标签:组件 cto erb 字符 方法 存在 dsc base only
一、 使用脚手架 create-react-app
参考:https://github.com/facebook/create-react-app#creating-an-app
1、使用该脚手架,你不需要安装或配置webpack、babel这些工具,它们已经预先配置好并隐藏起来。
1)使用npm初始化一个react应用:npm init react-app my-app(创建项目并自动安装相关依赖)
和以下两条命令的效果类似:
npm install -g create-react-app-》create-react-app my-app
2)以开发模式运行该项目:
cd my-app(进入项目根目录,package.json所在目录)-》npm start
2、构建react
public/index.html是页面模板,src/index.js是js入口。为了更长远的重建,只有src目录下的文件会被webpack处理,你需要把js和css文件放在src目录下。
// Button.js import React, { Component } from ‘react‘; class Button extends Component { render() { // ... } } export default Button; // DangerButton.js import React, { Component } from ‘react‘; import Button from ‘./Button‘; class DangerButton extends Component { render() { return <Button color="red" />; } } export default DangerButton;
官方建议当一个模块只暴露一个接口时使用默认的imports和exports,具名exports在暴露多个接口的模块中是有用的,一个模块最多有一个default export和任意个named exports。
二、React Router 4.x
参考:https://github.com/ReactTraining/react-router,
https://www.zcfy.cc/article/react-router-v4-the-complete-guide-mdash-sitepoint-4448.html,
http://reacttraining.cn/web/guides/quick-start
React Router 是一个基于 React 的路由库,它可以让你向应用中快速地添加视图和数据流,同时保持页面与 URL 间的同步。
React Router 4.x(以下简称 RR4)采用单代码仓库模型架构(monorepo),使用lerna(多包管理工具)管理。这意味者这个仓库里面有几个包,分别是:
react-router-dom包含了react-router的功能,并且比react-router多出了 <Link> <BrowserRouter> 这样的 DOM 类组件。因此我们只需引用 react-router-dom 这个包就行了。如果搭配 redux ,你还需要使用 react-router-redux。
1)安装:cnpm install react-router-dom
2)导航组件
a)<BrowserRouter>&<HashRouter>
// <BrowserRouter> ‘http://example.com/about‘ // <HashRouter> ‘http://example.com/#/about‘
<BrowserRouter>在两者中更常用是因为它使用了HTML5的history API来记录你的路由历史,而<HashRouter>使用URL(window.location.hash)的hash部分来记录。如果你想兼容老式浏览器,你应该使用<HashRouter>。// src/index.js import React from ‘react‘; import ReactDOM from ‘react-dom‘; import App from ‘./App‘; ReactDOM.render(<App />, document.getElementById(‘root‘)); // src/App.js import React from ‘react‘ import { BrowserRouter as Router, Route, Link } from ‘react-router-dom‘ const BasicExample = () => ( <Router basename="/test" forceRefresh> <div> <ul> <li><Link to="/">Home</Link></li> // http://localhost:3000/test/ <li><Link to="/about">About</Link></li> // http://localhost:3000/test/about </ul> <hr/> <Route exact path="/" component={Home}/> <Route path="/about" component={About}/> </div> </Router> ) const Home = () => ( <div><h2>Home</h2></div> ) const About = () => ( <div><h2>About</h2></div> ) export default BasicExample
渲染结果:
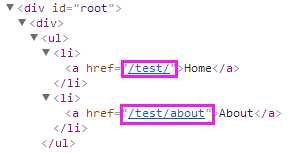
forceRefresh: bool(当设置为 true 时,在导航的过程中整个页面将会刷新。 只有当浏览器不支持 HTML5 的 history API 时,才设置为 true)
// HashRouter:子元素为html <HashRouter basename="/test"> <div> <ul> <li><Link to="/">Home</Link></li> // http://localhost:3000/#/test/ <li><Link to="/about">About</Link></li> // http://localhost:3000/#/test/about </ul> <hr/> <Route exact path="/" component={Home}/> <Route path="/about" component={About}/> </div> </HashRouter> // HashRouter:子元素为组件 <HashRouter> <Route exact path="/" component={Home}/> </HashRouter>
渲染结果:
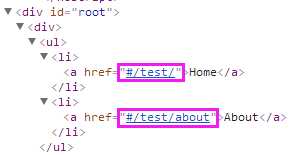
b)<Link>
用来跳转页面,在浏览器中会被渲染为a标签
<BrowserRouter basename="/test">
<div>
<ul>
<li><Link to="/" replace>Home</Link></li>
