标签:des style blog http color io os 使用 ar
在上一节中,了解了Tomcat服务器启动的整个过程,现在来了解一下Tomcat如何接收到HTTP请求,并将请求送达至Servlet,Servlet处理后,响应信息又是如何返回给浏览器的呢?这两个问题是接下来要研究的课题,本节先研究第一个问题。
了解一点点网络知识的人,都会知道TCP连接通信是基于Socket的,上一节也有提到这点。通过上一节的说明,可以了解到Tomcat服务器在内部已经使用Endpoint类封装了Socket。
本篇会包含大量的源码解读说,由于篇幅原因,就将源码折叠起来,如果想了解其过程,简易打开折叠的源码看看。
在查看源码之前,建议大家自己想一想,如果是你来设计,会怎么处理请求。我先自己想了一下请求处理过程:
1) ServerSocket accept客户端的请求得到Socket对象,这一部分肯定要与Connector关联起来,因为只有Connector上配置了与TCP相关的东西,例如:port, protocol等。
2) Tomcat中的某个组件(在Connector范围内)解析Socket对象,封装成一个Request对象
3) Tomcat中某个组件(在Connector范围内)根据Request对象在服务器上找出于这个连接器关联的Container,也就是Engine。因为Connector和Engine都是Service范围内的,并且一个Service内可以有多个Connector,只能有一个Engine,所以在Connector确定的情况下,Engine就是确定的。接下来只需要找到所在的虚拟主机Host就行了。
4) 找到请求所属的主机Host,根据HTTP请求的URL就可以了。这是因为URL由遵循下面的结构:Protocol://host:port/context/path
5)找到请求所属的context,也就是说找到请求那个web app的。
6)根据请求的path部分找到所在的Web app的资源处理Servlet
因为在web.xml中配置了Servlet的url-pattern,也就是那个Servlet处理哪些路径下的资源请求。
7)如果有filter,先filter处理。
8)调用Servlet#doService()方法。这是在做Java Web开发时了解到的。然后根据请求的method(GET、POST、PUT等),自动的解析为doXxx(doGet, doPost)
在了解这一部分前,我简单的看了一下源码,做了一个简单的类图:
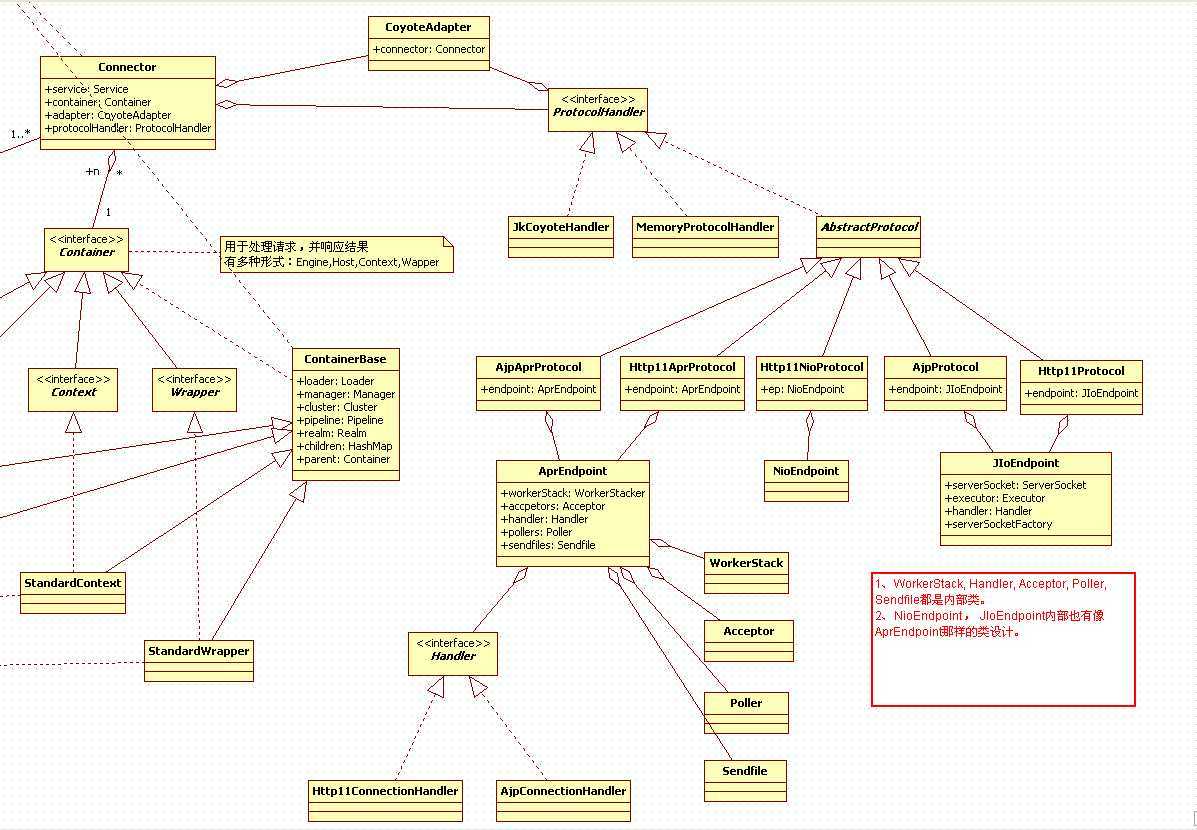
接下来,就通过调试说明这个处理过程:
调试前,先看看系统中已有的线程:
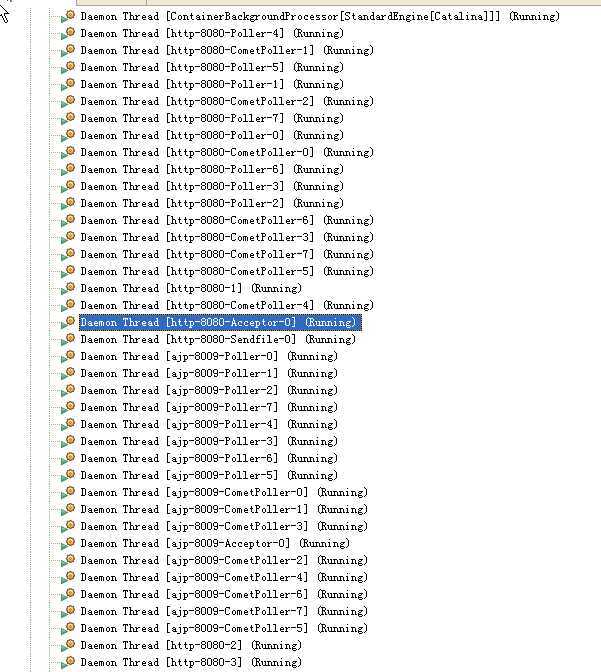
从这个线程列表里可以看出来,这些线程都是各个Endpoint内部的属性(Acceptor、CometPoller、Poller)的线程。所以我们发送的请求肯定是这几类线程中的一个来处理的。
