标签:示例 设置 runtime atp admin 模式 tar 相关 资源库
在开发中经常需要依赖第三方的包,包与包之间存在依赖关系,版本间还有兼容性问题,有时还里要将旧的包升级或降级,当项目复杂到一定程度时包管理变得非常重要。
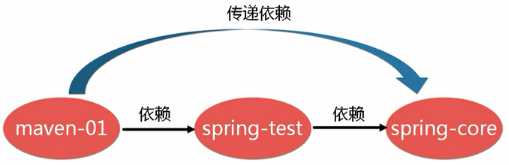
Maven是当前最受欢迎的Java项目管理构建自动化综合工具,类似以前Java中的Ant、node.js中的npm、dotNet中的nuget、PHP中的Composer。
Maven这个单词来自于意第绪语(犹太语),意为知识的积累。

Maven提供了开发人员构建一个完整的生命周期框架。开发团队可以自动完成项目的基础工具建设,Maven使用标准的目录结构和默认构建生命周期。Maven让开发人员的工作更轻松,同时创建报表,检查,构建和测试自动化设置。Maven简化和标准化项目建设过程。处理编译,分配,文档,团队协作和其他任务的无缝连接。 Maven增加可重用性并负责建立相关的任务。
每个Java项目的目录结构都没有一个统一的标准,配置文件到处都是,单元测试代码到底应该放在那里也没有一个权威的规范。
因此,我们就要用到Maven(使用Ant也可以,不过编写Ant的xml脚本比较麻烦)----一个项目管理工具。
Maven主要做了两件事:
如果没有Maven,你可能不得不经历下面的过程:
1 如果使用了spring,去spring的官网下载jar包;如果使用hibernate,去hibernate的官网下载Jar包;如果使用Log4j,去log4j的官网下载jar包..... 2 当某些jar包有依赖的时候,还要去下载对应的依赖jar包 3 当jar包依赖有冲突时,不得不一个一个的排查 4 执行构建时,需要使用ant写出很多重复的任务代码 5 当新人加入开发时,需要拷贝大量的jar包,然后重复进行构建 6 当进行测试时,需要一个一个的运行....检查
有了Maven,它提供了三种功能:
1 依赖的管理:仅仅通过jar包的几个属性,就能确定唯一的jar包,在指定的文件pom.xml中,只要写入这些依赖属性,就会自动下载并管理jar包。 2 项目的构建:内置很多的插件与生命周期,支持多种任务,比如校验、编译、测试、打包、部署、发布... 3 项目的知识管理:管理项目相关的其他内容,比如开发者信息,版本等等
教程:https://www.yiibai.com/maven/
中央仓库资源:
Maven 是一个Java项目管理工具,主要功能是统一开发规范与包的依赖管理。
Maven项目对象模型(POM),可以通过一小段描述信息来管理项目的构建,报告和文档的软件项目管理工具。
版本
maven有自己的版本定义和规则
构建
maven支持许多种的应用程序类型,对于每一种支持的应用程序类型都定义好了一组构建规则和工具集。
输出管理
maven可以管理项目构建的产物,并将其加入到用户库中。这个功能可以用于项目组和其他部门之间的交付行为
依赖关系
maven对依赖关系的特性进行细致的分析和划分,避免开发过程中的依赖混乱和相互污染行为
文档和构建结果
maven的site命令支持各种文档信息的发布,包括构建过程的各种输出,javadoc,产品文档等。
项目关系
一个大型的项目通常有几个小项目或者模块组成,用maven可以很方便地管理
移植性管理
maven可以针对不同的开发场景,输出不同种类的输出结果
maven把项目的构建划分为不同的生命周期(lifecycle)。粗略一点的话,它这个过程(phase)包括:编译、测试、打包、集成测试、验证、部署。maven中所有的执行动作(goal)都需要指明自己在这个过程中的执行位置,然后maven执行的时候,就依照过程的发展依次调用这些goal进行各种处理。
这个也是maven的一个基本调度机制。一般来说,位置稍后的过程都会依赖于之前的过程。当然,maven同样提供了配置文件,可以依照用户要求,跳过某些阶段。
Maven的标准工程结构如下:
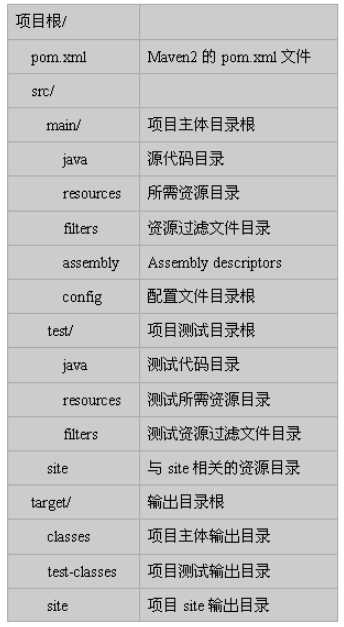
所谓的"约定优于配置",在maven中并不是完全不可以修改的,他们只是一些配置的默认值而已。但是除非必要,并不需要去修改那些约定内容。maven默认的文件存放结构如下:
每一个阶段的任务都知道怎么正确完成自己的工作,比如compile任务就知道从src/main/java下编译所有的java文件,并把它的输出class文件存放到target/classes中。
对maven来说,采用"约定优于配置"的策略可以减少修改配置的工作量,也可以降低学习成本,更重要的是,给项目引入了统一的规范。
maven使用如下几个要素来唯一定位某一个输出物:
团体、组织的标识符。团体标识的约定是,它以创建这个项目的组织名称的逆向域名(reverse domain name)开头。一般对应着JAVA的包的结构。例如org.apache
单独项目的唯一标识符。比如我们的tomcat, commons等。不要在artifactId中包含点号(.)。
一个项目的特定版本。
项目的类型,默认是jar,描述了项目打包后的输出。类型为jar的项目产生一个JAR文件,类型为war的项目产生一个web应用。
maven有自己的版本规范,一般是如下定义 <major version>.<minor version>.<incremental version>-<qualifier> ,比如1.2.3-beta-01。要说明的是,maven自己判断版本的算法是major,minor,incremental部分用数字比较,qualifier部分用字符串比较,所以要小心 alpha-2和alpha-15的比较关系,最好用 alpha-02的格式。
maven在版本管理时候可以使用几个特殊的字符串 SNAPSHOT,LATEST,RELEASE。比如"1.0-SNAPSHOT"。各个部分的含义和处理逻辑如下说明:
这个版本一般用于开发过程中,表示不稳定的版本。
指某个特定构件的最新发布,这个发布可能是一个发布版,也可能是一个snapshot版,具体看哪个时间最后。
指最后一个发布版。
什么是Maven Archetype? 简单的说就是一个Maven项目的基础模板,利用这个模板我们就可快速的建立一个新的该类型项目,同时也可以建立自己的项目骨架。
Maven所提供的archetype功能都是由插件Maven Archetype Plugin完成的
官网地址:http://maven.apache.org/archetype/maven-archetype-plugin/
主要命令:
使用archetype:generate创建项目
mvn archetype:generate命令参数解释
项目相关参数:
|
参数 |
含义 |
|
groupId |
当前应用程序隶属的Group的ID |
|
artifactId |
当前应用程序的ID |
|
package |
代码生成时使用的根包的名字,如果没有给出,默认使用archetypeGroupId |
原型有关参数表
| 参数 | 含义 |
|
archetypeGroupId |
原型(archetype)的Group ID |
|
archetypeArtifactId |
原型(archetype)ID |
|
archetypeVersion |
原型(archetype)版本 |
|
archetypeRepository |
包含原型(archetype)的资源库 |
|
archetypeCatalog |
archetype分类,这里按位置分类有: |
|
filter |
查找时过滤artifactId or groupId:artifactId |
|
package |
代码生成时使用的根包的名字,如果没有给出,默认使用archetypeGroupId |
命令示例:
新建一个简单web项目
mvn archetype:generate -DgroupId=com.domain
-DartifactId=webappdemo
-Dpackage=com.domain.webappdemo
-DarchetypeArtifactId=maven-archetype-webapp
-Dversion=1.0 -DinteractiveMode=No
新建一个struts2 web项目
mvn archetype:generate -B -DgroupId=com.mycompany.mysystem
-DartifactId=myWebApp
-DarchetypeGroupId=org.apache.struts
-DarchetypeArtifactId=struts2-archetype-convention
-DarchetypeVersion=<CURRENT_STRUTS_VERSION>
-DremoteRepositories=http://struts.apache.org
maven默认提供的archetype类型可以参考http://maven.apache.org/guides/introduction/introduction-to-archetypes.html
mvn clean archetype:create-from-project -Darchetype.properties=./archetype.properties -Darchetype.filteredExtentions=java,xml,jsp,properties,sql
这里首先定义了一个archetype.properties文件在命令行被执行的目录,里面的内容是
tablePrefix是QucikStart项目里用到的,想在新项目中替换掉的内容。
-DfilteredExtentions,因为maven默认不会扫描sql文件,而这里是希望修改tablePrefix的.
