标签:val 部分 element journey 字典 ping play ble 方便
计算几何基础
Jack Straws(POJ 1127)
| Time Limit: 1000MS | Memory Limit: 10000K |
| Total Submissions: 5494 | Accepted: 2504 |
Description
Input
Output
Sample Input
7 1 6 3 3 4 6 4 9 4 5 6 7 1 4 3 5 3 5 5 5 5 2 6 3 5 4 7 2 1 4 1 6 3 3 6 7 2 3 1 3 0 0 2 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 2 2 1 2 0 0 0
Sample Output
CONNECTED NOT CONNECTED CONNECTED CONNECTED NOT CONNECTED CONNECTED CONNECTED CONNECTED CONNECTED
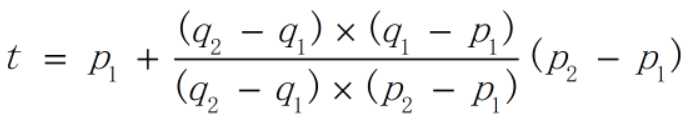

1 #include <cstdio> 2 #include <cmath> 3 #include <algorithm> 4 5 using namespace std; 6 7 const double EPS=1e-10; 8 9 double add(double a, double b) 10 { 11 if (fabs(a+b)<EPS*(fabs(a)+fabs(b))) return 0; 12 return a+b; 13 } 14 15 struct P 16 { 17 double x,y; 18 P(){}; 19 P(double x, double y):x(x),y(y){} 20 P operator + (P p) 21 { 22 return P(add(x, p.x), add(y, p.y)); 23 } 24 P operator - (P p) 25 { 26 return P(add(x, -p.x), add(y, -p.y)); 27 } 28 P operator * (double d) 29 { 30 return P(x*d, y*d); 31 } 32 double dot(P p) 33 { 34 return add(x*p.x, y*p.y); 35 } 36 double det(P p) 37 { 38 return add(x*p.y, -y*p.x); 39 } 40 }; 41 42 bool on_seg(P p1, P p2, P q) 43 { 44 return (p1-q).det(p2-q)==0 && (p1-q).dot(p2-q)<=0; 45 } 46 47 P intersection(P p1, P p2, P q1, P q2) 48 { 49 return p1+(p2-p1)*((q2-q1).det(q1-p1)/(q2-q1).det(p2-p1)); 50 } 51 52 const int MAX_N=15; 53 const int MAX_M=2000; 54 int n; 55 P p[MAX_N], q[MAX_N]; 56 int m; 57 int a[MAX_M], b[MAX_M]; 58 bool g[MAX_N][MAX_N]; 59 60 int main() 61 { 62 while (~scanf("%d", &n) && n) 63 { 64 fill(g[0], g[0]+sizeof(bool)*15*15, false); 65 for (int i=0; i<n; i++) 66 { 67 scanf("%lf %lf %lf %lf", &p[i].x, &p[i].y, &q[i].x, &q[i].y); 68 } 69 for (int i=0;;i++) 70 { 71 scanf("%d %d",&a[i], &b[i]); 72 if (a[i]==0 && b[i]==0) 73 { 74 m=i; 75 break; 76 } 77 } 78 for (int i=0; i<n; i++) 79 { 80 g[i][i]=true; 81 for (int j=0; j<i; j++) 82 { 83 if ((p[i]-q[i]).det(p[j]-q[j])==0) 84 { 85 g[i][j]=g[j][i]=on_seg(p[i], q[i], p[j]) 86 || on_seg(p[i], q[i], q[j]) 87 || on_seg(p[j], q[j], p[i]) 88 || on_seg(p[j], q[j], q[i]); 89 } 90 else 91 { 92 P r=intersection(p[i], q[i], p[j], q[j]); 93 g[i][j]=g[j][i]=on_seg(p[i], q[i], r) && on_seg(p[j], q[j], r); 94 } 95 } 96 } 97 for (int k=0; k<n; k++) 98 for (int i=0; i<n; i++) 99 for (int j=0; j<n; j++) 100 { 101 g[i][j] |= g[i][k]&&g[k][j]; 102 } 103 for (int i=0; i<m; i++) 104 { 105 puts(g[a[i]-1][b[i]-1] ? "CONNECTED" : "NOT CONNECTED"); 106 } 107 } 108 }
计算误差
对于double类型,尾数部分大致相当于10进制下的15位,多数情况下,就其计算结果而言,精度已经足够了,但当我们要比较两个计算后的结果时,就需要特别注意。由于误差,原本应该相等的结果有可能实际上并不相等。比较包含舍入误差的浮点数时所采用的方法,一般是选取合适的足够小的常数EPS,按如下规则处理:
a<0→a<-EPS
a<=0→a<EPS
a==0→fabs(a)<EPS
在大多数计算结果不是太大的情况下,都可以使用该方法处理。在比较大的结果时要格外注意,假设所取的EPS为10-10,现在要求对因为误差导致原本相等却实际不等的大约108大小的两个数作差,并判断是否等于0,由于double的精度只有约十进制15位,所得差的绝对值将大于EPS,所以会被误判为不等。像这样,求两个非常接近的数的差时会发生有效位丢失,导致所得结果的有效数字位数大大减少。前面的程序所用的方法是,在进行浮点数减法时,如果两个数按相对误差比较是相等的就另结果为0,这样我们在计算的过程中处理了误差,所以在与0进行比较时,就可以不考虑误差直接比较了。
