标签:去除 else The ons 难点 atm 就是 不同 obs
- VGG-19的介绍和训练这里不做说明,网上资源很多,而且相对比较简单.
- 本博文主要介绍VGG-19模型调用官方已经训练好的模型,进行测试使用.
[TOC]
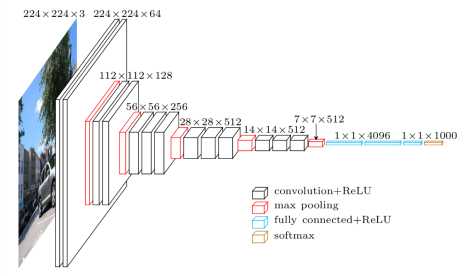
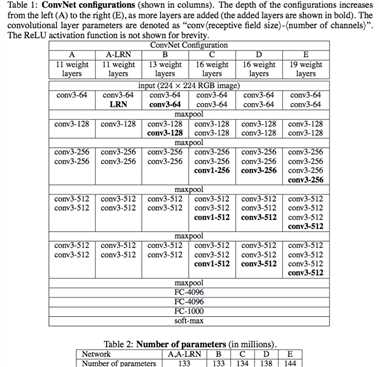
这里是重难点,VGG-19模型存储的方式有点复杂
- 可以通过作者文档说明去查看
- 可以通过在线调试查看结构,对比模型得出结论
首先我们通过scipy模块(当然你可以用其它方式入opencv / sklearn等)读取scipy.io.loadmat()文件
data = scipy.io.loadmat(data_path)接下来使用Pycharm在线查看data数据结构:
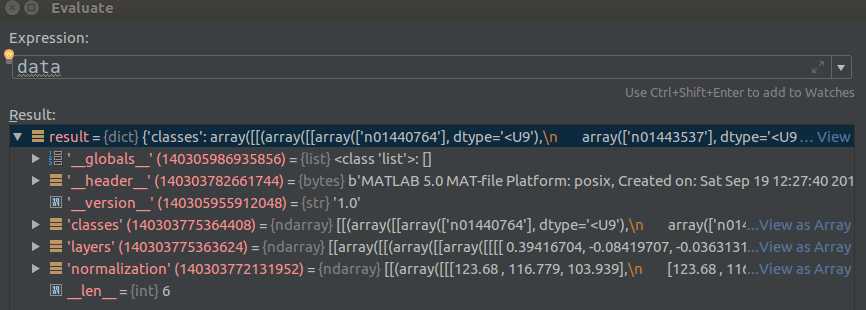
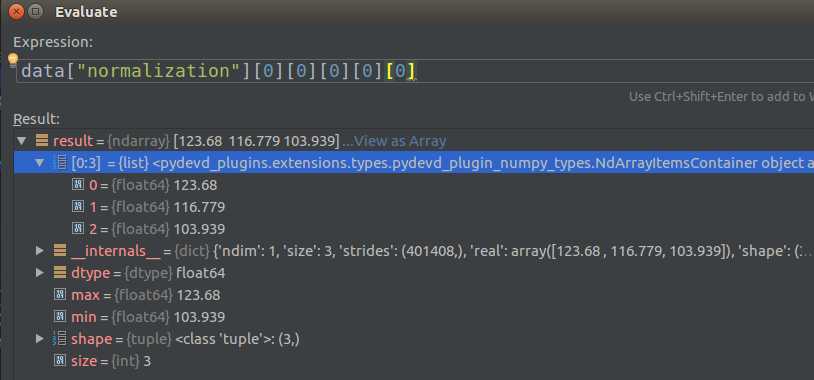
首先查看normalization的mean值:
这里使用笨方法,直接带入:
data["normalization"][0][0][0][0][0]
先看大概看一下数据结构,然后一个一个测试,因为在线调试,这样很快,比你精确的去找要快很多.
