标签:9.png int img stc color png 改变 函数 参考
一、先来看一下没有继承的情况
类中的变量访问:
(1)类内访问方式:通过public成员函数访问
(2)类外访问方式:直接访问
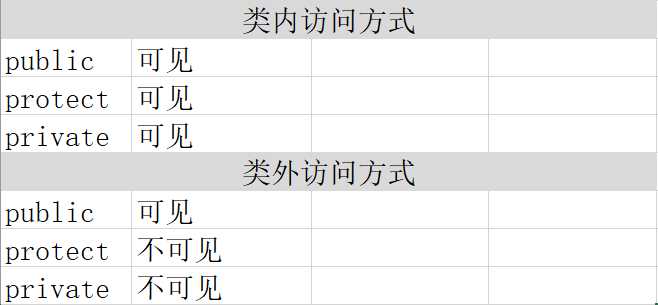
表 1
class A { public: int a; protected: int b; private: int c; public: int getAll(){ return a + b + c; } }; int main() { A testA; //类外访问方式 testA.a; testA.b; testA.c; //类内访问方式 testA.getAll(); return 0; }
其中标红的部分表示编译器会报错,你可以复制到IDE里试一下。
对照表1,类外访问是 可见/不可见/不可见,类内访问是 可见/可见/可见
二、再来看一下有继承的情况
有继承的情况主要是对子类进行讨论,因为子类中的public/protect/private属性会发生变化。
表2
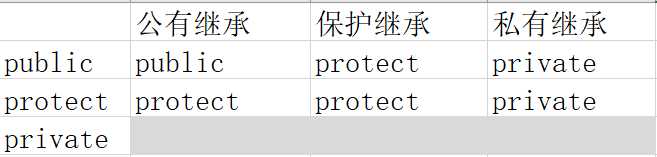
上表可以这么来记,private不可继承,公有继承不改变属性,保护继承属性全为protect,私有继承属性全为private。
class A { public: int a; protected: int b; private: int c; public: int getAll(){ return a + b + c; } }; //公有继承 class B :public A { public: int getA(){ return a; } int getB(){ return b; } int getC(){ return c; } }; //保护继承 class C :protected A { public: int getA(){ return a; } int getB(){ return b; } int getC(){ return c; } }; //私有继承 class D :private A { public: int getA(){ return a; } int getB(){ return b; } int getC(){ return c; } }; int main() { B testB; C testC; D testD; //类外访问方式
//公有继承 testB.a; testB.b; testB.c; //保护继承 testC.a; testC.b; testC.c; //私有继承 testD.a; testD.b; testD.c; //类内访问方式
//公有继承 testB.getA(); testB.getB(); testB.getC(); //保护继承 testC.getA(); testC.getB(); testC.getC(); //私有继承 testD.getA(); testD.getB(); testD.getC(); return 0; }
代码中标红的部分表示编译器会报错,我们逐个解释:
1、对照表2,公有继承后,属性变为 public /protect/无;对照表1,类外访问是 可见/不可见/无,类内访问是 可见/可见/无
2、对照表2,保护继承后,属性变为 protect/protect/无;对照表1,类外访问是 不可见/不可见/无,类内访问是 可见/可见/无
2、对照表2,私有继承后,属性变为 private/private/无;对照表1,类外访问是 不可见/不可见/无,类内访问是 可见/可见/无
注意:以上全为博主自己琢磨的,没有参考过权威文献,仅供提供思路。
public/protect/private和公有继承/保护继承/私有继承的简单理解
标签:9.png int img stc color png 改变 函数 参考
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/hustwx/p/9463969.html