极限情况
White Bird (AOJ 2308)
Angry Birds is a mobile game of a big craze all over the world. You were convinced that it was a waste of time to play the game, so you decided to create an automatic solver.
You are describing a routine that optimizes the white bird‘s strategy to defeat a pig (enemy) by hitting an egg bomb. The white bird follows a parabolic trajectory from the initial position, and it can vertically drop egg bombs on the way.
In order to make it easy to solve, the following conditions hold for the stages.
The acceleration of gravity is 9.8 {\rm m/s^2}. Gravity exerts a force on the objects in the decreasing direction of y-coordinate.
A dataset follows the format shown below:
NVXY
L_1B_1R_1T_1
...
L_NB_NR_NT_N
All inputs are integer.
(0 \leq N \leq 50, 0 \leq V \leq 50, 0 \leq X, Y \leq 300, X \neq 0)
for 1 \leq i \leq N,
(0 \leq L_i, B_i, R_i, T_i \leq 300)
It is guaranteed that the answer remains unaffected by a change of L_i, B_i, R_i and T_i in 10^{-6}.
Yes/No
You should answer whether the white bird can drop an egg bomb toward the pig.
0 7 3 1
Yes
1 7 3 1 1 1 2 2
No
1 7 2 2 0 1 1 2
No

1 #include <cstdio> 2 #include <cmath> 3 4 using namespace std; 5 6 const double EPS=1e-10; 7 const int MAX_N=1000; 8 const double g=9.8; 9 int N,V,X,Y; 10 int L[MAX_N], B[MAX_N], R[MAX_N], T[MAX_N]; 11 12 double calc(double vy, double t) 13 { 14 return vy*t-g*t*t/2; 15 } 16 17 int cmp(double lb, double ub, double a) 18 { 19 return a<lb+EPS ? -1 : a>ub-EPS ? 1 : 0; 20 } 21 22 bool check(double qx, double qy) 23 { 24 double a=g*g/4, b=g*qy-V*V, c=qx*qx+qy*qy; 25 double D=b*b-4*a*c; 26 if (D<0 && D>-EPS) D=0; 27 if (D<0) return false; 28 for (int d=-1; d<=1; d+=2) 29 { 30 double t2=(-b+d*sqrt(D))/(2*a); 31 if (t2<=0) continue; 32 double t=sqrt(t2); 33 double vx=qx/t, vy=(qy+g*t*t/2)/t; 34 double yt=calc(vy, X/vx); 35 if (yt<Y-EPS) continue; 36 bool ok=true; 37 for (int i=0; i<N; i++) 38 { 39 if (L[i]>=X) continue; 40 if (R[i]==X && Y<=T[i] && B[i]<=yt) ok=false; 41 int yL=cmp(B[i], T[i], calc(vy, L[i]/vx)); 42 int yR=cmp(B[i], T[i], calc(vy, R[i]/vx)); 43 int xH=cmp(L[i], R[i], vx*(vy/g)); 44 int yH=cmp(B[i], T[i], calc(vy, vy/g)); 45 if (xH==0 && yH>=0 && yL<0) ok=false; 46 if (yL*yR<=0) ok=false; 47 } 48 if (ok) return true; 49 } 50 return false; 51 } 52 53 int min(int x, int y) 54 { 55 if (x<y) return x; 56 return y; 57 } 58 59 int main() 60 { 61 scanf("%d %d %d %d", &N, &V, &X, &Y); 62 for (int i=0; i<N; i++) 63 { 64 scanf("%d %d %d %d", &L[i], &B[i], &R[i], &T[i]); 65 } 66 for (int i=0; i<N; i++) 67 { 68 R[i]=min(R[i], X); 69 } 70 bool ok=check(X,Y); 71 for (int i=0; i<N; i++) 72 { 73 ok |= check(L[i], T[i]); 74 ok |= check(R[i], T[i]); 75 } 76 puts(ok ? "Yes" : "No"); 77 }
平面扫描
Coneology(POJ 2932)
| Time Limit: 5000MS | Memory Limit: 65536K |
| Total Submissions: 4805 | Accepted: 1067 |
Description