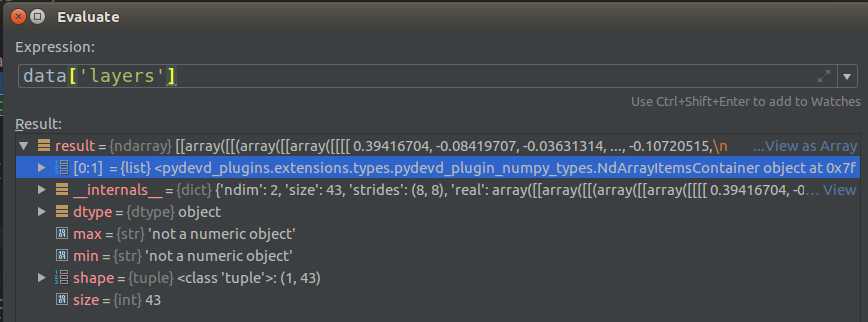
这里和mean查看方法不同,W和B得自习查看数据结构,因为太复杂了
Relu是没有数据的,因为Relu就是一个函数Pool的参数是固定的,因为大小为:[1,2,2,1],步长[1,2,2,1],这里可以自己写,也可以读取参数Weight Bias是存放在Relu Pool 中间的,而且两个值存在一起的.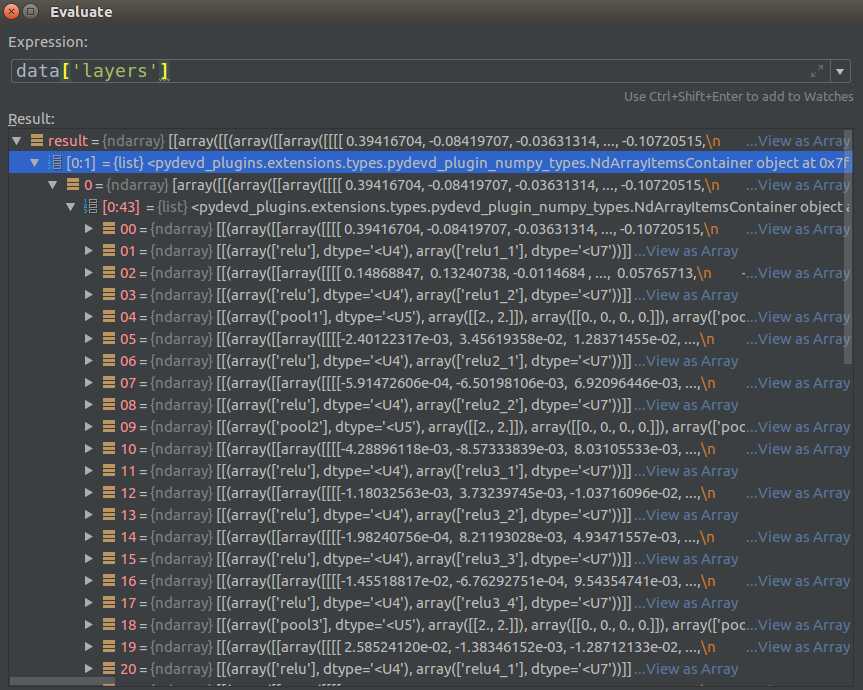
mean = data["normalization"][0][0][0][0][0]data['layers'][0][i][0][0][0][0])这里默认大家已经会CNN的基本操作了,代码不做详细说明
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import os
import scipy.io
import scipy.misc
from imagenet_classes import class_names
def _conv_layer(input,weight,bias):
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(input,weight,strides=[1,1,1,1],padding="SAME")
return tf.nn.bias_add(conv,bias)
def _pool_layer(input):
return tf.nn.max_pool(input,ksize=[1,2,2,1],strides=[1,2,2,1],padding="SAME")
def preprocess(image,mean_pixel):
'''简单预处理,全部图片减去平均值'''
return image-mean_pixel
def unprocess(image,mean_pixel):
return image+mean_pixel
def imread(path):
return scipy.misc.imread(path)
def imsave(image,path):
img = np.clip(image,0,255).astype(np.int8)
scipy.misc.imsave(path,image)
def net(data_path,input_image,sess=None):
"""
读取VGG模型参数,搭建VGG网络
:param data_path: VGG模型文件位置
:param input_image: 输入测试图像
:return:
"""
layers = (
'conv1_1', 'conv1_2', 'pool1',
'conv2_1', 'conv2_2', 'pool2',
'conv3_1', 'conv3_2', 'conv3_3','conv3_4', 'pool3',
'conv4_1', 'conv4_2', 'conv4_3','conv4_4', 'pool4',
'conv5_1', 'conv5_2', 'conv5_3','conv5_4', 'pool5',
'fc1' , 'fc2' , 'fc3' ,
'softmax'
)
data = scipy.io.loadmat(data_path)
mean = data["normalization"][0][0][0][0][0]
input_image = np.array([preprocess(input_image, mean)]).astype(np.float32)#去除平均值
net = {}
current = input_image
net["src_image"] = tf.constant(current) # 存储数据
count = 0 #计数存储
for i in range(43):
if str(data['layers'][0][i][0][0][0][0])[:4] == ("relu"):
continue
if str(data['layers'][0][i][0][0][0][0])[:4] == ("pool"):
current = _pool_layer(current)
elif str(data['layers'][0][i][0][0][0][0]) == ("softmax"):
