标签:xhtml 11.2 完成 xxxxx head rap defer 读取配置 doctype
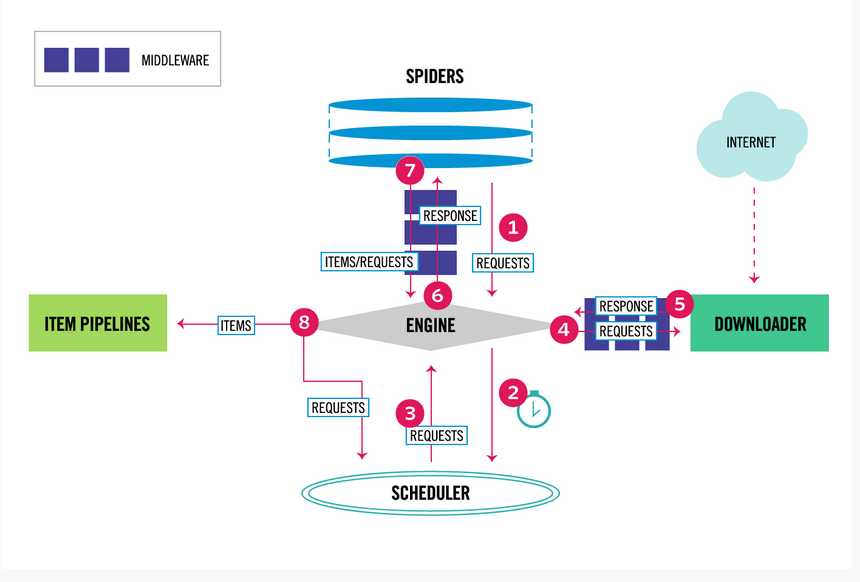
Scrapy有以下几大组件:
Scrapy Engine:核心引擎,负责控制和调度各个组件,保证数据流转;
Scheduler:负责管理任务、过滤任务、输出任务的调度器,存储、去重任务都在此控制;
Downloader:下载器,负责在网络上下载网页数据,输入待下载URL,输出下载结果;
Spiders:用户自己编写的爬虫脚本,可自定义抓取意图;
Item Pipeline:负责输出结构化数据,可自定义输出位置;
除此之外,还有两大中间件组件:
Downloader middlewares:介于引擎和下载器之间,可以在网页在下载前、后进行逻辑处理;
Spider middlewares:介于引擎和爬虫之间,可以在调用爬虫输入下载结果和输出请求/数据时进行逻辑处理;
执行流程:
1、引擎从自定义爬虫中获取初始化请求(url 种子) 2、引擎吧该请求放入调度器,同时引擎调度器获取一个带下载的请求(这辆步异步执行) 3、调度器返回给引擎一个待下载的请求 4、引擎发送请求给下载器,中间经历一系列下载器中间件 5、请求下载完成,生成相应对象,返回给引擎,中间经历一系列下载器中间件 6、引擎受到下载返回的响应对象,然后发送给爬虫,执行自定义逻辑,中间经过一系列爬虫中间件 7、爬虫执行对应的回掉方法,处理这个响应,完成用户逻辑后,生成结果对象或新的请求对象给引擎再次经过一系列爬虫中间件 8、引擎吧爬虫返回的结果对象交由结果处理器,把新的请求对象通过引擎在交给调度器 9、从1开始重复执行,直到调度器中没有新的请求
入口 __main__.py——〉execute(项目、运行环境的设置,解析命令,初始化CrawlerProcess,执行run函数)
http://kaito-kidd.com/2016/11/01/scrapy-code-analyze-architecture/

第一步: scrapy startproject xxxx cd xxxx scrapy genspider chouti chouti.com # 编写代码 scrapy crawl chouti --nolog 第二步:start_requests 第三步:parse函数 - 解析器 - yield item - yield Request() 第四步:携带cookie - 手动 - 自动 第五步:去重规则 第六步:下载中间件

# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import scrapy from bs4 import BeautifulSoup from scrapy.selector import HtmlXPathSelector # HtmlXPathSelector scrapy 自带 from .. items import PachongItem from scrapy.http import Request class ChoutiSpider(scrapy.Spider): name = ‘chouti‘ allowed_domains = [‘chouti.com‘] start_urls = [‘http://dig.chouti.com/‘] def parse(self, response): """ 当起始url下载完毕后,自动调用该函数,reponse封装了 :param response: :return: """ # print(response.text) # soup = BeautifulSoup(response.text,‘lxml‘)# scrap 继承了lxml # div = soup.find(name=‘id‘,attrs={"id":‘content-list‘}) # print(div) hxs = HtmlXPathSelector(response=response) # items= hxs.xpath("//div[@id=‘content-list‘]/div[@class=‘item‘]")[0:4] # with open(‘xxx.log‘, ‘w‘) as f: # 注意 打开文件不能写到for循环中 # for item in items: # href = item.xpath(".//div[@class=‘part1‘]/a[1]/@href").extract_first() #extract_first() 提取第一个 # text = item.xpath(".//div[@class=‘part1‘]/a[1]/text()").extract_first() #extract_first() # print(text.strip()) # f.write(href) items = hxs.xpath("//div[@id=‘content-list‘]/div[@class=‘item‘]") for item in items: text = item.xpath(".//div[@class=‘part1‘]/a[1]/text()").extract_first() # extract_first() 解析 href = item.xpath(".//div[@class=‘part1‘]/a[1]/@href").extract_first() # extract_first() 全部提取 # print(href,text) item = PachongItem(title=text,href=href) yield item #自动返回给已注册pipelines中的函数,去做持久化.必须是个对象,pipelines每次都执行 pages = hxs.xpath("//div[@id=‘page-area‘]//a[@class=‘ct_pagepa‘]/@href").extract() for page_url in pages: page_url = "https://dig.chouti.com" + page_url yield Request(url=page_url,callback=self.parse)

# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # Define your item pipelines here # # Don‘t forget to add your pipeline to the ITEM_PIPELINES setting # See: https://doc.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/item-pipeline.html class PachongPipeline(object): def process_item(self, item, spider): # print(item[‘href‘]) self.f.write(item[‘href‘]+"\n") self.f.flush() return item def open_spider(self, spider): """ 爬虫开始执行时,调用 :param spider: :return: """ self.f= open(‘ooo.log‘,‘w‘) def close_spider(self, spider): """ 爬虫关闭时,被调用 :param spider: :return: """ self.f.close()

# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # Scrapy settings for pachong project # # For simplicity, this file contains only settings considered important or # commonly used. You can find more settings consulting the documentation: # # https://doc.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/settings.html # https://doc.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/downloader-middleware.html # https://doc.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/spider-middleware.html BOT_NAME = ‘pachong‘ SPIDER_MODULES = [‘pachong.spiders‘] NEWSPIDER_MODULE = ‘pachong.spiders‘ # Crawl responsibly by identifying yourself (and your website) on the user-agent #USER_AGENT = ‘pachong (+http://www.yourdomain.com)‘ # Obey robots.txt rules ROBOTSTXT_OBEY = True # Configure maximum concurrent requests performed by Scrapy (default: 16) #CONCURRENT_REQUESTS = 32 # Configure a delay for requests for the same website (default: 0) # See https://doc.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/settings.html#download-delay # See also autothrottle settings and docs #DOWNLOAD_DELAY = 3 # The download delay setting will honor only one of: #CONCURRENT_REQUESTS_PER_DOMAIN = 16 #CONCURRENT_REQUESTS_PER_IP = 16 # Disable cookies (enabled by default) #COOKIES_ENABLED = False # Disable Telnet Console (enabled by default) #TELNETCONSOLE_ENABLED = False # Override the default request headers: #DEFAULT_REQUEST_HEADERS = { # ‘Accept‘: ‘text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,*/*;q=0.8‘, # ‘Accept-Language‘: ‘en‘, #} # Enable or disable spider middlewares # See https://doc.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/spider-middleware.html #SPIDER_MIDDLEWARES = { # ‘pachong.middlewares.PachongSpiderMiddleware‘: 543, #} # Enable or disable downloader middlewares # See https://doc.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/downloader-middleware.html #DOWNLOADER_MIDDLEWARES = { # ‘pachong.middlewares.PachongDownloaderMiddleware‘: 543, #} # Enable or disable extensions # See https://doc.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/extensions.html #EXTENSIONS = { # ‘scrapy.extensions.telnet.TelnetConsole‘: None, #} # Configure item pipelines # See https://doc.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/item-pipeline.html ITEM_PIPELINES = { ‘pachong.pipelines.PachongPipeline‘: 300,#300 优先级 } # Enable and configure the AutoThrottle extension (disabled by default) # See https://doc.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/autothrottle.html #AUTOTHROTTLE_ENABLED = True # The initial download delay #AUTOTHROTTLE_START_DELAY = 5 # The maximum download delay to be set in case of high latencies #AUTOTHROTTLE_MAX_DELAY = 60 # The average number of requests Scrapy should be sending in parallel to # each remote server #AUTOTHROTTLE_TARGET_CONCURRENCY = 1.0 # Enable showing throttling stats for every response received: #AUTOTHROTTLE_DEBUG = False # Enable and configure HTTP caching (disabled by default) # See https://doc.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/downloader-middleware.html#httpcache-middleware-settings #HTTPCACHE_ENABLED = True #HTTPCACHE_EXPIRATION_SECS = 0 #HTTPCACHE_DIR = ‘httpcache‘ #HTTPCACHE_IGNORE_HTTP_CODES = [] #HTTPCACHE_STORAGE = ‘scrapy.extensions.httpcache.FilesystemCacheStorage‘ DEPTH_LIMIT = 2 #爬取深度两层
http://www.cnblogs.com/wupeiqi/articles/6229292.html
scrapy 代码注释
start_request中的url 为起始url,是一个生成器,返回一个可迭代对象
spider中初始的request是通过调用 start_requests() 来获取的。 start_requests() 读取 start_urls 中的URL, 并以 parse 为回调函数生成 Request 。

该方法必须返回一个可迭代对象(iterable)。该对象包含了spider用于爬取的第一个Request。 当spider启动爬取并且未制定URL时,该方法被调用。 当指定了URL时,make_requests_from_url() 将被调用来创建Request对象。 该方法仅仅会被Scrapy调用一次,因此您可以将其实现为生成器。 该方法的默认实现是使用 start_urls 的url生成Request。 如果您想要修改最初爬取某个网站的Request对象,您可以重写(override)该方法。 例如,如果您需要在启动时以POST登录某个网站,你可以这么写: def start_requests(self): return [scrapy.FormRequest("http://www.example.com/login", formdata={‘user‘: ‘john‘, ‘pass‘: ‘secret‘}, callback=self.logged_in)] def logged_in(self, response): # here you would extract links to follow and return Requests for # each of them, with another callback pass

# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import scrapy from bs4 import BeautifulSoup from scrapy.selector import HtmlXPathSelector from scrapy.http import Request from ..items import XianglongItem from scrapy.http import HtmlResponse from scrapy.http.response.html import HtmlResponse """ obj = ChoutiSpider() obj.start_requests() """ class ChoutiSpider(scrapy.Spider): name = ‘chouti‘ allowed_domains = [‘chouti.com‘] start_urls = [‘https://dig.chouti.com/‘,] def start_requests(self): for url in self.start_urls: yield Request( url=url, callback=self.parse, headers={‘User-Agent‘:‘Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/63.0.3239.132 Safari/537.36‘} ) def parse(self, response): """ 当起始URL下载完毕后,自动执行parse函数:response封装了响应相关的所有内容。 :param response: :return: """ pages = response.xpath(‘//div[@id="page-area"]//a[@class="ct_pagepa"]/@href‘).extract() for page_url in pages: page_url = "https://dig.chouti.com" + page_url yield Request(url=page_url,callback=self.parse,headers={‘User-Agent‘:‘Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/63.0.3239.132 Safari/537.36‘})
功能:将字符串转换成对象

- 方式一:
response.xpath(‘//div[@id=‘content-list‘]/div[@class=‘item‘]‘)
- 方式二:
hxs = HtmlXPathSelector(response=response)
items = hxs.xpath("//div[@id=‘content-list‘]/div[@class=‘item‘]")
查找规则:
//a
//div/a
//a[re:test(@id, "i\d+")]
items = hxs.xpath("//div[@id=‘content-list‘]/div[@class=‘item‘]")
for item in items:
item.xpath(‘.//div‘)
解析:
标签对象:xpath(‘/html/body/ul/li/a/@href‘)
列表: xpath(‘/html/body/ul/li/a/@href‘).extract()
值: xpath(‘//body/ul/li/a/@href‘).extract_first()

from scrapy.selector import Selector, HtmlXPathSelector from scrapy.http import HtmlResponse html = """<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head lang="en"> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title></title> </head> <body> <ul> <li class="item-"><a id=‘i1‘ href="link.html">first item</a></li> <li class="item-0"><a id=‘i2‘ href="llink.html">first item</a></li> <li class="item-1"><a href="llink2.html">second item<span>vv</span></a></li> </ul> <div><a href="llink2.html">second item</a></div> </body> </html> """ response = HtmlResponse(url=‘http://example.com‘, body=html,encoding=‘utf-8‘) obj = response.xpath(‘//a[@id="i1"]/text()‘).extract_first() print(obj)
在setting中配置pipeline
ITEM_PIPELINES = { ‘pachong.pipelines.PachongPipeline‘: 300,#300 值越小 优先级越高 0~1000 ‘pachong.pipelines.DBPipeline‘: 300,#300 优先级 }
多pipelines ,pipelines返回值会传递给下一个pipelines的process_item
想要丢弃: 使用rasie DropItem
示例