properties参考http://maven.apache.org/archetype/maven-archetype-plugin/create-from-project-mojo.html
其实主流的开发工具如IDEA、Eclipse都集成了Maven(可见重要性),但为了更加深刻的学习与管理该工具(比如多个IDE共享的问题),个人建议还是单独安装比较好。
http://maven.apache.org/download.cgi
注意:安装maven之前,必须先确保你的机器中已经安装了JDK。
1.解压压缩包(以apache-maven-3.3.9-bin.zip为例)
2.添加环境变量MAVEN_HOME,值为apache-maven-3.3.9的安装路径
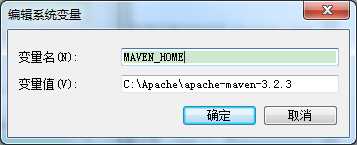
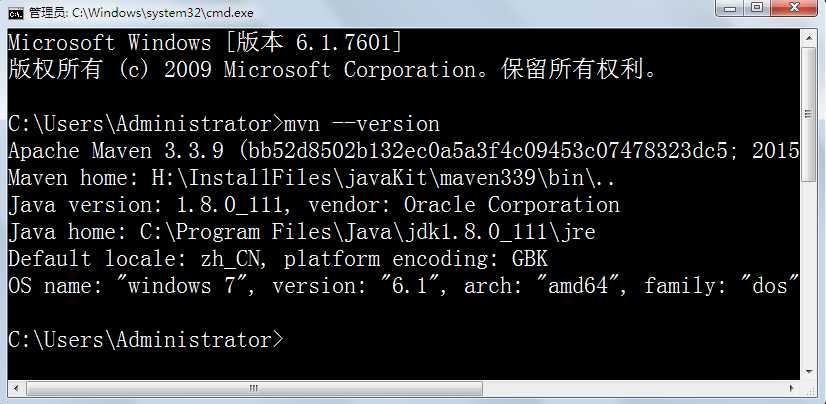
3.在Path环境变量的变量值末尾添加%MAVEN_HOME%\bin
4.在cmd输入mvn –version,如果出现maven的版本信息,说明配置成功。
5.命令行创建maven项目
方法一:
输入命令 mvn archetype:generate,按回车,根据提示输入参数,如果是第一次使用,需要下载插件,稍等几分钟即可。
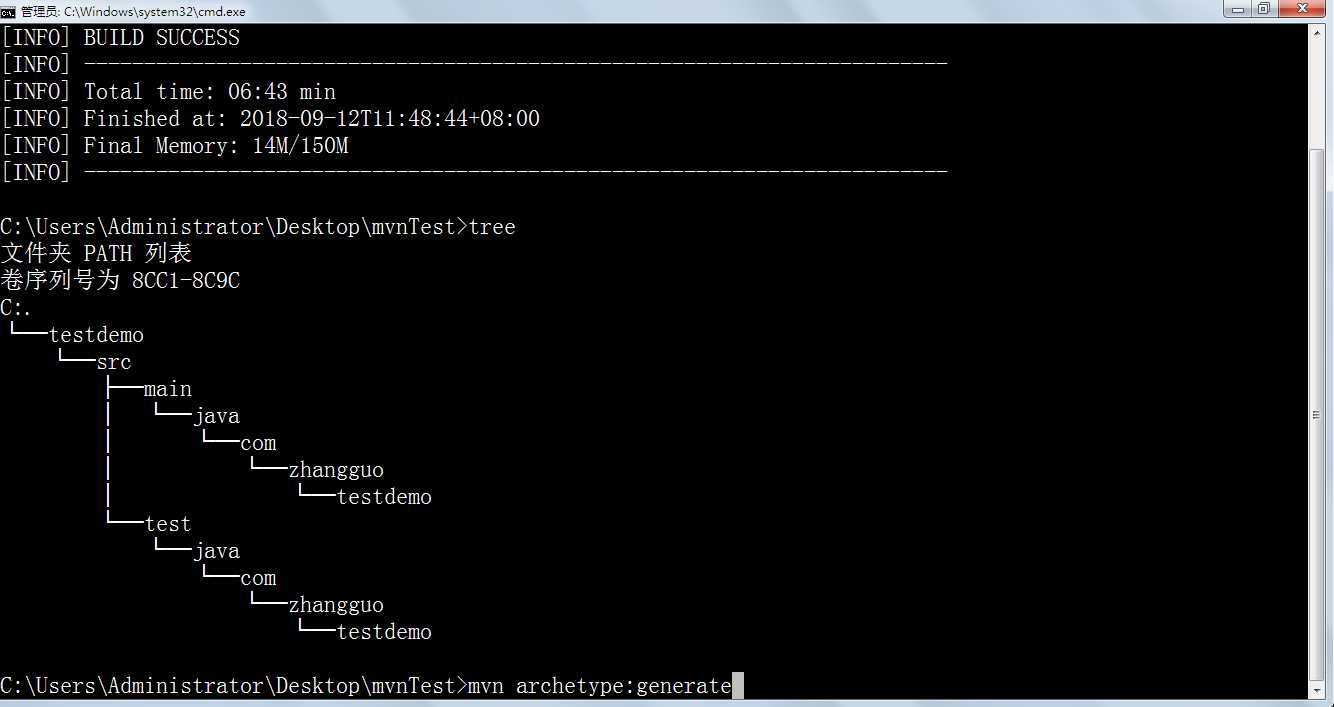
方法二:
在命令中指定参数
mvn archetype:generate -DgroupId=com.mycompany.app -DartifactId=myapp -DarchetypeArtifactId=maven-archetype-quickstart -DinteractiveMode=false
执行结果: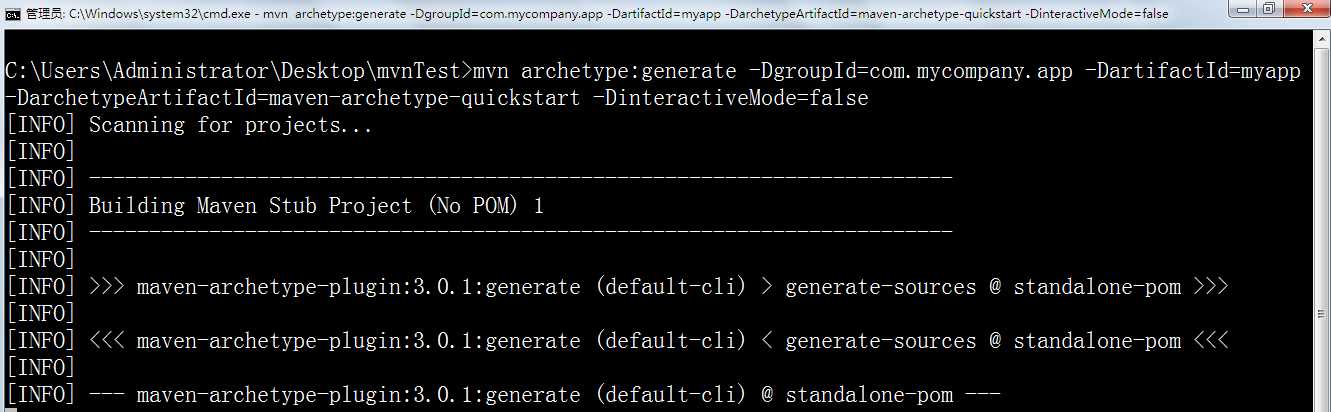
新建一个简单web项目
mvn archetype:generate -DgroupId=com.zhangguo -DartifactId=webappdemo -Dpackage=com.zhangguo.webappdemo -DarchetypeArtifactId=maven-archetype-webapp -Dversion=1.0 -DinteractiveMode=No
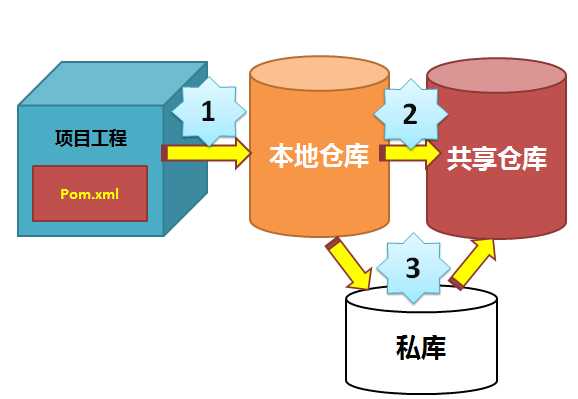
从中央仓库下载的jar包,都会统一存放到本地仓库中。我们需要配置本地仓库的位置。
打开maven安装目录,打开conf目录下的setting.xml文件。
可以参照下图配置本地仓储位置。
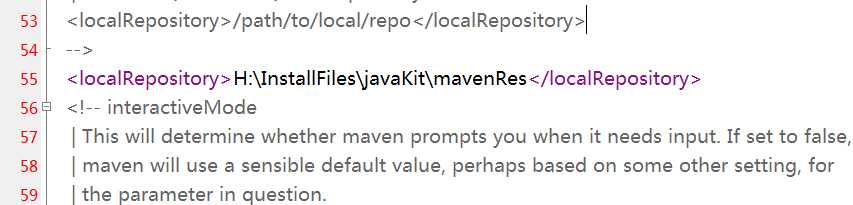
你还可以在运行时指定本地仓库位置:
mvn clean install -Dmaven.repo.local=/home/juven/myrepo/
当构建一个Maven项目时,首先检查pom.xml文件以确定依赖包的下载位置,执行顺序如下:
1、从本地资源库中查找并获得依赖包,如果没有,执行第2步。 2、从Maven默认中央仓库中查找并获得依赖包(http://repo1.maven.org/maven2/),如果没有,执行第3步。 3、如果在pom.xml中定义了自定义的远程仓库,那么也会在这里的仓库中进行查找并获得依赖包,如果都没有找到,那么Maven就会抛出异常。
修改默认中央仓库地址

常用地址:
1、http://www.sonatype.org/nexus/ 私服nexus工具使用 2、http://mvnrepository.com/ (推荐) 3、http://repo1.maven.org/maven2 4、http://maven.aliyun.com/nexus/content/groups/public/ 阿里云 (强力推荐) 5、http://repo2.maven.org/maven2/ 私服nexus工具使用 6、http://uk.maven.org/maven2/ 7、http://repository.jboss.org/nexus/content/groups/public 8、http://maven.oschina.net/content/groups/public/ 9、http://mirrors.ibiblio.org/maven2/ 10、http://maven.antelink.com/content/repositories/central/ 11、http://nexus.openkoala.org/nexus/content/groups/Koala-release/ 12、http://maven.tmatesoft.com/content/groups/public/
完整配置文件:

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!-- Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership. The ASF licenses this file to you under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License. --> <!-- | This is the configuration file for Maven. It can be specified at two levels: | | 1. User Level. This settings.xml file provides configuration for a single user, | and is normally provided in ${user.home}/.m2/settings.xml. | | NOTE: This location can be overridden with the CLI option: | | -s /path/to/user/settings.xml | | 2. Global Level. This settings.xml file provides configuration for all Maven | users on a machine (assuming they‘re all using the same Maven | installation). It‘s normally provided in | ${maven.home}/conf/settings.xml. | | NOTE: This location can be overridden with the CLI option: | | -gs /path/to/global/settings.xml | | The sections in this sample file are intended to give you a running start at | getting the most out of your Maven installation. Where appropriate, the default | values (values used when the setting is not specified) are provided. | |--> <settings xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/SETTINGS/1.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/SETTINGS/1.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/settings-1.0.0.xsd"> <!-- localRepository | The path to the local repository maven will use to store artifacts. | | Default: ${user.home}/.m2/repository <localRepository>/path/to/local/repo</localRepository> --> <localRepository>H:\InstallFiles\javaKit\mavenRes</localRepository> <!-- interactiveMode | This will determine whether maven prompts you when it needs input. If set to false, | maven will use a sensible default value, perhaps based on some other setting, for | the parameter in question. | | Default: true <interactiveMode>true</interactiveMode> --> <!-- offline | Determines whether maven should attempt to connect to the network when executing a build. | This will have an effect on artifact downloads, artifact deployment, and others. | | Default: false <offline>false</offline> --> <!-- pluginGroups | This is a list of additional group identifiers that will be searched when resolving plugins by their prefix, i.e. | when invoking a command line like "mvn prefix:goal". Maven will automatically add the group identifiers | "org.apache.maven.plugins" and "org.codehaus.mojo" if these are not already contained in the list. |--> <pluginGroups> <!-- pluginGroup | Specifies a further group identifier to use for plugin lookup. <pluginGroup>com.your.plugins</pluginGroup> --> </pluginGroups> <!-- proxies | This is a list of proxies which can be used on this machine to connect to the network. | Unless otherwise specified (by system property or command-line switch), the first proxy | specification in this list marked as active will be used. |--> <proxies> <!-- proxy | Specification for one proxy, to be used in connecting to the network. | <proxy> <id>optional</id> <active>true</active> <protocol>http</protocol> <username>proxyuser</username> <password>proxypass</password> <host>proxy.host.net</host> <port>80</port> <nonProxyHosts>local.net|some.host.com</nonProxyHosts> </proxy> --> </proxies> <!-- servers | This is a list of authentication profiles, keyed by the server-id used within the system. | Authentication profiles can be used whenever maven must make a connection to a remote server. |--> <servers> <!-- server | Specifies the authentication information to use when connecting to a particular server, identified by | a unique name within the system (referred to by the ‘id‘ attribute below). | | NOTE: You should either specify username/password OR privateKey/passphrase, since these pairings are | used together. | <server> <id>deploymentRepo</id> <username>repouser</username> <password>repopwd</password> </server> --> <!