<li><Link to={{ pathname: ‘/about‘, search: ‘?param=1‘}} replace>About</Link></li>
</ul>
<Route exact path="/" component={Home}/>
<Route path="/about" component={About}/>
</div>
</BrowserRouter>
渲染结果:
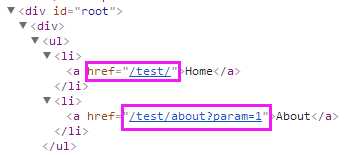
to:需要跳转到的地址(string或object)
replace: bool(默认为 false)
当设置为 true 时,点击链接后将使用新地址替换掉访问历史记录里面的原地址。当设置为 false 时,点击链接后将在原有访问历史记录的基础上添加一个新的纪录。
c)<Route>
<Route>的基本功能是当location与route的路径匹配时渲染界面,它有三种渲染方式:component、render和children。大部分情况下使用到的是component方式。这三种渲染方式都会传递三个route属性:match、location和history。
<BrowserRouter>
<div>
<ul>
<li><Link to="/">Home</Link></li>
<li><Link to="/about">About</Link></li>
</ul>
<hr/>
<Route exact path="/" component={Home}/>
<Route path="/about" component={About}/>
</div>
</BrowserRouter>
path:路由组件对应的url路径;component:路径匹配时会渲染的组件;exact(bool):当设为true时,只有当path与路径完全相同时才会匹配;render(func):路径匹配时方法会被调用来渲染界面。
path属性可以使用path-to-regexp(npm包:将一个类似于/user/:name的字符串转化为一个正则表达式),path-to-regexp暴露了一个compile方法可以将字符串转为一个有效的路径。
var toPath = pathToRegexp.compile(‘/user/:id‘) toPath({ id: 123 }) //=> "/user/123" toPath({ id: ‘/‘ }) //=> "/user/%2F"
当路由路径和当前路径成功匹配,会生成一个match对象。match对象包含下面这些属性:
match.url.返回URL匹配部分的字符串。对于创建嵌套的<Link>很有用。
match.path.返回用于匹配的路径字符串 - 就是<Route path="">。对于创建嵌套的<Route>很有用。
match.isExact.如果整个url准确匹配(没有任何多余字符)则返回true。
match.params.对于路径的动态部分,从URL解析出的键值对。
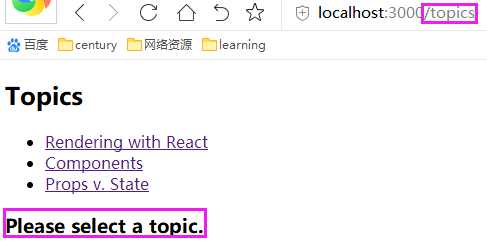
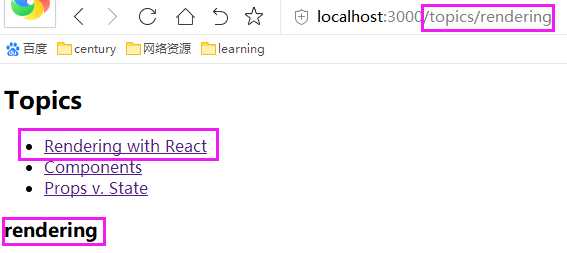
import React from ‘react‘ import { BrowserRouter as Router, Route, Link } from ‘react-router-dom‘ const BasicExample = () => ( <Router> <Route path="/topics" component={Topics}/> </Router> ) const Topics = ({ match }) => ( <div> <h2>Topics</h2> <ul> <li> <Link to={`${match.url}/rendering`}>Rendering with React</Link> </li> <li> <Link to={`${match.url}/components`}>Components</Link> </li> <li> <Link to={`${match.url}/props-v-state`}>Props v. State</Link> </li> </ul> <Route path={`${match.url}/:topicId`} component={Topic}/> <Route exact path={match.url} render={() => ( <h3>Please select a topic.</h3> )}/> </div> ) const Topic = ({ match }) => ( <div> <h3>{match.params.topicId}</h3> </div> ) export default BasicExample
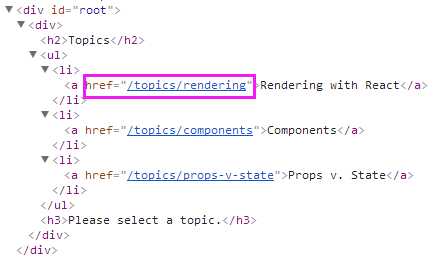
children(func):有时你需要渲染route组件,无论路由是否匹配(比如导航栏菜单),此时你可以使用<Route>组件的children属性。它和render属性很像,区别是children属性对应的方法,无论路由是否匹配都会被调用。
children属性和component、render属性一样,接收所有的route props(match、location、history)。但是当路由不匹配时,match为null(可以根据此动态调整匹配与不匹配路由组件的页面展示)。
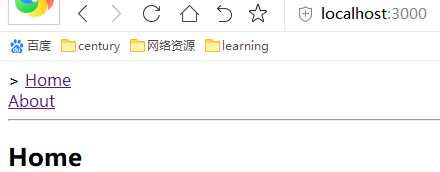
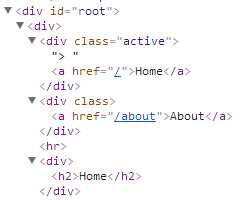
import React from ‘react‘ import { BrowserRouter as Router, Route, Link } from ‘react-router-dom‘ const CustomLinkExample = () => ( <Router> <div> <OldSchoolMenuLink activeOnlyWhenExact={true} to="/" label="Home"/> <OldSchoolMenuLink to="/about" label="About"/> <hr/> <Route exact path="/" component={Home}/> <Route path="/about" component={About}/> </div> </Router> ) const OldSchoolMenuLink = ({ label, to, activeOnlyWhenExact }) => ( <Route path={to} exact={activeOnlyWhenExact} children={({ match }) => ( <div className={match ? ‘active‘ : ‘‘}> {match ? ‘> ‘ : ‘‘}<Link to={to}>{label}</Link> </div> )}/> ) const Home = () => ( <div><h2>Home</h2></div> ) const About = () => ( <div><h2>About</h2></div> ) export default CustomLinkExample