A student named Round Square loved to play with cones. He would arrange cones with different base radii arbitrarily on the floor and would admire the intrinsic beauty of the arrangement. The student even began theorizing about how some cones dominate other cones: a cone A dominates another cone B when cone B is completely within the cone A. Furthermore, he noted that there are some cones that not only dominate others, but are themselves dominated, thus creating complex domination relations. After studying the intricate relations of the cones in more depth, the student reached an important conclusion: there exist some cones, all-powerful cones, that have unique properties: an all-powerful cone is not dominated by any other cone. The student became so impressed by the mightiness of the all-powerful cones that he decided to worship these all-powerful cones.
Unfortunately, after having arranged a huge number of cones and having worked hard on developing this grandiose cone theory, the student become quite confused with all these cones, and he now fears that he might worship the wrong cones (what if there is an evil cone that tries to trick the student into worshiping it?). You need to help this student by finding the cones he should worship.
Input
The input le specifies an arrangement of the cones. There are in total N cones (1 ≤ N ≤ 40000). Cone i has radius and height equal to Ri, i = 1 … N. Each cone is hollow on the inside and has no base, so it can be placed over another cone with smaller radius. No two cones touch.
The first line of the input contains the integer N. The next N lines each contain three real numbers Ri, xi, yi separated by spaces, where (xi, yi) are the coordinates of the center of the base of cone i.
Output
The first line of the output le should contain the number of cones that the student should worship. The second line contains the indices of the cones that the student should worship in increasing order. Two consecutive numbers should be separated by a single space.
Sample Input
5 1 0 -2 3 0 3 10 0 0 1 0 1.5 10 50 50
Sample Output
2 3 5

1 #include <cstdio> 2 #include <utility> 3 #include <set> 4 #include <vector> 5 #include <algorithm> 6 7 using namespace std; 8 9 const int MAX_N=40000; 10 int N; 11 double x[MAX_N], y[MAX_N], r[MAX_N]; 12 13 bool inside(int i, int j) 14 { 15 double dx=x[i]-x[j], dy=y[i]-y[j]; 16 return dx*dx+dy*dy<=r[j]*r[j]; 17 } 18 19 void solve() 20 { 21 vector<pair<double, int> > events; 22 for (int i=0; i<N; i++) 23 { 24 events.push_back(make_pair(x[i]-r[i], i)); 25 events.push_back(make_pair(x[i]+r[i], i+N)); 26 } 27 sort(events.begin(), events.end()); 28 set<pair<double, int> > outers; 29 vector<int> res; 30 for (int i=0; i<events.size(); i++) 31 { 32 int id=events[i].second % N; 33 if (events[i].second<N) 34 { 35 set<pair<double, int> >::iterator it=outers.lower_bound(make_pair(y[id], id)); 36 if (it !=outers.end() && inside(id, it->second)) continue; 37 if (it !=outers.begin() && inside(id, (--it)->second)) continue; 38 res.push_back(id); 39 outers.insert(make_pair(y[id], id)); 40 } 41 else 42 { 43 outers.erase(make_pair(y[id], id)); 44 } 45 } 46 sort(res.begin(), res.end()); 47 printf("%d\n", res.size()); 48 for (int i=0; i<res.size(); i++) 49 { 50 printf("%d%c", res[i]+1, i+1==res.size() ? ‘\n‘ : ‘ ‘); 51 } 52 } 53 54 int main() 55 { 56 scanf("%d", &N); 57 for (int i=0; i<N; i++) 58 { 59 scanf("%lf%lf%lf", &r[i], &x[i], &y[i]); 60 } 61 solve(); 62 }
