标签:read rom 过程 其他 相互 生产者和消费者 方法 art on()
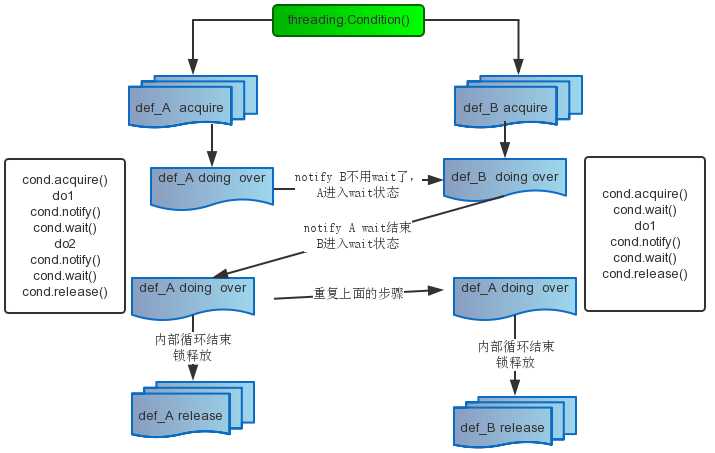
上图中def_A和def_B两个方法是相互依赖的,描述了A、B两个方法同步工作的过程
import threading,time
from random import randint
class Producer(threading.Thread):
def run(self):
global L
while True:
val = randint(0, 100)
print(‘生产者‘, self.name, ":Append"+str(val), L)
if lock_con.acquire():
L.append(val)
lock_con.notify()
lock_con.release()
time.sleep(3)
class Consumer(threading.Thread):
def run(self):
global L
while True:
lock_con.acquire()
if len(L) == 0:
lock_con.wait()
print(‘消费者‘, self.name, ":Delete"+str(L[0]), L)
del L[0]
lock_con.release()
time.sleep(0.25)
if __name__ == "__main__":
L = []
lock_con = threading.Condition()
threads = []
for i in range(5):
threads.append(Producer())
threads.append(Consumer())
for t in threads:
t.start()
for t in threads:
t.join()
标签:read rom 过程 其他 相互 生产者和消费者 方法 art on()
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/dongmengze/p/9578691.html