通过类图知道,在AprEndpoint内部有很多的Acceptor,应该是用于接收不同端口的TCP连接的吧。
猜想不能解决问题,经过调试,确实发现这里开始接收TCP连接请求了:

public void run() { // Loop until we receive a shutdown command while (running) { // Loop if endpoint is paused while (paused && running) { try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { // Ignore } } if (!running) { break; } try { // Accept the next incoming connection from the server socket long socket = Socket.accept(serverSock); /* * In the case of a deferred accept unlockAccept needs to * send data. This data will be rubbish, so destroy the * socket and don‘t process it. */ if (deferAccept && (paused || !running)) { destroySocket(socket); continue; } // Hand this socket off to an appropriate processor if (!processSocketWithOptions(socket)) { // Close socket and pool right away destroySocket(socket); } } catch (Throwable t) { if (running) { String msg = sm.getString("endpoint.accept.fail"); if (t instanceof Error) { Error e = (Error) t; if (e.getError() == 233) { // Not an error on HP-UX so log as a warning // so it can be filtered out on that platform // See bug 50273 log.warn(msg, t); } else { log.error(msg, t); } } else { log.error(msg, t); } } } // The processor will recycle itself when it finishes } }
这里附加一些Java的基本知识:它只用接收请求就行了,别的什么也不用做。
它并没有拿到一个Socket,也没有将socket传递给其他的类,但是却能够完成请求的处理,这是为什么呢?