-- Another sample, using keys to authenticate. <server> <id>siteServer</id> <privateKey>/path/to/private/key</privateKey> <passphrase>optional; leave empty if not used.</passphrase> </server> --> <server> <id>admin</id> <username>admin</username> <password>admin</password> </server> </servers> <!-- mirrors | This is a list of mirrors to be used in downloading artifacts from remote repositories. | | It works like this: a POM may declare a repository to use in resolving certain artifacts. | However, this repository may have problems with heavy traffic at times, so people have mirrored | it to several places. | | That repository definition will have a unique id, so we can create a mirror reference for that | repository, to be used as an alternate download site. The mirror site will be the preferred | server for that repository. |--> <mirrors> <!-- mirror | Specifies a repository mirror site to use instead of a given repository. The repository that | this mirror serves has an ID that matches the mirrorOf element of this mirror. IDs are used | for inheritance and direct lookup purposes, and must be unique across the set of mirrors. | <mirror> <id>mirrorId</id> <mirrorOf>repositoryId</mirrorOf> <name>Human Readable Name for this Mirror.</name> <url>http://my.repository.com/repo/path</url> </mirror> --> <mirror> <id>nexus-aliyun</id> <mirrorOf>*,!jeecg,!jeecg-snapshots</mirrorOf> <name>Nexus aliyun</name> <url>http://maven.aliyun.com/nexus/content/groups/public</url> </mirror> </mirrors> <!-- profiles | This is a list of profiles which can be activated in a variety of ways, and which can modify | the build process. Profiles provided in the settings.xml are intended to provide local machine- | specific paths and repository locations which allow the build to work in the local environment. | | For example, if you have an integration testing plugin - like cactus - that needs to know where | your Tomcat instance is installed, you can provide a variable here such that the variable is | dereferenced during the build process to configure the cactus plugin. | | As noted above, profiles can be activated in a variety of ways. One way - the activeProfiles | section of this document (settings.xml) - will be discussed later. Another way essentially | relies on the detection of a system property, either matching a particular value for the property, | or merely testing its existence. Profiles can also be activated by JDK version prefix, where a | value of ‘1.4‘ might activate a profile when the build is executed on a JDK version of ‘1.4.2_07‘. | Finally, the list of active profiles can be specified directly from the command line. | | NOTE: For profiles defined in the settings.xml, you are restricted to specifying only artifact | repositories, plugin repositories, and free-form properties to be used as configuration | variables for plugins in the POM. | |--> <profiles> <!-- profile | Specifies a set of introductions to the build process, to be activated using one or more of the | mechanisms described above. For inheritance purposes, and to activate profiles via <activatedProfiles/> | or the command line, profiles have to have an ID that is unique. | | An encouraged best practice for profile identification is to use a consistent naming convention | for profiles, such as ‘env-dev‘, ‘env-test‘, ‘env-production‘, ‘user-jdcasey‘, ‘user-brett‘, etc. | This will make it more intuitive to understand what the set of introduced profiles is attempting | to accomplish, particularly when you only have a list of profile id‘s for debug. | | This profile example uses the JDK version to trigger activation, and provides a JDK-specific repo. <profile> <id>jdk-1.4</id> <activation> <jdk>1.4</jdk> </activation> <repositories> <repository> <id>jdk14</id> <name>Repository for JDK 1.4 builds</name> <url>http://www.myhost.com/maven/jdk14</url> <layout>default</layout> <snapshotPolicy>always</snapshotPolicy> </repository> </repositories> </profile> --> <!-- | Here is another profile, activated by the system property ‘target-env‘ with a value of ‘dev‘, | which provides a specific path to the Tomcat instance. To use this, your plugin configuration | might hypothetically look like: | | ... | <plugin> | <groupId>org.myco.myplugins</groupId> | <artifactId>myplugin</artifactId> | | <configuration> | <tomcatLocation>${tomcatPath}</tomcatLocation> | </configuration> | </plugin> | ... | | NOTE: If you just wanted to inject this configuration whenever someone set ‘target-env‘ to | anything, you could just leave off the <value/> inside the activation-property. | <profile> <id>env-dev</id> <activation> <property> <name>target-env</name> <value>dev</value> </property> </activation> <properties> <tomcatPath>/path/to/tomcat/instance</tomcatPath> </properties> </profile> --> <profile> <id>jdk1.7</id> <activation> <activeByDefault>true</activeByDefault> <jdk>1.7</jdk> </activation> <properties> <maven.compiler.source>1.7</maven.compiler.source> <maven.compiler.target>1.7</maven.compiler.target> <maven.compiler.compilerVersion>1.7</maven.compiler.compilerVersion> </properties> </profile> </profiles> <!-- activeProfiles | List of profiles that are active for all builds. | <activeProfiles> <activeProfile>alwaysActiveProfile</activeProfile> <activeProfile>anotherAlwaysActiveProfile</activeProfile> </activeProfiles> --> </settings>
步骤一:首先先创建一个project,上次我说过了创建一个project就是一个工作空间,在这里就是创建一个maven的工作空间
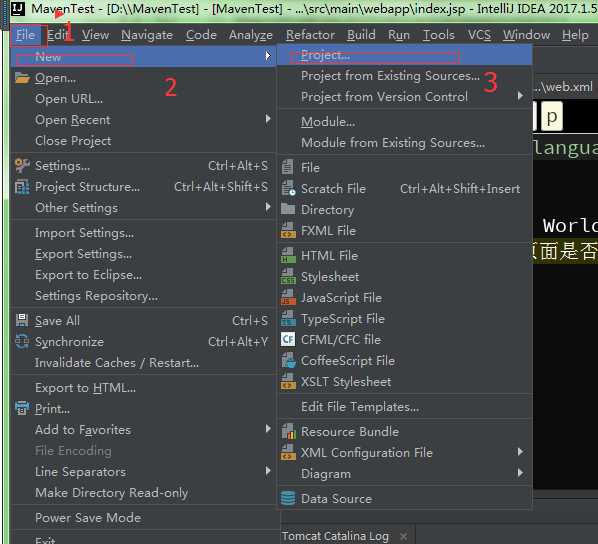
步骤二:你要选择maven然后按照下面图片 的指示操作就可以了---》最后点击next按钮
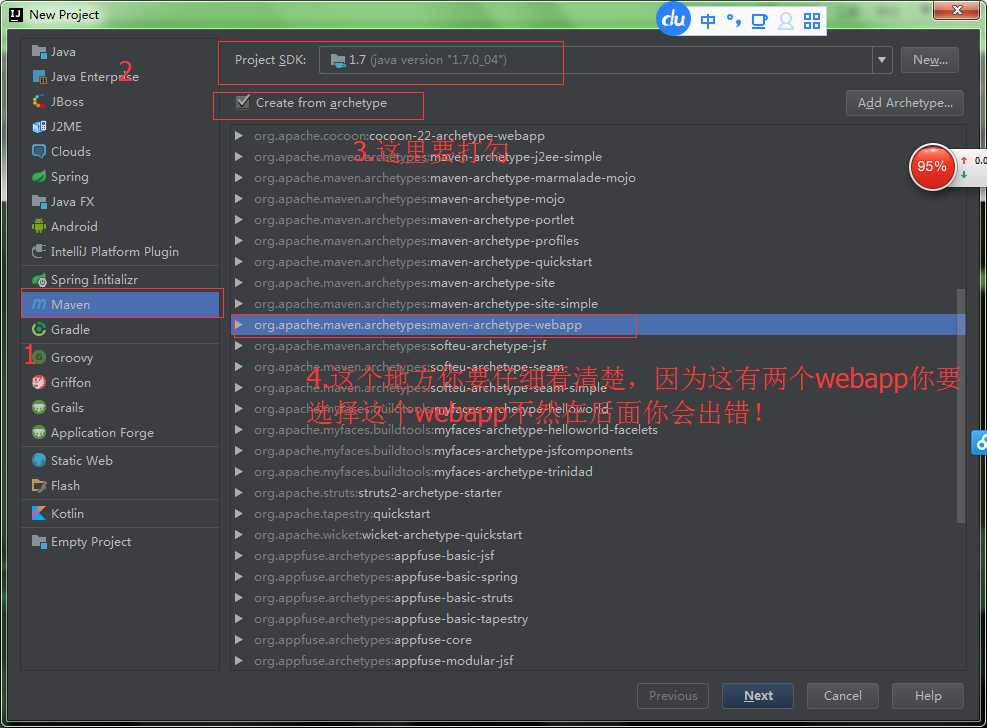
步骤三:如图:
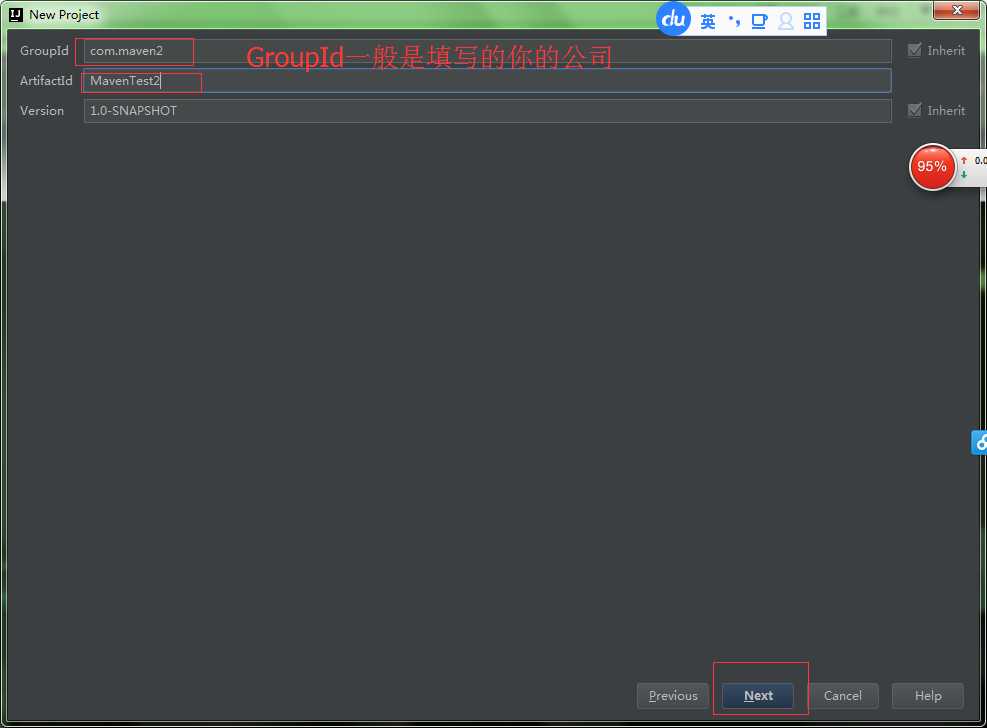
步骤四:这里如何设置自己的maven的本地仓库的位置,是通过修改settings.xml中的文件的位置放置问题,还有你要加上阿里巴巴的仓库,这样你的下载速度就会加快,如果你不采用阿里巴巴的仓库,你要下载你需要的jar包的话,你就要通过FQ去下载,你的速度就会变慢,是某些包!!!!