from scrapy.exceptions import DropItem
class FilePipeline(object):
def process_item(self, item, spider):
print(‘写入文件‘,item[‘href‘])
# return item
raise DropItem()
pipelines 方法有4种:
1) __init__() 构造方法
2) open_spider()
3) close_spider()
4) from_crawler(), 属于类方法,可以进行类定制
当根据配置文件: ITEM_PIPELINES = { ‘xianglong.pipelines.FilePipeline‘: 300, ‘xianglong.pipelines.DBPipeline‘: 301, } 找到相关的类:FilePipeline之后,会优先判断类中是否含有 from_crawler 如果有: obj = FilePipeline.from_crawler() 没有则: obj = FilePipeline() #执行顺序 obj.open_spider(..) ob.process_item(..) obj.close_spider(..)
根据配置文件读取相关值,再进行pipeline处理 ——现在使用了from_crawler方法

from scrapy.exceptions import DropItem class FilePipeline(object): def __init__(self,path): self.path = path self.f = None @classmethod def from_crawler(cls, crawler): """ 初始化时候,用于创建pipeline对象 :param crawler: :return: """ # return cls() path = crawler.settings.get(‘XL_FILE_PATH‘) return cls(path) def process_item(self, item, spider): self.f.write(item[‘href‘]+‘\n‘) return item def open_spider(self, spider): """ 爬虫开始执行时,调用 :param spider: :return: """ self.f = open(self.path,‘w‘) def close_spider(self, spider): """ 爬虫关闭时,被调用 :param spider: :return: """ self.f.close() class DBPipeline(object): def process_item(self, item, spider): print(‘数据库‘,item) return item def open_spider(self, spider): """ 爬虫开始执行时,调用 :param spider: :return: """ print(‘打开数据‘) def close_spider(self, spider): """ 爬虫关闭时,被调用 :param spider: :return: """ print(‘关闭数据库‘)
Post请求头示例

from scrapy.http import Request req = Request( url=‘http://dig.chouti.com/login‘, method=‘POST‘, body=‘phone=8613121758648&password=woshiniba&oneMonth=1‘, headers={‘Content-Type‘: ‘application/x-www-form-urlencoded; charset=UTF-8‘}, cookies={}, callback=self.parse_check_login, )
第一种
res.headers.getlist(‘Set-Cookie‘)获取cookie
第二种:手动获取

cookie_dict = {} cookie_jar = CookieJar() cookie_jar.extract_cookies(response, response.request) for k, v in cookie_jar._cookies.items(): for i, j in v.items(): for m, n in j.items(): cookie_dict[m] = n.value req = Request( url=‘http://dig.chouti.com/login‘, method=‘POST‘, headers={‘Content-Type‘: ‘application/x-www-form-urlencoded; charset=UTF-8‘}, body=‘phone=8615131255089&password=pppppppp&oneMonth=1‘, cookies=cookie_dict, # 手动携带 callback=self.check_login ) yield req
第三种 自动设置
meta={"cookiejar"=True}
def start_requests(self):
for url in self.start_urls:
yield Request(url=url,callback=self.parse_index,meta={‘cookiejar‘:True})
默认允许操作cookie

在setting中配置
DUPEFILTER_CLASS = ‘scrapy.dupefilter.RFPDupeFilter‘ #自定义去重规则 DUPEFILTER_DEBUG = False JOBDIR = "保存范文记录的日志路径,如:/root/" # 最终路径为 /root/requests.seen
和pipelines很像,需要自己编写类,定义去重规则,但是scrapy采用bloomfilter 进行去重

class MyDupeFilter(BaseDupeFilter):
def __init__(self):
self.record = set()
@classmethod
def from_settings(cls, settings):
return cls()
def request_seen(self, request):
if request.url in self.record:
print(‘已经访问过了‘, request.url)
return True
self.record.add(request.url)
def open(self): # can return deferred
pass
def close(self, reason): # can return a deferred
pass

http://www.oldboyedu.com?id=1&age=2 http://www.oldboyedu.com?age=2&id=1 如上面的两个url只是请求参数变换位置,其实还是指向同一个地址
对url的识别需要使用到request_fingerprint(request)函数
对url排序后hash

from scrapy.http import Request u1 = Request(url=‘http://www.oldboyedu.com?id=1&age=2‘) u2 = Request(url=‘http://www.oldboyedu.com?age=2&id=1‘) result1 = request_fingerprint(u1) result2 = request_fingerprint(u2) print(result1,result2)
问题:记录到低要不要放在数据库?
【使用redis集合存储】 访问记录可以放在redis中。
from scrapy.core.scheduler import Scheduler
def enqueue_request(self, request):
# request.dont_filter=False
# self.df.request_seen(request):
# - True,已经访问
# - False,未访问
# request.dont_filter=True,全部加入到调度器
if not request.dont_filter and self.df.request_seen(request):
self.df.log(request, self.spider)
return False
# 如果往下走,把请求加入调度器
dqok = self._dqpush(request)
问题:对爬虫中所有请求发送时,携带请求头?
方案一:在每个Request对象中添加一个请求头
方案二:下载中间件
setting中配置:
DOWNLOADER_MIDDLEWARES = {‘xianglong.middlewares.UserAgentDownloaderMiddleware‘: 543,}
编写类:

class UserAgentDownloaderMiddleware(object):
@classmethod
def from_crawler(cls, crawler):
# This method is used by Scrapy to create your spiders.
s = cls()
return s
def process_request(self, request, spider):
# Called for each request that goes through the downloader
# middleware.
# Must either:
# - return None: continue processing this request
# - or return a Response object
# - or return a Request object
# - or raise IgnoreRequest: process_exception() methods of
# installed downloader middleware will be called
request.headers[‘User-Agent‘] = "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/63.0.3239.132 Safari/537.36"
# return None # 继续执行后续的中间件的process_request
# from scrapy.http import Request
# return Request(url=‘www.baidu.com‘) # 重新放入调度器中,当前请求不再继续处理
# from scrapy.http import HtmlResponse # 执行从最后一个开始执行所有的process_response
# return HtmlResponse(url=‘www.baidu.com‘,body=b‘asdfuowjelrjaspdoifualskdjf;lajsdf‘)
def process_response(self, request, response, spider):
# Called with the response returned from the downloader.
# Must either;
# - return a Response object
# - return a Request object
# - or raise IgnoreRequest
return response
def process_exception(self, request, exception, spider):
# Called when a download handler or a process_request()
# (from other downloader middleware) raises an exception.
# Must either:
# - return None: continue processing this exception
# - return a Response object: stops process_exception() chain
# - return a Request object: stops process_exception() chain
pass
如return none 继续执行下一个中间件,returen Request(...)返回调度器产生死循环
四种返回结果如下图

