标签:base coding package EDA 之间 design 适合 ota 存在
JMH,即Java Microbenchmark Harness,是专门用于代码微基准测试的工具套件。何谓Micro Benchmark呢?简单的来说就是基于方法层面的基准测试,精度可以达到微秒级。当你定位到热点方法,希望进一步优化方法性能的时候,就可以使用JMH对优化的结果进行量化的分析。
JMH比较典型的应用场景有:
1、JMH环境搭建
1 <dependency> 2 <groupId>org.openjdk.jmh</groupId> 3 <artifactId>jmh-core</artifactId> 4 <version>0.7.1</version> 5 </dependency> 6 <dependency> 7 <groupId>org.openjdk.jmh</groupId> 8 <artifactId>jmh-generator-annprocess</artifactId> 9 <version>0.7.1</version> 10 <scope>provided</scope> 11 </dependency> 12 13 <plugin> 14 <groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId> 15 <artifactId>maven-shade-plugin</artifactId> 16 <executions> 17 <execution> 18 <phase>package</phase> 19 <goals> 20 <goal>shade</goal> 21 </goals> 22 <configuration> 23 <finalName>microbenchmarks</finalName> 24 <transformers> 25 <transformer implementation="org.apache.maven.plugins.shade.resource.ManifestResourceTransformer"> 26 <mainClass>org.openjdk.jmh.Main</mainClass> 27 </transformer> 28 </transformers> 29 </configuration> 30 </execution> 31 </executions> 32 </plugin>
2、用例(此用例用于对比Calendar和dateTime在高并发情况下的性能情况):
1 package jmh; 2 import java.util.Calendar; 3 import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; 4 5 import org.joda.time.DateTime; 6 import org.openjdk.jmh.annotations.Benchmark; 7 import org.openjdk.jmh.annotations.BenchmarkMode; 8 import org.openjdk.jmh.annotations.Mode; 9 import org.openjdk.jmh.annotations.OutputTimeUnit; 10 import org.openjdk.jmh.annotations.Threads; 11 import org.openjdk.jmh.runner.Runner; 12 import org.openjdk.jmh.runner.options.Options; 13 import org.openjdk.jmh.runner.options.OptionsBuilder; 14 15 @OutputTimeUnit(TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS) 16 @BenchmarkMode(Mode.AverageTime) 17 public class JMHTest { 18 19 static int millis = 24 * 3600 * 1000; 20 21 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { 22 Options options = new OptionsBuilder().include(JMHTest.class.getName()).forks(1).build(); 23 new Runner(options).run(); 24 } 25 26 @Benchmark 27 @Threads(5) 28 public void runCalendar() { 29 Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance(); 30 } 31 32 @Benchmark 33 @Threads(5) 34 public void runJoda() { 35 DateTime dateTime = new DateTime(); 36 } 37 38 // 39 @Benchmark 40 @Threads(5) 41 public void runSystem() { 42 long result = System.currentTimeMillis() / millis; 43 } 44 }
3、执行
可能会遇到报错:
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.RuntimeException: ERROR: Unable to find the resource: /META-INF/BenchmarkList
解决方法:
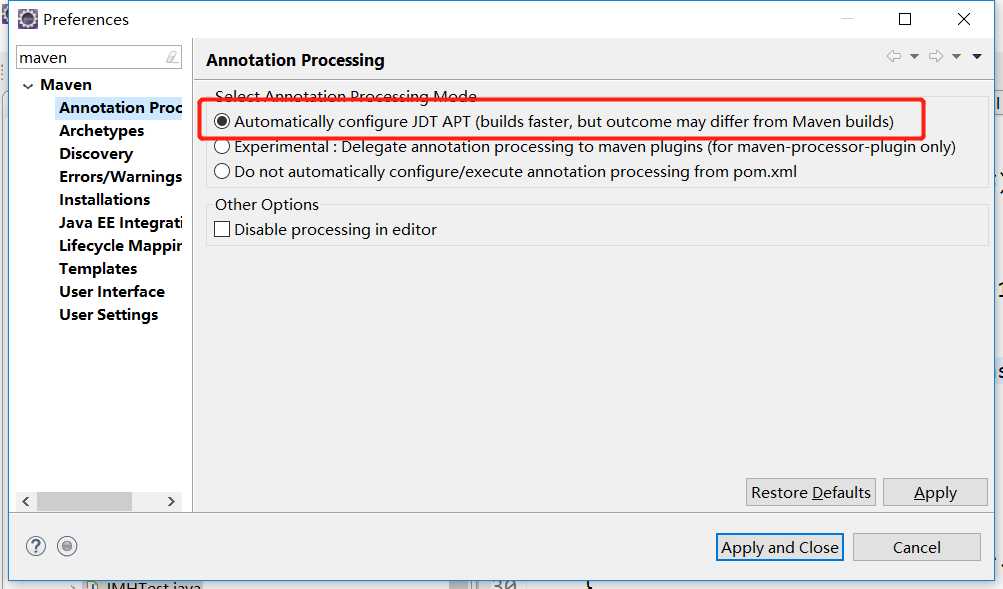
在eclipse中安装m2e-apt插件,然后启用Automatically configure JDT APT选项;
运行如果报错如下,是因为jmh不支持debug模式运行
