标签:python 2 web 支持 print 属性 扩展 第一个 3.2 技术
使用Beautiful Soup
Beautiful Soup在解析时实际上依赖解析器,它除了支持Python标准库中的HTML解析器外,还支持一些第三方解析器(比如lxml)。
|
解析器 |
使用方法 |
优势 |
劣势 |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Python标准库 |
|
Python的内置标准库、执行速度适中、文档容错能力强 |
Python 2.7.3及Python 3.2.2之前的版本文档容错能力差 |
|
lxml HTML解析器 |
|
速度快、文档容错能力强 |
需要安装C语言库 |
|
lxml XML解析器 |
|
速度快、唯一支持XML的解析器 |
需要安装C语言库 |
|
html5lib |
|
最好的容错性、以浏览器的方式解析文档、生成HTML5格式的文档 |
速度慢、不依赖外部扩展 |
一、lxml解析器有解析HTML和XML的功能,而且速度快,容错能力强,所以先用它来解析。
用户名(1) 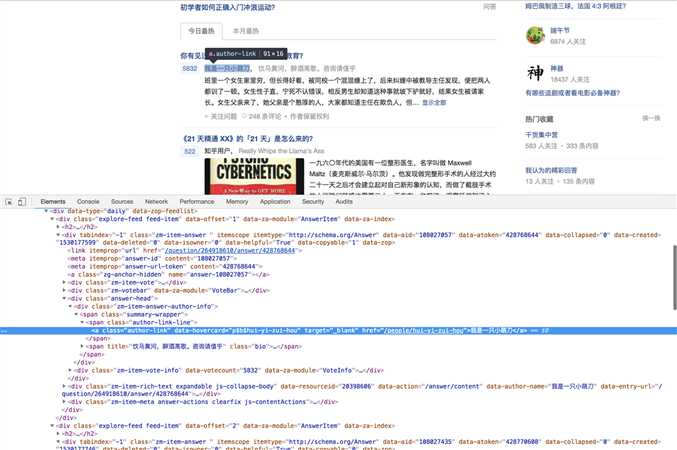
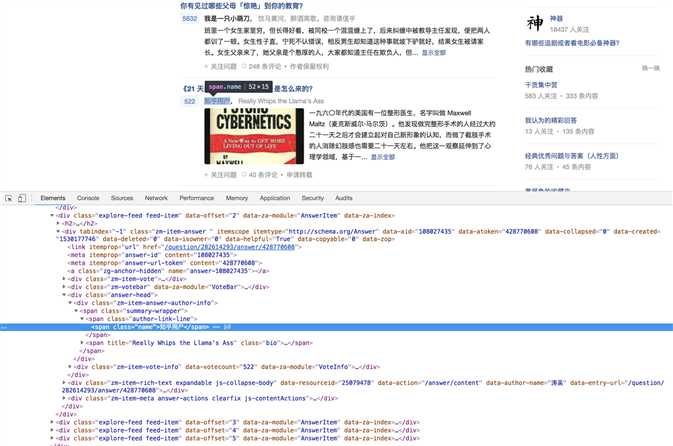
用户名(2)
if item.find_all(class_ = ‘author-link‘):
author = item.find_all(class_ = ‘author-link‘)[0].string
else:
author = item.find_all(class_ = ‘name‘)[0].string
另外,还有许多查询方法,其用法与find_all()、find()方法完全相同,只不过查询范围不同。
另外,还有许多查询方法,其用法与前面介绍的find_all()、find()方法完全相同,只不过查询范围不同,这里简单说明一下。
find_parents()和find_parent():前者返回所有祖先节点,后者返回直接父节点。
find_next_siblings()和find_next_sibling():前者返回后面所有的兄弟节点,后者返回后面第一个兄弟节点。
find_previous_siblings()和find_previous_sibling():前者返回前面所有的兄弟节点,后者返回前面第一个兄弟节点。
find_all_next()和find_next():前者返回节点后所有符合条件的节点,后者返回第一个符合条件的节点。
find_all_previous()和find_previous():前者返回节点后所有符合条件的节点,后者返回第一个符合条件的节点。
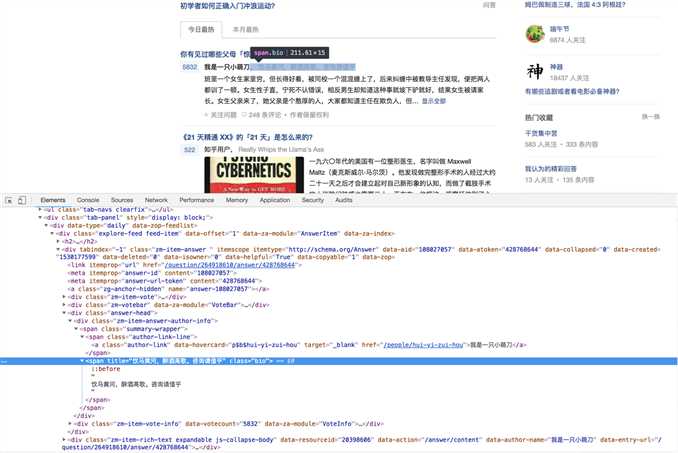
既可以为属性值,也可以为文本
q = item.find_all(class_ = ‘bio‘)[0].string
q = item.find_all(class_ = ‘bio‘)[0].attrs[‘title‘]
1 import requests 2 import json 3 from bs4 import BeautifulSoup 4 5 url = ‘https://www.zhihu.com/explore‘ 6 headers = { 7 ‘User-Agent‘: ‘Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_12_3) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/58.0.3029.110 Safari/537.36‘ 8 } 9 r = requests.get(url, headers=headers) 10 soup = BeautifulSoup(r.text, ‘lxml‘) 11 explore = {} 12 items = soup.find_all(class_ = ‘explore-feed feed-item‘) 13 for item in items: 14 question = item.find_all(‘h2‘)[0].string 15 #print(question) 16 if item.find_all(class_ = ‘author-link‘): 17 author = item.find_all(class_ = ‘author-link‘)[0].string 18 else: 19 author = item.find_all(class_ = ‘name‘)[0].string 20 #print(author) 