: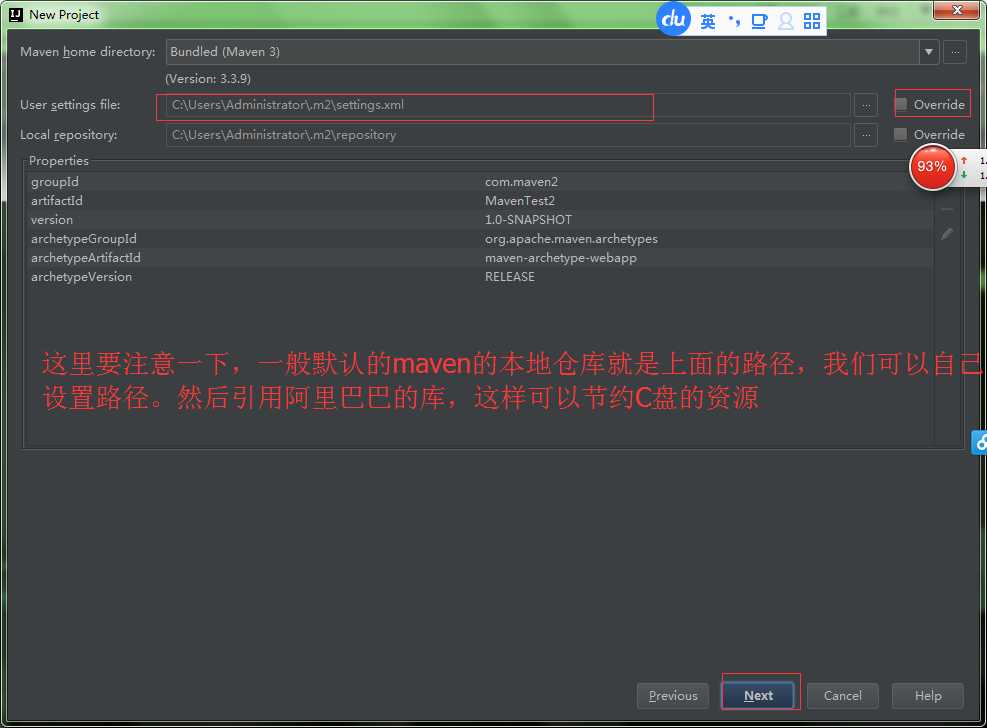
步骤五:你自己选择你自己的本地仓库的位置,至于如何设置本地仓库的位置,我在上一篇博客中有写到:你可以参考一下:http://www.cnblogs.com/1314wamm/p/7476199.html
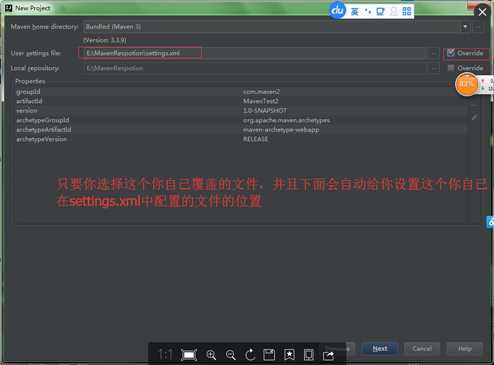
步骤七:点击next
步骤八: 点击那个倒立的三角形,然后点击Edit Configurations;
步骤八: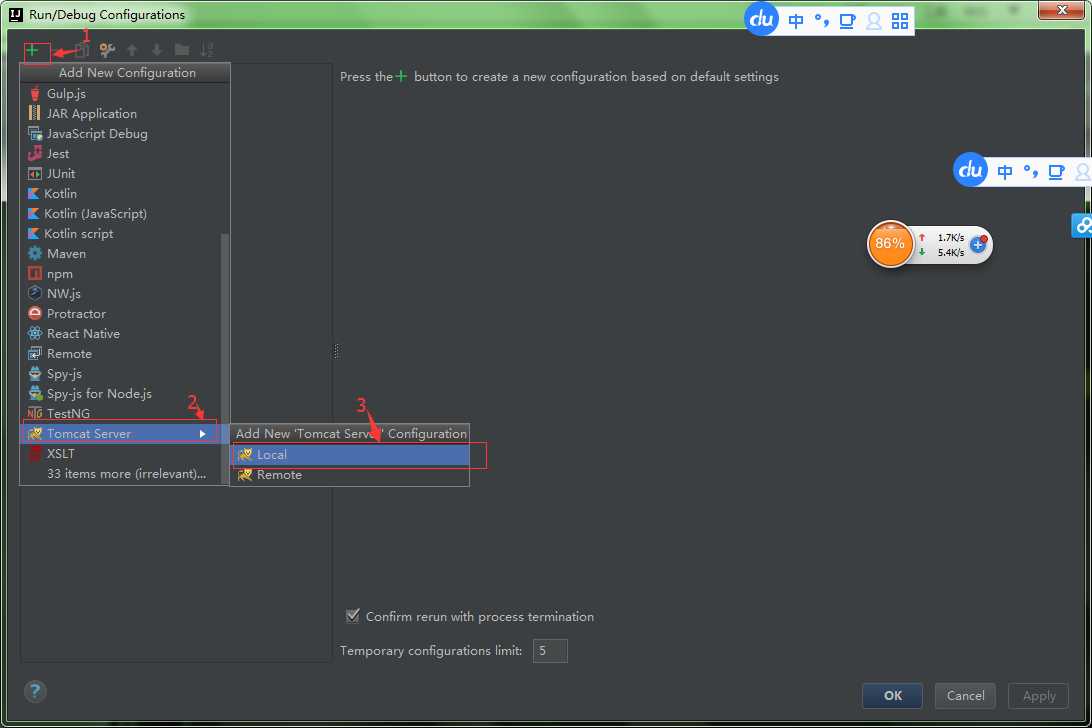
步骤九:配置tocat服务器
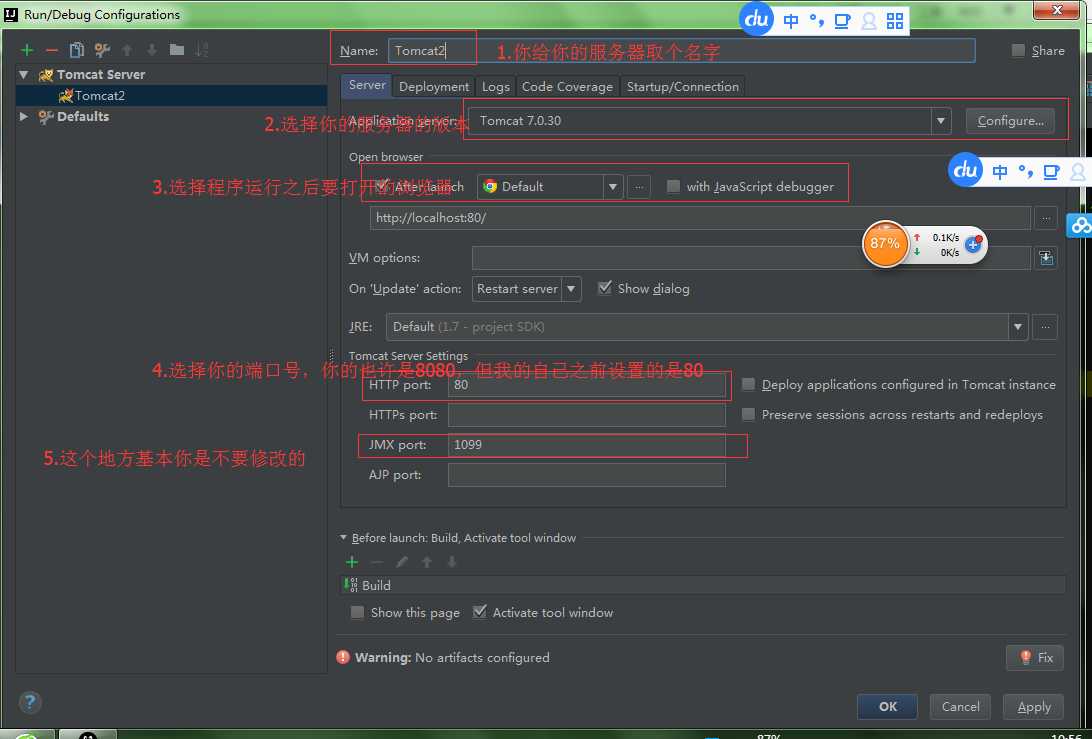
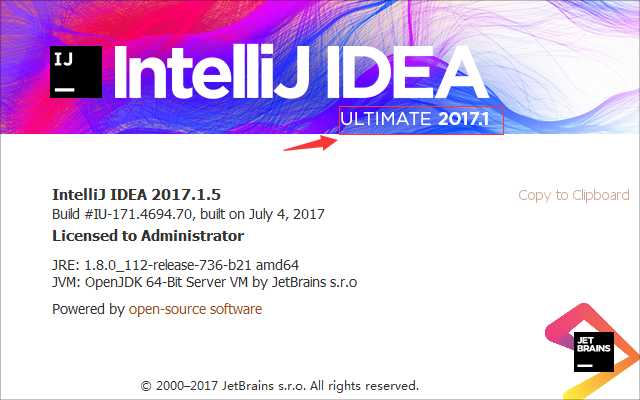
步骤十:哎,发现,我怎么就只有一个选项呀,artifact这个选项怎么没有呢?