标签:使用 shadow private 为什么 package auth reg arraylist interface
一:什么是Iterator模式?将循环变量i的作用抽象化,通用化形成的模式,在设计模式中称为Iterator模式(迭代器模式),该模式用于在数据集合中按照顺序遍历集合
为了回答这个问题,我们先看示例程序:
?1.?示例程序的类图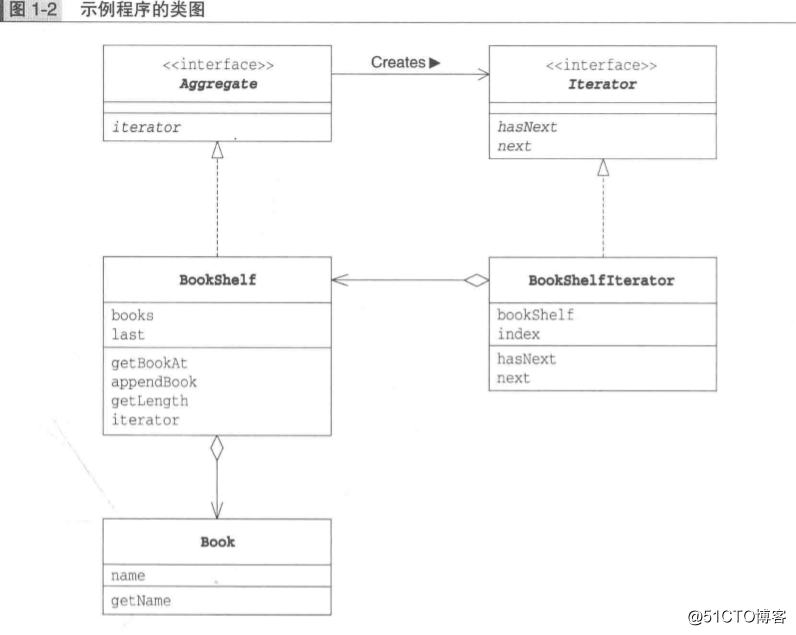
?2.?类和接口的示意图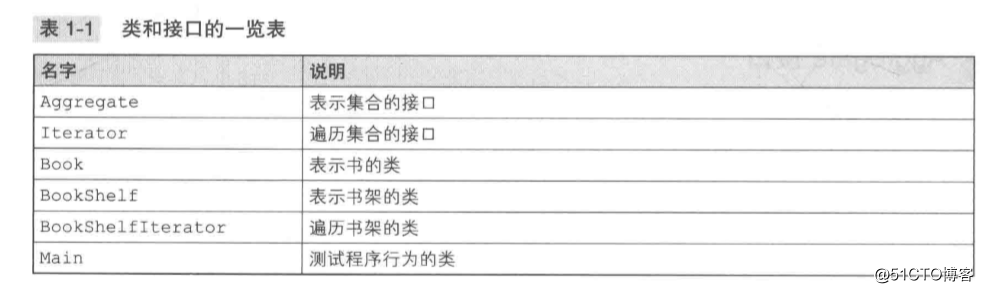
?3.?示例程序
??>1.?Aggregate接口
package com.zgz.dm.Iterator;
/**
* 表示集合的接口
* @author guozhenZhao
* @date 2018年6月12日
*/
public interface Aggregate {
//该方法生成一个用于遍历集合的迭代器
public abstract Iterator iterator();
}
??>2.?Iterator接口
package com.zgz.dm.Iterator;
/**
* 该接口用于遍历集合中的元素
* @author guozhenZhao
* @date 2018年6月12日
*/
public interface Iterator {
//判断集合中是否存在下一个元素
public abstract boolean hasNext();
//获取集合中的下一个元素
public abstract Object next();
}
??>3.?Book类
package com.zgz.dm.Iterator;
/**
* 表示书这个类
* @author guozhenZhao
* @date 2018年6月12日
*/
public class Book {
private String name;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public Book(String name) {
super();
this.name = name;
}
}
??>4.?BookShelf类
package com.zgz.dm.Iterator;
/**
* 表示书架的类
* @author guozhenZhao
* @date 2018年6月12日
*/
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class BookShelf implements Aggregate {
//private Book[] books;
//private int last = 0;
private List<Book> books;
public BookShelf() {
super();
this.books = new ArrayList<Book>();
}
//获取书架中对应的书
public Book getBookAt(int index) {
//return books[index];
return books.get(index);
}
//向书架中添加书
public void appendBook(Book book) {
//this.books[last] = book;
//last++;
this.books.add(book);
}
//获取书架的长度
public int getLength() {
//return last;
return books.size();
}
//遍历书架中的书
@Override
public Iterator iterator() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return new BookShelfIterator(this);
}
}
??>5.?BookShelfIterator类
package com.zgz.dm.Iterator;
/**
* 遍历书架的类
* @author guozhenZhao
* @date 2018年6月12日
*/
public class BookShelfIterator implements Iterator{
private BookShelf bookShelf;
private int index;
public BookShelfIterator(BookShelf bookShelf) {
super();
this.bookShelf = bookShelf;
this.index = 0;
}
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
if (index < bookShelf.getLength()) {
return true;
}else {
return false;
}
}
@Override
public Object next() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Book book = bookShelf.getBookAt(index);
index++;
return book;
}
}
??>6.?测试类
package com.zgz.dm.Iterator;
/**
* 测试类
* @author guozhenZhao
* @date 2018年6月12日
*/
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
BookShelf bookShelf = new BookShelf();
bookShelf.appendBook(new Book("追风筝的人"));
bookShelf.appendBook(new Book("java编程思想"));
bookShelf.appendBook(new Book("SSM整合"));
bookShelf.appendBook(new Book("平凡的世界"));
bookShelf.appendBook(new Book("springBoot"));
Iterator it = bookShelf.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()) {
Book book = (Book)it.next();
System.out.println(book.getName());
}
}
}
读完示例程序,回答上面的问题,为什么要有Iterator模式呢?如果是数组的话直接使用for循环遍历不就得了。在上面的程序中有一个BookShelf类,其中一个方法,如下图:
在这个方法中返回的是Iterator并不是对应的对象类,在测试类中遍历的时候,如下图:
上面的代码调用的是Iterator的hasNext()方法和next方法,此时的while循环不依赖BookShelf类的实现。所以引入Iterator后可以将遍历和实现分离开。设计模式的作用就是帮助我们编写可以复用的类,所谓的可复用就是将类实现为一个组件,在需要变动时,便于修改,所以也就不难理解为啥上图代码返回的是Iterator类型了。学习设计模式,其思想在于:
不要只使用具体类编程,优先使用抽象类和借口来编程
标签:使用 shadow private 为什么 package auth reg arraylist interface
原文地址:http://blog.51cto.com/13416247/2130725