标签:waiting 错误 互斥 clu complete share hang att error
读写锁很像一个互斥量,他阻止多个线程同时修改共享数据的另一种方法,区分不同互斥量的是他是分读数据和写数据,一个读写锁允许同时多个线程读数据,只要他们不修改数据。
当一个线程锁住一个读写锁时,他选择共享读访问或独占写访问。当有任何线程在写访问时,想要访问的读线程不能继续;当其他线程进行读写时,想要获取写存取其他线程不能继续。
当一个写锁被释放时,如果读数据写数据同时等待,读数据有优先访问权限。
看下具体代码:
//rwlock.h
#include <pthread.h> typedef struct rwlock_tag { pthread_mutex_t mutex; pthread_cond_t r;//读存取 pthread_cond_t w;//写存取 int valid;//检测普通的语法错误,如试图加锁一个没有初始化的读写锁 int r_active;//读线程活跃 int w_active;//写线程活跃 int r_wait;//读线程等待数 int w_wait;//写线程等待数 }rwlock_t; #define RWL_INITIALIZER \ { PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER,PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER, PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER,RWLOCK_VALID,0,0,0,0 } #define RWLOCK_VALID 0xfacade int rwl_init(rwlock_t* rwlock); int rwl_destroy(rwlock_t* rwlock); int rwl_readlock(rwlock_t* rwlock); int rwl_readtrylock(rwlock_t* rwlock); int rwl_readunlock(rwlock_t* rwlock); int rwl_writelock(rwlock_t* rwlock); int rwl_writetrylock(rwlock_t* rwlock); int rwl_writeunlock(rwlock_t* rwlock);
/* *rwlock.c *实现了rwlock.h中的各个函数 */ #include <pthread.h> #include "errors.h" #include "rwlock.h" int rwl_init(rwlock_t *rwl)//初始化读写锁 { rwl->r_active=rwl->w_active=0; rwl->r_wait=rwl->w_wait=0; int status=pthread_mutex_init(&rwl->mutex,NULL); if(status) return status; status=pthread_cond_init(&rwl->r,NULL); if(status) { pthread_mutex_destroy(&rwl->mutex); return status; } status=pthread_cond_init(&rwl->w,NULL); if(status) { pthread_cond_destroy(&rwl->r); pthread_mutex_destroy(&rwl->mutex); return status; } rwl->valid=RWLOCK_VALID; return 0; } int rwl_destroy(rwlock_t *rwl)//释放读写锁 { if(rwl->valid!=RWLOCK_VALID) return EINVAL; int status=pthread_mutex_lock(&rwl->mutex); if(status) return status; //check whether any threads own the lock or //whether any thread known to be waiting if((rwl->r_active>0||rwl->w_active>0)|| (rwl->r_wait>0||rwl->w_wait>0)) { pthread_mutex_unlock(&rwl->mutex); return EBUSY; } rwl->valid=0; status=pthread_mutex_unlock(&rwl->mutex); if(status) return status; status=pthread_mutex_destroy(&rwl->mutex); int status1=pthread_cond_destroy(&rwl->r); int status2=pthread_cond_destroy(&rwl->w); return status!=0?status:(status1!=0?status1:status2); } //cleanup when the reads clock condition variable wait canceled. //record that the thread is no longer waiting,and unlock the mutex. static void rwl_readcleanup(void *arg)//read/write is a cancel point { rwlock_t *rwl=(rwlock_t*)arg; rwl->r_wait--; pthread_mutex_unlock(&rwl->mutex); } //cleanup when the write lock condition variable wait is canceled. //record that the thread is no longer waiting and unlock the mutex. static void rwl_writecleanup(void* arg) { rwlock_t* rwl=(rwlock_t*)arg; rwl->w_wait--; pthread_mutex_unlock(&rwl->mutex); } //lock a reads/write for reads access. write thread priority. this is very important!!! int rwl_readlock(rwlock_t* rwl) { if(rwl->valid!=RWLOCK_VALID) return EINVAL; int status=pthread_mutex_lock(&rwl->mutex); if(status) return status; if(rwl->w_active) { rwl->r_wait++; pthread_cleanup_push(rwl_readcleanup,(void*)rwl); while(rwl->w_active) { status=pthread_cond_wait(&rwl->r,&rwl->mutex);//wait reads if(status) return status; } pthread_cleanup_pop(0); } if(status==0) rwl->r_active++; pthread_mutex_unlock(&rwl->mutex); return status; } int rwl_readtrylock(rwlock_t* rwl)//attempt to lock a read/write lock for read access { if(rwl->valid!=RWLOCK_VALID) return EINVAL; int status=pthread_mutex_lock(&rwl->mutex); if(status) return status; if(rwl->w_active) status=EBUSY; else rwl->r_active++; int status1=pthread_mutex_unlock(&rwl->mutex); return status1!=0?status1:status; } int rwl_readunlock(rwlock_t* rwl) { if(rwl->valid!=RWLOCK_VALID) return EINVAL; int status=pthread_mutex_lock(&rwl->mutex); if(status) return status; rwl->r_active--; if(rwl->r_active==0&&rwl->w_wait>0) status=pthread_cond_signal(&rwl->w);//signal write int status1=pthread_mutex_unlock(&rwl->mutex); return status1==0?status:status1; } int rwl_writelock(rwlock_t* rwl) { if(rwl->valid!