不要着急,只要你不是下载的社区版本的IDEA就行了,你要查看你是不是下载的免费版的IDEA,如果是免费版的那就是阉割过的,有些查看时没有的,想要查看你的是那个版本的你可以点击上面一栏的help---->about就可以看到相应的版本了
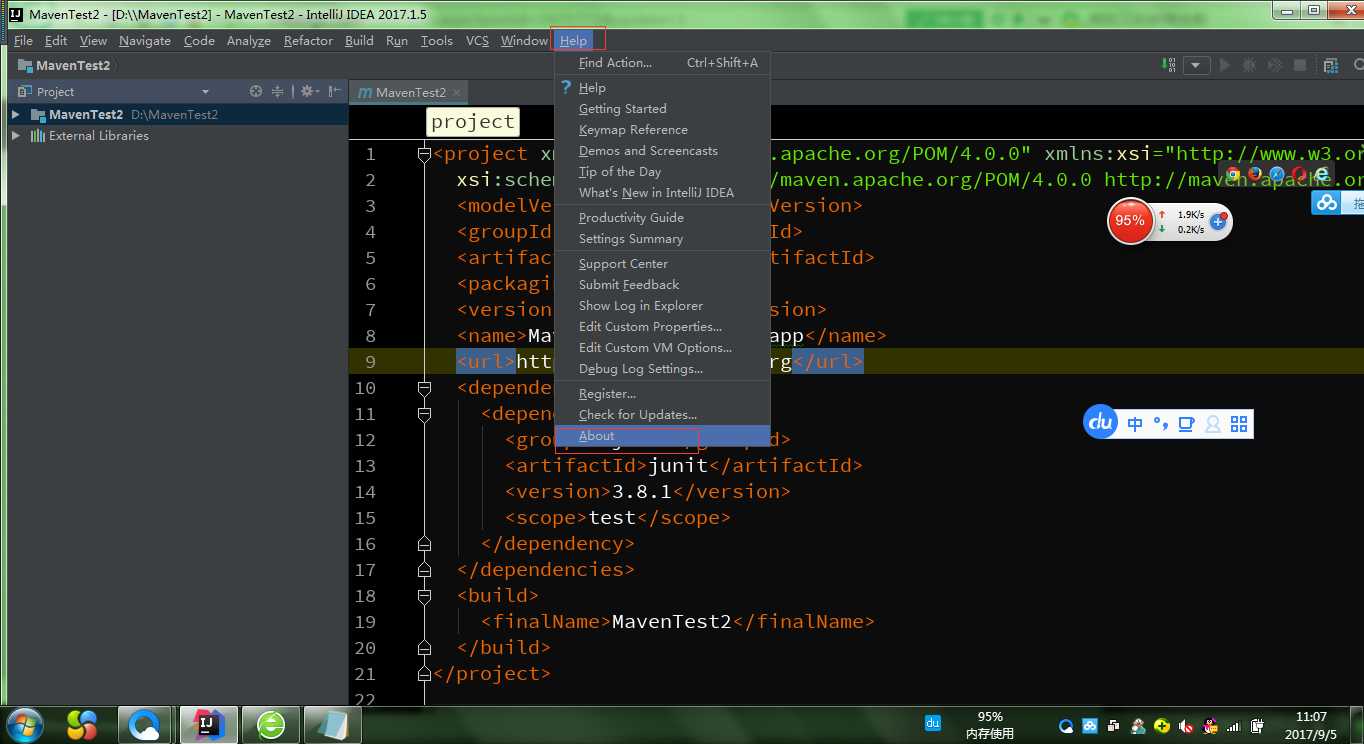
如果你看到这个,就说明你的不是社区版的了:
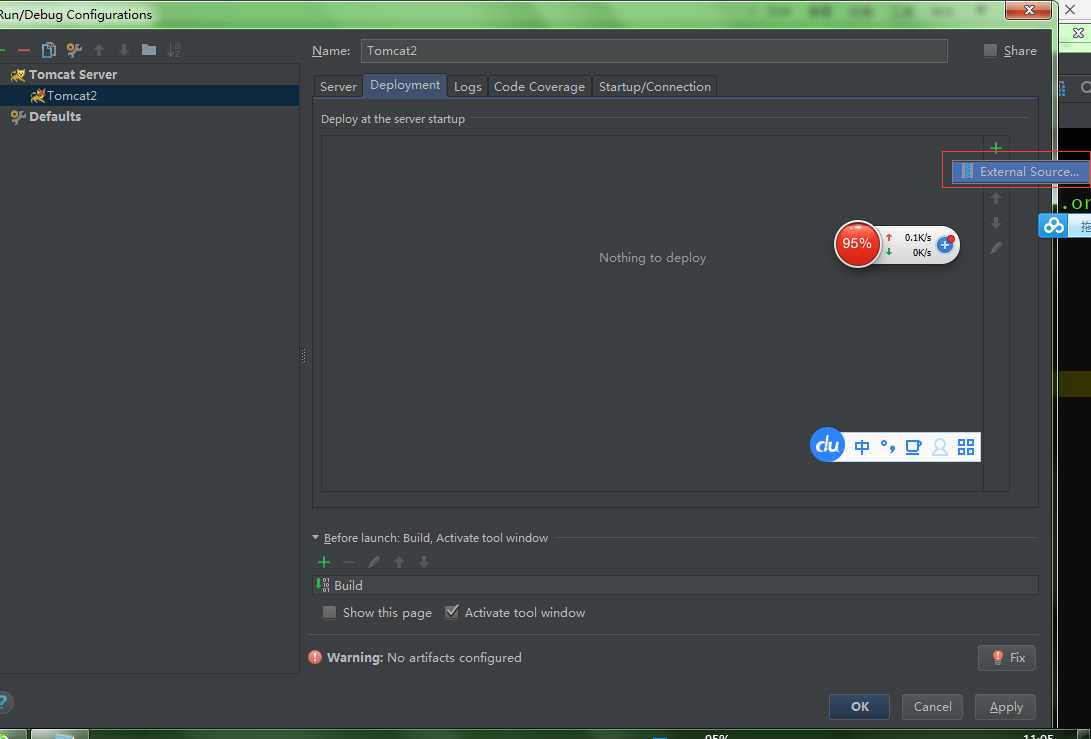
步骤十一:点击你右上方那个按钮
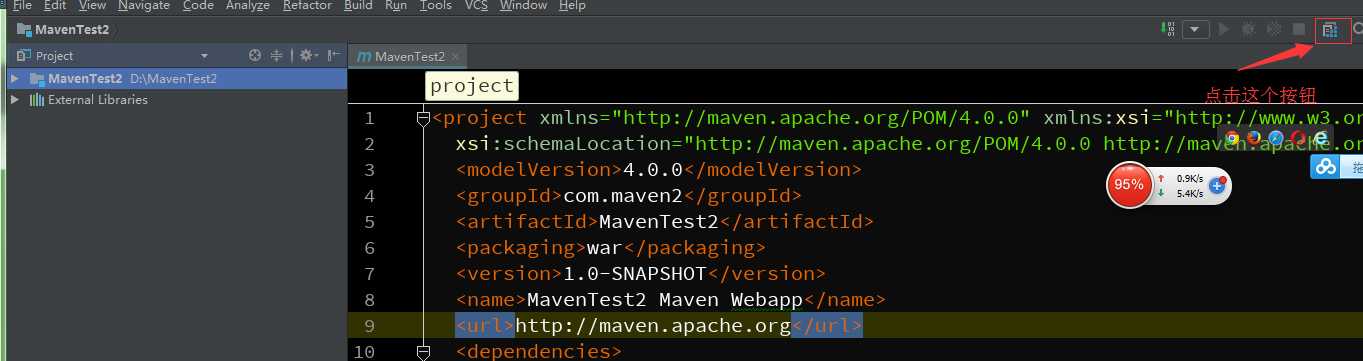
步骤十二: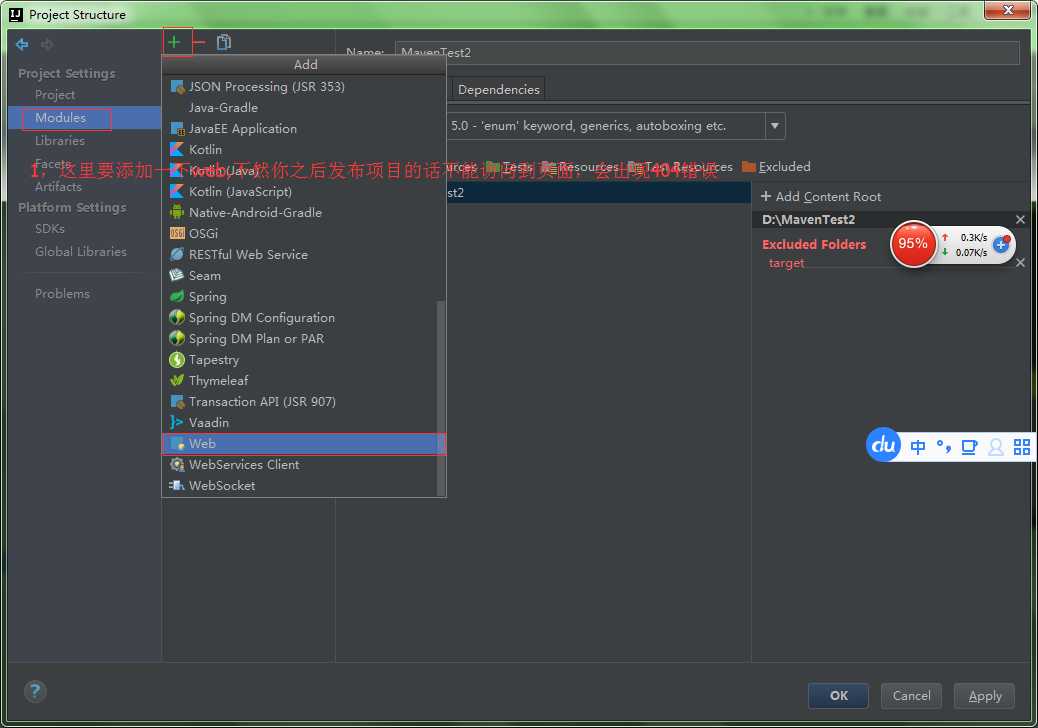
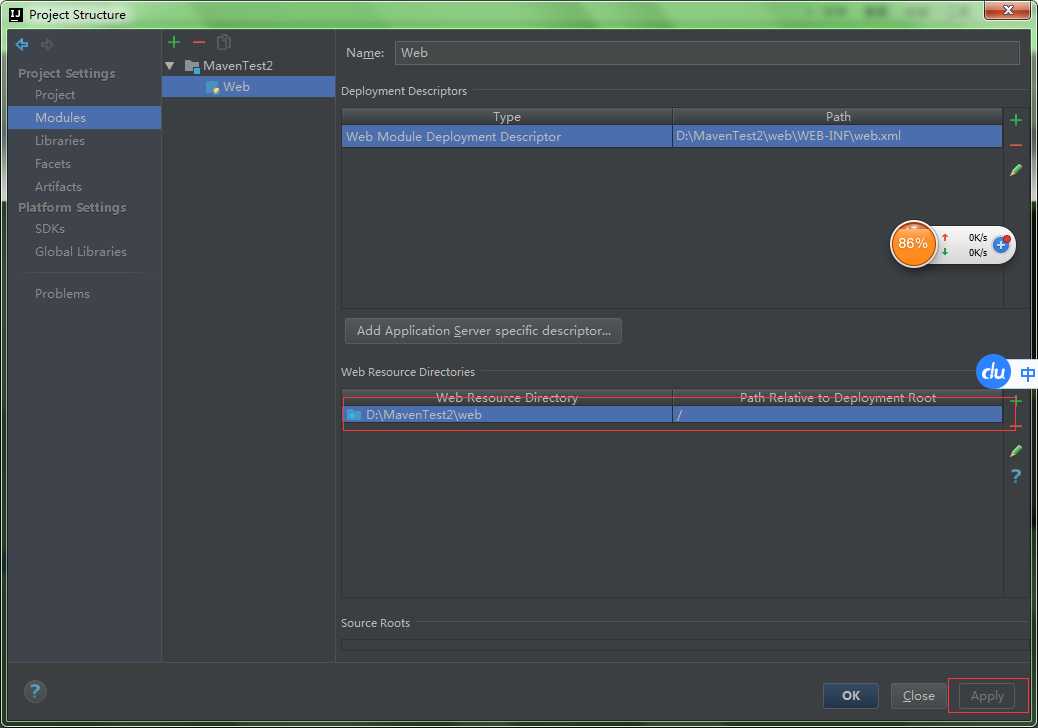
步骤十三:
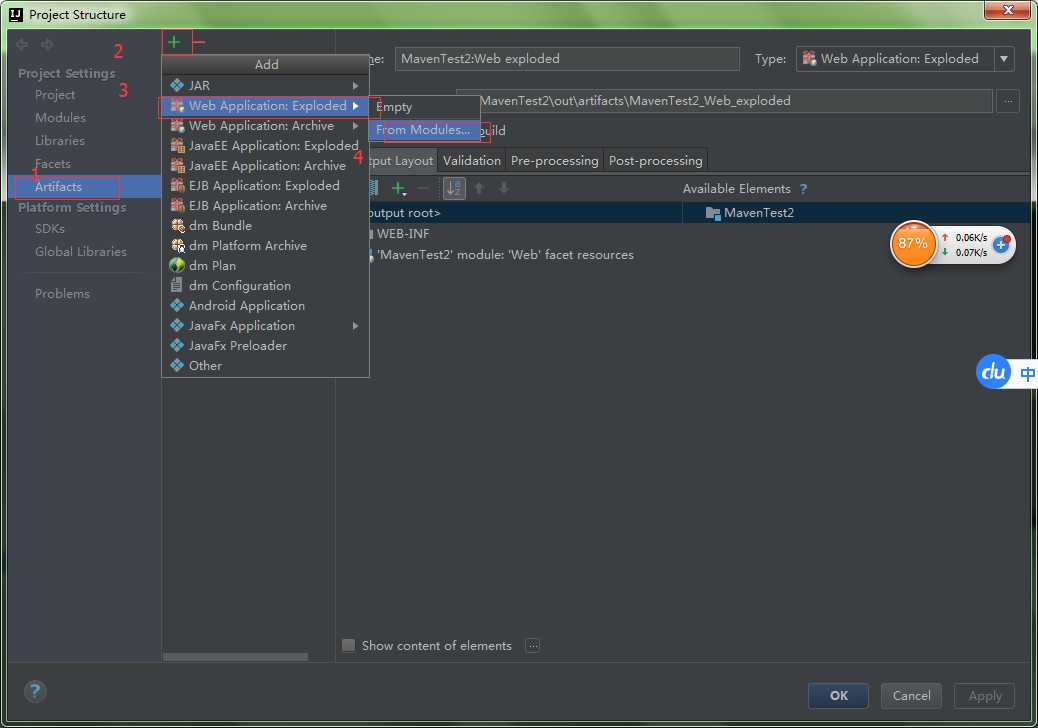
步骤十四: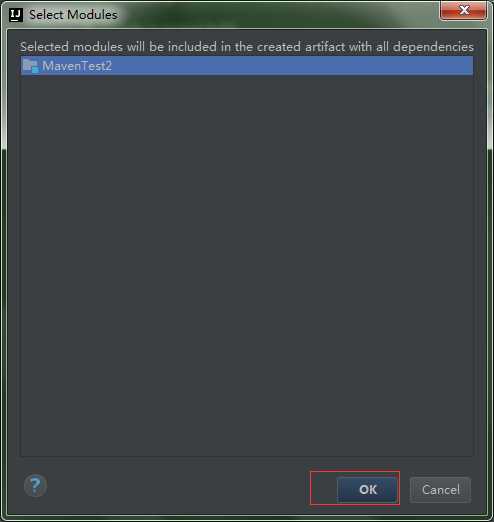
步骤十五:你会发现你想要的Artifacts出来了!!!