上面的代码中Socket.acccpt(serverSocket),就是接收一个Socket请求,标示是serverSocket 。
因为使用了内部类,这样的好处是内部类方法和属性对于外部类是可见的,外部类的方法属性对内部类也是可见的。其实内部类的方法可以认为是对于外部类的扩充,只是在其他的类中不能使用这些方法而已,只能在外部类,内部类本身里使用而已(当然了,如果内部类是public,方法也是public情况下,第三方类还是可以使用的)。

public void run() { // Process requests until we receive a shutdown signal while (running) { // Wait for the next socket to be assigned // 拿到Acceptor接收到的请求 long socket = await(); if (socket == 0) continue; if (!deferAccept && options) { if (setSocketOptions(socket)) { getPoller().add(socket); } else { // Close socket and pool destroySocket(socket); socket = 0; } } else { // Process the request from this socket if ((status != null) && (handler.event(socket, status) == Handler.SocketState.CLOSED)) { // Close socket and pool destroySocket(socket); socket = 0; // 调用Handler.process处理Socket // 在Handler对象内部,会找到一个HTTP11AprProcessor处理器,用于处理Socket请求 // 然后在HTTP11AprProcessor处理过程中,又会转给 } else if ((status == null) && ((options && !setSocketOptions(socket)) || handler.process(socket) == Handler.SocketState.CLOSED)) { // Close socket and pool destroySocket(socket); socket = 0; } } // Finish up this request recycleWorkerThread(this); } }
由于方法比较长,就不粘了,只粘出主要代码:
inputBuffer.setSocket(socket);
inputBuffer.parseHeaders();
而inputBuffer#parseHeader():
/** * Parse the HTTP headers. */ public void parseHeaders() throws IOException { // 每一次调用parseHeader(),就是解析HTTP Header中的一条。 这个是基于HTTP Header的格式来解析的,这个不明白,可以先了解一下HTTP协议 while (parseHeader()) { } parsingHeader = false; end = pos; }
InputBuffer# parseHeader(),这个过程比较复杂,就不贴了。下面贴出来解析后的消息头:
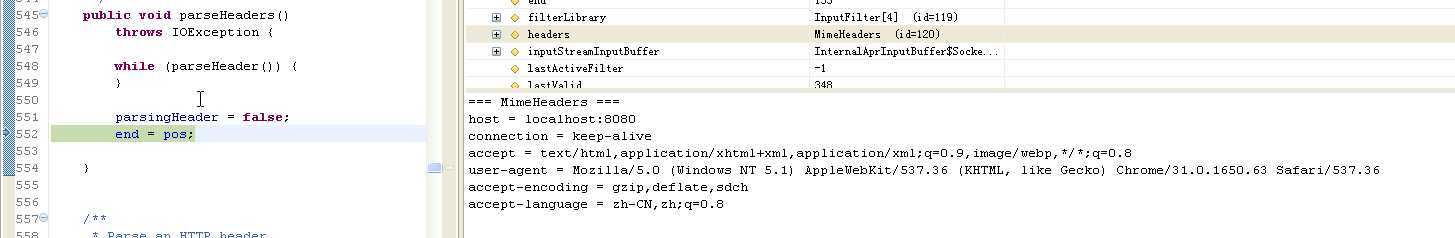
准备Request,其实就是做一些额外的处理,例如根据消息头解析host, port,context,path等等,将其封装为StandardContext对象,然后放在Request对象里。

public void service(org.apache.coyote.Request req, org.apache.coyote.Response res) throws Exception { Request request = (Request) req.getNote(ADAPTER_NOTES); Response response = (Response) res.getNote(ADAPTER_NOTES); if (request == null) { // Create objects request = (Request) connector.createRequest(); request.setCoyoteRequest(req); response = (Response) connector.createResponse(); response.setCoyoteResponse(res); // Link objects request.setResponse(response); response.setRequest(request); // Set as notes req.setNote(ADAPTER_NOTES, request); res.setNote(ADAPTER_NOTES, response); // Set query string encoding req.getParameters().setQueryStringEncoding (connector.getURIEncoding()); } if (connector.getXpoweredBy()) { response.addHeader("X-Powered-By", POWERED_BY); } boolean comet = false; try { // Parse and set Catalina and configuration specific // request parameters req.getRequestProcessor().setWorkerThreadName(Thread.currentThread().getName()); if (postParseRequest(req, request, res, response)) { // Calling the container // 通过这一步,获取到与Connector关联的Container【也就是Engine】,如此就将流程转给了Tomcat容器处理了。 //这也是这个CoyoteApapter的作用 // 这里connector.getContainer()得到的是一个Engine // engine.getPipeline().getFirst()得到的其实是Engine的pipeliene中的一个StandardEngineValue。 Tomcat中的Value是用于执行一些任务的。至于为什么起名为Value,就不太清楚了。只需要知道这段代码执行的是StandardEngineValue#invoke()就可以了。 