标签:type fine strong ... 它的 设置 允许 i++ cat
我们在上节博客中说到,在 SeqList 下又可以衍生出 StaticList 和 DynamicList 两个子类。那么我们今天就来看看这两个子类,它们是如何实现的以及它们之间有何区别。A、StaticList 的设计要点:首先必须是一个类模板。其次是使用原生数组作为顺序存储空间,最后是使用模板参数决定数组大小。定义如下
template < typename T, int N >
class StaticList : public SeqList<T>
{
protected:
T m_space[N]; // 顺序存储空间,N 为模板参数
public:
StaticList(); // 指定父类成员的具体值
int capacity() const;
};我们下来来实现 StaticList ,代码如下
StaticList.h 源码
#ifndef STATICLIST_H
#define STATICLIST_H
#include "Seqlist.h"
namespace DTLib
{
template < typename T, int N >
class StaticList : public SeqList<T>
{
protected:
T m_space[N]; // 顺序存储空间,N 为模板参数
public:
StaticList() // 指定父类成员的具体值
{
this->m_array = m_space;
this->m_length = 0;
}
int capacity() const
{
return N;
}
};
}
#endif // STATICLIST_H我们来写个测试代码测试下这个 StaticList ,main.cpp 代码如下
#include <iostream>
#include "StaticList.h"
using namespace std;
using namespace DTLib;
int main()
{
StaticList<int, 5> l;
for(int i=0; i<l.capacity(); i++)
{
l.insert(0, i);
}
for(int i=0; i<l.capacity(); i++)
{
cout << l[i] << endl;
}
l[0] *= l[0];
for(int i=0; i<l.capacity(); i++)
{
cout << l[i] << endl;
}
try
{
l[5] = 5;
}
catch(const Exception& e)
{
cout << e.message() << endl;
cout << e.location() << endl;
}
return 0;
}我们来看看输出结果
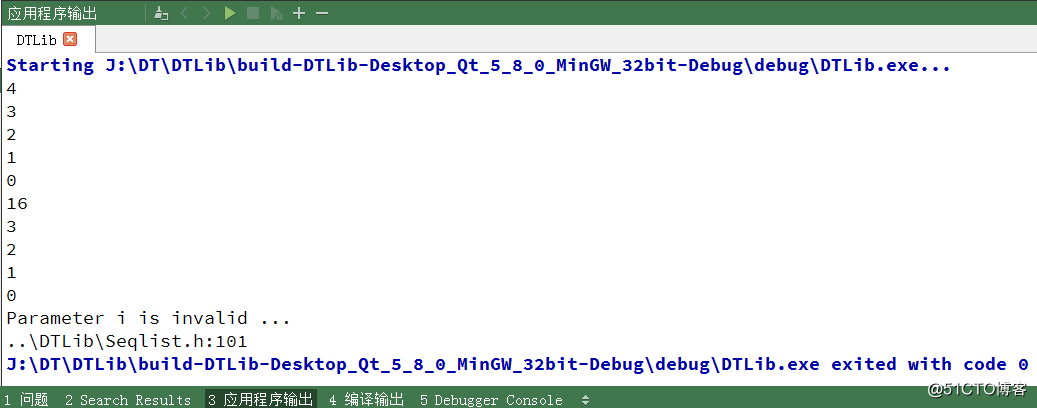
结果正是我们想要的,这个 StaticList 类已经实现完毕。接下来我们再来实现 DynamicList 类。
B、DynamicList 类的设计要点:它也必须得是一个类模板。申请连续堆空间作为顺序存储空间;动态设置顺序存储空间的大小;保证重置顺序存储空间时的异常安全性。
a> 函数异常安全的概念:1、不泄露任何资源;2、不允许破坏数据。
b> 函数异常安全的基本保证,如果对象被抛出:对象内的任何成员仍然能保持有效状态;没有数据的破坏及资源泄漏。
下来我们来看看它的定义
template < typename T >
class DynamicList : public SeqList<T>
{
protected:
int m_capacity; // 顺序存储空间的大小
public:
DynamicList(int capacity); // 申请空间
int capacity() const;
// 重新设置顺序存储空间的大小
void resize(int capacity);
~DynamicList(); // 归还空间
};下来我们来实现这个 DynamicList 类
DynamicList.h 源码
#ifndef DYNAMICLIST_H
#define DYNAMICLIST_H
#include "SeqList.h"
#include "Exception.h"
namespace DTLib
{
template < typename T >
class DynamicList : public SeqList<T>
{
protected:
int m_capacity; // 顺序存储空间的大小