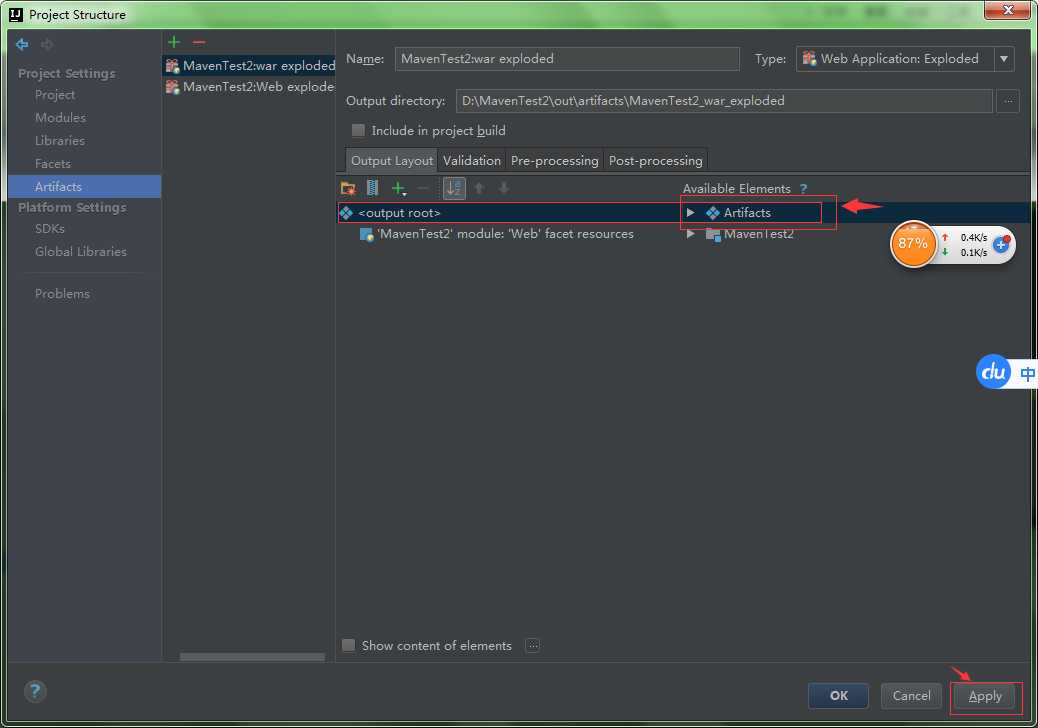
即使我配到这里,我发布项目也无法进行访问,这时你就要查看一下你的web项目那里是否进行了配置;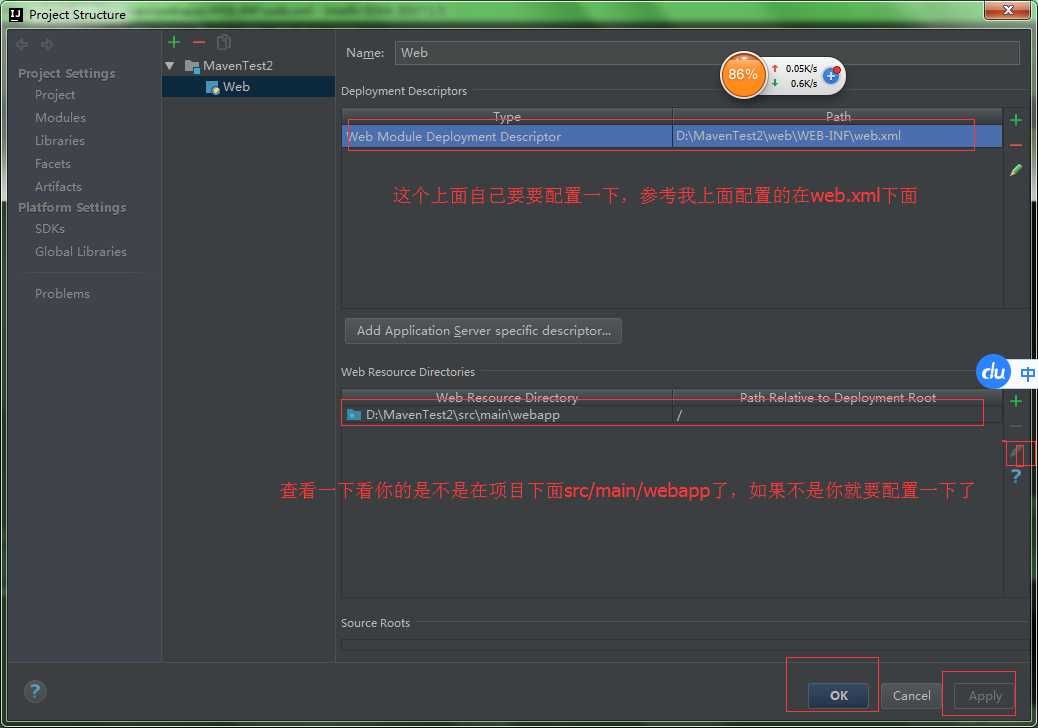
然后我又一次发布项目页面是空白的,这个时候我发现我的访问路劲没有设置,所以
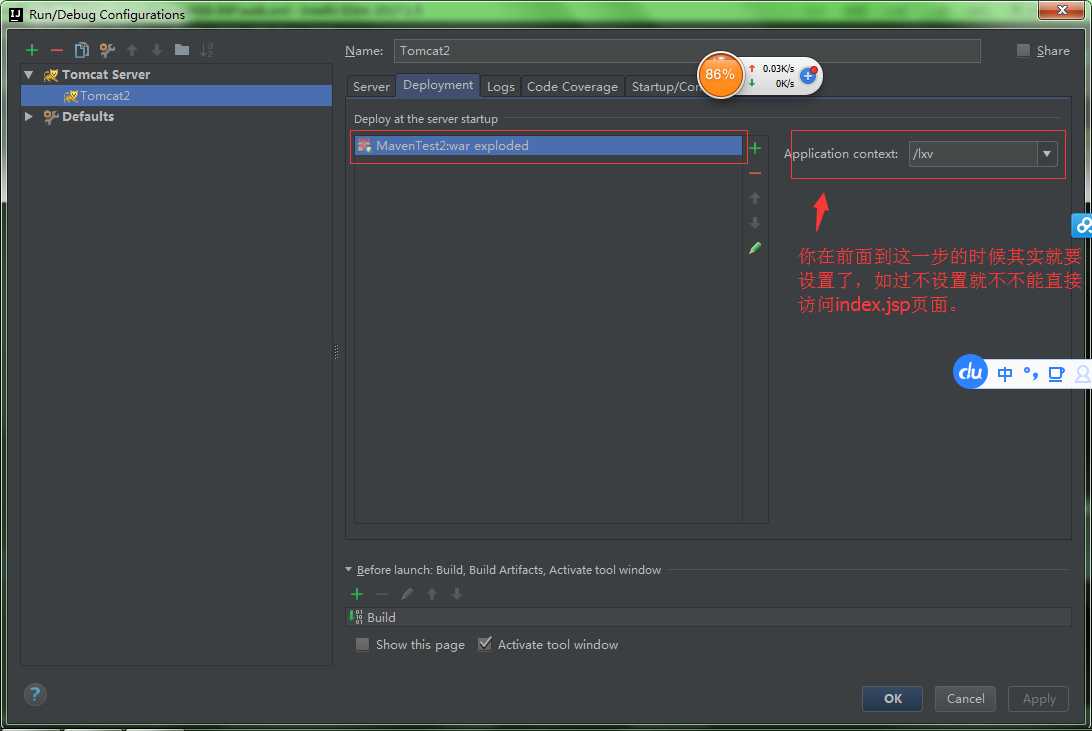
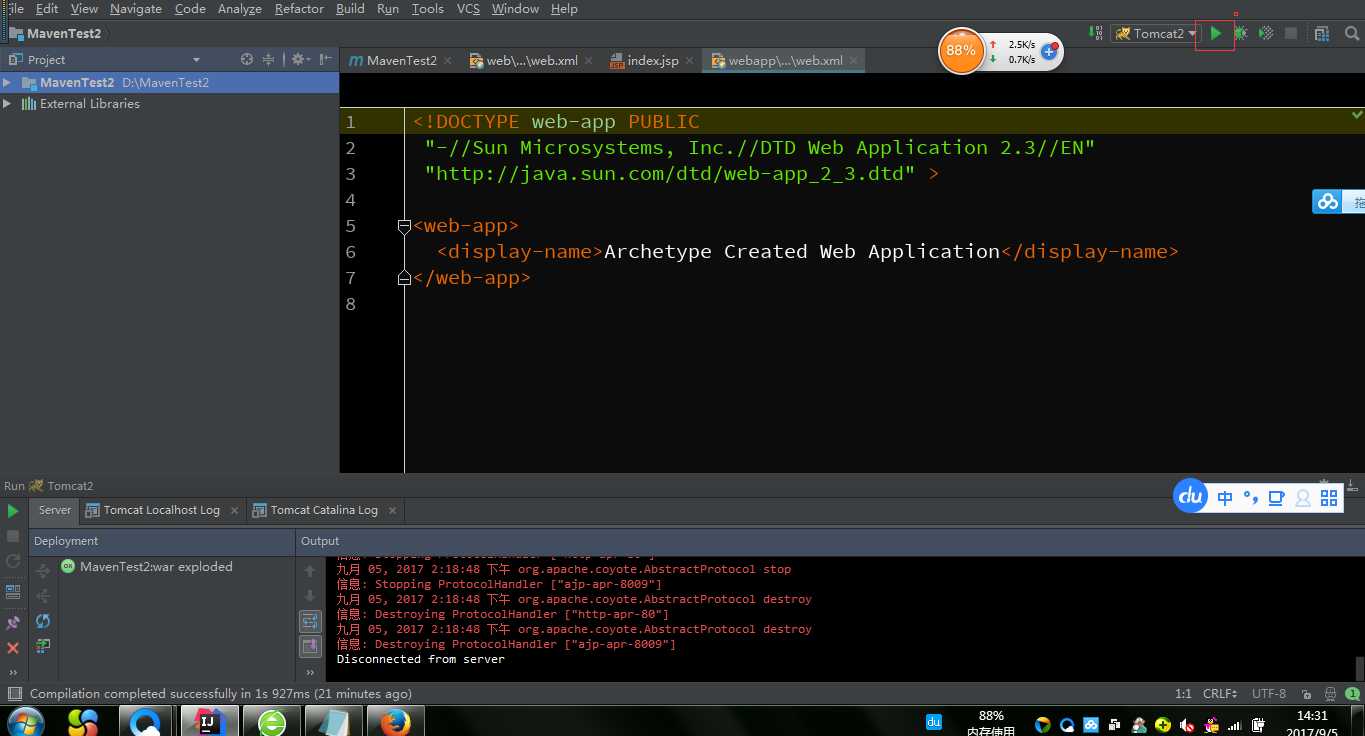
IDEA还有一个好处就是热布置,这个呢在实际开发中是很管用的web开发,你后台,改了啥他就热部署,不用你重启tomcat,前台的也是,你修改jsp,css,js什么的都可以直接进行热部署,你只要自己刷新一下你的页面就行了。
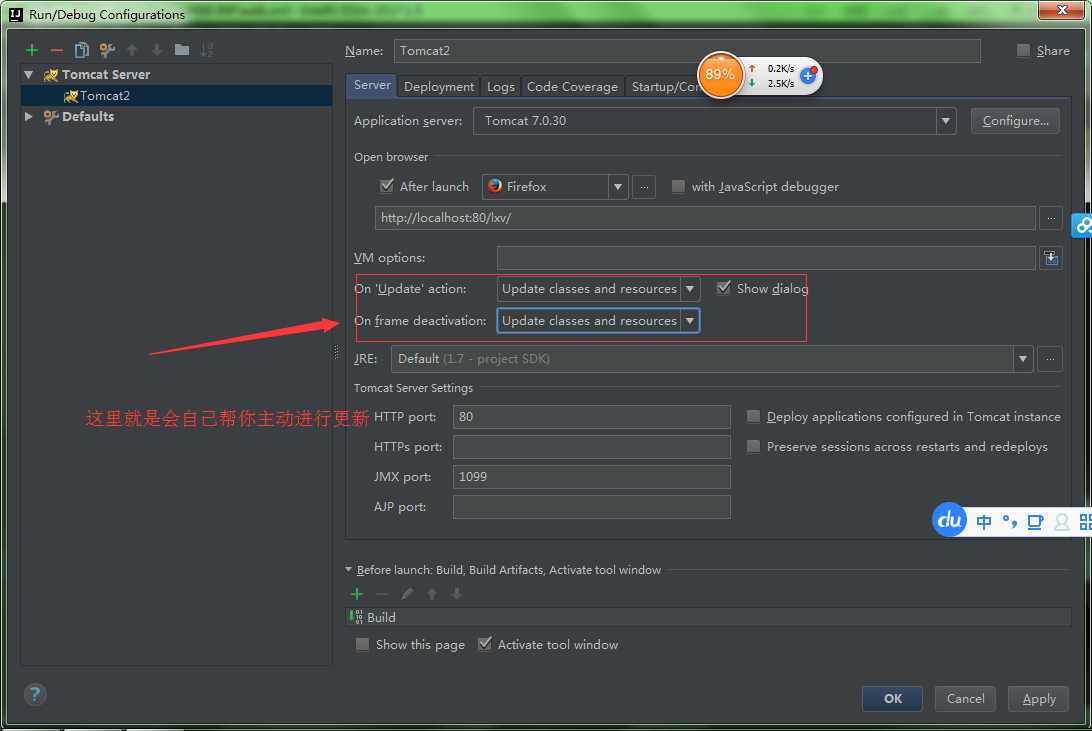
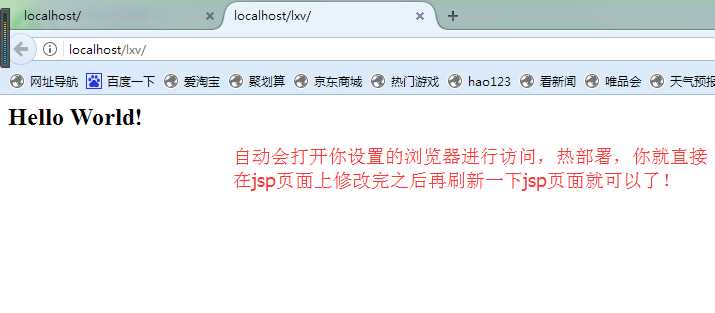
下面只要你运行了这个项目之后,就会自己帮你直接启动你开始设置的浏览器直接进行访问,
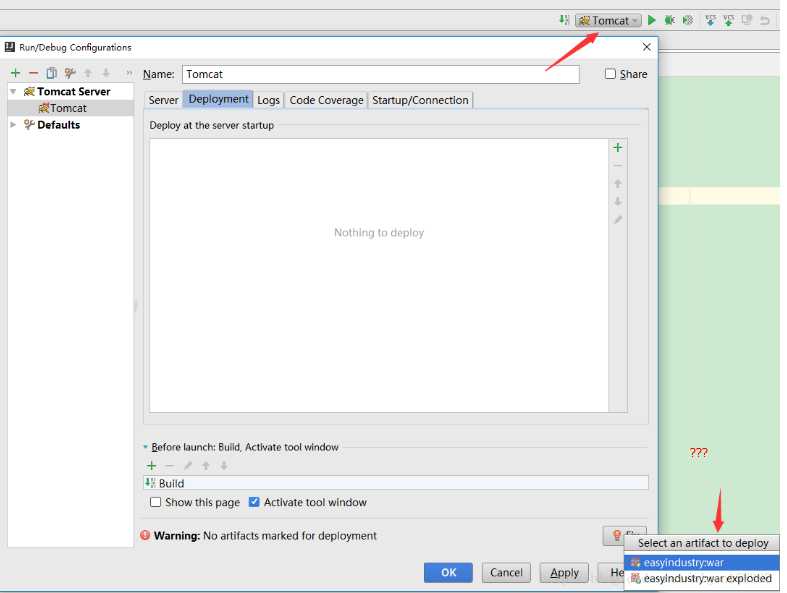
是选择war还是war exploded 这里首先看一下他们两个的区别:
(1)war模式这种可以称之为是发布模式,看名字也知道,这是先打成war包,再发布;
(2)war exploded模式是直接把文件夹、jsp页面 、classes等等移到Tomcat 部署文件夹里面,进行加载部署。因此这种方式支持热部署,一般在开发的时候也是用这种方式。
(3)在平时开发的时候,使用热部署的话,应该对Tomcat进行相应的设置,这样的话修改的jsp界面什么的东西才可以及时的显示出来。
两种方式得部署方式是不一样的,在获取项目的路径的时候得到的结果是不一样的
String contextPath = request.getSession().getServletContext().getRealPath("/");
在Eclipse中创建Maven工程,需要安装Maven插件。
一般较新版本的Eclipse都会带有Maven插件,如果你的Eclipse中已经有Maven插件,可以跳过这一步骤。
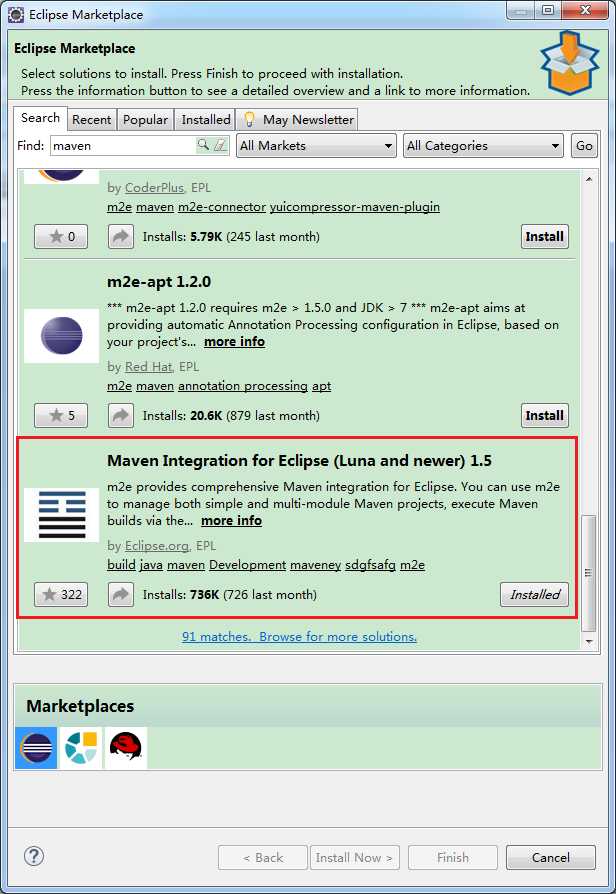
点击Help -> Eclipse Marketplace,搜索maven关键字,选择安装红框对应的Maven插件。
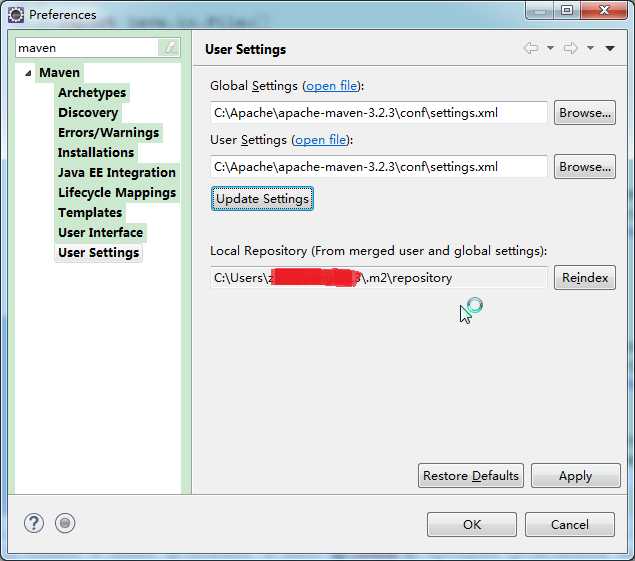
点击Window -> Preferences
如下图所示,配置settings.xml文件的位置
File -> New -> Maven Project -> Next,在接下来的窗口中会看到一大堆的项目模板,选择合适的模板。
接下来设置项目的参数,如下:
groupId是项目组织唯一的标识符,实际对应JAVA的包的结构,是main目录里java的目录结构。
artifactId就是项目的唯一的标识符,实际对应项目的名称,就是项目根目录的名称。
点击Finish,Eclipse会创建一个Maven工程。
Eclipse中构建方式
在Elipse项目上右击 -> Run As 就能看到很多Maven操作。这些操作和maven命令是等效的。例如Maven clean,等同于mvn clean命令。
你也可以点击Maven build,输入组合命令,并保存下来。如下图:
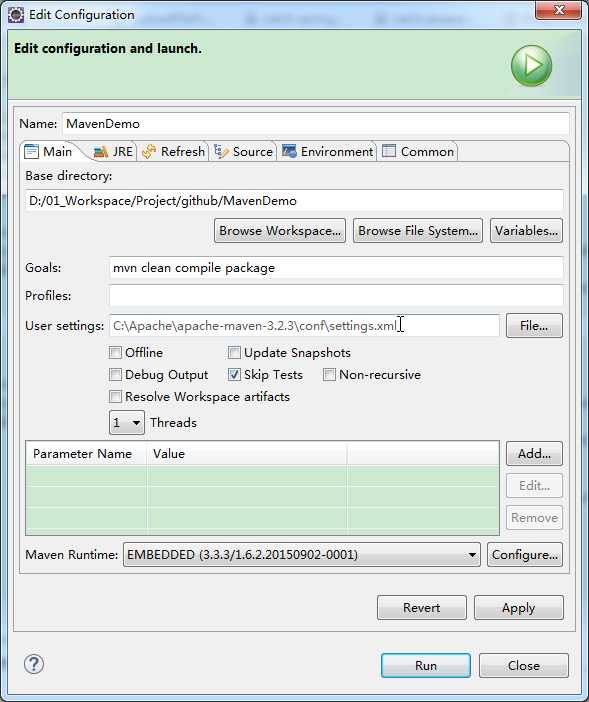
Maven命令构建方式
当然,你也可以直接使用maven命令进行构建。
进入工程所在目录,输入maven命令就可以了。
如下图
在Maven工程中添加依赖jar包,很简单,只要在POM文件中引入对应的<dependency>标签即可。
参考下例:
|
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>com.zp.maven</groupId> <artifactId>MavenDemo</artifactId> <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> <packaging>jar</packaging> <name>MavenDemo</name> <url>http://maven.apache.org</url>
<properties> <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding> <junit.version>3.8.1</junit.version> </properties>
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <version>${junit.version}</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>log4j</groupId> <artifactId>log4j</artifactId> <version>1.2.12</version> <scope>compile</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> </project>
|
<dependency>标签最常用的四个属性标签:
groupId:项目组织唯一的标识符,实际对应JAVA的包的结构。
artifactId:项目唯一的标识符,实际对应项目的名称,就是项目根目录的名称。
version:jar包的版本号。可以直接填版本数字,也可以在properties标签中设置属性值。
scope:jar包的作用范围。可以填写compile、runtime、test、system和provided。用来在编译、测试等场景下选择对应的classpath。
可以在http://mvnrepository.com/站点搜寻你想要的jar包版本
例如,想要使用log4j,可以找到需要的版本号,然后拷贝对应的maven标签信息,将其添加到pom .xml文件中。
要添加Maven插件,可以在pom.xml文件中添加<plugin>标签。
|
<build> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId> <artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId> <version>3.3</version> <source>1.7</source> <target>1.7</target> </configuration> </plugin> </plugins> </build> |
<configuration>标签用来配置插件的一些使用参数。
在Maven中,允许一个Maven Project中有多个Maven Module
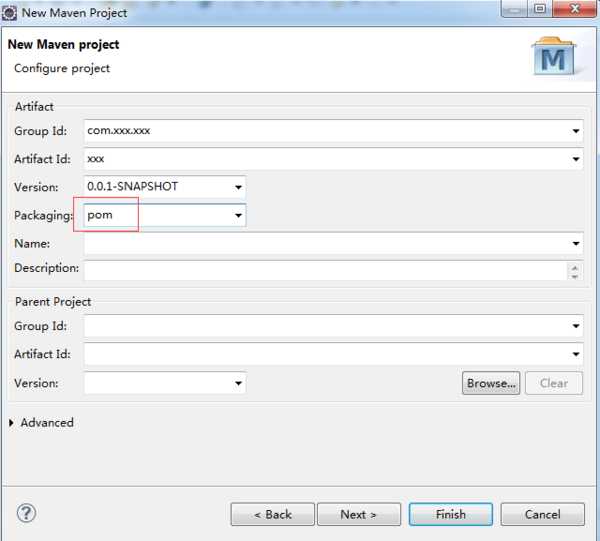
1.创建maven父工程步骤:new-->other-->选择maven project-->next-->勾选create a simple project-->next-->填写Group Id、Artifact Id、Version --> packaging选择pom-->finish。
2.创建maven子工程步骤:选中刚才创建的父工程右键-->new-->other-->选择maven module-->next-->勾选create a simple project-->填写module name(其实就是artifact id)-->next-->GAV继承父工程-->packaging选择你需要的-->finish。
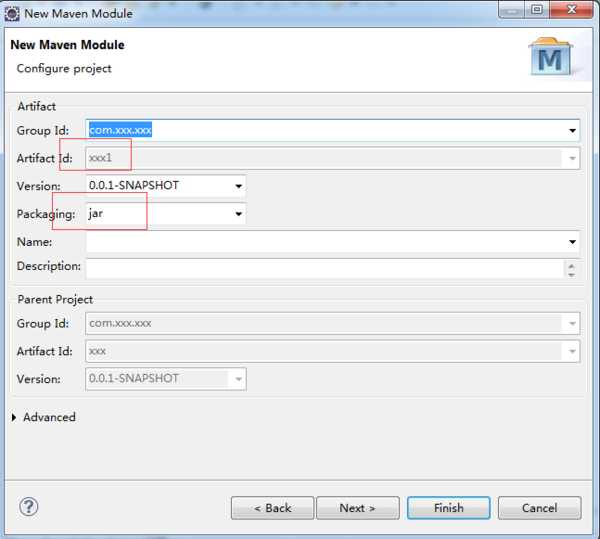