connector.getContainer().getPipeline().getFirst().invoke(request, response); if (request.isComet()) { if (!response.isClosed() && !response.isError()) { if (request.getAvailable() || (request.getContentLength() > 0 && (!request.isParametersParsed()))) { // Invoke a read event right away if there are available bytes if (event(req, res, SocketStatus.OPEN)) { comet = true; res.action(ActionCode.ACTION_COMET_BEGIN, null); } } else { comet = true; res.action(ActionCode.ACTION_COMET_BEGIN, null); } } else { // Clear the filter chain, as otherwise it will not be reset elsewhere // since this is a Comet request request.setFilterChain(null); } } } if (!comet) { response.finishResponse(); req.action(ActionCode.ACTION_POST_REQUEST , null); } } catch (IOException e) { ; } finally { req.getRequestProcessor().setWorkerThreadName(null); // Recycle the wrapper request and response if (!comet) { request.recycle(); response.recycle(); } else { // Clear converters so that the minimum amount of memory // is used by this processor request.clearEncoders(); response.clearEncoders(); } } }
下面是StandardEngineValue#invoke()的源码:

/** * Select the appropriate child Host to process this request, * based on the requested server name. If no matching Host can * be found, return an appropriate HTTP error. * */ public final void invoke(Request request, Response response) throws IOException, ServletException { // Select the Host to be used for this Request Host host = request.getHost(); if (host == null) { response.sendError (HttpServletResponse.SC_BAD_REQUEST, sm.getString("standardEngine.noHost", request.getServerName())); return; } // Ask this Host to process this request // 这个设计与之前的设计思路是一致的,调用的是StandardHostValue#invoke() host.getPipeline().getFirst().invoke(request, response); }
从invoke方法的注释就可以知道,是要从engine范围内,根据第3)步找到的HOST信息,将请求交给host处理。
这一步与上面是类似的,将请求交给了StandardContextValue处理。

/** * Select the appropriate child Context to process this request, * based on the specified request URI. If no matching Context can * be found, return an appropriate HTTP error. */ public final void invoke(Request request, Response response) throws IOException, ServletException { // Select the Context to be used for this Request Context context = request.getContext(); if (context == null) { response.sendError (HttpServletResponse.SC_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR, sm.getString("standardHost.noContext")); return; } // Bind the context CL to the current thread if( context.getLoader() != null ) { // Not started - it should check for availability first // This should eventually move to Engine, it‘s generic. Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader (context.getLoader().getClassLoader()); } // Ask this Context to process this request context.getPipeline().getFirst().invoke(request, response); // Access a session (if present) to update last accessed time, based on a // strict interpretation of the specification if (Globals.STRICT_SERVLET_COMPLIANCE) { request.getSession(false); } // Error page processing response.setSuspended(false); Throwable t = (Throwable) request.getAttribute(Globals.EXCEPTION_ATTR); if (t != null) { throwable(request, response, t); } else { status(request, response); } // Restore the context classloader Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader (StandardHostValve.class.getClassLoader()); }
至此,请求终于到达处理它的WEB应用程序了。