加代理,只是在请求头中设置信息
方式一:
内置加ip
os.envriron[‘HTTP_PROXY‘]=‘http://192.168.0.0.1‘
方式二:自定义下载中间件

import random import base64 import six def to_bytes(text, encoding=None, errors=‘strict‘): """Return the binary representation of `text`. If `text` is already a bytes object, return it as-is.""" if isinstance(text, bytes): return text if not isinstance(text, six.string_types): raise TypeError(‘to_bytes must receive a unicode, str or bytes ‘ ‘object, got %s‘ % type(text).__name__) if encoding is None: encoding = ‘utf-8‘ return text.encode(encoding, errors) class MyProxyDownloaderMiddleware(object): def process_request(self, request, spider): proxy_list = [ {‘ip_port‘: ‘111.11.228.75:80‘, ‘user_pass‘: ‘xxx:123‘}, {‘ip_port‘: ‘120.198.243.22:80‘, ‘user_pass‘: ‘‘}, {‘ip_port‘: ‘111.8.60.9:8123‘, ‘user_pass‘: ‘‘}, {‘ip_port‘: ‘101.71.27.120:80‘, ‘user_pass‘: ‘‘}, {‘ip_port‘: ‘122.96.59.104:80‘, ‘user_pass‘: ‘‘}, {‘ip_port‘: ‘122.224.249.122:8088‘, ‘user_pass‘: ‘‘}, ] proxy = random.choice(proxy_list) if proxy[‘user_pass‘] is not None: request.meta[‘proxy‘] = to_bytes("http://%s" % proxy[‘ip_port‘]) encoded_user_pass = base64.encodestring(to_bytes(proxy[‘user_pass‘])) request.headers[‘Proxy-Authorization‘] = to_bytes(‘Basic ‘ + encoded_user_pass) else: request.meta[‘proxy‘] = to_bytes("http://%s" % proxy[‘ip_port‘])
setting配置:

DOWNLOADER_MIDDLEWARES = { # ‘xiaohan.middlewares.MyProxyDownloaderMiddleware‘: 543, }
自己定制,不掏钱
DOWNLOA....两个变量需要在setting中配置

DOWNLOADER_HTTPCLIENTFACTORY = "scrapy.core.downloader.webclient.ScrapyHTTPClientFactory" DOWNLOADER_CLIENTCONTEXTFACTORY = "xiaohan.middlewares.MySSLFactory"

class MySSLFactory(ScrapyClientContextFactory): def getCertificateOptions(self): from OpenSSL import crypto v1 = crypto.load_privatekey(crypto.FILETYPE_PEM, open(‘/Users/wupeiqi/client.key.unsecure‘, mode=‘r‘).read()) v2 = crypto.load_certificate(crypto.FILETYPE_PEM, open(‘/Users/wupeiqi/client.pem‘, mode=‘r‘).read()) return CertificateOptions( privateKey=v1, # pKey对象 certificate=v2, # X509对象 verify=False, method=getattr(self, ‘method‘, getattr(self, ‘_ssl_method‘, None)) )
在每次下载前和下载后对请求和相应可以定制功能。例如:user_Agent / 代理 / cookie

class XiaohanSpiderMiddleware(object): # Not all methods need to be defined. If a method is not defined, # scrapy acts as if the spider middleware does not modify the # passed objects. def __init__(self): pass @classmethod def from_crawler(cls, crawler): # This method is used by Scrapy to create your spiders. s = cls() return s # 每次下载完成之后,未执行parse函数之前。 def process_spider_input(self, response, spider): # Called for each response that goes through the spider # middleware and into the spider. # Should return None or raise an exception. print(‘process_spider_input‘,response) return None def process_spider_output(self, response, result, spider): # Called with the results returned from the Spider, after # it has processed the response. # Must return an iterable of Request, dict or Item objects. print(‘process_spider_output‘,response) for i in result: yield i def process_spider_exception(self, response, exception, spider): # Called when a spider or process_spider_input() method # (from other spider middleware) raises an exception. # Should return either None or an iterable of Response, dict # or Item objects. pass # 爬虫启动时,第一次执行start_requests时,触发。(只执行一次) def process_start_requests(self, start_requests, spider): # Called with the start requests of the spider, and works # similarly to the process_spider_output() method, except # that it doesn’t have a response associated. # Must return only requests (not items). print(‘process_start_requests‘) for r in start_requests: yield r
setting中配置spidermiddleware

SPIDER_MIDDLEWARES = { ‘xiaohan.middlewares.XiaohanSpiderMiddleware‘: 543, }
应用:
先定义中间件
在setting中配置
扩展+信号

from scrapy import signals class MyExtension(object): def __init__(self): pass @classmethod def from_crawler(cls, crawler): obj = cls() # 在爬虫打开时,触发spider_opened信号相关的所有函数:xxxxxxxxxxx crawler.signals.connect(obj.xxxxxxxxxxx1, signal=signals.spider_opened) # 在爬虫关闭时,触发spider_closed信号相关的所有函数:xxxxxxxxxxx crawler.signals.connect(obj.uuuuuuuuuu, signal=signals.spider_closed) return obj def xxxxxxxxxxx1(self, spider): print(‘open‘) def uuuuuuuuuu(self, spider): print(‘close‘) return obj

EXTENSIONS = { ‘xiaohan.extends.MyExtension‘:500, }

from scrapy.commands import ScrapyCommand from scrapy.utils.project import get_project_settings class Command(ScrapyCommand): requires_project = True def syntax(self): return ‘[options]‘ def short_desc(self): return ‘Runs all of the spiders‘ def run(self, args, opts): spider_list = self.crawler_process.spiders.list() for name in spider_list: self.crawler_process.crawl(name, **opts.__dict__) self.crawler_process.start() PS:源码 def run(self, args, opts): from scrapy.crawler import CrawlerProcess CrawlerProcess.crawl CrawlerProcess.start """ self.crawler_process对象中含有:_active = {d,} """ self.crawler_process.crawl(‘chouti‘,**opts.__dict__) self.crawler_process.crawl(‘cnblogs‘,**opts.__dict__) # self.crawler_process.start()
scrapy-redis扩展