# JMH version: 1.21 # VM version: JDK 1.8.0_91, Java HotSpot(TM) 64-Bit Server VM, 25.91-b15 # VM invoker: C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_91\jre\bin\java.exe # VM options: -agentlib:jdwp=transport=dt_socket,suspend=y,address=localhost:55262 -Dfile.encoding=UTF-8 # Warmup: 5 iterations, 10 s each # Measurement: 5 iterations, 10 s each # Timeout: 10 min per iteration # Threads: 5 threads, will synchronize iterations # Benchmark mode: Average time, time/op # Benchmark: org.lz.apply.soa.JMHTest.runCalendar # Run progress: 0.00% complete, ETA 00:05:00 # Fork: 1 of 1 FATAL ERROR in native method: JDWP No transports initialized, jvmtiError=AGENT_ERROR_TRANSPORT_INIT(197) ERROR: transport error 202: connect failed: Connection refused ERROR: JDWP Transport dt_socket failed to initialize, TRANSPORT_INIT(510) JDWP exit error AGENT_ERROR_TRANSPORT_INIT(197): No transports initialized [debugInit.c:750] <forked VM failed with exit code 1> <stdout last=‘20 lines‘> FATAL ERROR in native method: JDWP No transports initialized, jvmtiError=AGENT_ERROR_TRANSPORT_INIT(197) </stdout> <stderr last=‘20 lines‘> ERROR: transport error 202: connect failed: Connection refused ERROR: JDWP Transport dt_socket failed to initialize, TRANSPORT_INIT(510) JDWP exit error AGENT_ERROR_TRANSPORT_INIT(197): No transports initialized [debugInit.c:750] </stderr> # JMH version: 1.21 # VM version: JDK 1.8.0_91, Java HotSpot(TM) 64-Bit Server VM, 25.91-b15 # VM invoker: C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_91\jre\bin\java.exe # VM options: -agentlib:jdwp=transport=dt_socket,suspend=y,address=localhost:55262 -Dfile.encoding=UTF-8 # Warmup: 5 iterations, 10 s each # Measurement: 5 iterations, 10 s each # Timeout: 10 min per iteration # Threads: 5 threads, will synchronize iterations # Benchmark mode: Average time, time/op # Benchmark: org.lz.apply.soa.JMHTest.runJoda # Run progress: 0.00% complete, ETA 00:05:00 # Fork: 1 of 1 FATAL ERROR in native method: JDWP No transports initialized, jvmtiError=AGENT_ERROR_TRANSPORT_INIT(197) ERROR: transport error 202: connect failed: Connection refused ERROR: JDWP Transport dt_socket failed to initialize, TRANSPORT_INIT(510) JDWP exit error AGENT_ERROR_TRANSPORT_INIT(197): No transports initialized [debugInit.c:750] <forked VM failed with exit code 1> <stdout last=‘20 lines‘> FATAL ERROR in native method: JDWP No transports initialized, jvmtiError=AGENT_ERROR_TRANSPORT_INIT(197) </stdout> <stderr last=‘20 lines‘> ERROR: transport error 202: connect failed: Connection refused ERROR: JDWP Transport dt_socket failed to initialize, TRANSPORT_INIT(510) JDWP exit error AGENT_ERROR_TRANSPORT_INIT(197): No transports initialized [debugInit.c:750] </stderr> # JMH version: 1.21 # VM version: JDK 1.8.0_91, Java HotSpot(TM) 64-Bit Server VM, 25.91-b15 # VM invoker: C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_91\jre\bin\java.exe # VM options: -agentlib:jdwp=transport=dt_socket,suspend=y,address=localhost:55262 -Dfile.encoding=UTF-8 # Warmup: 5 iterations, 10 s each # Measurement: 5 iterations, 10 s each # Timeout: 10 min per iteration # Threads: 5 threads, will synchronize iterations # Benchmark mode: Average time, time/op # Benchmark: org.lz.apply.soa.JMHTest.runSystem # Run progress: 0.00% complete, ETA 00:05:00 # Fork: 1 of 1 FATAL ERROR in native method: JDWP No transports initialized, jvmtiError=AGENT_ERROR_TRANSPORT_INIT(197) ERROR: transport error 202: connect failed: Connection refused ERROR: JDWP Transport dt_socket failed to initialize, TRANSPORT_INIT(510) JDWP exit error AGENT_ERROR_TRANSPORT_INIT(197): No transports initialized [debugInit.c:750] <forked VM failed with exit code 1> <stdout last=‘20 lines‘> FATAL ERROR in native method: JDWP No transports initialized, jvmtiError=AGENT_ERROR_TRANSPORT_INIT(197) </stdout> <stderr last=‘20 lines‘> ERROR: transport error 202: connect failed: Connection refused ERROR: JDWP Transport dt_socket failed to initialize, TRANSPORT_INIT(510) JDWP exit error AGENT_ERROR_TRANSPORT_INIT(197): No transports initialized [debugInit.c:750] </stderr> # Run complete. Total time: 00:00:00 REMEMBER: The numbers below are just data. To gain reusable insights, you need to follow up on why the numbers are the way they are. Use profilers (see -prof, -lprof), design factorial experiments, perform baseline and negative tests that provide experimental control, make sure the benchmarking environment is safe on JVM/OS/HW level, ask for reviews from the domain experts. Do not assume the numbers tell you what you want them to tell. Benchmark Mode Cnt Score Error Units ERROR: JDWP Unable to get JNI 1.2 environment, jvm->GetEnv() return code = -2 JDWP exit error AGENT_ERROR_NO_JNI_ENV(183): [util.c:840]
改为run运行之后运行结果:
# JMH version: 1.21
# VM version: JDK 1.8.0_91, Java HotSpot(TM) 64-Bit Server VM, 25.91-b15
# VM invoker: C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_91\jre\bin\java.exe
# VM options: -Dfile.encoding=UTF-8
# Warmup: 5 iterations, 10 s each
# Measurement: 5 iterations, 10 s each
# Timeout: 10 min per iteration
# Threads: 5 threads, will synchronize iterations
# Benchmark mode: Average time, time/op
# Benchmark: org.lz.apply.soa.JMHTest.runCalendar
# Run progress: 0.00% complete, ETA 00:05:00
# Fork: 1 of 1
# Warmup Iteration 1: 625.707 ±(99.9%) 24.593 ns/op
# Warmup Iteration 2: 623.766 ±(99.9%) 41.928 ns/op
# Warmup Iteration 3: 639.438 ±(99.9%) 8.543 ns/op
# Warmup Iteration 4: 651.421 ±(99.9%) 25.146 ns/op
# Warmup Iteration 5: 638.751 ±(99.9%) 26.477 ns/op
Iteration 1: 631.098 ±(99.9%) 14.580 ns/op
Iteration 2: 603.567 ±(99.9%) 25.887 ns/op
Iteration 3: 609.097 ±(99.9%) 24.528 ns/op
Iteration 4: 638.006 ±(99.9%) 20.327 ns/op
Iteration 5: 614.077 ±(99.9%) 33.736 ns/op
Result "org.lz.apply.soa.JMHTest.runCalendar":
619.169 ±(99.9%) 56.722 ns/op [Average]