/** * Select the appropriate child Wrapper to process this request, * based on the specified request URI. If no matching Wrapper can * be found, return an appropriate HTTP error. * * @param request Request to be processed * @param response Response to be produced * @param valveContext Valve context used to forward to the next Valve * * @exception IOException if an input/output error occurred * @exception ServletException if a servlet error occurred */ public final void invoke(Request request, Response response) throws IOException, ServletException { // Disallow any direct access to resources under WEB-INF or META-INF // META-INF 和WEB-INF目录是应用程序内部的专属空间,是不允许直接这两个目录下的内容的。所以如果你的请求URL上包含着两个目录,都不会被处理。 // 在应用程序内部,例如Servlet里,可以处理这两个目录下的文件。譬如JSP文件放在WEB-INF目录下,直接访问是不可见的,但是通过Servlet进行forward就可以。但是这都是请求到达Servlet之后的事了,现在请求还没到Servlet呢,别急。 MessageBytes requestPathMB = request.getRequestPathMB(); if ((requestPathMB.startsWithIgnoreCase("/META-INF/", 0)) || (requestPathMB.equalsIgnoreCase("/META-INF")) || (requestPathMB.startsWithIgnoreCase("/WEB-INF/", 0)) || (requestPathMB.equalsIgnoreCase("/WEB-INF"))) { notFound(response); return; } // Wait if we are reloading // 软重启应用程序,前提是Web应用程序下有资源改变,一般情况下,不会重启的。 boolean reloaded = false; while (context.getPaused()) { reloaded = true; try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { ; } } // Reloading will have stopped the old webappclassloader and // created a new one // 要是重启过,就得重新设置类加载器 if (reloaded && context.getLoader() != null && context.getLoader().getClassLoader() != null) { Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader( context.getLoader().getClassLoader()); } // Select the Wrapper to be used for this Request Wrapper wrapper = request.getWrapper(); if (wrapper == null) { notFound(response); return; } else if (wrapper.isUnavailable()) { // May be as a result of a reload, try and find the new wrapper wrapper = (Wrapper) container.findChild(wrapper.getName()); if (wrapper == null) { notFound(response); return; } } // Normal request processing // 取得所有的监听器,这些监听器都是我们在web.xml中配置的(有ServletContext(application)、Session、Request 级别的监听器) 不管属于哪个级别的,全部查出来。 Object instances[] = context.getApplicationEventListeners(); ServletRequestEvent event = null; if ((instances != null) && (instances.length > 0)) { // 封装一个request级别的Event event = new ServletRequestEvent (((StandardContext) container).getServletContext(), request.getRequest()); // create pre-service event // 轮询前面取到所有的listener,处理RequestListener for (int i = 0; i < instances.length; i++) { if (instances[i] == null) continue; if (!(instances[i] instanceof ServletRequestListener)) continue; ServletRequestListener listener = (ServletRequestListener) instances[i]; try { // listener处理 listener.requestInitialized(event); } catch (Throwable t) { container.getLogger().error(sm.getString("standardContext.requestListener.requestInit", instances[i].getClass().getName()), t); ServletRequest sreq = request.getRequest(); sreq.setAttribute(Globals.EXCEPTION_ATTR,t); return; } } } // 同之前的设计一样,找到StandardWrapperValue,处理Request wrapper.getPipeline().getFirst().invoke(request, response); // 监听器结束生命周期 if ((instances !=null ) && (instances.length > 0)) { // create post-service event for (int i = 0; i < instances.length; i++) { if (instances[i] == null) continue; if (!(instances[i] instanceof ServletRequestListener)) continue; ServletRequestListener listener = (ServletRequestListener) instances[i]; try { listener.requestDestroyed(event); } catch (Throwable t) { container.getLogger().error(sm.getString("standardContext.requestListener.requestDestroy", instances[i].getClass().getName()), t); ServletRequest sreq = request.getRequest(); sreq.setAttribute(Globals.EXCEPTION_ATTR,t); } } } }