自定义扩展

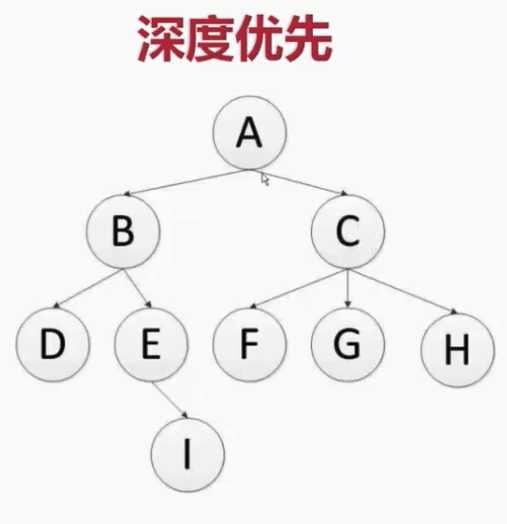
引擎调用调度器,默认广度度优先

加上scrapy_redis 把调度器和Request放入redis中
setting中的配置
算法:递归实现

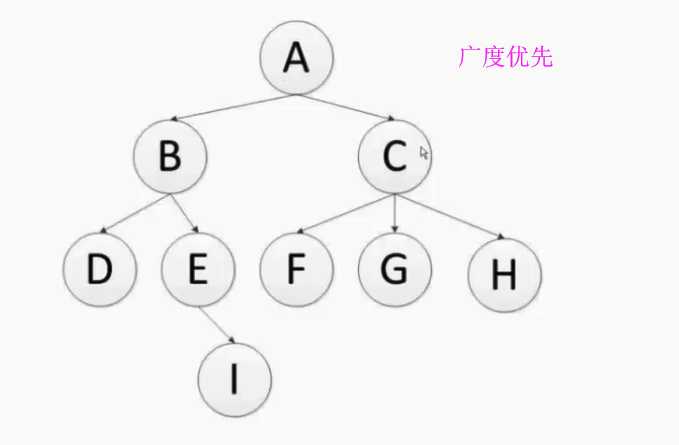

目的:帮助开发者实现分布式爬虫程序

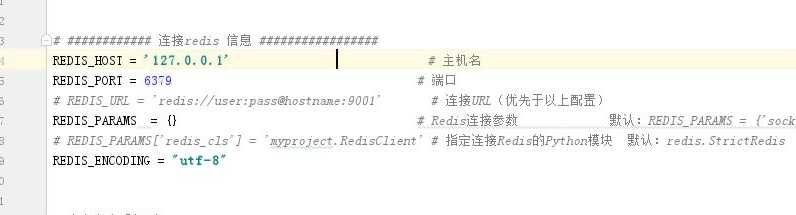
# ############ 连接redis 信息 ################# REDIS_HOST = ‘127.0.0.1‘ # 主机名 REDIS_PORT = 6379 # 端口 # REDIS_URL = ‘redis://user:pass@hostname:9001‘ # 连接URL(优先于以上配置) REDIS_PARAMS = {} # Redis连接参数 默认:REDIS_PARAMS = {‘socket_timeout‘: 30,‘socket_connect_timeout‘: 30,‘retry_on_timeout‘: True,‘encoding‘: REDIS_ENCODING,}) # REDIS_PARAMS[‘redis_cls‘] = ‘myproject.RedisClient‘ # 指定连接Redis的Python模块 默认:redis.StrictRedis REDIS_ENCODING = "utf-8" # 自定义去重规则 DUPEFILTER_CLASS = "scrapy_redis.dupefilter.RFPDupeFilter"

from scrapy_redis.dupefilter import RFPDupeFilter class MyRFPDupeFilter(RFPDupeFilter): pass # 自定义去重规则 DUPEFILTER_CLASS = "wenwen.dup.MyRFPDupeFilter"

# 有引擎来执行:自定义调度器 SCHEDULER = "scrapy_redis.scheduler.Scheduler" SCHEDULER_QUEUE_CLASS = ‘scrapy_redis.queue.FifoQueue‘ # 默认使用优先级队列(默认),其他:PriorityQueue(有序集合),FifoQueue(列表)、LifoQueue(列表) SCHEDULER_QUEUE_KEY = ‘%(spider)s:requests‘ # 调度器中请求存放在redis中的key SCHEDULER_SERIALIZER = "scrapy_redis.picklecompat" # 对保存到redis中的数据进行序列化,默认使用pickle SCHEDULER_PERSIST = True # 是否在关闭时候保留原来的调度器和去重记录,True=保留,False=清空 SCHEDULER_FLUSH_ON_START = True # 是否在开始之前清空 调度器和去重记录,True=清空,False=不清空 # SCHEDULER_IDLE_BEFORE_CLOSE = 10 # 去调度器中获取数据时,如果为空,最多等待时间(最后没数据,未获取到)。 SCHEDULER_DUPEFILTER_KEY = ‘%(spider)s:dupefilter‘ # 去重规则,在redis中保存时对应的key chouti:dupefilter SCHEDULER_DUPEFILTER_CLASS = ‘scrapy_redis.dupefilter.RFPDupeFilter‘ # 去重规则对应处理的类 DUPEFILTER_DEBUG = False

class RFPDupeFilter(BaseDupeFilter): """Request Fingerprint duplicates filter""" def __init__(self, path=None, debug=False): self.fingerprints = set() @classmethod def from_settings(cls, settings): debug = settings.getbool(‘DUPEFILTER_DEBUG‘) return cls(job_dir(settings), debug) def request_seen(self, request): # 将request对象转换成唯一标识。 fp = self.request_fingerprint(request) # 判断在集合中是否存在,如果存在则返回True,表示已经访问过。 if fp in self.fingerprints: return True # 之前未访问过,将url添加到访问记录中。 self.fingerprints.add(fp) def request_fingerprint(self, request): return request_fingerprint(request)

class RFPDupeFilter(BaseDupeFilter): """Redis-based request duplicates filter. This class can also be used with default Scrapy‘s scheduler. """ logger = logger def __init__(self, server, key, debug=False): # self.server = redis连接 self.server = server # self.key = dupefilter:123912873234 self.key = key @classmethod def from_settings(cls, settings): # 读取配置,连接redis server = get_redis_from_settings(settings) # key = dupefilter:123912873234 key = defaults.DUPEFILTER_KEY % {‘timestamp‘: int(time.time())} debug = settings.getbool(‘DUPEFILTER_DEBUG‘) return cls(server, key=key, debug=debug) @classmethod def from_crawler(cls, crawler): return cls.from_settings(crawler.settings) def request_seen(self, request): fp = self.request_fingerprint(request) # This returns the number of values added, zero if already exists. # self.server=redis连接 # 添加到redis集合中:1,添加工程;0,已经存在 added = self.server.sadd(self.key, fp) return added == 0 def request_fingerprint(self, request): return request_fingerprint(request) def close(self, reason=‘‘): self.clear() def clear(self): """Clears fingerprints data.""" self.server.delete(self.key)

