标签:pthreads \n 规则 image 运算 为什么 article 内核 32bit
_start到main()函数之间的栈介绍将以如下函数为例:
#include<stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int func_A(int x1, int x2, int x3, int x4, int x5, int x6){
int sum = 0;
sum = x1 + x2;
sum = sum + x3 + x4;
sum = sum + x5 + x6;
return sum;
}
int func_B(int x1, int x2, int x3, int x4, int x5, int x6, char x7){
int sum = 0;
sum = func_A(x1, x2, x3, x4, x5,x6);
sum = sum + x7;
return sum;
}
void func_C(void){
int sum = 0;
int x1 = 1;
int x2 = 2;
int x3 = 3;
int x4 = 4;
int x5 = 5;
int x6 = 6;
char x7 = ‘c‘;
sum = func_B(x1, x2, x3, x4, x5, x6, x7);
printf("sum = %d\n", sum);
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int c = argc;
char **p = argv;
func_C();
return 0;
}
X86-64的寄存器相对于X86有扩展,主要不同体现在:
16个64bit寄存器 为:RAX,RBX,RCX,RDX,RDI,RSI,RBP,RSP,R8,R9,R10,R11,R12,R13,R14,R15
在X86-64架构的处理器上,Windows和Linux的函数调用规则是不一样。
暂不介绍
Linux使用System V Application Binary Interface的函数调用规则。在《System V Applocation Binary Interface》中3.2.2 The Stack Frame中写道:
In addition to registers, each function has a frame on the run-time stack. This stack grows downwards from high addresses. Figure 3.3 shows the stack organization. The end of the input argument area shall be aligned on a 16 (32 or 64, if __m256 or __m512 is passed on stack) byte boundary. In other words, the value (%rsp + 8) is always a multiple of 16 (32 or 64) when control is transferred to the function entry point. The stack pointer, %rsp, always points to the end of the latest allocated stack frame.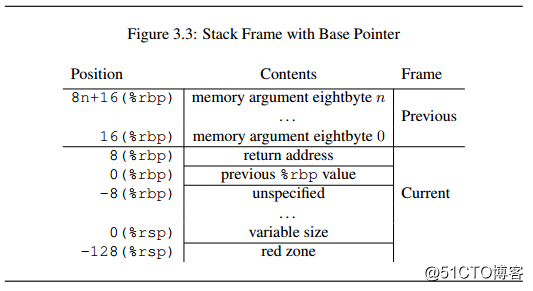
在输入参数的结尾处rsp必须对齐到16字节,当调用函数时,首先rsp会减8,rip会压栈,在栈中占8个字节,然后rip指向另一个函数的entry point,也即控制转移到了函数的entry point。由于rip压栈了,rsp+8应该是16字节对齐。