current = tf.nn.softmax(current)
elif i == (37):
shape = int(np.prod(current.get_shape()[1:]))
current = tf.reshape(current, [-1, shape])
kernels, bias = data['layers'][0][i][0][0][0][0]
kernels = np.reshape(kernels,[-1,4096])
bias = bias.reshape(-1)
current = tf.nn.relu(tf.add(tf.matmul(current,kernels),bias))
elif i == (39):
kernels, bias = data['layers'][0][i][0][0][0][0]
kernels = np.reshape(kernels,[4096,4096])
bias = bias.reshape(-1)
current = tf.nn.relu(tf.add(tf.matmul(current,kernels),bias))
elif i == 41:
kernels, bias = data['layers'][0][i][0][0][0][0]
kernels = np.reshape(kernels, [4096, 1000])
bias = bias.reshape(-1)
current = tf.add(tf.matmul(current, kernels), bias)
else:
kernels,bias = data['layers'][0][i][0][0][0][0]
#注意VGG存储方式为[,]
#kernels = np.transpose(kernels,[1,0,2,3])
bias = bias.reshape(-1)#降低维度
current = tf.nn.relu(_conv_layer(current,kernels,bias))
net[layers[count]] = current #存储数据
count += 1
return net, mean
if __name__ == '__main__':
VGG_PATH = os.getcwd()+"/imagenet-vgg-verydeep-19.mat"
input_image = scipy.misc.imread("234.jpeg")
input_image = scipy.misc.imresize(input_image,[224,224,3])
shape = (1, input_image.shape[0], input_image.shape[1], input_image.shape[2])
#image = tf.placeholder('float', shape=shape)
with tf.Session() as sess:
nets, mean_pixel, = net(VGG_PATH, input_image, sess=sess)
#print(sess.run(nets,feed_dict={image:input_image}))
nets = sess.run(nets)
'''
for key, values in nets.items():
if len(values.shape)<4:
continue
plt.figure(key)
plt.matshow(values[0, :, :, 0],)
plt.title(key)
plt.colorbar()
plt.show()
'''
#打印概率最大的三个数据
net_sort = list(reversed(np.argsort(nets["softmax"]).reshape(-1).tolist()))
net_softmax = nets["softmax"].reshape(-1).tolist()
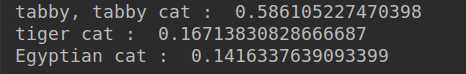
for i in range(3):
print(class_names[net_sort[i]],": ",net_softmax[net_sort[i]])输入图片:

结果显示:
百度验证:
完整模型下载地址:
以下是训练的代码:
这部分随便看看就好,比较简单~~主要看思想和细节!