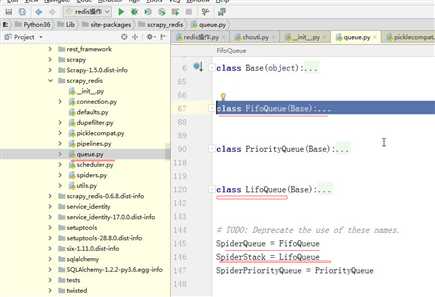
将request对象全部放到内存维护的队列:self.q = deque() 将request对象全部放到硬盘维护的队列:文件操作 SCHEDULER_DISK_QUEUE = ‘scrapy.squeues.PickleLifoDiskQueue‘ SCHEDULER_MEMORY_QUEUE = ‘scrapy.squeues.LifoMemoryQueue‘ SCHEDULER_PRIORITY_QUEUE = ‘queuelib.PriorityQueue‘ class Scheduler(object): def __init__(self, dupefilter, jobdir=None, dqclass=None, mqclass=None, logunser=False, stats=None, pqclass=None): self.df = dupefilter self.dqdir = self._dqdir(jobdir) self.pqclass = pqclass self.dqclass = dqclass self.mqclass = mqclass self.logunser = logunser self.stats = stats @classmethod def from_crawler(cls, crawler): settings = crawler.settings dupefilter_cls = load_object(settings[‘DUPEFILTER_CLASS‘]) dupefilter = dupefilter_cls.from_settings(settings) pqclass = load_object(settings[‘SCHEDULER_PRIORITY_QUEUE‘]) dqclass = load_object(settings[‘SCHEDULER_DISK_QUEUE‘]) mqclass = load_object(settings[‘SCHEDULER_MEMORY_QUEUE‘]) logunser = settings.getbool(‘LOG_UNSERIALIZABLE_REQUESTS‘, settings.getbool(‘SCHEDULER_DEBUG‘)) return cls(dupefilter, jobdir=job_dir(settings), logunser=logunser, stats=crawler.stats, pqclass=pqclass, dqclass=dqclass, mqclass=mqclass) def has_pending_requests(self): return len(self) > 0 def open(self, spider): self.spider = spider self.mqs = self.pqclass(self._newmq) self.dqs = self._dq() if self.dqdir else None return self.df.open() def close(self, reason): if self.dqs: prios = self.dqs.close() with open(join(self.dqdir, ‘active.json‘), ‘w‘) as f: json.dump(prios, f) return self.df.close(reason) def enqueue_request(self, request): # request.dont_filter=False # self.df.request_seen(request): # - True,已经访问 # - False,未访问 # request.dont_filter=True,全部加入到调度器 if not request.dont_filter and self.df.request_seen(request): self.df.log(request, self.spider) return False # 如果往下走,把请求加入调度器 dqok = self._dqpush(request) if dqok: self.stats.inc_value(‘scheduler/enqueued/disk‘, spider=self.spider) else: self._mqpush(request) self.stats.inc_value(‘scheduler/enqueued/memory‘, spider=self.spider) self.stats.inc_value(‘scheduler/enqueued‘, spider=self.spider) return True def next_request(self): request = self.mqs.pop() if request: self.stats.inc_value(‘scheduler/dequeued/memory‘, spider=self.spider) else: request = self._dqpop() if request: self.stats.inc_value(‘scheduler/dequeued/disk‘, spider=self.spider) if request: self.stats.inc_value(‘scheduler/dequeued‘, spider=self.spider) return request def __len__(self): return len(self.dqs) + len(self.mqs) if self.dqs else len(self.mqs) def _dqpush(self, request): if self.dqs is None: return try: reqd = request_to_dict(request, self.spider) self.dqs.push(reqd, -request.priority) except ValueError as e: # non serializable request if self.logunser: msg = ("Unable to serialize request: %(request)s - reason:" " %(reason)s - no more unserializable requests will be" " logged (stats being collected)") logger.warning(msg, {‘request‘: request, ‘reason‘: e}, exc_info=True, extra={‘spider‘: self.spider}) self.logunser = False self.stats.inc_value(‘scheduler/unserializable‘, spider=self.spider) return else: return True def _mqpush(self, request): self.mqs.push(request, -request.priority) def _dqpop(self): if self.dqs: d = self.dqs.pop() if d: return request_from_dict(d, self.spider) def _newmq(self, priority): return self.mqclass() def _newdq(self, priority): return self.dqclass(join(self.dqdir, ‘p%s‘ % priority)) def _dq(self): activef = join(self.dqdir, ‘active.json‘) if exists(activef): with open(activef) as f: prios = json.load(f) else: prios = () q = self.pqclass(self._newdq, startprios=prios) if q: logger.info("Resuming crawl (%(queuesize)d requests scheduled)", {‘queuesize‘: len(q)}, extra={‘spider‘: self.spider}) return q def _dqdir(self, jobdir): if jobdir: dqdir = join(jobdir, ‘requests.queue‘) if not exists(dqdir): os.makedirs(dqdir) return dqdir