至于为什么需要16字节对齐,查了一些资料发现和Sreaming SIMD Extensions(SSE)有关,它是一组CPU指令,用于像信号处理、科学计算或者3D图形计算一样的应用(SSE入门)。SIMD 也是几个单词的首写字母组成的: Single Instruction, Multiple Data。 一个指令发出后,同一时刻被放到不同的数据上执行。16个128bitXMM寄存器可以被SSE指令操控,SSE利用这些寄存器可以同时做多个数据的运算,从而加快运算速度。但是数据被装进XMM寄存器时,要求数据的地址需要16字节对齐,而数据经常会在栈上分配,因此只有要求栈以16字节对齐,才能更好的支持数据的16字节对齐。
当参数的数目小于7个时,使用rdi,rsi, rdx, rcx, r8 and r9传递参数,大于等于7个时使用stack传参数。具体的规则见《System V Applocation Binary Interface》中3.2.3 Parameter Passing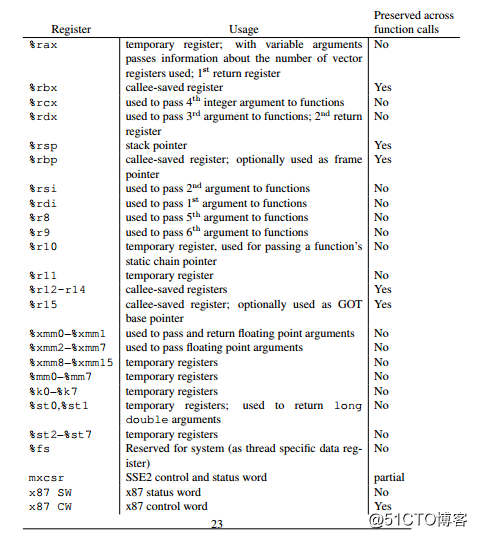
0000000000000540 <_start>:
540: 31 ed xor %ebp,%ebp
542: 49 89 d1 mov %rdx,%r9
545: 5e pop %rsi
546: 48 89 e2 mov %rsp,%rdx
549: 48 83 e4 f0 and $0xfffffffffffffff0,%rsp
54d: 50 push %rax
54e: 54 push %rsp
54f: 4c 8d 05 da 02 00 00 lea 0x2da(%rip),%r8 # 830 <__libc_csu_fini>
556: 48 8d 0d 63 02 00 00 lea 0x263(%rip),%rcx # 7c0 <__libc_csu_init>
55d: 48 8d 3d 2c 02 00 00 lea 0x22c(%rip),%rdi # 790 <main>
564: ff 15 76 0a 20 00 callq *0x200a76(%rip) # 200fe0 <__libc_start_main@GLIBC_2.2.5>
56a: f4 hlt
56b: 0f 1f 44 00 00 nopl 0x0(%rax,%rax,1)跟据上述汇编:
r9 < ----- rdx
r8 <------ __libc_csu_fini
rcx <------ __libc_csu_init
rdx <------ argv
rsi <------ argc
rdi <------ main
rsp 的值压栈
and $0xfffffffffffffff0,%rsp的目的是使rsp对齐到16字节。
push %rax 为了使rsp对齐到16字节
push %rsp, rsp的值入栈
执行_start的第一条指令时,rsp的值是多少呢?谁设置的呢?rsp的值是bprm->p,Linux内核设置的,在上面的内容中有介绍。下图结合了Linux Kernel和_start设置的栈。其实_start来自glibc,在x86-64平台上,可以在文件sysdeps/x86_64/start.S中找到代码。这段代码的目的很单纯,只是给函数__libc_start_main准备参数。函数__libc_start_main同样来自glibc,它定义在文件csu/libc-start.c中。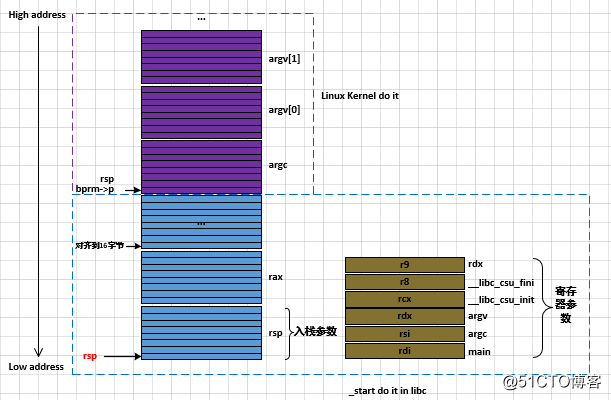
函数__libc_start_main的原型如下:
int __libc_start_main(
(int (*main) (int, char**, char**),
int argc,
char **argv,
__typeof (main) init,
void (*fini) (void),
void (*rtld_fini) (void),
void* stack_end)在《How statically linked programs run on Linux 》中介绍了__libc_start_main的作用:
待完善
X86-64和ARM64用户栈的结构 (3) ---_start到main
标签:pthreads \n 规则 image 运算 为什么 article 内核 32bit
原文地址:http://blog.51cto.com/iamokay/2155957