(min, avg, max) = (603.567, 619.169, 638.006), stdev = 14.731
CI (99.9%): [562.446, 675.891] (assumes normal distribution)
# JMH version: 1.21
# VM version: JDK 1.8.0_91, Java HotSpot(TM) 64-Bit Server VM, 25.91-b15
# VM invoker: C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_91\jre\bin\java.exe
# VM options: -Dfile.encoding=UTF-8
# Warmup: 5 iterations, 10 s each
# Measurement: 5 iterations, 10 s each
# Timeout: 10 min per iteration
# Threads: 5 threads, will synchronize iterations
# Benchmark mode: Average time, time/op
# Benchmark: org.lz.apply.soa.JMHTest.runJoda
# Run progress: 33.33% complete, ETA 00:03:22
# Fork: 1 of 1
# Warmup Iteration 1: 38.363 ±(99.9%) 6.992 ns/op
# Warmup Iteration 2: 34.713 ±(99.9%) 2.364 ns/op
# Warmup Iteration 3: 35.779 ±(99.9%) 2.657 ns/op
# Warmup Iteration 4: 36.549 ±(99.9%) 2.201 ns/op
# Warmup Iteration 5: 34.805 ±(99.9%) 3.346 ns/op
Iteration 1: 33.694 ±(99.9%) 2.354 ns/op
Iteration 2: 34.348 ±(99.9%) 2.880 ns/op
Iteration 3: 34.194 ±(99.9%) 3.279 ns/op
Iteration 4: 35.187 ±(99.9%) 4.125 ns/op
Iteration 5: 35.056 ±(99.9%) 3.453 ns/op
Result "org.lz.apply.soa.JMHTest.runJoda":
34.496 ±(99.9%) 2.395 ns/op [Average]
(min, avg, max) = (33.694, 34.496, 35.187), stdev = 0.622
CI (99.9%): [32.101, 36.890] (assumes normal distribution)
# JMH version: 1.21
# VM version: JDK 1.8.0_91, Java HotSpot(TM) 64-Bit Server VM, 25.91-b15
# VM invoker: C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_91\jre\bin\java.exe
# VM options: -Dfile.encoding=UTF-8
# Warmup: 5 iterations, 10 s each
# Measurement: 5 iterations, 10 s each
# Timeout: 10 min per iteration
# Threads: 5 threads, will synchronize iterations
# Benchmark mode: Average time, time/op
# Benchmark: org.lz.apply.soa.JMHTest.runSystem
# Run progress: 66.67% complete, ETA 00:01:41
# Fork: 1 of 1
# Warmup Iteration 1: 8.881 ±(99.9%) 1.253 ns/op
# Warmup Iteration 2: 8.773 ±(99.9%) 1.206 ns/op
# Warmup Iteration 3: 9.506 ±(99.9%) 0.462 ns/op
# Warmup Iteration 4: 9.496 ±(99.9%) 0.490 ns/op
# Warmup Iteration 5: 9.122 ±(99.9%) 0.220 ns/op
Iteration 1: 9.085 ±(99.9%) 0.172 ns/op
Iteration 2: 9.341 ±(99.9%) 0.326 ns/op
Iteration 3: 9.254 ±(99.9%) 0.293 ns/op
Iteration 4: 9.021 ±(99.9%) 0.164 ns/op
Iteration 5: 9.294 ±(99.9%) 0.359 ns/op
Result "org.lz.apply.soa.JMHTest.runSystem":
9.199 ±(99.9%) 0.534 ns/op [Average]
(min, avg, max) = (9.021, 9.199, 9.341), stdev = 0.139
CI (99.9%): [8.665, 9.733] (assumes normal distribution)
# Run complete. Total time: 00:05:03
REMEMBER: The numbers below are just data. To gain reusable insights, you need to follow up on
why the numbers are the way they are. Use profilers (see -prof, -lprof), design factorial
experiments, perform baseline and negative tests that provide experimental control, make sure
the benchmarking environment is safe on JVM/OS/HW level, ask for reviews from the domain experts.