3.完成,刷新父工程;如有多个子工程,继续按照第二步骤创建。
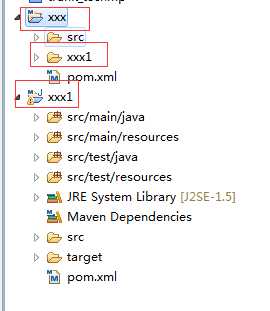
这时打开XXX中的pom.xml可以看到其中有以下标签
<modules>
<module>xxx1</module>
</modules>
选择编译XXX时,会依次对它的所有Module执行相同操作。
http://maven.apache.org/plugins/maven-antrun-plugin/
maven-antrun-plugin能让用户在Maven项目中运行Ant任务。用户可以直接在该插件的配置以Ant的方式编写Target,然后交给该插件的run目标去执行。在一些由Ant往Maven迁移的项目中,该插件尤其有用。此外当你发现需要编写一些自定义程度很高的任务,同时又觉得Maven不够灵活时,也可以以Ant的方式实现之。maven-antrun-plugin的run目标通常与生命周期绑定运行。
http://maven.apache.org/archetype/maven-archetype-plugin/
Archtype指项目的骨架,Maven初学者最开始执行的Maven命令可能就是mvn archetype:generate,这实际上就是让maven-archetype-plugin生成一个很简单的项目骨架,帮助开发者快速上手。可能也有人看到一些文档写了mvn archetype:create,但实际上create目标已经被弃用了,取而代之的是generate目标,该目标使用交互式的方式提示用户输入必要的信息以创建项目,体验更好。 maven-archetype-plugin还有一些其他目标帮助用户自己定义项目原型,例如你由一个产品需要交付给很多客户进行二次开发,你就可以为他们提供一个Archtype,帮助他们快速上手。
http://maven.apache.org/plugins/maven-assembly-plugin/
maven-assembly-plugin的用途是制作项目分发包,该分发包可能包含了项目的可执行文件、源代码、readme、平台脚本等等。
maven-assembly-plugin支持各种主流的格式如zip、tar.gz、jar和war等,具体打包哪些文件是高度可控的,例如用户可以按文件级别的粒度、文件集级别的粒度、模块级别的粒度、以及依赖级别的粒度控制打包,此外,包含和排除配置也是支持的。maven-assembly-
plugin要求用户使用一个名为assembly.xml的元数据文件来表述打包,它的single目标可以直接在命令行调用,也可以被绑定至生命周期。
http://maven.apache.org/plugins/maven-dependency-plugin/
maven-dependency-plugin最大的用途是帮助分析项目依赖,dependency:list能够列出项目最终解析到的依赖列表,dependency:tree能进一步的描绘项目依赖树,dependency:analyze可以告诉你项目依赖潜在的问题,如果你有直接使用到的却未声明的依赖,该目标就会发出警告。maven-dependency-plugin还有很多目标帮助你操作依赖文件,例如dependency:copy-dependencies能将项目依赖从本地Maven仓库复制到某个特定的文件夹下面。
http://maven.apache.org/plugins/maven-enforcer-plugin/
在一个稍大一点的组织或团队中,你无法保证所有成员都熟悉Maven,那他们做一些比较愚蠢的事情就会变得很正常,例如给项目引入了外部的 SNAPSHOT依赖而导致构建不稳定,使用了一个与大家不一致的Maven版本而经常抱怨构建出现诡异问题。maven-enforcer- plugin能够帮助你避免之类问题,它允许你创建一系列规则强制大家遵守,包括设定Java版本、设定Maven版本、禁止某些依赖、禁止 SNAPSHOT依赖。只要在一个父POM配置规则,然后让大家继承,当规则遭到破坏的时候,Maven就会报错。除了标准的规则之外,你还可以扩展该插件,编写自己的规则。maven-enforcer-plugin的enforce目标负责检查规则,它默认绑定到生命周期的validate阶段。
http://maven.apache.org/plugins/maven-help-plugin/
maven-help-plugin是一个小巧的辅助工具,最简单的help:system可以打印所有可用的环境变量和Java系统属性。help:effective-pom和help:effective-settings最为有用,它们分别打印项目的有效POM和有效settings,有效POM是指合并了所有父POM(包括Super POM)后的XML,当你不确定POM的某些信息从何而来时,就可以查看有效POM。有效settings同理,特别是当你发现自己配置的 settings.xml没有生效时,就可以用help:effective-settings来验证。此外,maven-help-plugin的describe目标可以帮助你描述任何一个Maven插件的信息,还有all-profiles目标和active-profiles目标帮助查看项目的Profile。
http://maven.apache.org/plugins/maven-release-plugin/
maven-release-plugin的用途是帮助自动化项目版本发布,它依赖于POM中的SCM信息。release:prepare用来准备版本发布,具体的工作包括检查是否有未提交代码、检查是否有SNAPSHOT依赖、升级项目的SNAPSHOT版本至RELEASE版本、为项目打标签等等。release:perform则是签出标签中的RELEASE源码,构建并发布。版本发布是非常琐碎的工作,它涉及了各种检查,而且由于该工作仅仅是偶尔需要,因此手动操作很容易遗漏一些细节,maven-release-plugin让该工作变得非常快速简便,不易出错。maven-release-plugin的各种目标通常直接在命令行调用,因为版本发布显然不是日常构建生命周期的一部分。
http://maven.apache.org/plugins/maven-resources-plugin/
为了使项目结构更为清晰,Maven区别对待Java代码文件和资源文件,maven-compiler-plugin用来编译Java代码,maven-resources-plugin则用来处理资源文件。默认的主资源文件目录是src/main/resources,很多用户会需要添加额外的资源文件目录,这个时候就可以通过配置maven-resources-plugin来实现。此外,资源文件过滤也是Maven的一大特性,你可以在资源文件中使用${propertyName}形式的Maven属性,然后配置maven-resources-plugin开启对资源文件的过滤,之后就可以针对不同环境通过命令行或者Profile传入属性的值,以实现更为灵活的构建。
http://maven.apache.org/plugins/maven-surefire-plugin/
可能是由于历史的原因,Maven 2/3中用于执行测试的插件不是maven-test-plugin,而是maven-surefire-plugin。其实大部分时间内,只要你的测试类遵循通用的命令约定(以Test结尾、以TestCase结尾、或者以Test开头),就几乎不用知晓该插件的存在。然而在当你想要跳过测试、排除某些测试类、或者使用一些TestNG特性的时候,了解maven-surefire-plugin的一些配置选项就很有用了。例如 mvn test -Dtest=FooTest 这样一条命令的效果是仅运行FooTest测试类,这是通过控制maven-surefire-plugin的test参数实现的。
http://mojo.codehaus.org/build-helper-maven-plugin/