请求并不是直接就让Servlet处理的,这点做过Web开发的人都知道,至少中间还有个Filter要处理吧。
下面是StandardWrapperValue#invoke()的源码,就来了解一下它是咋处理的。
这点代码包含了很多内容,解析来会一一说明:

/** * Invoke the servlet we are managing, respecting the rules regarding * servlet lifecycle and SingleThreadModel support. * */ public final void invoke(Request request, Response response) throws IOException, ServletException { // Initialize local variables we may need boolean unavailable = false; Throwable throwable = null; // This should be a Request attribute... long t1=System.currentTimeMillis(); requestCount++; StandardWrapper wrapper = (StandardWrapper) getContainer(); Servlet servlet = null; Context context = (Context) wrapper.getParent(); // 检查context是否可用,就是检查web应用程序是否可用,因为可能出现应用程序挂了,或者软重启了 if (!context.getAvailable()) { response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE, sm.getString("standardContext.isUnavailable")); unavailable = true; } // 检查要处理请求的Servlet是否可用,如果Servlet被删除,然后也重启Context了,servlet就没有了,所以又必要检查一下。 if (!unavailable && wrapper.isUnavailable()) { container.getLogger().info(sm.getString("standardWrapper.isUnavailable", wrapper.getName())); long available = wrapper.getAvailable(); if ((available > 0L) && (available < Long.MAX_VALUE)) { response.setDateHeader("Retry-After", available); response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE, sm.getString("standardWrapper.isUnavailable", wrapper.getName())); } else if (available == Long.MAX_VALUE) { response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_FOUND, sm.getString("standardWrapper.notFound", wrapper.getName())); } unavailable = true; } // 分配一个Servlet对象来处理请求,下面8.1会详细说明如何分配的 try { if (!unavailable) { servlet = wrapper.allocate(); } } catch (UnavailableException e) { container.getLogger().error( sm.getString("standardWrapper.allocateException", wrapper.getName()), e); long available = wrapper.getAvailable(); if ((available > 0L) && (available < Long.MAX_VALUE)) { response.setDateHeader("Retry-After", available); response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE, sm.getString("standardWrapper.isUnavailable", wrapper.getName())); } else if (available == Long.MAX_VALUE) { response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_FOUND, sm.getString("standardWrapper.notFound", wrapper.getName())); } } catch (ServletException e) { container.getLogger().error(sm.getString("standardWrapper.allocateException", wrapper.getName()), StandardWrapper.getRootCause(e)); throwable = e; exception(request, response, e); servlet = null; } catch (Throwable e) { container.getLogger().error(sm.getString("standardWrapper.allocateException", wrapper.getName()), e); throwable = e; exception(request, response, e); servlet = null; } // Identify if the request is Comet related now that the servlet has been allocated boolean comet = false; if (servlet instanceof CometProcessor && request.getAttribute("org.apache.tomcat.comet.support") == Boolean.TRUE) { comet = true; request.setComet(true); } // 告诉Connector:已经拿到处理的Servlet了。 