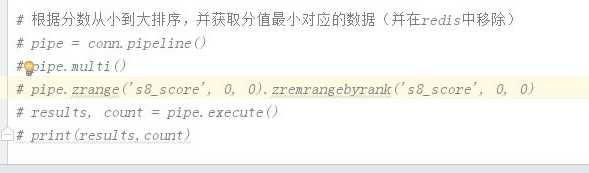
将请求通过pickle进行序列化,然后添加到redis: 列表或有序结合中。 SCHEDULER_QUEUE_CLASS = ‘scrapy_redis.queue.LifoQueue‘ class Scheduler(object): def __init__(self, server, persist=False, flush_on_start=False, queue_key=defaults.SCHEDULER_QUEUE_KEY, queue_cls=defaults.SCHEDULER_QUEUE_CLASS, dupefilter_key=defaults.SCHEDULER_DUPEFILTER_KEY, dupefilter_cls=defaults.SCHEDULER_DUPEFILTER_CLASS, idle_before_close=0, serializer=None): if idle_before_close < 0: raise TypeError("idle_before_close cannot be negative") self.server = server self.persist = persist self.flush_on_start = flush_on_start self.queue_key = queue_key self.queue_cls = queue_cls self.dupefilter_cls = dupefilter_cls self.dupefilter_key = dupefilter_key self.idle_before_close = idle_before_close self.serializer = serializer self.stats = None def __len__(self): return len(self.queue) @classmethod def from_settings(cls, settings): kwargs = { ‘persist‘: settings.getbool(‘SCHEDULER_PERSIST‘), ‘flush_on_start‘: settings.getbool(‘SCHEDULER_FLUSH_ON_START‘), ‘idle_before_close‘: settings.getint(‘SCHEDULER_IDLE_BEFORE_CLOSE‘), } # If these values are missing, it means we want to use the defaults. optional = { # TODO: Use custom prefixes for this settings to note that are # specific to scrapy-redis. ‘queue_key‘: ‘SCHEDULER_QUEUE_KEY‘, ‘queue_cls‘: ‘SCHEDULER_QUEUE_CLASS‘, ‘dupefilter_key‘: ‘SCHEDULER_DUPEFILTER_KEY‘, # We use the default setting name to keep compatibility. ‘dupefilter_cls‘: ‘DUPEFILTER_CLASS‘, ‘serializer‘: ‘SCHEDULER_SERIALIZER‘, } for name, setting_name in optional.items(): val = settings.get(setting_name) if val: kwargs[name] = val # Support serializer as a path to a module. if isinstance(kwargs.get(‘serializer‘), six.string_types): kwargs[‘serializer‘] = importlib.import_module(kwargs[‘serializer‘]) server = connection.from_settings(settings) # Ensure the connection is working. server.ping() return cls(server=server, **kwargs) @classmethod def from_crawler(cls, crawler): instance = cls.from_settings(crawler.settings) # FIXME: for now, stats are only supported from this constructor instance.stats = crawler.stats return instance def open(self, spider): self.spider = spider try: self.queue = load_object(self.queue_cls)( server=self.server, spider=spider, key=self.queue_key % {‘spider‘: spider.name}, serializer=self.serializer, ) except TypeError as e: raise ValueError("Failed to instantiate queue class ‘%s‘: %s", self.queue_cls, e) try: self.df = load_object(self.dupefilter_cls)( server=self.server, key=self.dupefilter_key % {‘spider‘: spider.name}, debug=spider.settings.getbool(‘DUPEFILTER_DEBUG‘), ) except TypeError as e: raise ValueError("Failed to instantiate dupefilter class ‘%s‘: %s", self.dupefilter_cls, e) if self.flush_on_start: self.flush() # notice if there are requests already in the queue to resume the crawl if len(self.queue): spider.log("Resuming crawl (%d requests scheduled)" % len(self.queue)) def close(self, reason): if not self.persist: self.flush() def flush(self): self.df.clear() self.queue.clear() def enqueue_request(self, request): if not request.dont_filter and self.df.request_seen(request): self.df.log(request, self.spider) return False if self.stats: self.stats.inc_value(‘scheduler/enqueued/redis‘, spider=self.spider) self.queue.push(request) return True def next_request(self): block_pop_timeout = self.idle_before_close request = self.queue.pop(block_pop_timeout) if request and self.stats: self.stats.inc_value(‘scheduler/dequeued/redis‘, spider=self.spider) return request def has_pending_requests(self): return len(self) > 0 相关Queue源码: class Base(object): """Per-spider base queue class""" def __init__(self, server, spider, key, serializer=None): """Initialize per-spider redis queue. Parameters ---------- server : StrictRedis Redis client instance. spider : Spider Scrapy spider instance. key: str Redis key where to put and get messages. serializer : object Serializer object with ``loads`` and ``dumps`` methods. """ if serializer is None: # Backward compatibility. # TODO: deprecate pickle. serializer = picklecompat if not hasattr(serializer, ‘loads‘): raise TypeError("serializer does not implement ‘loads‘ function: %r" % serializer) if not hasattr(serializer, ‘dumps‘): raise TypeError("serializer ‘%s‘ does not implement ‘dumps‘ function: %r" % serializer) self.server = server self.spider = spider self.key = key % {‘spider‘: spider.name} self.serializer = serializer def _encode_request(self, request): """Encode a request object""" obj = request_to_dict(request, self.spider) return self.serializer.dumps(obj) def _decode_request(self, encoded_request): """Decode an request previously encoded""" obj = self.serializer.loads(encoded_request) return request_from_dict(obj, self.spider) def __len__(self): """Return the length of the queue""" raise NotImplementedError def push(self, request): """Push a request""" raise NotImplementedError def pop(self, timeout=0): """Pop a request""" raise NotImplementedError def clear(self): """Clear queue/stack""" self.server.delete(self.key) class FifoQueue(Base): """Per-spider FIFO queue""" def __len__(self): """Return the length of the queue""" return self.server.llen(self.key) def push(self, request): """Push a request""" self.server.lpush(self.key, self._encode_request(request)) def pop(self, timeout=0): """Pop a request""" if timeout > 0: data = self.server.brpop(self.key, timeout) if isinstance(data, tuple): data = data[1] else: data = self.server.rpop(self.key) if data: return self._decode_request(data) class PriorityQueue(Base): """Per-spider priority queue abstraction using redis‘ sorted set""" def __len__(self): """Return the length of the queue""" return self.server.zcard(self.key) def push(self, request): """Push a request""" data = self._encode_request(request) score = -request.priority # We don‘t use zadd method as the order of arguments change depending on # whether the class is Redis or StrictRedis, and the option of using # kwargs only accepts strings, not bytes. self.server.execute_command(‘ZADD‘, self.key, score, data) def pop(self, timeout=0): """ Pop a request timeout not support in this queue class """ # use atomic range/remove using multi/exec pipe = self.server.pipeline() pipe.multi() pipe.zrange(self.key, 0, 0).zremrangebyrank(self.key, 0, 0) results, count = pipe.execute() if results: return self._decode_request(results[0]) class LifoQueue(Base): """Per-spider LIFO queue.""" def __len__(self): """Return the length of the stack""" return self.server.llen(self.key) def push(self, request): """Push a request""" self.server.lpush(self.key, self._encode_request(request)) def pop(self, timeout=0): """Pop a request""" if timeout > 0: data = self.server.blpop(self.key, timeout) if isinstance(data, tuple): data = data[1] else: data = self.server.lpop(self.key) if data: return self._decode_request(data) # TODO: Deprecate the use of these names. SpiderQueue = FifoQueue SpiderStack = LifoQueue SpiderPriorityQueue = PriorityQueue
注意:爬虫爬取数据时存在层级和优先级:爬虫中间件实现

配置: # ############ 连接redis 信息 ################# REDIS_HOST = ‘127.0.0.1‘ # 主机名 REDIS_PORT = 6379 # 端口 # REDIS_URL = ‘redis://user:pass@hostname:9001‘ # 连接URL(优先于以上配置) REDIS_PARAMS = {} # Redis连接参数 默认:REDIS_PARAMS = {‘socket_timeout‘: 30,‘socket_connect_timeout‘: 30,‘retry_on_timeout‘: True,‘encoding‘: REDIS_ENCODING,}) # REDIS_PARAMS[‘redis_cls‘] = ‘myproject.RedisClient‘ # 指定连接Redis的Python模块 默认:redis.StrictRedis REDIS_ENCODING = "utf-8" # 自定义去重规则 DUPEFILTER_CLASS = "scrapy_redis.dupefilter.RFPDupeFilter"

# ############ 连接redis 信息 ################# REDIS_HOST = ‘127.0.0.1‘ # 主机名 REDIS_PORT = 6379 # 端口 # REDIS_URL = ‘redis://user:pass@hostname:9001‘ # 连接URL(优先于以上配置) REDIS_PARAMS = {} # Redis连接参数 默认:REDIS_PARAMS = {‘socket_timeout‘: 30,‘socket_connect_timeout‘: 30,‘retry_on_timeout‘: True,‘encoding‘: REDIS_ENCODING,}) # REDIS_PARAMS[‘redis_cls‘] = ‘myproject.RedisClient‘ # 指定连接Redis的Python模块 默认:redis.StrictRedis REDIS_ENCODING = "utf-8" # 有引擎来执行:自定义调度器 SCHEDULER = "scrapy_redis.scheduler.Scheduler" SCHEDULER_QUEUE_CLASS = ‘scrapy_redis.queue.LifoQueue‘ # 默认使用优先级队列(默认广度优先),其他:PriorityQueue(有序集合),FifoQueue(列表)、LifoQueue(列表) SCHEDULER_QUEUE_KEY = ‘%(spider)s:requests‘ # 调度器中请求存放在redis中的key SCHEDULER_SERIALIZER = "scrapy_redis.picklecompat" # 对保存到redis中的数据进行序列化,默认使用pickle SCHEDULER_PERSIST = True # 是否在关闭时候保留原来的调度器和去重记录,True=保留,False=清空 SCHEDULER_FLUSH_ON_START = False # 是否在开始之前清空 调度器和去重记录,True=清空,False=不清空 # SCHEDULER_IDLE_BEFORE_CLOSE = 10 # 去调度器中获取数据时,如果为空,最多等待时间(最后没数据,未获取到)。 SCHEDULER_DUPEFILTER_KEY = ‘%(spider)s:dupefilter‘ # 去重规则,在redis中保存时对应的key chouti:dupefilter SCHEDULER_DUPEFILTER_CLASS = ‘scrapy.dupefilter.RFPDupeFilter‘ # 去重规则对应处理的类 #去重规则对应处理的类 DUPEFILTER_DEBUG = False