渲染结果:
d)<Redirect>
应用场景:访问一个页面a,若未登录则需要重定向到登录页面,若已登录就可以直接访问。
<Redirect>会重定向到新地址,默认将history堆栈的当前路径替换为新路径;to(string或object):重定向地址。
import React from ‘react‘ import { BrowserRouter, Route, Link, Redirect } from ‘react-router-dom‘ const AuthExample = () => ( <BrowserRouter> <div> <ul> <li><Link to="/public">Public Page</Link></li> <li><Link to="/protected">Protected Page</Link></li> </ul> <Route path="/public" component={Public}/> <Route path="/protected" render={() => (<Redirect to="/public"/>)}/> // <Route path="/protected" render={() => (<Redirect to={{pathname:"/public"}}/>/> </div> </BrowserRouter> ) const Public = () => <h3>Public</h3> export default AuthExample
路由会在以下几个地方提供一个location对象(props.location)

import React from ‘react‘ import { BrowserRouter, Route, Link, Redirect } from ‘react-router-dom‘ const AuthExample = () => ( <BrowserRouter> <div> <ul> <li><Link to="/protected">Protected Page</Link></li> </ul> <Route path="/login" component={Login}/> <PrivateRoute path="/protected" component={Protected}/> </div> </BrowserRouter> ) const fakeAuth = { isAuthenticated: false, authenticate(cb) { this.isAuthenticated = true setTimeout(cb, 100) // fake async } } const PrivateRoute = ({ component: Component, ...rest }) => ( <Route {...rest} render={props => ( fakeAuth.isAuthenticated ? ( <Component/> ) : ( <Redirect to={{ pathname: ‘/login‘, state: { from: props.location } }}/> ) )}/> ) class Login extends React.Component { constructor() { super() this.state = { redirectToReferrer: false } this.login = this.login.bind(this) } login() { fakeAuth.authenticate(() => { this.setState({ redirectToReferrer: true }) }) } render() { const { from } = this.props.location.state || { from: { pathname: ‘/‘ } } const { redirectToReferrer } = this.state if (redirectToReferrer) { return ( <Redirect to={from}/> ) } return ( <div> <p>You must log in to view the page at {from.pathname}</p> <button onClick={this.login}>Log in</button> </div> ) } } const Protected = () => <h3>Protected</h3> export default AuthExample
<Redirect to={{pathname: ‘/login‘, state: {from: props.location}}}:你可以将当前路径的信息存在location.state里进行传递。
e)withRouter
当路由变化时,withRouter会重新渲染组件,它和 <Route>组件有相同的render props: { match, location, history }
import React from ‘react‘ import { BrowserRouter, Route, Link, Redirect, withRouter } from ‘react-router-dom‘ const AuthExample = () => ( <BrowserRouter> <div> <AuthButton/> <ul> <li><Link to="/protected">Protected Page</Link></li> </ul> <Route path="/login" component={Login}/> <PrivateRoute path="/protected" component={Protected}/> </div> </BrowserRouter> ) const fakeAuth = { isAuthenticated: false, authenticate(cb) { this.isAuthenticated = true setTimeout(cb, 100) // fake async }, signout(cb) { this.isAuthenticated = false setTimeout(cb, 100) } } const AuthButton = withRouter(({ history }) => ( fakeAuth.isAuthenticated ? ( <p> Welcome! <button onClick={() => { fakeAuth.signout(() => history.push(‘/‘)) }}>Sign out</button> </p> ) : ( <p>You are not logged in.</p> ) ))
标签:组件 cto erb 字符 方法 存在 dsc base only
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/colorful-coco/p/9260019.html