凸包
Beauty Contest(POJ 2187)
| Time Limit: 3000MS | Memory Limit: 65536K |
| Total Submissions: 42728 | Accepted: 13233 |
Description
Input
Output
Sample Input
4 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0
Sample Output
2
Hint
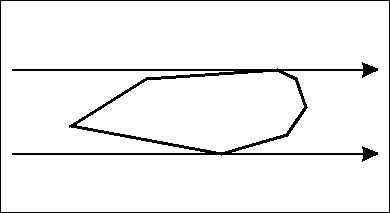

1 #include <cstdio> 2 #include <vector> 3 #include <algorithm> 4 #include <cmath> 5 6 using namespace std; 7 8 const double EPS=1e-10; 9 10 double add(double a, double b) 11 { 12 if (fabs(a+b)<EPS*(fabs(a)+fabs(b))) return 0; 13 return a+b; 14 } 15 16 struct P 17 { 18 double x, y; 19 P(){} 20 P(double x, double y): x(x), y(y) {} 21 P operator - (P p) 22 { 23 return P(add(x, -p.x), add(y, -p.y)); 24 } 25 double det(P p) 26 { 27 return add(x*p.y, -y*p.x); 28 } 29 double dot(P p) 30 { 31 return add(x*p.x, y*p.y); 32 } 33 }; 34 35 const int MAX_N=50005; 36 int N; 37 P ps[MAX_N]; 38 39 bool cmp_x(const P &p, P &q) 40 { 41 if (p.x!=q.x) return p.x<q.x; 42 return p.y<q.y; 43 } 44 45 vector<P> convex_hull(P * ps, int n) 46 { 47 sort(ps, ps+n, cmp_x); 48 int k=0; 49 vector<P> qs(n*2); 50 for (int i=0; i<n; i++) 51 { 52 while (k>1 && (qs[k-1]-qs[k-2]).det(ps[i]-qs[k-1])<=0) k--; 53 qs[k++]=ps[i]; 54 } 55 for (int i=n-2, t=k; i>=0; i--) 56 { 57 while (k>t && (qs[k-1]-qs[k-2]).det(ps[i]-qs[k-1])<=0) k--; 58 qs[k++]=ps[i]; 59 } 60 qs.resize(k-1); 61 return qs; 62 } 63 64 double max(int x, int y) 65 { 66 if (x>y) return x; 67 return y; 68 } 69 70 double dist(P p, P q) 71 { 72 return (p-q).dot(p-q); 73 } 74 75 int main() 76 { 77 scanf("%d", &N); 78 for (int i=0; i<N; i++) 79 { 80 scanf("%lf %lf", &ps[i].x, &ps[i].y); 81 } 82 vector<P> qs=convex_hull(ps, N); 83 double res=0; 84 for (int i=0; i<qs.size(); i++) 85 { 86 for (int j=0; j<i; j++) 87 { 88 res=max(res, dist(qs[i], qs[j])); 89 } 90 } 91 printf("%.0f\n", res); 92 }

1 #include <cstdio> 2 #include <cmath> 3 #include <algorithm> 4 #include <vector> 5 6 using namespace std; 7 8 const double EPS=1e-10; 9 10 double max(double x, double y) 11 { 12 if (x>y+EPS) return x; 13 return y; 14 } 15 16 double add(double x, double y) 17 { 18 if (fabs(x+y)<EPS*(fabs(x)+fabs(y))) return 0; 19 return x+y; 20 } 21 struct P 22 { 23 double x, y; 24 P(){} 25 P(double x, double y): x(x), y(y) {} 26 P operator + (P p) 27 { 28 return P(add(x, p.x), add(y, p.y)); 29 } 30 P operator - (P p) 31 { 32 return P(add(x, -p.x), add(y, -p.y)); 33 } 34 double dot(P p) 35 { 36 return add(x*p.x, y*p.y); 37 } 38 double det(P p) 39 { 40 return add(x*p.y, -y*p.x); 41 } 42 }; 43 44 const int MAX_N=50005; 45 int N; 46 P ps[MAX_N]; 47 48 bool cmp_x(const P &p, const P &q) 49 { 50 if (p.x!