=RWLOCK_VALID) return EINVAL; int status=pthread_mutex_lock(&rwl->mutex); if(status) return status; if(rwl->w_active||rwl->r_active>0) { rwl->w_wait++; pthread_cleanup_push(rwl_writecleanup,(void*)rwl); while(rwl->w_active||rwl->r_active>0) { //wait write status=pthread_cond_wait(&rwl->w,&rwl->mutex); if(status) break; } pthread_cleanup_pop(0); rwl->w_wait--; } if(status==0) rwl->w_active=1; pthread_mutex_unlock(&rwl->mutex); return status; } int rwl_writetrylock(rwlock_t* rwl) { if(rwl->valid!=RWLOCK_VALID) return EINVAL; int status=pthread_mutex_lock(&rwl->mutex); if(status) return status; if(rwl->w_active||rwl->r_active>0) status=EBUSY; else rwl->w_active=1; int status1=pthread_mutex_unlock(&rwl->mutex); return status!=0?status:status1; } int rwl_writeunlock(rwlock_t* rwl) { if(rwl->valid!=RWLOCK_VALID) return EINVAL; int status=pthread_mutex_lock(&rwl->mutex); if(status) return status; rwl->w_active=0; if(rwl->r_wait>0) { status=pthread_cond_broadcast(&rwl->r);//broadcast reads if(status) { pthread_mutex_unlock(&rwl->mutex); return status; } } else if(rwl->w_wait>0) { status=pthread_cond_signal(&rwl->w);//signal write if(status) { pthread_mutex_unlock(&rwl->mutex); return status; } } status=pthread_mutex_unlock(&rwl->mutex); return status; }
//main.c #include <stdio.h> #include "rwlock.h" #include "errors.h" #define THREADS 5 #define DATASIZE 15 #define INERATIONS 6 typedef struct thread_tag { int thread_num;//array index pthread_t tid; int updates; int reads; int interval;//how many times when exce write. }thread_t; typedef struct data_tag { rwlock_t lock; int data; int updates; }data_t; thread_t threads[THREADS]; data_t data[DATASIZE]; void* thread_routine(void* arg) { thread_t* self=(thread_t*)arg; int repeats=0; int j=0; int i=0; int status; for(i=0;i<INERATIONS;++i) { if((i%self->interval)==0) { status=rwl_writelock(&data[j].lock); if(status) err_abort(status,"write lock"); data[j].data=self->thread_num; data[j].updates++; self->updates++; status=rwl_writeunlock(&data[j].lock); if(status) err_abort(status,"write unlok"); } else { status=rwl_readlock(&data[j].lock); if(status) err_abort(status,"reads lock"); self->reads++; if(data[j].data==self->thread_num) repeats++; status=rwl_readunlock(&data[j].lock); if(status) err_abort(status,"reads unlock"); } j++; if(j>=DATASIZE) j=0; } if(repeats>0) printf("threads %d found unchanged elements %d times:\n", self->thread_num,repeats); return NULL; } int main() { pthread_setconcurrency(THREADS); int status; int i,j; unsigned int seed=1; int thread_updates=0; int data_updates=0; //initialize the share data for(i=0;i<DATASIZE;++i) { data[i].data=0; data[i].updates=0; status=rwl_init(&data[i].lock); if(status) err_abort(status,"Init rwlock"); } //create threads to access shared data for(j=0;j<THREADS;++j) { threads[j].thread_num=j; threads[j].updates=0; threads[j].reads=0; threads[j].interval=rand_r(&seed)%6; status=pthread_create(&threads[j].tid,NULL,thread_routine,(void*)&threads[j]); if(status) err_abort(status,"create thread"); } //wait for all threads to complete,and collect statistics for(j=0;j<THREADS;++j) { status=pthread_join(threads[j].tid,NULL); if(status) err_abort(status,"join threads"); thread_updates+=threads[j].updates; printf("%02d: interval %d,updates %d,reads %d\n", j,threads[j].interval,threads[j].updates,threads[j].reads); } //collect statistics for the data for(i=0;i<DATASIZE;++i) { data_updates+=data[i].updates; printf("data %02d: value %d,%d updates\n",i,data[i].data, data[i].updates); rwl_destroy(&data[i].lock); } printf("%d threads updates,%d data updates\n",thread_updates, data_updates); return 0; }
写一个Makefile将各个源文件一块编译
下面是执行结果:
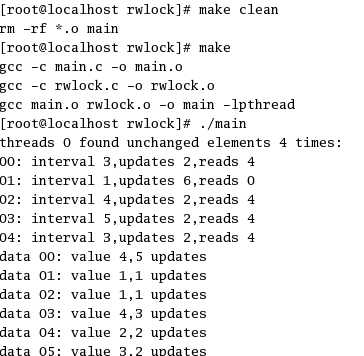
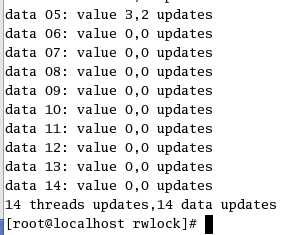
标签:waiting 错误 互斥 clu complete share hang att error
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/tianzeng/p/9328362.html