########################################################################################
# Davi Frossard, 2016 #
# VGG16 implementation in TensorFlow #
# Details: #
# http://www.cs.toronto.edu/~frossard/post/vgg16/ #
# #
# Model from https://gist.github.com/ksimonyan/211839e770f7b538e2d8#file-readme-md #
# Weights from Caffe converted using https://github.com/ethereon/caffe-tensorflow #
########################################################################################
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
from scipy.misc import imread, imresize
from imagenet_classes import class_names
class vgg16:
def __init__(self, imgs, weights=None, sess=None):
self.imgs = imgs
self.convlayers()
self.fc_layers()
self.probs = tf.nn.softmax(self.fc3l)
if weights is not None and sess is not None:
self.load_weights(weights, sess)
def convlayers(self):
self.parameters = []
# zero-mean input
with tf.name_scope('preprocess') as scope:
mean = tf.constant([123.68, 116.779, 103.939], dtype=tf.float32, shape=[1, 1, 1, 3], name='img_mean')
images = self.imgs-mean
# conv1_1
with tf.name_scope('conv1_1') as scope:
kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3, 3, 3, 64], dtype=tf.float32,
stddev=1e-1), name='weights')
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(images, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[64], dtype=tf.float32),
trainable=True, name='biases')
out = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
self.conv1_1 = tf.nn.relu(out, name=scope)
self.parameters += [kernel, biases]
# conv1_2
with tf.name_scope('conv1_2') as scope:
kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3, 3, 64, 64], dtype=tf.float32,
stddev=1e-1), name='weights')
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(self.conv1_1, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[64], dtype=tf.float32),
trainable=True, name='biases')
out = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
self.conv1_2 = tf.nn.relu(out, name=scope)
self.parameters += [kernel, biases]
# pool1
self.pool1 = tf.nn.max_pool(self.conv1_2,
ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1],
strides=[1, 2, 2, 1],
padding='SAME',
name='pool1')
# conv2_1
with tf.name_scope('conv2_1') as scope:
kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3, 3, 64, 128], dtype=tf.float32,
stddev=1e-1), name='weights')
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(self.pool1, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[128], dtype=tf.float32),
trainable=True, name='biases')
out = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
self.conv2_1 = tf.nn.relu(out, name=scope)
self.parameters += [kernel, biases]
# conv2_2
with tf.name_scope('conv2_2') as scope:
kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3, 3, 128, 128], dtype=tf.float32,
stddev=1e-1), name='weights')
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(self.conv2_1, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[128], dtype=tf.float32),
trainable=True, name='biases')
out = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
self.conv2_2 = tf.nn.relu(out, name=scope)
self.parameters += [kernel, biases]
# pool2
self.pool2 = tf.nn.max_pool(self.conv2_2,
ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1],
strides=[1, 2, 2, 1],
padding='SAME',
name='pool2')
# conv3_1
with tf.name_scope('conv3_1') as scope:
kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3, 3, 128, 256], dtype=tf.float32,
stddev=1e-1), name='weights')
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(self.pool2, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[256], dtype=tf.float32),
trainable=True, name='biases')
out = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
self.conv3_1 = tf.nn.relu(out, name=scope)
self.parameters += [kernel, biases]
# conv3_2
with tf.name_scope('conv3_2') as scope:
kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3, 3, 256, 256], dtype=tf.float32,
stddev=1e-1), name='weights')
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(self.conv3_1, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[256], dtype=tf.float32),
trainable=True, name='biases')
out = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
self.conv3_2 = tf.nn.relu(out, name=scope)
self.parameters += [kernel, biases]
# conv3_3
with tf.name_scope('conv3_3') as scope:
kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3, 3, 256, 256], dtype=tf.float32,
stddev=1e-1), name='weights')
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(self.conv3_2, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[256], dtype=tf.float32),
trainable=True, name='biases')
out = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
self.conv3_3 = tf.nn.relu(out, name=scope)
self.parameters += [kernel, biases]
# pool3
self.pool3 = tf.nn.max_pool(self.conv3_3,
ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1],
strides=[1, 2, 2, 1],
padding='SAME',
name='pool3')
# conv4_1
with tf.name_scope('conv4_1') as scope:
kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3, 3, 256, 512], dtype=tf.float32,