=q.x) return p.x<q.x; 51 return p.y<q.y; 52 } 53 54 double dist(P p, P q) 55 { 56 return (p-q).dot(p-q); 57 } 58 59 vector<P> convex_hull(P * ps, int n) 60 { 61 sort(ps, ps+n, cmp_x); 62 int k=0; 63 vector<P> qs(n*2); 64 for (int i=0; i<n; i++) 65 { 66 while (k>1 && (qs[k-1]-qs[k-2]).det(ps[i]-qs[k-1])<=0) k--; 67 qs[k++]=ps[i]; 68 } 69 for (int i=n-2, t=k; i>=0; i--) 70 { 71 while (k>t && (qs[k-1]-qs[k-2]).det(ps[i]-qs[k-1])<=0) k--; 72 qs[k++]=ps[i]; 73 } 74 qs.resize(k-1); 75 return qs; 76 } 77 78 int main() 79 { 80 scanf("%d", &N); 81 for (int i=0; i<N; i++) 82 { 83 scanf("%lf %lf", &ps[i].x, &ps[i].y); 84 } 85 vector<P> qs=convex_hull(ps, N); 86 int n=qs.size(); 87 if (n==2) 88 { 89 printf("%.0f\n", dist(qs[0], qs[1])); 90 return 0; 91 } 92 int i=0, j=0; 93 for (int k=0; k<n; k++) 94 { 95 if (!cmp_x(qs[i], qs[k])) i=k; 96 if (cmp_x(qs[j], qs[k])) j=k; 97 } 98 double res=0; 99 int si=i, sj=j; 100 while (i!=sj || j!=si) 101 { 102 res=max(res, dist(qs[i], qs[j])); 103 if ((qs[(i+1)%n]-qs[i]).det(qs[(j+1)%n]-qs[j])<0) 104 { 105 i=(i+1)%n; 106 } 107 else 108 { 109 j=(j+1)%n; 110 } 111 } 112 printf("%.0f\n", res); 113 }
数值积分
Intersection of Two Prisms(AOJ 1313)
Suppose that P1 is an infinite-height prism whose axis is parallel to the z-axis, and P2 is also an infinite-height prism whose axis is parallel to the y-axis. P1 is defined by the polygon C1 which is the cross section of P1 and the xy-plane, and P2is also defined by the polygon C2 which is the cross section of P2 and the xz-plane.
Figure I.1 shows two cross sections which appear as the first dataset in the sample input, and Figure I.2 shows the relationship between the prisms and their cross sections.
Figure I.1: Cross sections of Prisms
Figure I.2: Prisms and their cross sections
Figure I.3: Intersection of two prisms
Figure I.3 shows the intersection of two prisms in Figure I.2, namely, P1 and P2.
Write a program which calculates the volume of the intersection of two prisms.
The input is a sequence of datasets. The number of datasets is less than 200.
Each dataset is formatted as follows.
m n
x11 y11
x12 y12
.
.
.
x1m y1m
x21 z21
x22 z22
.
.
.
x2n z2n
m and n are integers (3 ≤ m ≤ 100, 3 ≤ n ≤ 100) which represent the numbers of the vertices of the polygons, C1 and C2, respectively.
x1i, y 1 i, x 2j and z 2j are integers between -100 and 100, inclusive. ( x 1i, y 1i) and ( x 2j , z 2j) mean the i-th and j-th vertices‘ positions of C 1 and C 2respectively.
The sequences of these vertex positions are given in the counterclockwise order either on the xy-plane or the xz-plane as in Figure I.1.
You may assume that all the polygons are convex, that is, all the interior angles of the polygons are less than 180 degrees. You may also assume that all the polygons are simple, that is, each polygon‘s boundary does not cross nor touch itself.
The end of the input is indicated by a line containing two zeros.