try { response.sendAcknowledgement(); } catch (IOException e) { request.removeAttribute(Globals.JSP_FILE_ATTR); container.getLogger().warn(sm.getString("standardWrapper.acknowledgeException", wrapper.getName()), e); throwable = e; exception(request, response, e); } catch (Throwable e) { container.getLogger().error(sm.getString("standardWrapper.acknowledgeException", wrapper.getName()), e); throwable = e; exception(request, response, e); servlet = null; } MessageBytes requestPathMB = null; if (request != null) { requestPathMB = request.getRequestPathMB(); } request.setAttribute (ApplicationFilterFactory.DISPATCHER_TYPE_ATTR, ApplicationFilterFactory.REQUEST_INTEGER); request.setAttribute (ApplicationFilterFactory.DISPATCHER_REQUEST_PATH_ATTR, requestPathMB); // 为request创建Filter链,是创建,是为每一个请求创建过滤器链,不是获取已有的。 ApplicationFilterFactory factory = ApplicationFilterFactory.getInstance(); ApplicationFilterChain filterChain = factory.createFilterChain(request, wrapper, servlet); // Reset comet flag value after creating the filter chain request.setComet(false); //调用filter chain处理请求,这个过程我还有一篇文章专门讲述 try { String jspFile = wrapper.getJspFile(); if (jspFile != null) request.setAttribute(Globals.JSP_FILE_ATTR, jspFile); else request.removeAttribute(Globals.JSP_FILE_ATTR); if ((servlet != null) && (filterChain != null)) { // Swallow output if needed if (context.getSwallowOutput()) { try { SystemLogHandler.startCapture(); if (comet) { filterChain.doFilterEvent(request.getEvent()); request.setComet(true); } else { filterChain.doFilter(request.getRequest(), response.getResponse()); } } finally { String log = SystemLogHandler.stopCapture(); if (log != null && log.length() > 0) { context.getLogger().info(log); } } } else { if (comet) { request.setComet(true); filterChain.doFilterEvent(request.getEvent()); } else { filterChain.doFilter (request.getRequest(), response.getResponse()); } } } request.removeAttribute(Globals.JSP_FILE_ATTR); } catch (ClientAbortException e) { request.removeAttribute(Globals.JSP_FILE_ATTR); throwable = e; exception(request, response, e); } catch (IOException e) { request.removeAttribute(Globals.JSP_FILE_ATTR); container.getLogger().error(sm.getString("standardWrapper.serviceException", wrapper.getName()), e); throwable = e; exception(request, response, e); } catch (UnavailableException e) { request.removeAttribute(Globals.JSP_FILE_ATTR); container.getLogger().error(sm.getString("standardWrapper.serviceException", wrapper.getName()), e); // throwable = e; // exception(request, response, e); wrapper.unavailable(e); long available = wrapper.getAvailable(); if ((available > 0L) && (available < Long.MAX_VALUE)) { response.setDateHeader("Retry-After", available); response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE, sm.getString("standardWrapper.isUnavailable", wrapper.getName())); } else if (available == Long.MAX_VALUE) { response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_FOUND, sm.getString("standardWrapper.notFound", wrapper.getName())); } // Do not save exception in ‘throwable‘, because we // do not want to do exception(request, response, e) processing } catch (ServletException e) { request.removeAttribute(Globals.JSP_FILE_ATTR); Throwable rootCause = StandardWrapper.getRootCause(e); if (!(rootCause instanceof ClientAbortException)) { container.getLogger().error(sm.getString("standardWrapper.serviceException", wrapper.getName()), rootCause); } throwable = e; exception(request, response, e); } catch (Throwable e) { request.removeAttribute(Globals.JSP_FILE_ATTR); container.getLogger().error(sm.getString("standardWrapper.serviceException", wrapper.getName()), e); throwable = e; exception(request, response, e); } // 释放过滤器链,此时Servlet已经执行完毕。 