# ############ 连接redis 信息 ################# REDIS_HOST = ‘127.0.0.1‘ # 主机名 REDIS_PORT = 6379 # 端口 # REDIS_URL = ‘redis://user:pass@hostname:9001‘ # 连接URL(优先于以上配置) REDIS_PARAMS = {} # Redis连接参数 默认:REDIS_PARAMS = {‘socket_timeout‘: 30,‘socket_connect_timeout‘: 30,‘retry_on_timeout‘: True,‘encoding‘: REDIS_ENCODING,}) # REDIS_PARAMS[‘redis_cls‘] = ‘myproject.RedisClient‘ # 指定连接Redis的Python模块 默认:redis.StrictRedis REDIS_ENCODING = "utf-8" # 有引擎来执行:自定义调度器 SCHEDULER = "scrapy_redis.scheduler.Scheduler" SCHEDULER_QUEUE_CLASS = ‘scrapy_redis.queue.LifoQueue‘ # 默认使用优先级队列(默认广度优先),其他:PriorityQueue(有序集合),FifoQueue(列表)、LifoQueue(列表) SCHEDULER_QUEUE_KEY = ‘%(spider)s:requests‘ # 调度器中请求存放在redis中的key SCHEDULER_SERIALIZER = "scrapy_redis.picklecompat" # 对保存到redis中的数据进行序列化,默认使用pickle SCHEDULER_PERSIST = True # 是否在关闭时候保留原来的调度器和去重记录,True=保留,False=清空 SCHEDULER_FLUSH_ON_START = False # 是否在开始之前清空 调度器和去重记录,True=清空,False=不清空 # SCHEDULER_IDLE_BEFORE_CLOSE = 10 # 去调度器中获取数据时,如果为空,最多等待时间(最后没数据,未获取到)。 SCHEDULER_DUPEFILTER_KEY = ‘%(spider)s:dupefilter‘ # 去重规则,在redis中保存时对应的key chouti:dupefilter SCHEDULER_DUPEFILTER_CLASS = ‘scrapy_redis.dupefilter.RFPDupeFilter‘ # 去重规则对应处理的类 DUPEFILTER_DEBUG = False
使用scrapy-redis内置的pipeline做持久化:就是将item对象保存到redis的列表中,如下代码所示

配置: # ############ 连接redis 信息 ################# REDIS_HOST = ‘127.0.0.1‘ # 主机名 REDIS_PORT = 6379 # 端口 # REDIS_URL = ‘redis://user:pass@hostname:9001‘ # 连接URL(优先于以上配置) REDIS_PARAMS = {} # Redis连接参数 默认:REDIS_PARAMS = {‘socket_timeout‘: 30,‘socket_connect_timeout‘: 30,‘retry_on_timeout‘: True,‘encoding‘: REDIS_ENCODING,}) # REDIS_PARAMS[‘redis_cls‘] = ‘myproject.RedisClient‘ # 指定连接Redis的Python模块 默认:redis.StrictRedis REDIS_ENCODING = "utf-8" ITEM_PIPELINES = { ‘scrapy_redis.pipelines.RedisPipeline‘: 300, } 以上功能全部应用的配置: # ############ 连接redis 信息 ################# REDIS_HOST = ‘127.0.0.1‘ # 主机名 REDIS_PORT = 6379 # 端口 # REDIS_URL = ‘redis://user:pass@hostname:9001‘ # 连接URL(优先于以上配置) REDIS_PARAMS = {} # Redis连接参数 默认:REDIS_PARAMS = {‘socket_timeout‘: 30,‘socket_connect_timeout‘: 30,‘retry_on_timeout‘: True,‘encoding‘: REDIS_ENCODING,}) # REDIS_PARAMS[‘redis_cls‘] = ‘myproject.RedisClient‘ # 指定连接Redis的Python模块 默认:redis.StrictRedis REDIS_ENCODING = "utf-8" DUPEFILTER_CLASS = "scrapy_redis.dupefilter.RFPDupeFilter" # 有引擎来执行:自定义调度器 SCHEDULER = "scrapy_redis.scheduler.Scheduler" SCHEDULER_QUEUE_CLASS = ‘scrapy_redis.queue.LifoQueue‘ # 默认使用优先级队列(默认广度优先),其他:PriorityQueue(有序集合),FifoQueue(列表)、LifoQueue(列表) SCHEDULER_QUEUE_KEY = ‘%(spider)s:requests‘ # 调度器中请求存放在redis中的key SCHEDULER_SERIALIZER = "scrapy_redis.picklecompat" # 对保存到redis中的数据进行序列化,默认使用pickle SCHEDULER_PERSIST = True # 是否在关闭时候保留原来的调度器和去重记录,True=保留,False=清空 SCHEDULER_FLUSH_ON_START = False # 是否在开始之前清空 调度器和去重记录,True=清空,False=不清空 # SCHEDULER_IDLE_BEFORE_CLOSE = 10 # 去调度器中获取数据时,如果为空,最多等待时间(最后没数据,未获取到)。 SCHEDULER_DUPEFILTER_KEY = ‘%(spider)s:dupefilter‘ # 去重规则,在redis中保存时对应的key chouti:dupefilter SCHEDULER_DUPEFILTER_CLASS = ‘scrapy_redis.dupefilter.RFPDupeFilter‘ # 去重规则对应处理的类 DUPEFILTER_DEBUG = False # 深度和优先级相关 DEPTH_PRIORITY = 1

配置: REDIS_START_URLS_BATCH_SIZE = 1 # REDIS_START_URLS_AS_SET = True # 把起始url放到redis的集合 REDIS_START_URLS_AS_SET = False # 把起始url放到redis的列表 爬虫: from scrapy_redis.spiders import RedisSpider from scrapy.http import Request from ..items import WenwenItem class ChoutiSpider(RedisSpider): name = ‘chouti‘ allowed_domains = [‘chouti.com‘] def parse(self, response): # 随着深度的增加、优先级一直在递减 print(response) 放置起始URL: import redis conn = redis.Redis(host=‘127.0.0.1‘,port=6379) # 起始url的Key: chouti:start_urls conn.lpush("chouti:start_urls",‘https://dig.chouti.com/r/ask/hot/12‘)
1
标签:xhtml 11.2 完成 xxxxx head rap defer 读取配置 doctype
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/huyangblog/p/9021728.html