public:
DynamicList(int capacity) // 申请空间
{
this->m_array = new T[capacity];
if( this->m_array != NULL )
{
this->m_length = 0;
this->m_capacity = capacity;
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(NoEnoughMemoryException, "No memory to create DynamicList ...");
}
}
int capacity() const
{
return m_capacity;
}
void resize(int capacity)
{
if( capacity != m_capacity )
{
T* array = new T[capacity];
if( array != NULL )
{
int length = (this->m_length < capacity ? this->m_length : capacity);
for(int i=0; i<length; i++)
{
array[i] = this->m_array[i];
}
T* temp = this->m_array;
this->m_array = array;
this->m_length = length;
this->m_capacity = capacity;
delete[] temp;
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(NoEnoughMemoryException, "No memory to resize DynamicList Object ...");
}
}
}
~DynamicList()
{
delete[] this->m_array;
}
};
}
#endif // DYNAMICLIST_H我们同样还是写个示例代码来验证下这个 DynamicList 类,main.cpp 代码如下
#include <iostream>
#include "DynamicList.h"
using namespace std;
using namespace DTLib;
int main()
{
DynamicList<int> l(5);
for(int i=0; i<l.capacity(); i++)
{
l.insert(0, i);
}
for(int i=0; i<l.length(); i++)
{
cout << l[i] << endl;
}
l[0] *= l[0];
for(int i=0; i<l.length(); i++)
{
cout << l[i] << endl;
}
try
{
l[5] = 5;
}
catch(const Exception& e)
{
cout << e.message() << endl;
cout << e.location() << endl;
l.resize(10);
l.insert(4, 40);
}
l[5] = 5;
for(int i=0; i<l.length(); i++)
{
cout << l[i] << endl;
}
l.resize(3);
for(int i=0; i<l.length(); i++)
{
cout << l[i] << endl;
}
return 0;
}我们来看看编译结果
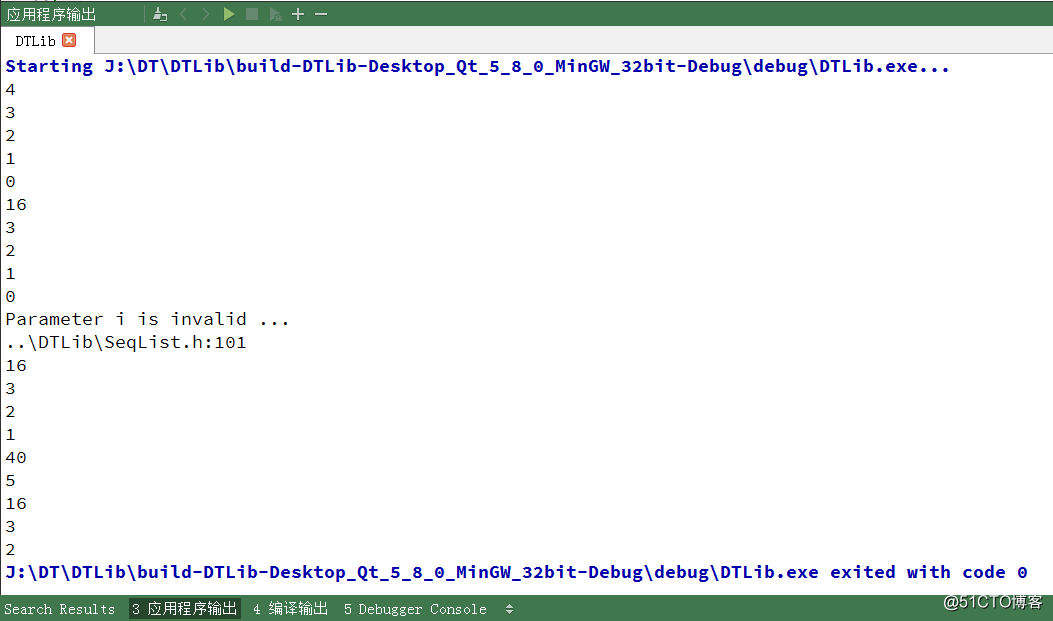
结果已经正确输出了。那么回到我们之前的问题:是否能将 DynamicList 作为 StaticList 的子类实现呢?答案肯定是不行的,因为 DynamicList 和 StaticList 两个类在存储结构上完全是不同的。因此他们是等价的,所以不能将 DynamicList 作为 StaticList 的子类实现。通过今天对 DynamicList 和 StaticList 的学习,总结如下:1、StaticList 通过模板参数定义顺序存储空间;2、DynamicList 通过动态内存申请定义顺序存储空间;3、DynamicList 支持动态重置顺序存储空间的大小;4、DynamicList 中的 resize() 函数实现需要保证异常安全。
标签:type fine strong ... 它的 设置 允许 i++ cat
原文地址:http://blog.51cto.com/12810168/2159479