if (filterChain != null) { if (request.isComet()) { // If this is a Comet request, then the same chain will be used for the // processing of all subsequent events. filterChain.reuse(); } else { filterChain.release(); } } // 回收servlet try { if (servlet != null) { wrapper.deallocate(servlet); } } catch (Throwable e) { container.getLogger().error(sm.getString("standardWrapper.deallocateException", wrapper.getName()), e); if (throwable == null) { throwable = e; exception(request, response, e); } } // If this servlet has been marked permanently unavailable, // unload it and release this instance try { if ((servlet != null) && (wrapper.getAvailable() == Long.MAX_VALUE)) { wrapper.unload(); } } catch (Throwable e) { container.getLogger().error(sm.getString("standardWrapper.unloadException", wrapper.getName()), e); if (throwable == null) { throwable = e; exception(request, response, e); } } long t2=System.currentTimeMillis(); long time=t2-t1; processingTime += time; if( time > maxTime) maxTime=time; if( time < minTime) minTime=time; }
要让Servlet处理请求,得先分配Servlet,分配Servlet对象也是有讲究的,因为Servlet有两种运行模式,单线程运行模式和多线程运行模式。

public Servlet allocate() throws ServletException { // If we are currently unloading this servlet, throw an exception if (unloading) throw new ServletException (sm.getString("standardWrapper.unloading", getName())); boolean newInstance = false; // If not SingleThreadedModel, return the same instance every time if (!singleThreadModel) { // 如果是第一次请求这个Servlet,Servlet肯定还没有创建,这时就要创建一个Servlet实例,并初始化。这一点,我想有的面试官会问到的。 if (instance == null) { synchronized (this) { if (instance == null) { try { if (log.isDebugEnabled()) log.debug("Allocating non-STM instance"); // loadServlet()过程也做了很多事: // 如果是jsp请求:解析JSP成一个Servlet类,编译,加载(解析,编译过程只在第一次请求该JSP文件时进行) // 如果是html,img,css,js等就返回DefaultServlet instance = loadServlet(); // For non-STM, increment here to prevent a race // condition with unload. Bug 43683, test case #3 if (!singleThreadModel) { newInstance = true; countAllocated.incrementAndGet(); } } catch (ServletException e) { throw e; } catch (Throwable e) { throw new ServletException (sm.getString("standardWrapper.allocate"), e); } } } } // 返回Servlet实例。 if (!singleThreadModel) { if (log.isTraceEnabled()) log.trace(" Returning non-STM instance"); // For new instances, count will have been incremented at the // time of creation if (!newInstance) { countAllocated.incrementAndGet(); } return (instance); } } // 要是单线程模式下运行的Sevlet,就得等Servlet执行完毕,被回收后,再分配给你这个请求 synchronized (instancePool) { while (countAllocated.get() >= nInstances) { // Allocate a new instance if possible, or else wait if (nInstances < maxInstances) { try { instancePool.push(loadServlet()); nInstances++; } catch (ServletException e) { throw e; } catch (Throwable e) { throw new ServletException (sm.getString("standardWrapper.allocate"), e); } } else { try { instancePool.wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { ; } } } if (log.isTraceEnabled()) log.trace(" Returning allocated STM instance"); countAllocated.incrementAndGet(); return (Servlet) instancePool.pop(); } }
参考博客:Filter
过滤器对象里有个属性就是servelt,在过滤器链处理完毕,就直接调用了Servlet了。

官方说法中前三步中涉及到的类,可能有我调试时不同,这是因为采用的协议不同,协议不同,与protocol相关的processor也就不同。但是整个流程就是这个样子的。
Tomcat源码解读:我们发起的HTTP请求如何到达Servlet的
标签:des style blog http color io os 使用 ar
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/f1194361820/p/3999520.html