stddev=1e-1), name='weights')
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(self.pool3, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[512], dtype=tf.float32),
trainable=True, name='biases')
out = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
self.conv4_1 = tf.nn.relu(out, name=scope)
self.parameters += [kernel, biases]
# conv4_2
with tf.name_scope('conv4_2') as scope:
kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3, 3, 512, 512], dtype=tf.float32,
stddev=1e-1), name='weights')
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(self.conv4_1, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[512], dtype=tf.float32),
trainable=True, name='biases')
out = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
self.conv4_2 = tf.nn.relu(out, name=scope)
self.parameters += [kernel, biases]
# conv4_3
with tf.name_scope('conv4_3') as scope:
kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3, 3, 512, 512], dtype=tf.float32,
stddev=1e-1), name='weights')
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(self.conv4_2, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[512], dtype=tf.float32),
trainable=True, name='biases')
out = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
self.conv4_3 = tf.nn.relu(out, name=scope)
self.parameters += [kernel, biases]
# pool4
self.pool4 = tf.nn.max_pool(self.conv4_3,
ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1],
strides=[1, 2, 2, 1],
padding='SAME',
name='pool4')
# conv5_1
with tf.name_scope('conv5_1') as scope:
kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3, 3, 512, 512], dtype=tf.float32,
stddev=1e-1), name='weights')
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(self.pool4, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[512], dtype=tf.float32),
trainable=True, name='biases')
out = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
self.conv5_1 = tf.nn.relu(out, name=scope)
self.parameters += [kernel, biases]
# conv5_2
with tf.name_scope('conv5_2') as scope:
kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3, 3, 512, 512], dtype=tf.float32,
stddev=1e-1), name='weights')
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(self.conv5_1, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[512], dtype=tf.float32),
trainable=True, name='biases')
out = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
self.conv5_2 = tf.nn.relu(out, name=scope)
self.parameters += [kernel, biases]
# conv5_3
with tf.name_scope('conv5_3') as scope:
kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3, 3, 512, 512], dtype=tf.float32,
stddev=1e-1), name='weights')
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(self.conv5_2, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[512], dtype=tf.float32),
trainable=True, name='biases')
out = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
self.conv5_3 = tf.nn.relu(out, name=scope)
self.parameters += [kernel, biases]
# pool5
self.pool5 = tf.nn.max_pool(self.conv5_3,
ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1],
strides=[1, 2, 2, 1],
padding='SAME',
name='pool4')
def fc_layers(self):
# fc1
with tf.name_scope('fc1') as scope:
shape = int(np.prod(self.pool5.get_shape()[1:]))
fc1w = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([shape, 4096],
dtype=tf.float32,
stddev=1e-1), name='weights')
fc1b = tf.Variable(tf.constant(1.0, shape=[4096], dtype=tf.float32),
trainable=True, name='biases')
pool5_flat = tf.reshape(self.pool5, [-1, shape])
fc1l = tf.nn.bias_add(tf.matmul(pool5_flat, fc1w), fc1b)
self.fc1 = tf.nn.relu(fc1l)
self.parameters += [fc1w, fc1b]
# fc2
with tf.name_scope('fc2') as scope:
fc2w = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([4096, 4096],
dtype=tf.float32,
stddev=1e-1), name='weights')
fc2b = tf.Variable(tf.constant(1.0, shape=[4096], dtype=tf.float32),
trainable=True, name='biases')
fc2l = tf.nn.bias_add(tf.matmul(self.fc1, fc2w), fc2b)
self.fc2 = tf.nn.relu(fc2l)
self.parameters += [fc2w, fc2b]
# fc3
with tf.name_scope('fc3') as scope:
fc3w = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([4096, 1000],
dtype=tf.float32,
stddev=1e-1), name='weights')
fc3b = tf.Variable(tf.constant(1.0, shape=[1000], dtype=tf.float32),
trainable=True, name='biases')
self.fc3l = tf.nn.bias_add(tf.matmul(self.fc2, fc3w), fc3b)
self.parameters += [fc3w, fc3b]
def load_weights(self, weight_file, sess):
weights = np.load(weight_file)
keys = sorted(weights.keys())
for i, k in enumerate(keys):
print i, k, np.shape(weights[k])
sess.run(self.parameters[i].assign(weights[k]))
if __name__ == '__main__':
sess = tf.Session()
imgs = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 224, 224, 3])
vgg = vgg16(imgs, 'vgg16_weights.npz', sess)
img1 = imread('laska.png', mode='RGB')
img1 = imresize(img1, (224, 224))
prob = sess.run(vgg.probs, feed_dict={vgg.imgs: [img1]})[0]
preds = (np.argsort(prob)[::-1])[0:5]
for p in preds:
print class_names[p], prob[p]标签:去除 else The ons 难点 atm 就是 不同 obs
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/wjy-lulu/p/9175529.html