Do not assume the numbers tell you what you want them to tell.
Benchmark Mode Cnt Score Error Units
JMHTest.runCalendar avgt 5 619.169 ± 56.722 ns/op
JMHTest.runJoda avgt 5 34.496 ± 2.395 ns/op
JMHTest.runSystem avgt 5 9.199 ± 0.534 ns/op
测试结果表明:
runCalendar方法平均运行时间为:619微秒
runJoda方法的平均运行时间为:34微秒
据用例测试结果可以看到,Calendar(非线程安全)在高并发情况下性能远远比不上dateTime(线程安全)。对代码性能和安全性要求比较高的可以放弃使用Calendar和SimpleDateFormat(底层实现是Calendar),转而使用joda-time
4、基本概念
Mode
Mode 表示 JMH 进行 Benchmark 时所使用的模式。通常是测量的维度不同,或是测量的方式不同。目前 JMH 共有四种模式:
Iteration
Iteration 是 JMH 进行测试的最小单位。在大部分模式下,一次 iteration 代表的是一秒,JMH 会在这一秒内不断调用需要 benchmark 的方法,然后根据模式对其采样,计算吞吐量,计算平均执行时间等。
Warmup
Warmup 是指在实际进行 benchmark 前先进行预热的行为。为什么需要预热?因为 JVM 的 JIT 机制的存在,如果某个函数被调用多次之后,JVM 会尝试将其编译成为机器码从而提高执行速度。为了让 benchmark 的结果更加接近真实情况就需要进行预热。
5、注解与选项
@BenchmarkMode
对应Mode选项,可用于类或者方法上, 需要注意的是,这个注解的value是一个数组,可以把几种Mode集合在一起执行,还可以设置为Mode.All,即全部执行一遍。
@State
类注解,JMH测试类必须使用@State注解,State定义了一个类实例的生命周期,可以类比Spring Bean的Scope。由于JMH允许多线程同时执行测试,不同的选项含义如下:
@OutputTimeUnit
benchmark 结果所使用的时间单位,可用于类或者方法注解,使用java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit中的标准时间单位。
@Benchmark
方法注解,表示该方法是需要进行 benchmark 的对象。
@Setup
方法注解,会在执行 benchmark 之前被执行,正如其名,主要用于初始化。
@TearDown
方法注解,与@Setup 相对的,会在所有 benchmark 执行结束以后执行,主要用于资源的回收等。
@Param
成员注解,可以用来指定某项参数的多种情况。特别适合用来测试一个函数在不同的参数输入的情况下的性能。@Param注解接收一个String数组,在@setup方法执行前转化为为对应的数据类型。多个@Param注解的成员之间是乘积关系,譬如有两个用@Param注解的字段,第一个有5个值,第二个字段有2个值,那么每个测试方法会跑5*2=10次。
6、参考资料
https://blog.csdn.net/lxbjkben/article/details/79410740
标签:base coding package EDA 之间 design 适合 ota 存在
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/tranquillity/p/9488572.html