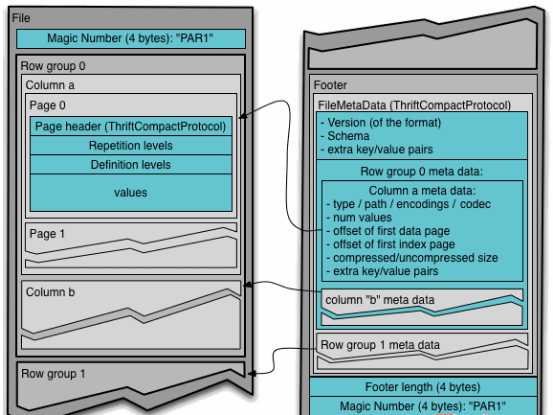
上图展示了一个Parquet文件的内容,一个文件中可以存储多个行组,文件的首位都是该文件的Magic Code,用于校验它是否是一个Parquet文件,Footer length记录了文件元数据的大小,通过该值和文件长度可以计算出元数据的偏移量,文件的元数据中包括每一个行组的元数据信息和该文件存储数据的Schema信息。除了文件中每一个行组的元数据,每一页的开始都会存储该页的元数据,在Parquet中,有三种类型的页:数据页、字典页和索引页。数据页用于存储当前行组中该列的值,字典页存储该列值的编码字典,每一个列块中最多包含一个字典页,索引页用来存储当前行组下该列的索引,目前Parquet中还不支持索引页。
7.5.5 主流文件存储格式对比实验
从存储文件的压缩比和查询速度两个角度对比。
存储文件的压缩比测试:
0)测试数据
1)TextFile
(1)创建表,存储数据格式为TEXTFILE
|
create table log_text ( track_time string, url string, session_id string, referer string, ip string, end_user_id string, city_id string ) row format delimited fields terminated by ‘\t‘ stored as textfile ; |
(2)向表中加载数据
|
hive (default)> load data local inpath ‘/opt/module/datas/log.data‘ into table log_text ; |
(3)查看表中数据大小
|
dfs -du -h /user/hive/warehouse/log_text; |
18.1 M /user/hive/warehouse/log_text/log.data
2)ORC
(1)创建表,存储数据格式为ORC
|
create table log_orc( track_time string, url string, session_id string, referer string, ip string, end_user_id string, city_id string ) row format delimited fields terminated by ‘\t‘ stored as orc ; |
(2)向表中加载数据
|
insert into table log_orc select * from log_text ; |
(3)查看表中数据大小
|
dfs -du -h /user/hive/warehouse/log_orc/ ; |
2.8 M /user/hive/warehouse/log_orc/000000_0
3)Parquet
(1)创建表,存储数据格式为parquet
|
create table log_parquet( track_time string, url string, session_id string, referer string, ip string, end_user_id string, city_id string ) row format delimited fields terminated by ‘\t‘ stored as parquet ; |
(2)向表中加载数据
|
insert into table log_parquet select * from log_text ; |
(3)查看表中数据大小
|
dfs -du -h /user/hive/warehouse/log_parquet/ ; |
13.1 M /user/hive/warehouse/log_parquet/000000_0
存储文件的压缩比总结:
ORC > Parquet > textFile
存储文件的查询速度测试:
1)TextFile
hive (default)> select count(*) from log_text;
_c0
100000
Time taken: 21.54 seconds, Fetched: 1 row(s)
2)ORC
hive (default)> select count(*) from log_orc;
_c0
100000
Time taken: 20.867 seconds, Fetched: 1 row(s)
3)Parquet
hive (default)> select count(*) from log_parquet;
_c0
100000
Time taken: 22.922 seconds, Fetched: 1 row(s)
存储文件的查询速度总结:
ORC > TextFile > Parquet
官网:https://cwiki.apache.org/confluence/display/Hive/LanguageManual+ORC
ORC存储方式的压缩:
|
Key |
Default |
Notes |
|
orc.compress |
ZLIB |
high level compression (one of NONE, ZLIB, SNAPPY) |
|
orc.compress.size |
262,144 |
number of bytes in each compression chunk |
|
orc.stripe.size |
67,108,864 |
number of bytes in each stripe |
|
orc.row.index.stride |
10,000 |
number of rows between index entries (must be >= 1000) |
|
orc.create.index |
true |
whether to create row indexes |
|
orc.bloom.filter.columns |
"" |
comma separated list of column names for which bloom filter should be created |
|
orc.bloom.filter.fpp |
0.05 |
false positive probability for bloom filter (must >0.0 and <1.0) |
1)创建一个非压缩的的ORC存储方式
(1)建表语句
|
create table log_orc_none( track_time string, url string, session_id string, referer string, ip string, end_user_id string, city_id string ) row format delimited fields terminated by ‘\t‘ stored as orc tblproperties ("orc.compress"="NONE"); |
(2)插入数据
|
insert into table log_orc_none select * from log_text ; |
(3)查看插入后数据
|
dfs -du -h /user/hive/warehouse/log_orc_none/ ; |
7.7 M /user/hive/warehouse/log_orc_none/000000_0
2)创建一个SNAPPY压缩的ORC存储方式
(1)建表语句
|
create table log_orc_snappy( track_time string, url string, session_id string, referer string, ip string, end_user_id string, city_id string ) row format delimited fields terminated by ‘\t‘ stored as orc tblproperties ("orc.compress"="SNAPPY"); |
(2)插入数据
|
insert into table log_orc_snappy select * from log_text ; |
(3)查看插入后数据
|
dfs -du -h /user/hive/warehouse/log_orc_snappy/ ; |
3.8 M /user/hive/warehouse/log_orc_snappy/000000_0
3)上一节中默认创建的ORC存储方式,导入数据后的大小为
2.8 M /user/hive/warehouse/log_orc/000000_0
比Snappy压缩的还小。原因是orc存储文件默认采用ZLIB压缩。比snappy压缩的小。
4)存储方式和压缩总结:
在实际的项目开发当中,hive表的数据存储格式一般选择:orc或parquet。压缩方式一般选择snappy。
标签:算法 用户 create 基本 如何 因子 bool home 默认值
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/frankdeng/p/9126088.html