21 answer = item.find_all(class_ = ‘content‘)[0].string 22 #print(answer) 23 #q = item.find_all(class_ = ‘bio‘)[0].string 24 q = item.find_all(class_ = ‘bio‘)[0].attrs[‘title‘] 25 #print(q) 26 27 explore = { 28 "question" : question, 29 "author" : author, 30 "answer" : answer, 31 "q": q, 32 } 33 34 with open("explore.json", "a") as f: 35 #f.write(json.dumps(items, ensure_ascii = False).encode("utf-8") + "\n") 36 f.write(json.dumps(explore, ensure_ascii = False) + "\n")
for t in item.find_all(class_ = ‘bio‘):
q =t.get(‘title‘)
1 import requests 2 import json 3 from bs4 import BeautifulSoup 4 5 url = ‘https://www.zhihu.com/explore‘ 6 headers = { 7 ‘User-Agent‘: ‘Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_12_3) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/58.0.3029.110 Safari/537.36‘ 8 } 9 r = requests.get(url, headers=headers) 10 soup = BeautifulSoup(r.text, ‘lxml‘) 11 explore = {} 12 items = soup.find_all(class_ = ‘explore-feed feed-item‘) 13 for item in items: 14 question = item.find_all(‘h2‘)[0].string 15 #print(question) 16 if item.find_all(class_ = ‘author-link‘): 17 author = item.find_all(class_ = ‘author-link‘)[0].string 18 else: 19 author = item.find_all(class_ = ‘name‘)[0].string 20 #print(author) 21 answer = item.find_all(class_ = ‘content‘)[0].string 22 #print(answer) 23 #q = item.find_all(class_ = ‘bio‘)[0].string 24 #q = item.find_all(class_ = ‘bio‘)[0].attrs[‘title‘] 25 for t in item.find_all(class_ = ‘bio‘): 26 q =t.get(‘title‘) 27 print(q) 28 29 explore = { 30 "question" : question, 31 "author" : author, 32 "answer" : answer, 33 "q": q, 34 } 35 36 with open("explore.json", "a") as f: 37 #f.write(json.dumps(items, ensure_ascii = False).encode("utf-8") + "\n") 38 f.write(json.dumps(explore, ensure_ascii = False) + "\n")
二、使用Python标准库中的HTML解析器
soup = BeautifulSoup(r.text, ‘html.parser‘)
三、Beautiful Soup还提供了另外一种选择器,那就是CSS选择器。
使用CSS选择器时,只需要调用select()方法,传入相应的CSS选择器即可。
标签:python 2 web 支持 print 属性 扩展 第一个 3.2 技术
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/wanglinjie/p/9249230.html