For each dataset, output the volume of the intersection of the two prisms, P1 and P2, with a decimal representation in a line.
None of the output values may have an error greater than 0.001. The output should not contain any other extra characters.
4 3 7 2 3 3 0 2 3 1 4 2 0 1 8 1 4 4 30 2 30 12 2 12 2 2 15 2 30 8 13 14 2 8 8 5 13 5 21 7 21 9 18 15 11 15 6 10 6 8 8 5 10 12 5 9 15 6 20 10 18 12 3 3 5 5 10 3 10 10 20 8 10 15 10 8 4 4 -98 99 -99 -99 99 -98 99 97 -99 99 -98 -98 99 -99 96 99 0 0
4.708333333333333 1680.0000000000005 491.1500000000007 0.0 7600258.4847715655
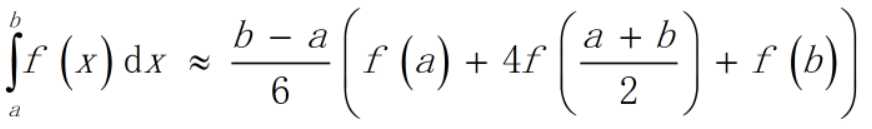
Simpson公式就是在数值积分中用二次函数来近似原函数进行积分而得到的公式,如果原函数本身就是次数不超过二的多项式,那么用Simpson公式就可以得到精确的积分值。利用该公式,无需求出关于x的多项式,而只要计算按区间的端点和中点切片得到的长方形的面积就够了。

1 #include<cstdio> 2 #include<algorithm> 3 #include<vector> 4 5 using namespace std; 6 7 const int INF=0x3f3f3f3f; 8 const double EPS=1e-10; 9 const int MAX_N=500; 10 int N,M; 11 int X1[MAX_N], Y1[MAX_N], X2[MAX_N], Z2[MAX_N]; 12 13 double max(double x, double y) 14 { 15 if (x>y+EPS) return x; 16 return y; 17 } 18 19 double min(double x, double y) 20 { 21 if (x<y-EPS) return x; 22 return y; 23 } 24 25 double width(int * X, int * Y, int n, double x) 26 { 27 double lb=INF, ub=-INF; 28 for (int i=0; i<n; i++) 29 { 30 double x1=X[i], y1=Y[i], x2=X[(i+1)%n], y2=Y[(i+1)%n]; 31 if ((x1-x)*(x2-x)<=0 && x1!=x2) 32 { 33 double y=y1+(y2-y1)*(x-x1)/(x2-x1); 34 lb=min(lb, y); 35 ub=max(ub, y); 36 } 37 } 38 return max(0.0, ub-lb); 39 } 40 41 int main() 42 { 43 while (~scanf("%d %d", &M, &N)) 44 { 45 if (M==0 && N==0) break; 46 for (int i=0; i<M; i++) 47 { 48 scanf("%d %d", &X1[i], &Y1[i]); 49 } 50 for (int i=0; i<N; i++) 51 { 52 scanf("%d %d", &X2[i], &Z2[i]); 53 } 54 int min1=*min_element(X1, X1+M), max1=*max_element(X1, X1+M); 55 int min2=*min_element(X2, X2+N), max2=*max_element(X2, X2+N); 56 vector<int> xs; 57 for (int i=0; i<M; i++) xs.push_back(X1[i]); 58 for (int i=0; i<N; i++) xs.push_back(X2[i]); 59 sort(xs.begin(), xs.end()); 60 double res=0; 61 for (int i=0; i+1<xs.size(); i++) 62 { 63 double a=xs[i], b=xs[i+1], c=(a+b)/2; 64 if (min1<=c && c<=max1 && min2<=c && c<=max2) 65 { 66 double fa=width(X1, Y1, M, a)*width(X2, Z2, N, a); 67 double fb=width(X1, Y1, M, b)*width(X2, Z2, N, b); 68 double fc=width(X1, Y1, M, c)*width(X2, Z2, N, c); 69 res+=(b-a)/6*(fa+4*fc+fb); 70 } 71 } 72 printf("%.10f\n", res); 73 } 74 }
标签:val 部分 element journey 字典 ping play ble 方便
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/Ymir-TaoMee/p/9628746.html