Maven默认只允许指定一个主Java代码目录和一个测试Java代码目录,虽然这其实是个应当尽量遵守的约定,但偶尔你还是会希望能够指定多个源码目录(例如为了应对遗留项目),build-helper-maven-plugin的add-source目标就是服务于这个目的,通常它被绑定到默认生命周期的generate-sources阶段以添加额外的源码目录。需要强调的是,这种做法还是不推荐的,因为它破坏了 Maven的约定,而且可能会遇到其他严格遵守约定的插件工具无法正确识别额外的源码目录。
build-helper-maven-plugin的另一个非常有用的目标是attach-artifact,使用该目标你可以以classifier的形式选取部分项目文件生成附属构件,并同时install到本地仓库,也可以deploy到远程仓库。
http://mojo.codehaus.org/exec-maven-plugin/
exec-maven-plugin很好理解,顾名思义,它能让你运行任何本地的系统程序,在某些特定情况下,运行一个Maven外部的程序可能就是最简单的问题解决方案,这就是exec:exec的用途,当然,该插件还允许你配置相关的程序运行参数。除了exec目标之外,exec-maven-plugin还提供了一个java目标,该目标要求你提供一个mainClass参数,然后它能够利用当前项目的依赖作为classpath,在同一个JVM中运行该mainClass。有时候,为了简单的演示一个命令行Java程序,你可以在POM中配置好exec-maven-plugin的相关运行参数,然后直接在命令运行mvn exec:java 以查看运行效果。
http://wiki.eclipse.org/Jetty/Feature/Jetty_Maven_Plugin
在进行Web开发的时候,打开浏览器对应用进行手动的测试几乎是无法避免的,这种测试方法通常就是将项目打包成war文件,然后部署到Web容器中,再启动容器进行验证,这显然十分耗时。为了帮助开发者节省时间,jetty-maven-plugin应运而生,它完全兼容
Maven项目的目录结构,能够周期性地检查源文件,一旦发现变更后自动更新到内置的Jetty
Web容器中。做一些基本配置后(例如Web应用的contextPath和自动扫描变更的时间间隔),你只要执行 mvn jetty:run ,然后在IDE中修改代码,代码经IDE自动编译后产生变更,再由jetty-maven-plugin侦测到后更新至Jetty容器,这时你就可以直接测试Web页面了。需要注意的是,jetty-maven-plugin并不是宿主于Apache或Codehaus的官方插件,因此使用的时候需要额外的配置settings.xml的pluginGroups元素,将org.mortbay.jetty这个pluginGroup加入。
http://mojo.codehaus.org/versions-maven-plugin/
很多Maven用户遇到过这样一个问题,当项目包含大量模块的时候,为他们集体更新版本就变成一件烦人的事情,到底有没有自动化工具能帮助完成这件事情呢?(当然你可以使用sed之类的文本操作工具,不过不在本文讨论范围)答案是肯定的,versions-maven- plugin提供了很多目标帮助你管理Maven项目的各种版本信息。例如最常用的,命令 mvn versions:set -DnewVersion=1.1-SNAPSHOT 就能帮助你把所有模块的版本更新到1.1-SNAPSHOT。该插件还提供了其他一些很有用的目标,display-dependency- updates能告诉你项目依赖有哪些可用的更新;类似的display-plugin-updates能告诉你可用的插件更新;然后use- latest-versions能自动帮你将所有依赖升级到最新版本。最后,如果你对所做的更改满意,则可以使用 mvn versions:commit 提交,不满意的话也可以使用 mvn versions:revert 进行撤销。
更多详情请参考https://maven.apache.org/plugins/
|
生命周期 |
阶段描述 |
|
mvn validate |
验证项目是否正确,以及所有为了完整构建必要的信息是否可用 |
|
mvn generate-sources |
生成所有需要包含在编译过程中的源代码 |
|
mvn process-sources |
处理源代码,比如过滤一些值 |
|
mvn generate-resources |
生成所有需要包含在打包过程中的资源文件 |
|
mvn process-resources |
复制并处理资源文件至目标目录,准备打包 |
|
mvn compile |
编译项目的源代码 |
|
mvn process-classes |
后处理编译生成的文件,例如对Java类进行字节码增强(bytecode enhancement) |
|
mvn generate-test-sources |
生成所有包含在测试编译过程中的测试源码 |
|
mvn process-test-sources |
处理测试源码,比如过滤一些值 |
|
mvn generate-test-resources |
生成测试需要的资源文件 |
|
mvn process-test-resources |
复制并处理测试资源文件至测试目标目录 |
|
mvn test-compile |
编译测试源码至测试目标目录 |
|
mvn test |
使用合适的单元测试框架运行测试。这些测试应该不需要代码被打包或发布 |
|
mvn prepare-package |
在真正的打包之前,执行一些准备打包必要的操作。这通常会产生一个包的展开的处理过的版本(将会在Maven 2.1+中实现) |
|
mvn package |
将编译好的代码打包成可分发的格式,如JAR,WAR,或者EAR |
|
mvn pre-integration-test |
执行一些在集成测试运行之前需要的动作。如建立集成测试需要的环境 |
|
mvn integration-test |
如果有必要的话,处理包并发布至集成测试可以运行的环境 |
|
mvn post-integration-test |
执行一些在集成测试运行之后需要的动作。如清理集成测试环境。 |
|
mvn verify |
执行所有检查,验证包是有效的,符合质量规范 |
|
mvn install |
安装包至本地仓库,以备本地的其它项目作为依赖使用 |
|
mvn deploy |
复制最终的包至远程仓库,共享给其它开发人员和项目(通常和一次正式的发布相关) |
使用参数
-Dmaven.test.skip=true: 跳过单元测试(eg: mcn clean package -Dmaven.test.skip=true)
dependencyManagement是表示依赖jar包的声明,即你在项目中的dependencyManagement下声明了依赖,maven不会加载该依赖,dependencyManagement声明可以被继承。
dependencyManagement的一个使用案例是当有父子项目的时候,父项目中可以利用dependencyManagement声明子项目中需要用到的依赖jar包,之后,当某个或者某几个子项目需要加载该插件的时候,就可以在子项目中dependencies节点只配置 groupId 和 artifactId就可以完成插件的引用。
dependencyManagement主要是为了统一管理插件,确保所有子项目使用的插件版本保持一致,类似的还是plugins和pluginManagement。
标签:示例 设置 runtime atp admin 模式 tar 相关 资源库
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/best/p/9622472.html